Bengal Cat Vs Tabby Cat Size, Weight, Overall Comparison
When delving into the world of feline companionship, one encounters a tapestry of coat patterns, personalities, and sizes. Among these, Bengal cats and tabby cats stand out, each bringing unique characteristics to the table. In this exploration of Bengal Cat vs Tabby Cat, we unravel key differences that set these two feline varieties apart, from distinctive stripe patterns to vocal personalities and pricing distinctions. Whether it’s the sleek elegance of a Bengal or the varied traits of other tabby cats, understanding these distinctions offers a deeper appreciation for the rich diversity within the realm of patterned cats.
I. Stripe Patterns:
– Both Bengal cats and tabby cats share a commonality in having stripe patterns on their fur. However, it’s essential to note that while tabby cats encompass a broad category of striped cats, Bengal cats belong to a specific breed within this patterned group.
II. Body Fur Whitening:
– One distinctive feature is that Bengal cats typically lack white on their body fur, setting them apart from other tabby cats. In contrast, many tabby cats may exhibit varying degrees of white markings on their fur.

III. Vocal Personality:
– Bengals often possess a more vocal and expressive personality compared to most other tabby cats. Their distinctive meows and communicative nature contribute to a unique and engaging feline companion.
IV. Height and Sleekness:
– Bengal cats are known for their sleek and tall stature, standing out in terms of physical elegance. On the contrary, many other tabby cats are often shorter in stature, showcasing a diverse range of sizes within the tabby cat category.
V. Pricing Distinctions:
– Bengals typically command a higher price compared to most other tabby cats due to their unique characteristics, exotic appearance, and demand in the market. The pricing for Bengal cats reflects their exclusivity within the world of tabby cats.
VI. Appreciating Breed Diversity:
– Understanding the distinctions between Bengal cats and tabby cats allows potential owners to appreciate the diversity within the tabby pattern category. Whether it’s the striking appearance of a Bengal or the varied traits of other tabby cats, each brings its own charm to the world of feline companionship.
*Details of Comparison
| Criteria | Bengal Cat | Tabby Cat |
| Taxonomy | Genus Prionailurus, Species P. bengalensis |
Genus Felis, Species F. catus
|
| Appearance | Distinctive spotted or marbled coat |
Varied coat patterns, diverse appearance
|
| Size | Medium to large | Varies widely |
| Weight | 8 to 15 pounds | Varies by breed |
| Personality | Energetic, playful, intelligent |
Generally affectionate, adaptable
|
| Relative Price/Cost | More expensive |
Generally more affordable
|
| Grooming and Maintenance | Minimal grooming, needs mental stimulation |
Varies by breed, regular brushing
|
| Health Concerns | Prone to genetic conditions |
Varied, regular vet visits
|
| Bite Force (PSI) | Moderately documented, considered moderate |
Generally moderate
|
| Physical Offensive Advantages | Strong, agile, sharp claws |
Varied based on individual and breed
|
| Physical Defensive Advantages | Quick reflexes, camouflaged coat |
Agility, varied coat patterns
|
| Speed | Up to 30 mph | Varies |
| Agility | Highly agile, efficient climbing | Agility varies |
| Senses | Keen vision, hearing, and smell |
Excellent night vision, sensitive whiskers
|
| Overall Physical Capacity | Robust, high energy |
Adaptable, well-suited to environments
|
| Habitat Preference(s) | Prefers areas with climbing opportunities |
Adaptable to various habitats
|
| Tracks | Resembles small wild cats |
Varies based on individual size
|
| Lifespan | 12-16 years | Varies by breed |
| Natural Mode of Feeding | Carnivorous | Carnivorous |
| Best Food as a Pet | High-quality, protein-rich |
Nutritionally balanced
|
| Intelligence | Intelligent, requires mental stimulation |
Varies by breed, adaptable
|
| Social Behavior | Social but may be independent |
Generally affectionate and social
|
| Mode of Reproduction | Sexual reproduction, multiple kittens |
Sexual reproduction, varied breeding cycles
|
| Parental Behavior | Strong maternal instincts |
Varies but generally cares for offspring
|
| Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas | Adaptable but retains wild instincts |
Well-adapted to living close to humans
|
| Behavior Toward Humans | Affectionate but may be independent |
Generally affectionate, behavior varies
|
| Danger Posed to Humans | Generally not dangerous, may scratch during play |
Minimal danger, scratches or bites usually due to playfulness or stress
|
| Associated Precautions | Supervised outdoor time, regular vet care |
Responsible ownership practices, enrichment for indoor cats
|
| Conservation Status | Domestic Bengal cats not conservation concerns |
Domestic cats, including tabby patterns, not conservation priorities
|
1. Taxonomy
Bengal Cat:
Family: Felidae
Subfamily: Felinae
Genus: Prionailurus
Species: P. bengalensis
Subspecies: P. b. bengalensis (domestic Bengal cat)
Tabby Cat:
Family: Felidae
Subfamily: Felinae
Genus: Felis
Species: F. catus
No specific subspecies (domestic cat with tabby coat pattern)
2. Appearance

Bengal Cat:
Distinctive spotted or marbled coat patterns.
Sleek, muscular build with a wild appearance.
Almond-shaped eyes with a variety of colors.
Unique coat often resembles that of a leopard.
Tabby Cat:
Varied coat patterns (striped, spotted, or swirled) in different colors.
Diverse appearance, as tabby refers to a coat pattern rather than a breed.
Eyes can be round or almond-shaped, and coat color varies widely.
Ecological Implications:
Bengal cats, with their wild appearance, may evoke interest in wild cat conservation, raising awareness.
Tabby cats, being a diverse group, reflect the adaptability of domestic cats to various environments.
3. Size
Bengal Cat:
Medium to large size.
Males typically larger than females.
Tabby Cat:
Size varies widely based on breed.
Domestic cats generally smaller than Bengal cats.
Ecological Implications:
Size influences the ecological impact on prey populations and the cat’s role in its environment.
4. Weight
Bengal Cat:
Average weight ranges from 8 to 15 pounds.
Tabby Cat:
Weight varies significantly based on breed and individual differences.
Ecological Implications:
Weight impacts the cat’s hunting capabilities and energy requirements within its ecosystem.
5. Personality
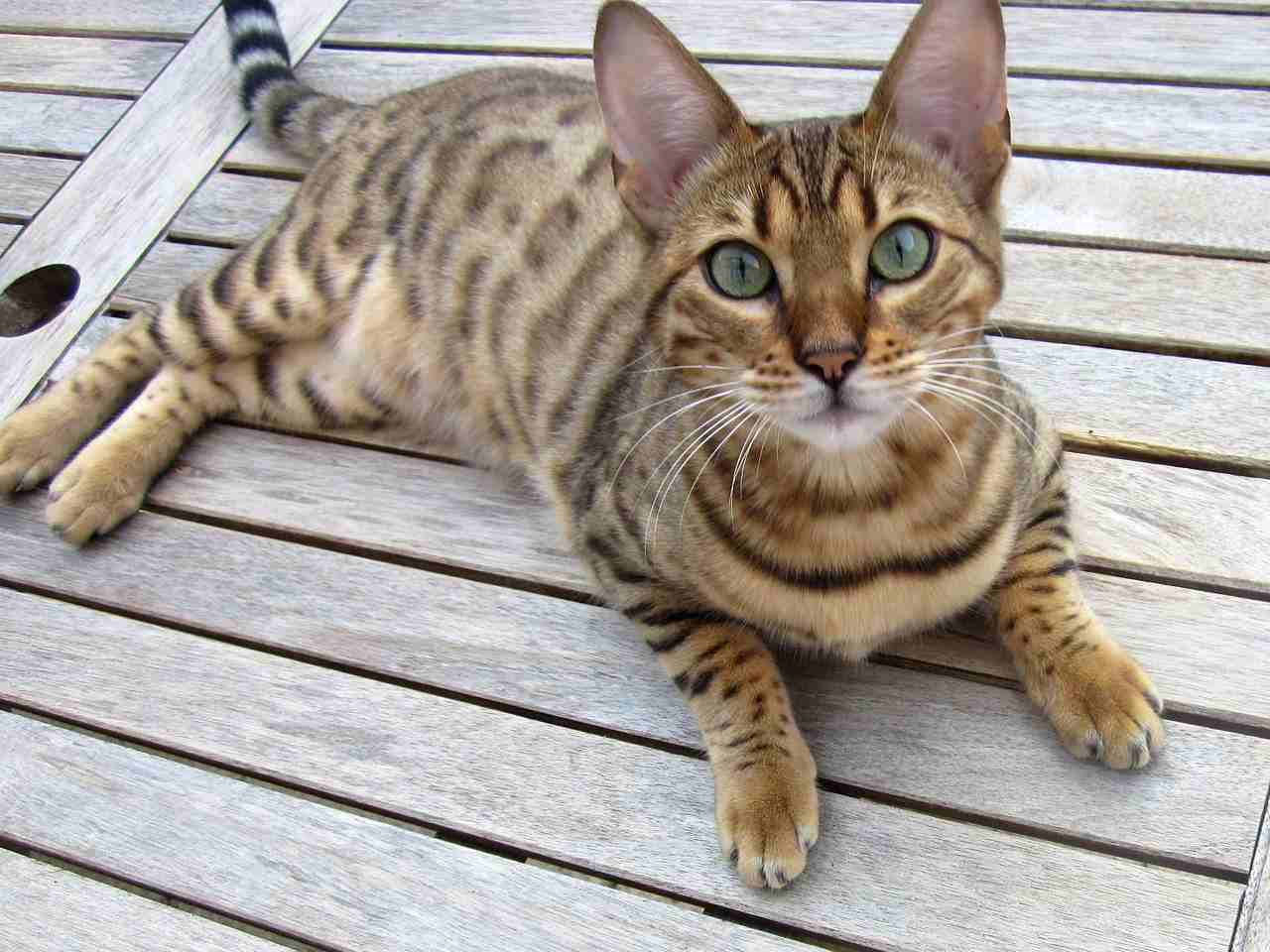

Bengal Cat:
Energetic, playful, and intelligent.
Strong hunting instincts and may enjoy interactive play.
Tabby Cat:
Personality traits vary widely among different breeds.
Generally affectionate, adaptable, and social.
Ecological Implications:
The personality traits of both cats influence their interactions with the environment and human cohabitation.
6. Relative Price/Cost
Bengal Cat:
Typically more expensive due to their distinct appearance and specific breeding practices.
Tabby Cat:
Generally more affordable, as it encompasses various breeds and mixed-breed cats.
Ecological Implications:
The cost may influence breeding practices and the demand for certain cat breeds.
7. Grooming and Maintenance Requirements
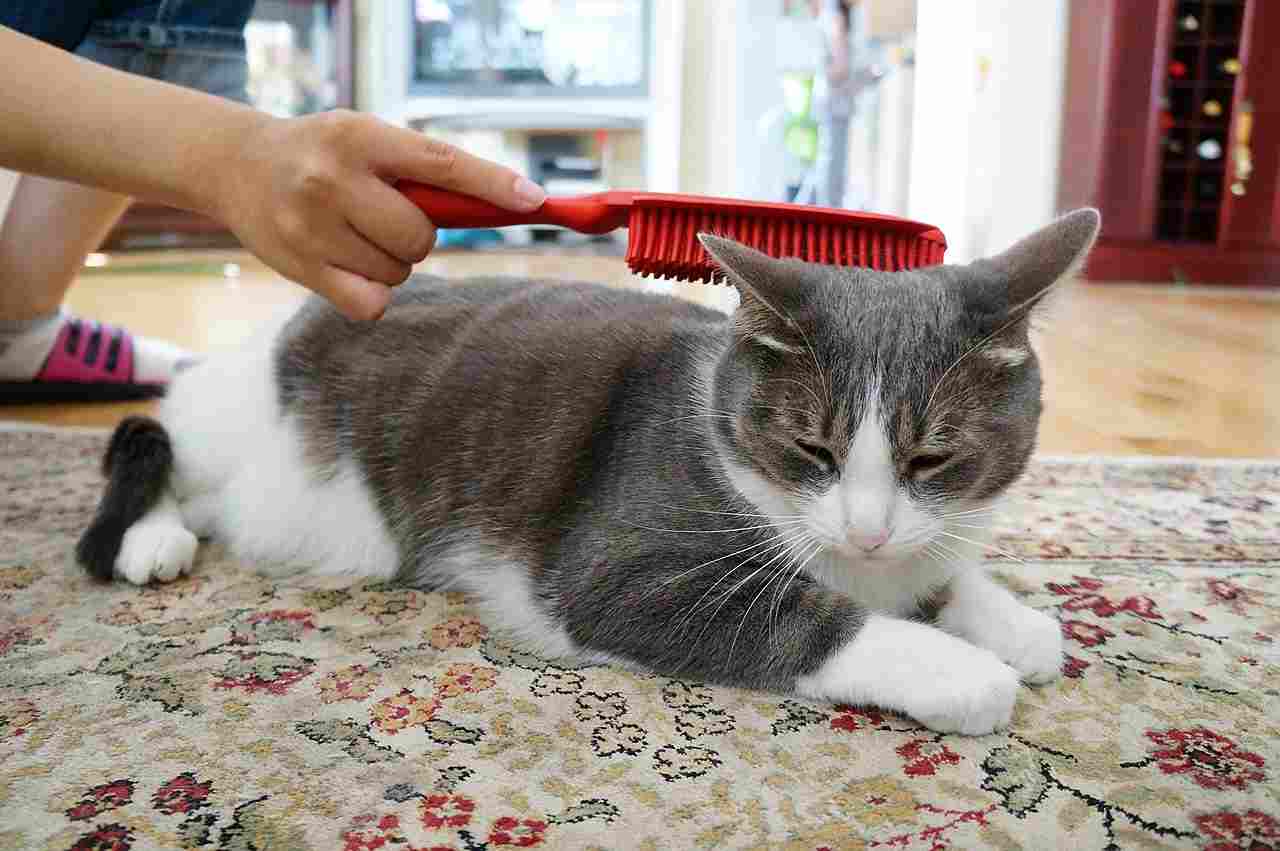

Bengal Cat:
Short, dense coat requires minimal grooming.
Regular playtime and mental stimulation are essential.
Tabby Cat:
Grooming needs vary by breed, but generally, regular brushing is sufficient.
Play and social interaction contribute to their well-being.
Ecological Implications:
Grooming habits impact the cat’s hygiene in different environments.
8. Health Concerns
Bengal Cat:
Prone to some genetic conditions like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial.
Tabby Cat:
Health concerns depend on the specific breed and genetics.
Regular vet visits for preventive care.
Ecological Implications:
Understanding health risks aids in managing domestic cats’ impact on local ecosystems.
9. Bite Force (PSI)

Bengal Cat:
Bite force not extensively documented for domestic cats but generally considered moderate.
Tabby Cat:
Bite force varies but is generally moderate in domestic cats.
Ecological Implications:
Bite force influences hunting efficiency and interactions with other species within their environment.
10. Physical Offensive Advantages
Bengal Cat:
Strong and agile, utilizing muscular build for effective hunting.
Sharp claws and teeth contribute to hunting prowess.
Tabby Cat:
Varied based on individual cat and breed characteristics.
Generally agile, using natural instincts for hunting.
Ecological Implications:
Offensive abilities impact the cat’s role in controlling local pest populations.
11. Physical Defensive Advantages
Bengal Cat:
Quick reflexes and agility for evasion.
Camouflaged coat aids in blending with surroundings.
Tabby Cat:
Agility and the ability to climb provide defensive advantages.
Varied coat patterns may offer some camouflage.
Ecological Implications:
Defensive capabilities affect the cat’s survival and interaction with potential threats.
12. Speed (Km/hour or Mile/hour)
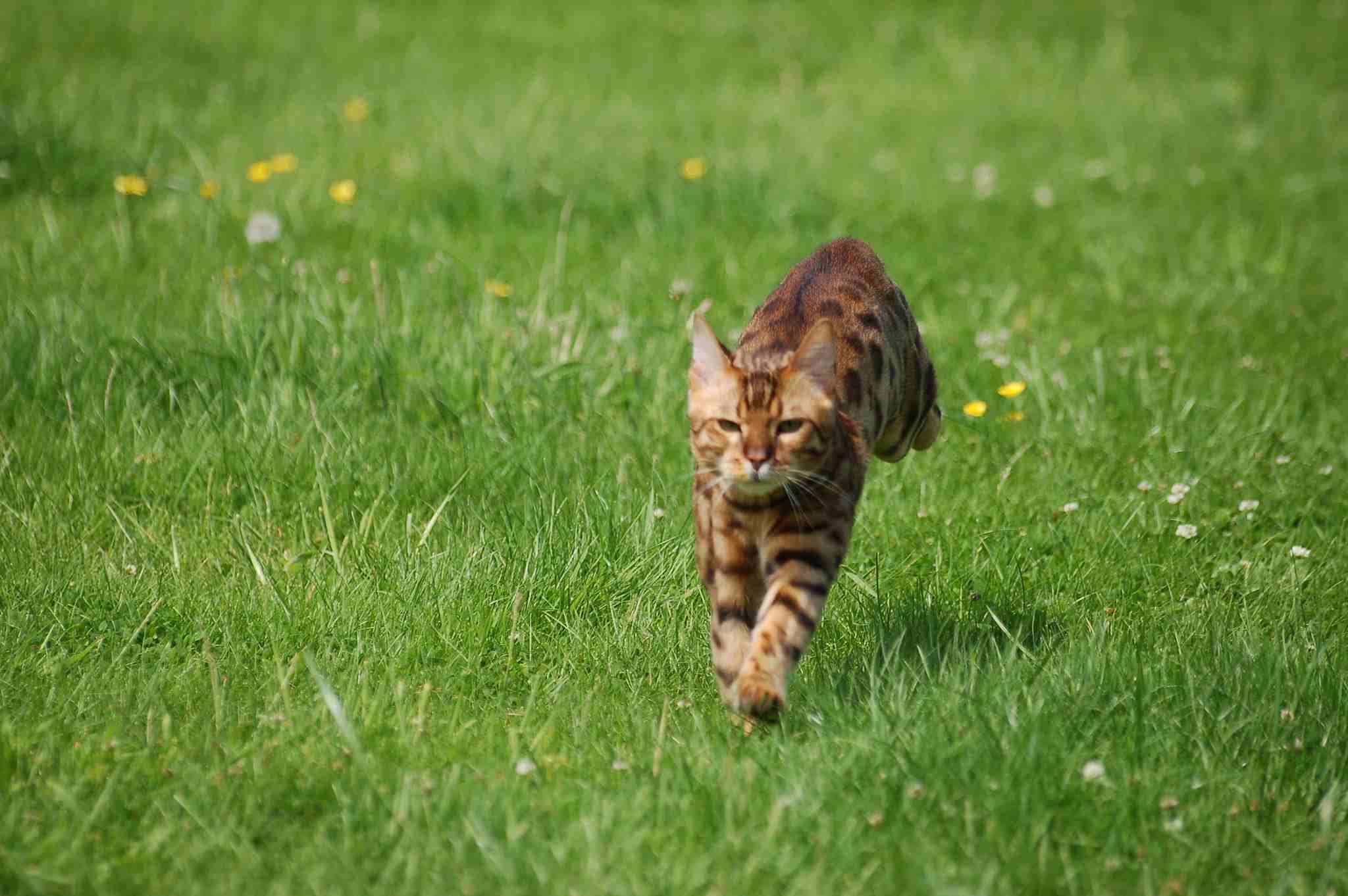

Bengal Cat:
Capable of reaching speeds up to 30 miles per hour.
Tabby Cat:
Speed varies based on individual fitness and breed characteristics.
Ecological Implications:
Speed influences the cat’s effectiveness as a predator in its environment.
13. Agility

Bengal Cat:
Highly agile, able to leap great distances and climb efficiently.
Tabby Cat:
Agility varies among breeds, with many domestic cats exhibiting good agility.
Ecological Implications:
Agility is crucial for navigating diverse environments and pursuing prey.
14. Senses
Bengal Cat:
Keen senses, including sharp vision and acute hearing.
Well-developed sense of smell for hunting.
Tabby Cat:
Senses vary, but domestic cats generally have excellent night vision and sensitive whiskers.
Hearing and sense of smell contribute to their awareness.
Ecological Implications:
Enhanced senses aid in adapting to and thriving in diverse environments.
15. Overall Physical Capacity
Bengal Cat:
Robust physical condition with a focus on muscular strength.
High energy levels contribute to overall agility.
Tabby Cat:
Physical capacity varies among breeds but generally adaptable to different lifestyles.
Well-suited to both indoor and outdoor environments.
Ecological Implications:
Physical capacity influences the cat’s ability to survive and thrive in various habitats.
16. Habitat Preference(s)
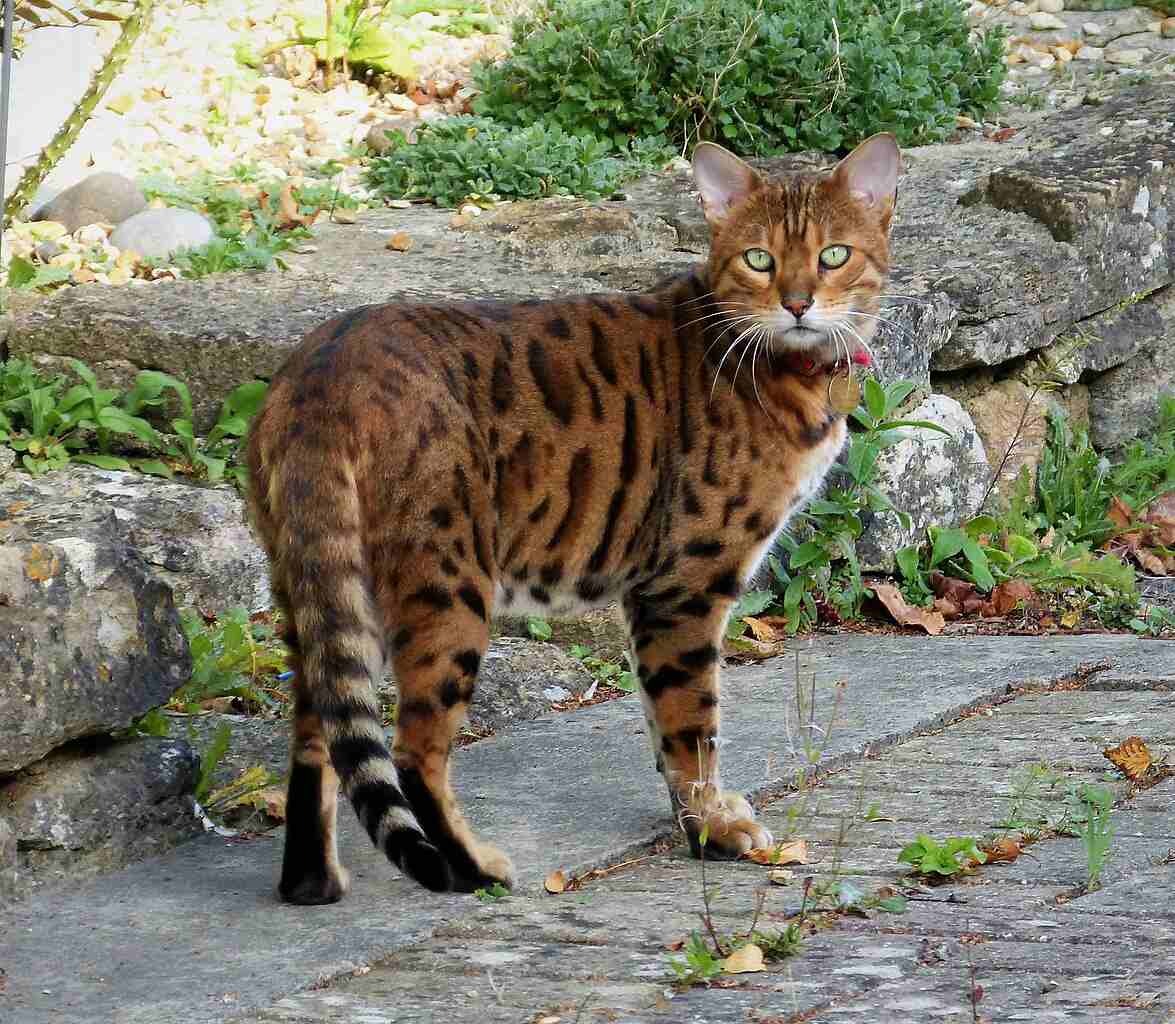

Bengal Cat:
Originating from Asian leopard cats, they may prefer environments with trees and climbing opportunities.
Tabby Cat:
Adaptable to various habitats, including urban, suburban, and rural areas.
Ecological Implications:
Understanding habitat preferences assists in managing and conserving local ecosystems.
17. Tracks

Bengal Cat:
Tracks may resemble those of a small wild cat, with distinct paw prints.
Tabby Cat:
Tracks vary based on individual cat size, with common paw print features.
Ecological Implications:
Tracking patterns can provide insights into the presence and behavior of these cats in an ecosystem.
18. Lifespan
Bengal Cat:
Generally, a lifespan of 12 to 16 years with proper care.
Tabby Cat:
Lifespan varies by breed, with many domestic cats living 12 to 15 years or more.
Ecological Implications:
Longevity impacts the cat’s role in local ecosystems and human households.
19. Natural Mode of Feeding
Bengal Cat:
Carnivorous, reflecting their wild ancestry, with a diet primarily consisting of meat.
Tabby Cat:
Carnivorous, sharing the same dietary requirements as other domestic cats.
Ecological Implications:
Dietary habits influence the cat’s impact on local prey populations and ecosystems.
20. Best Food as a Pet

Bengal Cat:
High-quality cat food, possibly with a focus on a protein-rich diet.
Tabby Cat:
Nutritionally balanced cat food suitable for the specific breed’s requirements.
Ecological Implications:
Dietary choices influence the cat’s health and well-being within human-inhabited areas.
21. Intelligence
Bengal Cat:
Intelligent and curious, requiring mental stimulation and interactive play.
Tabby Cat:
Intelligence varies by breed, but most domestic cats are adaptable and problem solvers.
Ecological Implications:
Intelligence affects the cat’s ability to navigate and adapt to different environmental challenges.
22. Social Behavior

Bengal Cat:
Social but may exhibit more independent traits.
Enjoys interactive play and may form strong bonds with its human companions.
Tabby Cat:
Social behavior varies among breeds, with many domestic cats being affectionate and forming close bonds with their owners.
Ecological Implications:
Social behavior impacts the cat’s interactions with other animals in shared environments.
23. Mode of Reproduction
Bengal Cat:
Reproduces through sexual reproduction, with litters typically consisting of multiple kittens.
Tabby Cat:
Same mode of sexual reproduction, with variations in breeding cycles among different breeds.
Ecological Implications:
Reproductive patterns influence the population dynamics of domestic cats in various habitats.
24. Parental Behavior
Bengal Cat:
Mothers exhibit strong maternal instincts, providing care and protection to their kittens.
Tabby Cat:
Parental behavior varies, but domestic cats generally care for their offspring during the early weeks of life.
Ecological Implications:
Parental behavior contributes to the survival and well-being of cat populations in different environments.
25. Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas
Bengal Cat:
May adapt well to living in homes but retains some wild instincts.
Tabby Cat:
Well-adapted to living in close proximity to humans, often as indoor or outdoor pets.
Ecological Implications:
The proximity of cats to human-inhabited areas influences interactions and potential impacts on local ecosystems.
26. Behavior Toward Humans

Bengal Cat:
Affectionate but may exhibit more independent behavior.
Enjoys interactive play and can form strong bonds with specific family members.
Tabby Cat:
Generally affectionate and social, forming close bonds with their human companions.
Varied behavior based on individual personality and breed.
Ecological Implications:
Human interactions influence the cat’s role in domestic settings and their impact on local wildlife.
27. Danger Posed to Humans
Bengal Cat:
Generally not dangerous, but strong hunting instincts may lead to scratches during play.
Tabby Cat:
Domestic cats pose minimal danger; scratches or bites are usually due to playfulness or stress.
Ecological Implications:
Understanding potential risks contributes to responsible pet ownership and cohabitation.
28. Associated Precautions
Bengal Cat:
Supervised outdoor time to prevent hunting of local wildlife.
Regular veterinary care due to potential genetic health concerns.
Tabby Cat:
Responsible pet ownership practices, including spaying/neutering and vaccination.
Indoor cats may require environmental enrichment.
Ecological Implications:
Precautions mitigate potential negative impacts on local ecosystems and ensure the well-being of the cat.
29. Conservation Status
Bengal Cat:
Domestic Bengal cats are not listed as a conservation concern.
Tabby Cat:
Domestic cats, including those with tabby patterns, are not considered conservation priorities.
Ecological Implications:
Conservation efforts focus on wild cat species, and responsible pet ownership minimizes impacts on local ecosystems.
Summary of Comparison
Taxonomy:
Bengal: Genus Prionailurus, Species P. bengalensis.
Tabby: Genus Felis, Species F. catus.
Appearance:
Bengal: Distinctive spotted or marbled coat, sleek build.
Tabby: Varied coat patterns, diverse appearance.
Size:
Bengal: Medium to large.
Tabby: Varies widely.
Weight:
Bengal: 8 to 15 pounds.
Tabby: Varies by breed.
Personality:
Bengal: Energetic, playful, intelligent.
Tabby: Generally affectionate, adaptable.
Relative Price/Cost:
Bengal: More expensive.
Tabby: Generally more affordable.
Grooming and Maintenance:
Bengal: Minimal grooming, needs mental stimulation.
Tabby: Varies by breed, regular brushing.
Health Concerns:
Bengal: Prone to genetic conditions.
Tabby: Varied, regular vet visits.
Bite Force (PSI):
Bengal: Moderately documented, considered moderate.
Tabby: Generally moderate.
Physical Offensive Advantages:
Bengal: Strong, agile, sharp claws.
Tabby: Varied based on individual and breed.
Physical Defensive Advantages:
Bengal: Quick reflexes, camouflaged coat.
Tabby: Agility, varied coat patterns.
Speed:
Bengal: Up to 30 mph.
Tabby: Varies.
Agility:
Bengal: Highly agile, efficient climbing.
Tabby: Agility varies.
Senses:
Bengal: Keen vision, hearing, and smell.
Tabby: Excellent night vision, sensitive whiskers.
Overall Physical Capacity:
Bengal: Robust, high energy.
Tabby: Adaptable, well-suited to different environments.
Habitat Preference(s):
Bengal: Prefers areas with climbing opportunities.
Tabby: Adaptable to various habitats.
Tracks:
Bengal: Resembles small wild cats.
Tabby: Varies based on individual size.
Lifespan:
Bengal: 12-16 years.
Tabby: Varies by breed.
Natural Mode of Feeding:
Bengal: Carnivorous.
Tabby: Carnivorous.
Best Food as a Pet:
Bengal: High-quality, protein-rich.
Tabby: Nutritionally balanced.
Intelligence:
Bengal: Intelligent, requires mental stimulation.
Tabby: Varies by breed, adaptable.
Social Behavior:
Bengal: Social but may be independent.
Tabby: Generally affectionate and social.
Mode of Reproduction:
Bengal: Sexual reproduction, multiple kittens.
Tabby: Sexual reproduction, varied breeding cycles.
Parental Behavior:
Bengal: Strong maternal instincts.
Tabby: Varies but generally cares for offspring.
Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Bengal: Adaptable but retains wild instincts.
Tabby: Well-adapted to living close to humans.
Behavior Toward Humans:
Bengal: Affectionate but may be independent.
Tabby: Generally affectionate, behavior varies.
Danger Posed to Humans:
Bengal: Generally not dangerous, may scratch during play.
Tabby: Minimal danger, scratches or bites usually due to playfulness or stress.
Associated Precautions:
Bengal: Supervised outdoor time, regular vet care.
Tabby: Responsible ownership practices, enrichment for indoor cats.
Conservation Status:
Bengal: Domestic Bengal cats not conservation concerns.
Tabby: Domestic cats, including tabby patterns, not conservation priorities.
Conclusion
I. Similarities
Both Bengal and Tabby cats share a carnivorous diet and are adaptable to living in human-inhabited areas.
II. Differences
Divergence in appearance, behavior, and ecological implications, with Bengal cats displaying more wild characteristics and potential impact on local wildlife. Tabby cats, being a diverse group, adapt well to various environments with varied personalities and impacts.








