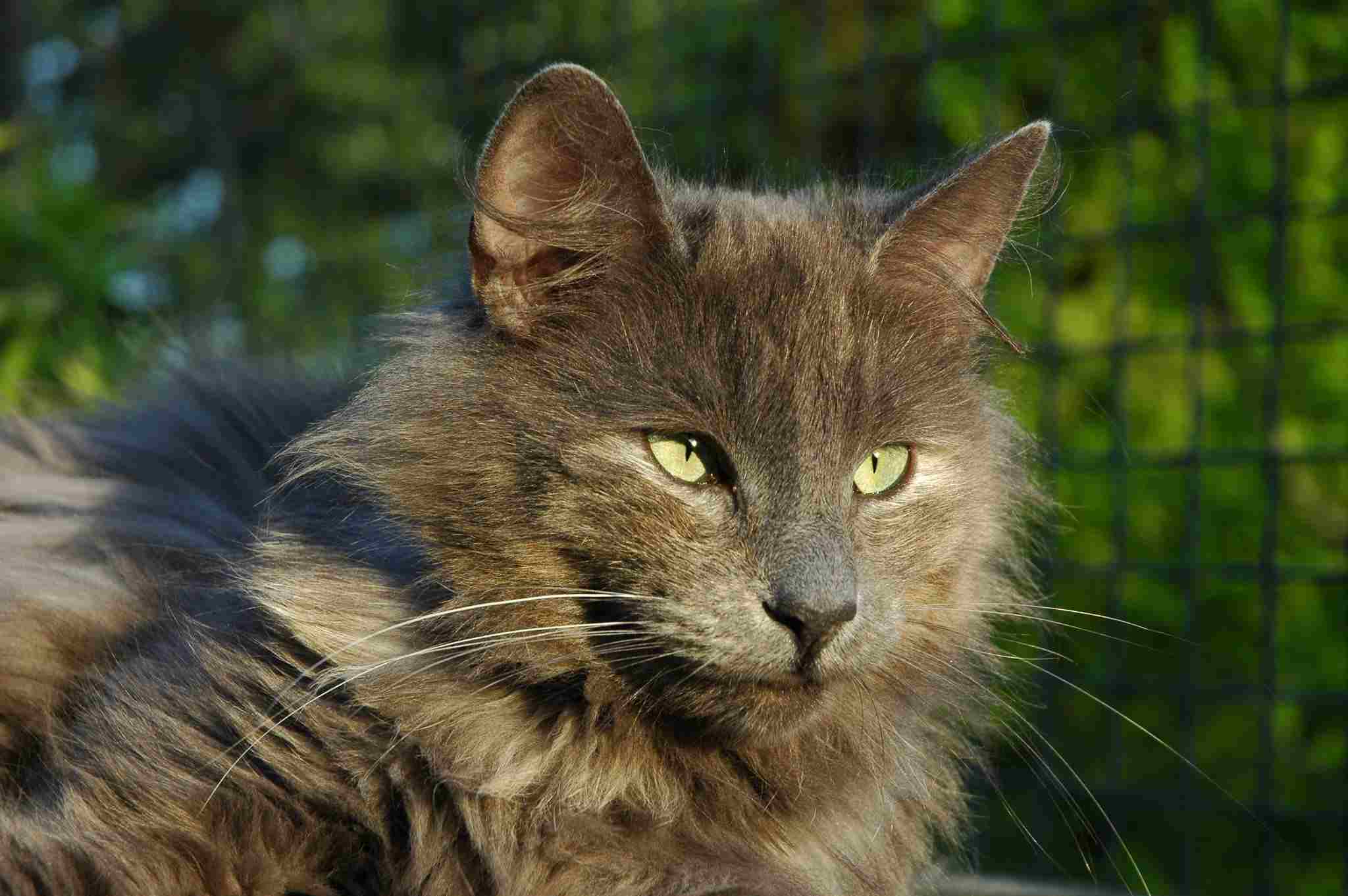
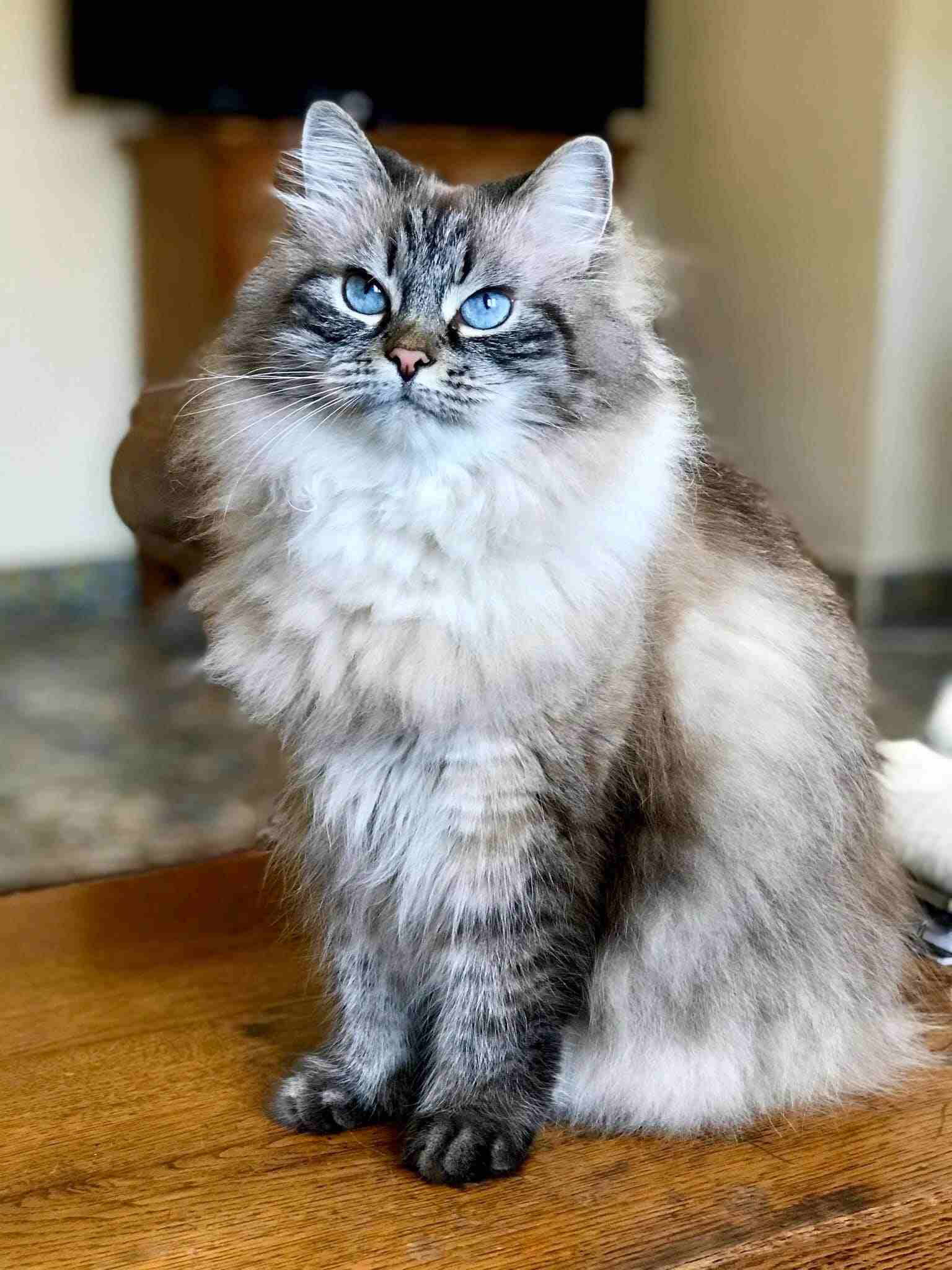
Norwegian Forest Cat Vs Siberian Size, Weight, Overall Comparison
The Norwegian Forest Cat and Siberian Cat are captivating options for a feline companion, with remarkable differences. From the majestic angular heads of Norwegian Forest Cats to the rounder, fluffier appearance of Siberian Cats, each breed brings distinct charm. As we navigate the realms of size, weight, and overall comparisons, key distinctions unfold – from coat compositions and color variations to the pricing nuances that make each breed uniquely appealing.
I. Physical Build:
– Norwegian Forest Cats are known for their angular-shaped heads, contributing to a regal and majestic appearance. In contrast, Siberian Cats boast rounder heads, adding to their overall fluffy and cuddly appearance.

II. Ear Characteristics:
– Siberian Cats typically have smaller ears compared to Norwegian Forest Cats. Their petite ear size complements their round head shape, enhancing their adorable and charming appearance.
III. Coat Composition:
– Siberian Cats possess a luxurious three-layer coat, consisting of a dense undercoat, a water-resistant middle layer, and a long, glossy topcoat. Conversely, Norwegian Forest Cats have a two-layer coat, which provides ample protection against harsh weather conditions.
IV. Color Variation:
– Norwegian Forest Cats exhibit a wide range of colors and patterns, including tabby, tortoiseshell, and solid colors. This diversity adds vibrancy and individuality to their appearance. Meanwhile, Siberian Cats may showcase a more limited color palette, often featuring traditional colors like brown, black, and white.
V. Size and Affection:
– Siberian Cats tend to grow larger in size compared to Norwegian Forest Cats, showcasing a more substantial build and muscular frame. Despite their larger size, Siberian Cats are known for their affectionate nature and enjoy bonding closely with their human companions.

VI. Pricing Distinctions:
– The pricing for Siberian Cats typically ranges from around $1000 to over $2500, reflecting their unique characteristics and high demand. On the other hand, Norwegian Forest Cats are generally priced between $900 and $1500, offering a more affordable option for potential owners.
VII. Appreciating Breed Diversity:
– Recognizing the distinctions between Norwegian Forest Cats and Siberian Cats allows prospective owners to appreciate the diverse qualities within each breed. Whether it’s the majestic appearance of the Norwegian Forest Cat or the affectionate nature of the Siberian Cat, both breeds offer unique companionship experiences.
*Details of Comparison
| Criteria | Norwegian Forest Cat | Siberian Cat |
| Appearance | Robust physique with distinctive features. |
Strong build with a triple-layered coat.
|
| Size | Larger size, males 13-22 lbs, females 9-16 lbs. |
Medium to large, males 15-20 lbs, females 8-12 lbs.
|
| Weight | Generally larger, males 13-22 lbs, females 9-16 lbs. |
Slightly smaller, males 15-20 lbs, females 8-12 lbs.
|
| Personality | Friendly, affectionate, sociable. |
Friendly, affectionate, sociable.
|
| Relative Price/Cost | High-priced, varies based on factors. |
Moderately to high-priced, varies based on factors.
|
| Grooming Requirements | Regular grooming, longer coat. |
Regular grooming, less dense coat.
|
| Health Concerns | Generally healthy, predisposition to certain issues. |
Generally healthy, lower prevalence of disorders.
|
| Bite Force (PSI) | Data not extensively studied. |
Data not extensively studied.
|
| Offensive Advantages | Sharp claws and teeth for hunting. |
Sharp claws and teeth for hunting.
|
| Defensive Advantages | Thick coat for insulation and agility. |
Triple-layered coat and robust physique.
|
| Speed
(Mile/hour) |
Up to 30 mph. | Up to 30 mph. |
| Agility | Highly agile, well-balanced. |
Agile and coordinated movements.
|
| Senses | Acute hearing, sight, and smell. |
Sharp senses and whiskers for spatial awareness.
|
| Overall Physical Capacity | Strong, agile, and well-adapted. |
Sturdy, agile, and well-muscled.
|
| Habitat Preference(s) | Wooded areas, adapted to Norway. |
Originating from Siberia, cold climates preference.
|
| Tracks | Paw prints reflect climbing and hunting behaviors. |
Paw prints reflect agility and hunting behaviors.
|
| Lifespan | Average 12-16 years. |
Average 12-15 years.
|
| Natural Feeding | Carnivorous diet, hunting small prey. |
Carnivorous diet, preference for meat-based food.
|
| Best Food as a Pet | High-quality cat food, protein-rich. |
Balanced, nutritious cat food, emphasis on protein.
|
| Intelligence | Intelligent, adaptable, responsive. |
Intelligent, quick learners, resourceful.
|
| Social Behavior | Sociable, forms strong bonds. |
Social, seeks attention and forms close connections.
|
| Reproduction | Sexual reproduction, heat cycles. |
Sexual reproduction, heat cycles.
|
| Parental Behavior | Nurturing and protective parental behaviors. |
Affectionate and attentive parental behaviors.
|
| Proximity to Humans | Well-adapted to human-inhabited areas. |
Domesticated and comfortable with humans.
|
| Behavior Toward Humans | Affectionate, enjoys human companionship. |
Affectionate, seeks attention and physical closeness.
|
| Danger Posed to Humans | Generally not dangerous, rarely aggressive. |
Generally not dangerous, gentle demeanor.
|
| Associated Precautions | Enriching environment, regular grooming. |
Enriching environment, regular grooming.
|
| Conservation Status | Not endangered, thriving domestic populations. |
Not endangered, thriving domestic populations.
|
1. Taxonomy:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Felidae
Genus: Felis
Species: Felis catus
Subspecies: Felis catus domesticus
Siberian Cat:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Felidae
Genus: Felis
Species: Felis catus
Subspecies: Felis catus domesticus
2. Appearance:
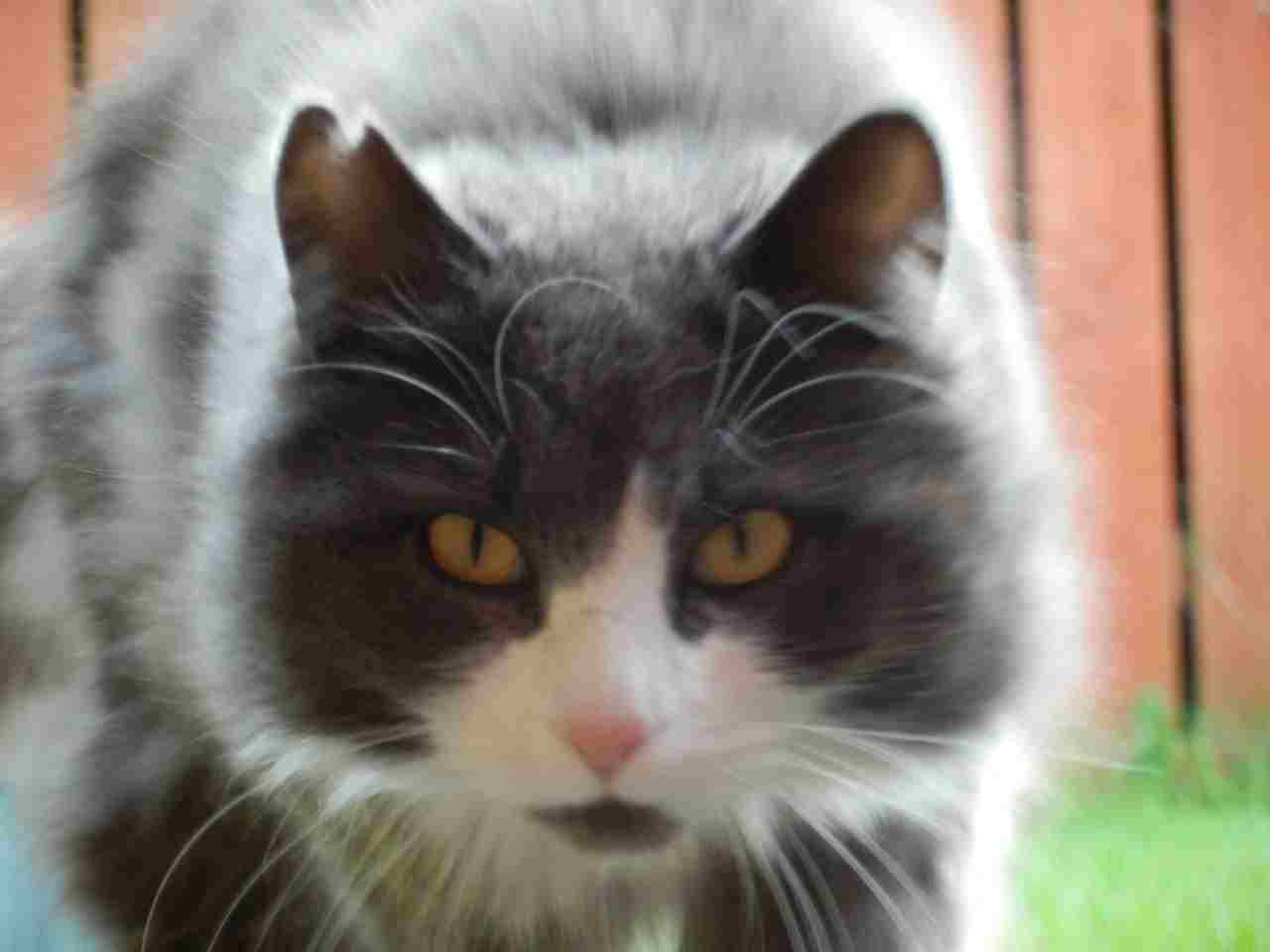
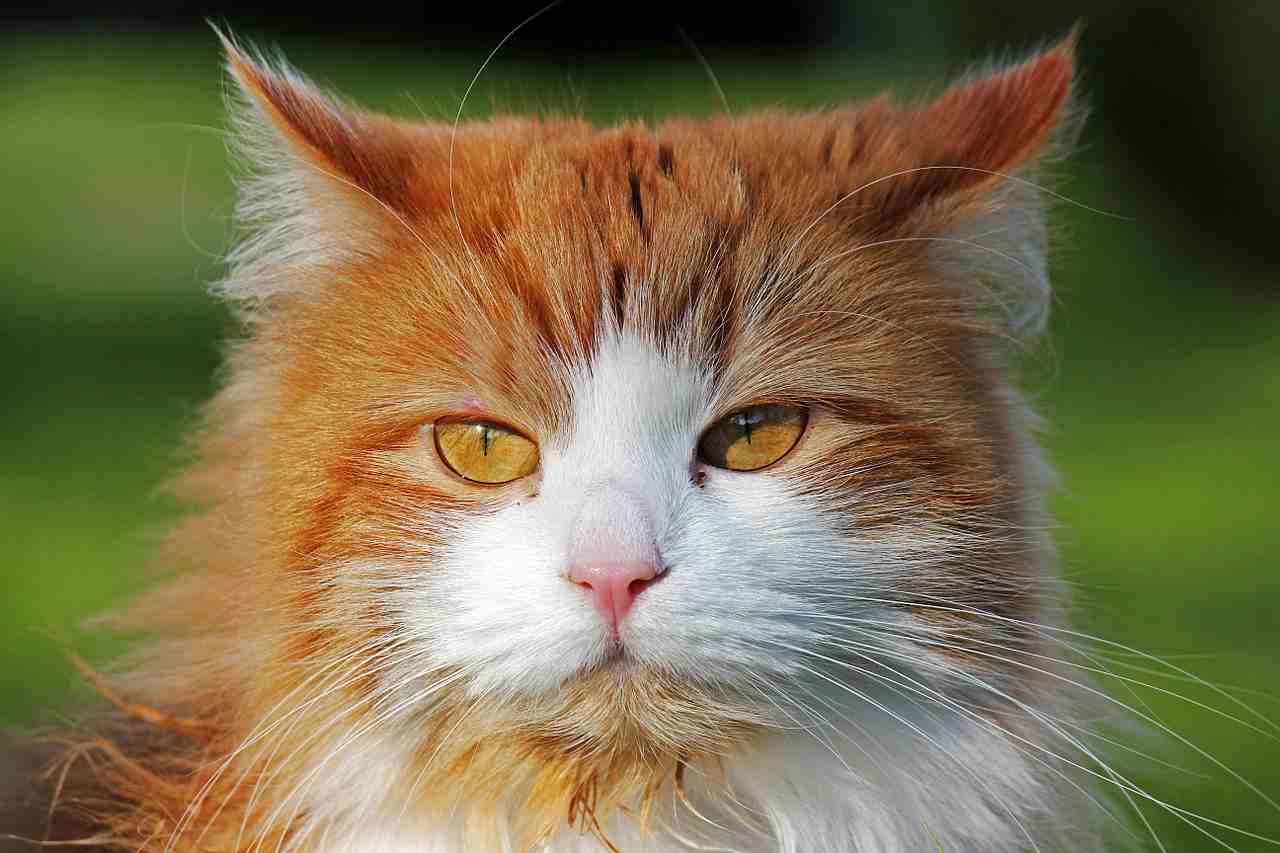


Norwegian Forest Cat:
Robust and well-muscled with a semi-long, thick double coat.
Tufted ears, bushy tail, and a ruff of fur around the neck.
Variety of coat colors and patterns, often with lynx-like tufted ears.
Siberian Cat:
Medium to large-sized cat with a strong build and a triple-layered coat.
Round face, broad nose, and large, expressive eyes.
Coat comes in various colors and patterns, contributing to its striking appearance.
Comparison:
Both breeds share a strong and well-defined physique.
Distinguishing features like tufted ears are present in both breeds, but with subtle variations.
Ecological Implications:
The appearance of these cats reflects adaptations to cold climates, providing insulation against harsh weather conditions.
Camouflaging coat patterns might aid in hunting or evading predators in their natural habitats.
3. Size:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Large-sized cat breed with males typically weighing between 13-22 lbs (6-10 kg) and females between 9-16 lbs (4-7 kg).
Siberian Cat:
Medium to large-sized cat with males weighing around 15-20 lbs (7-9 kg) and females around 8-12 lbs (4-6 kg).
Comparison:
Both breeds fall within the larger size range among domestic cats.
Siberian cats generally have a slightly smaller size range compared to Norwegian Forest Cats.
Ecological Implications:
Larger size may provide advantages in cold climates by conserving body heat.
4. Weight:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Adult males typically weigh between 13-22 lbs (6-10 kg), while females range from 9-16 lbs (4-7 kg).
Siberian Cat:
Adult males weigh around 15-20 lbs (7-9 kg), and females weigh approximately 8-12 lbs (4-6 kg).
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit a considerable weight range, with males being significantly larger than females in both cases.
The weight difference between the two breeds is relatively subtle.
Ecological Implications:
The weight of these cats may impact their ability to navigate different terrains in their natural habitats.
5. Personality:

Norwegian Forest Cat:
Intelligent, friendly, and sociable with a playful nature.
Known for their adaptability and getting along well with other pets.
Siberian Cat:
Gentle, affectionate, and good-natured, forming strong bonds with their owners.
Intelligent and often display problem-solving skills.
Comparison:
Both breeds share friendly and affectionate personalities.
Differences may be subtle, with individual variations playing a significant role.
Ecological Implications:
Sociable nature may enhance cooperation within feline social structures in the wild, contributing to hunting and survival.
6. Relative Price/Cost:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Generally, Norwegian Forest Cats are considered a high-priced breed.
Prices can vary based on factors such as pedigree, lineage, and breeder reputation.
Siberian Cat:
Siberian Cats are often priced moderately to high.
Costs may vary depending on factors like pedigree, coat quality, and breeder credentials.
Comparison:
Both breeds tend to be on the higher end of the price spectrum, reflecting their popularity and unique characteristics.
Individual variations in pricing may occur based on specific traits and breeder practices.
7. Grooming and Maintenance Requirements:

Norwegian Forest Cat:
Requires regular grooming due to its long, dense coat to prevent matting.
Brushing a few times a week helps manage shedding and maintain coat health.
Siberian Cat:
Regular brushing is essential to manage shedding, particularly during seasonal changes.
Siberian Cats generally have a less dense coat compared to the Norwegian Forest Cat.
Comparison:
Both breeds demand grooming attention, with the Norwegian Forest Cat needing slightly more due to its longer coat.
Regular grooming promotes overall well-being and reduces the risk of hairballs.
8. Health Concerns:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Generally healthy breed with a predisposition to certain genetic conditions like hip dysplasia and heart issues.
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential to monitor and address potential health issues.
Siberian Cat:
Robust breed with a lower prevalence of genetic disorders.
Regular veterinary care is crucial for preventive health measures.
Comparison:
Both breeds are relatively healthy, but the Norwegian Forest Cat may have a slightly higher likelihood of certain genetic conditions.
Responsible breeding practices and regular veterinary care contribute to maintaining their well-being.
9. Bite Force (PSI):

Norwegian Forest Cat:
Specific data on bite force in PSI for Norwegian Forest Cats is not readily available.
Siberian Cat:
Specific data on bite force in PSI for Siberian Cats is not readily available.
Comparison:
Bite force information for domestic cat breeds, including Norwegian Forest and Siberian, is not extensively studied.
Cats, in general, have sharp teeth designed for hunting and self-defense.
Ecological Implications:
Bite force in domestic cats is more related to their predatory instincts than ecological implications.
In the wild, strong bites would aid in capturing and eating prey.
10. Physical Offensive Advantages:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Sharp claws and teeth for hunting and self-defense.
Agile and muscular physique enhances effective pouncing and capturing of prey.
Siberian Cat:
Possesses sharp claws and teeth, adapted for hunting and protection.
Agile and sturdy build contributes to effective offensive maneuvers.
Comparison:
Both breeds share similar offensive capabilities, utilizing sharp claws and teeth for various purposes.
Individual variations may influence specific hunting techniques.
11. Physical Defensive Advantages:

Norwegian Forest Cat:
Thick, dense fur provides insulation against harsh weather conditions and potential attacks.
Agile and swift movements aid in evading predators.
Siberian Cat:
Triple-layered coat offers protection against cold climates and potential threats.
Agile and robust physique supports defensive maneuvers.
Comparison:
Both breeds possess defensive adaptations in their coats and physical agility.
These adaptations are essential for survival in their respective native environments.
12. Speed (Km/hour or Mile/hour):
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Domestic cats, including the Norwegian Forest Cat, can reach speeds of up to 30 miles per hour (48 km/h).
Siberian Cat:
Domestic cats, including the Siberian Cat, can reach speeds of up to 30 miles per hour (48 km/h).
Comparison:
Both breeds share similar speed capabilities typical of domestic cats.
Their speed is a crucial attribute for hunting and escaping potential threats.
13. Agility:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Agile and nimble, capable of navigating various terrains with ease.
Well-developed sense of balance contributes to climbing and jumping skills.
Siberian Cat:
Agile and coordinated, displaying grace in movements.
Excellent jumping and climbing abilities contribute to their overall agility.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit high levels of agility, a characteristic vital for survival in their natural habitats.
Agility aids in hunting, escaping predators, and exploring their surroundings.
14. Senses:

Norwegian Forest Cat:
Acute senses of hearing, sight, and smell.
Whiskers play a crucial role in detecting nearby objects and navigating in low-light conditions.
Siberian Cat:
Sharp senses of hearing, sight, and smell.
Whiskers serve as sensory tools for spatial awareness.
Comparison:
Both breeds have highly developed senses, crucial for hunting, navigating, and detecting potential threats.
Whiskers contribute significantly to their sensory perception.
15. Overall Physical Capacity:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Strong and robust physique, well-adapted for various environmental conditions.
Muscular build supports agility, climbing, and effective hunting.
Siberian Cat:
Sturdy and well-muscled body, suited for survival in colder climates.
Agile and coordinated, showcasing overall physical prowess.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit excellent overall physical capacity, combining strength, agility, and sensory awareness.
These traits enhance their survival skills in different environments.
16. Habitat Preference(s):

Norwegian Forest Cat:
Historically adapted to the forests of Norway, preferring wooded areas with ample opportunities for climbing and hunting.
Siberian Cat:
Originating from Siberia, these cats are well-suited to cold climates and may have a preference for environments with snow and foliage.
Comparison:
Both breeds have specific habitat preferences based on their geographical origins.
Preferences may include wooded areas, colder climates, or environments suitable for their hunting instincts.
17. Tracks:

Norwegian Forest Cat:
Paw prints typically show distinct features, including claw marks, reflecting their climbing and digging behaviors.
Siberian Cat:
Paw prints exhibit characteristics of a well-built cat, with features reflecting their agility and hunting behaviors.
Comparison:
Paw prints of both breeds display common feline traits, emphasizing their roles as hunters and climbers.
Individual variations may be observed based on environmental factors.
18. Lifespan:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
On average, Norwegian Forest Cats have a lifespan of 12 to 16 years.
Lifespan can be influenced by genetics, diet, and overall healthcare.
Siberian Cat:
Siberian Cats typically have a lifespan of 12 to 15 years.
Individual variations may occur based on factors such as genetics and living conditions.
Comparison:
Both breeds share a relatively similar lifespan range.
Proper veterinary care, nutrition, and a suitable environment contribute to their overall well-being and longevity.
19. Natural Mode of Feeding:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
In the wild, would rely on hunting small mammals and birds for food.
Carnivorous diet, similar to domestic cats, consisting primarily of meat.
Siberian Cat:
Wild ancestors would have hunted small prey in their natural habitats.
Carnivorous diet, with a preference for meat-based nutrition.
Comparison:
Both breeds share a natural instinct for hunting and consuming a carnivorous diet.
This instinct is reflected in their domestic behavior, often preferring meat-based cat food.
20. Best Food as a Pet:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
High-quality cat food, preferably with a protein-rich content to meet their carnivorous needs.
Regular access to fresh water is essential for hydration.
Siberian Cat:
Balanced and nutritious cat food, emphasizing protein sources.
Adequate hydration through access to fresh water.
Comparison:
Both breeds benefit from a diet that mirrors their natural carnivorous tendencies.
Quality, balanced cat food contributes to their overall health and well-being.
21. Intelligence:

Norwegian Forest Cat:
Intelligent and adaptable, capable of learning and problem-solving.
May display curiosity and an aptitude for interactive play.
Siberian Cat:
Intelligent and quick learners, with a knack for problem-solving.
Known for their resourcefulness and ability to adapt to various situations.
Comparison:
Both breeds are recognized for their intelligence, making them responsive to training and interactive engagement.
Individual variations may influence specific behaviors and problem-solving abilities.
22. Social Behavior:

Norwegian Forest Cat:
Generally sociable and friendly, forming strong bonds with their human companions.
Tends to get along well with other pets in the household.
Siberian Cat:
Social and affectionate, often seeking attention and forming close connections with their owners.
Can exhibit a friendly demeanor towards other pets.
Comparison:
Both breeds share social and affectionate behaviors, making them suitable companions.
Adaptability and friendliness contribute to positive interactions with humans and other animals.
23. Mode of Reproduction:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Like all domestic cats, Norwegian Forest Cats reproduce through sexual reproduction.
Females go through a heat cycle, and mating occurs between a male and a female.
Siberian Cat:
Reproduction is through sexual mating, with females experiencing heat cycles.
The birth of kittens is the result of successful mating between a male and a female.
Comparison:
Both breeds share the typical reproductive characteristics of domestic cats.
The mode of reproduction involves mating, pregnancy, and the birth of live kittens.
24. Parental Behavior:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Generally exhibits nurturing and protective parental behaviors.
Mothers are attentive to their kittens, providing care and teaching essential skills.
Siberian Cat:
Display affectionate and attentive parental behaviors, ensuring the well-being of their kittens.
Mothers actively engage in grooming and teaching behaviors.
Comparison:
Both breeds demonstrate caring and protective parental instincts.
Active involvement in grooming, teaching, and nurturing contributes to the well-being of their offspring.
25. Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Well-adapted to living in human-inhabited areas, forming close bonds with families.
Sociable nature makes them comfortable in indoor settings.
Siberian Cat:
Domesticated and comfortable living in human-inhabited areas.
Social and adaptable, making them suitable for indoor living with human companions.
Comparison:
Both breeds are well-suited to living in close proximity to humans.
Their social and adaptable nature allows for integration into households as beloved pets.
26. Behavior Toward Humans:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Typically affectionate and enjoys human companionship.
May follow their owners around and seek attention.
Siberian Cat:
Affectionate and social, forming strong bonds with their human family.
Enjoys interactive play and may seek physical closeness.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit friendly behavior toward humans, making them popular choices as family pets.
Individual variations may influence specific interaction preferences.
27. Danger Posed to Humans:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Generally poses no significant danger to humans.
May exhibit playful behaviors but rarely aggressive unless provoked.
Siberian Cat:
Typically not dangerous to humans.
Gentle demeanor, and any aggression is usually a response to perceived threats.
Comparison:
Neither breed is known for posing a danger to humans.
Domestication and socialization contribute to their overall gentle nature.
28. Associated Precautions:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Ensure a safe environment for climbing and exploring due to their agile nature.
Regular grooming to manage their dense coat.
Siberian Cat:
Provide a stimulating environment for play and exploration.
Regular grooming to manage shedding.
Comparison:
Precautions for both breeds include creating an enriching environment that supports their natural behaviors.
Regular grooming and veterinary care are essential for overall well-being.
29. Conservation Status:
Norwegian Forest Cat:
Not listed as a conservation concern.
Popularity as a domestic breed contributes to their thriving population.
Siberian Cat:
Not listed as a conservation concern.
Recognized as a well-established domestic breed.
Comparison:
Both breeds are not considered endangered, with thriving populations as popular domestic cats.
Conservation efforts are not directed towards maintaining their wild populations.
Summary of Comparison
Appearance:
Both breeds exhibit a robust and well-defined physique.
Distinguishing features such as tufted ears are present in both but with subtle variations.
Size:
Norwegian Forest Cats are generally larger, with males weighing 13-22 lbs and females 9-16 lbs.
Siberian Cats have a medium to large size, with males around 15-20 lbs and females 8-12 lbs.
Weight:
Both breeds fall within a larger size range among domestic cats.
Siberian cats generally have a slightly smaller size range compared to Norwegian Forest Cats.
Personality:
Both are known for being friendly, affectionate, and sociable.
Individual variations may exist, but they share common positive traits.
Relative Price/Cost:
Both breeds are generally high-priced, reflecting their popularity and unique characteristics.
Prices may vary based on factors such as pedigree, lineage, and breeder reputation.
Grooming and Maintenance Requirements:
Both demand regular grooming, with the Norwegian Forest Cat needing slightly more due to its longer coat.
Regular grooming promotes overall well-being and reduces the risk of hairballs.
Health Concerns:
Both breeds are relatively healthy, but the Norwegian Forest Cat may have a slightly higher likelihood of certain genetic conditions.
Responsible breeding practices and regular veterinary care contribute to maintaining their well-being.
Bite Force (PSI):
Specific data on bite force for domestic cats, including both breeds, is not extensively studied.
Cats, in general, have sharp teeth designed for hunting and self-defense.
Physical Offensive Advantages:
Both breeds share similar offensive capabilities, utilizing sharp claws and teeth for various purposes.
Individual variations may influence specific hunting techniques.
Physical Defensive Advantages:
Both breeds possess defensive adaptations in their coats and physical agility.
These adaptations are essential for survival in their respective native environments.
Speed and Agility:
Both breeds exhibit similar speed capabilities typical of domestic cats (up to 30 mph) and high levels of agility.
Agility aids in hunting, escaping predators, and exploring their surroundings.
Senses:
Both breeds have highly developed senses crucial for hunting, navigating, and detecting potential threats.
Whiskers contribute significantly to their sensory perception.
Overall Physical Capacity:
Both breeds exhibit excellent overall physical capacity, combining strength, agility, and sensory awareness.
These traits enhance their survival skills in different environments.
Habitat Preference(s):
Both breeds have specific habitat preferences based on their geographical origins, such as wooded areas and colder climates.
Preferences may include environments suitable for their hunting instincts.
Tracks:
Paw prints of both breeds display common feline traits, emphasizing their roles as hunters and climbers.
Individual variations may be observed based on environmental factors.
Lifespan:
Both breeds share a relatively similar lifespan range (12-16 years for Norwegian Forest Cats and 12-15 years for Siberian Cats).
Proper veterinary care, nutrition, and a suitable environment contribute to their overall well-being and longevity.
Natural Mode of Feeding:
Both breeds share a natural instinct for hunting and consuming a carnivorous diet.
This instinct is reflected in their domestic behavior, often preferring meat-based cat food.
Best Food as a Pet:
Both benefit from a diet that mirrors their natural carnivorous tendencies, emphasizing protein sources.
Quality, balanced cat food contributes to their overall health and well-being.
Intelligence:
Both breeds are recognized for their intelligence, making them responsive to training and interactive engagement.
Individual variations may influence specific behaviors and problem-solving abilities.
Social Behavior:
Both breeds exhibit sociable and affectionate behaviors, forming strong bonds with their human family.
Adaptability and friendliness contribute to positive interactions with humans and other animals.
Mode of Reproduction and Parental Behavior:
Both breeds share typical reproductive characteristics and demonstrate caring and protective parental instincts.
Active involvement in grooming, teaching, and nurturing contributes to the well-being of their offspring.
Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Both breeds are well-suited to living in close proximity to humans, with social and adaptable natures.
Their comfort in indoor settings makes them suitable for integration into households as beloved pets.
Behavior Toward Humans and Danger Posed to Humans:
Neither breed is known for posing a danger to humans, displaying generally friendly and gentle behavior.
Individual variations may influence specific interaction preferences.
Associated Precautions:
Precautions for both breeds include creating an enriching environment that supports their natural behaviors.
Regular grooming and veterinary care are essential for overall well-being.
Conservation Status:
Both breeds are not considered endangered, with thriving populations as popular domestic cats.
Conservation efforts are not directed towards maintaining their wild populations.
Conclusion
I. Similarities:
Both Norwegian Forest Cats and Siberian Cats share similarities in appearance, size, and social behaviors.
They have comparable lifespans, intelligence, and overall suitability as family pets.
II. Differences:
Distinctive features include coat characteristics, with the Norwegian Forest Cat having a longer, denser coat.
Variations in size, weight, and grooming requirements set them apart, with subtle differences in temperament and preferences.