Savannah Cat Vs Bengal Cat Size, Weight, Overall Comparison
Comparing the Savannah Cat and Bengal Cat unveils intriguing differences in both their origins and characteristics. The Savannah Cat, a cross between a domestic cat and a serval, boasts a larger and heavier frame compared to the Bengal Cat, which stems from the crossing of a domestic cat with an Asian leopard cat. In a confrontation, the Savannah Cat’s size advantage positions it as the likely victor. Additionally, their distinct personalities, expenses, and care requirements contribute to the nuanced world of feline companionship.
Savannah Cat vs Bengal Cat: Navigating Feline Distinctions
I. Origins and Crossbreeding:
– The Savannah Cat is a crossbreed between a domestic cat and a serval, while the Bengal Cat results from the crossbreeding of a domestic cat with an Asian leopard cat. These unique origins influence their physical characteristics and temperaments.
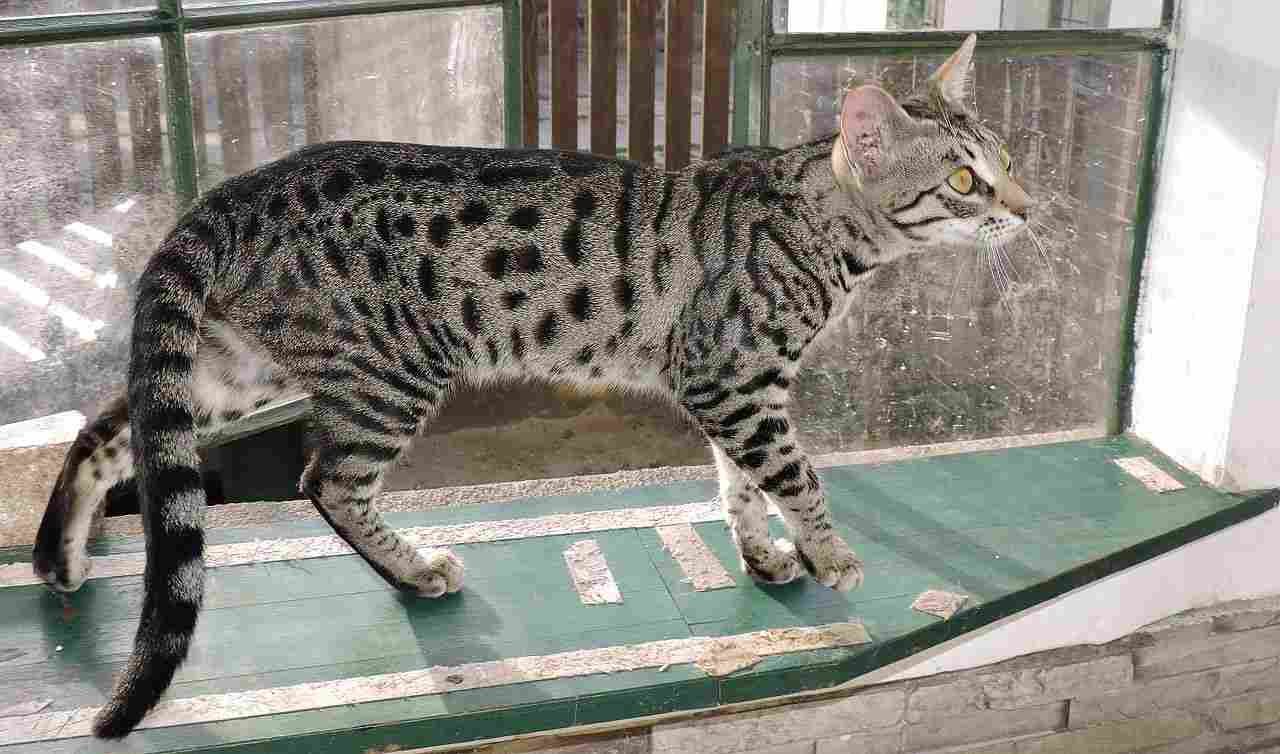

II. Size and Weight:
– Savannah Cats, with their serval lineage, tend to be larger and heavier than Bengal Cats. This size disparity plays a pivotal role in their potential dominance in a hypothetical physical confrontation.
III. Personality Traits:
– Bengal Cats are known for their playful nature, making them lively and engaging companions. However, in some cases, their playfulness may verge on being overbearing. On the other hand, Savannah Cats are also playful but exhibit slightly less activity, contributing to a balanced interaction with their owners.
IV. Cost Considerations:
– Both Savannah and Bengal Cats fall within a wide price range, with costs ranging from $1000 to $20000 and above, depending on factors such as generation, sex, and other characteristics. However, Bengal Cats, in most cases, tend to be more expensive for initial purchase.
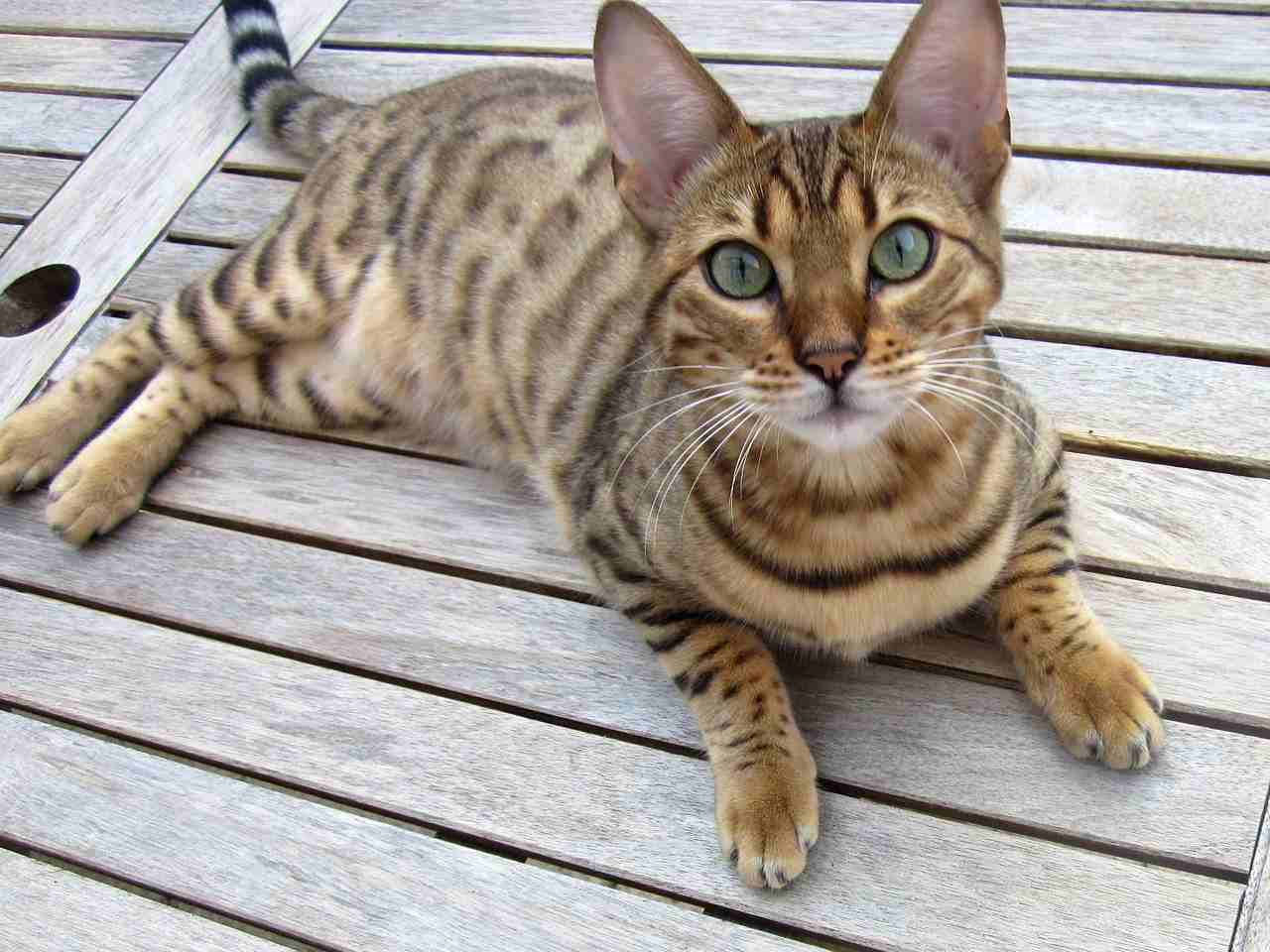

V. Maintenance Expenses:
– Savannah Cats, being larger and requiring more space, food, attention, and health care, incur higher maintenance expenses compared to Bengal Cats. This distinction underscores the importance of considering the long-term financial commitment associated with each breed.
VI. Hypothetical Confrontation:
– In a hypothetical fight, the larger, heavier, and potentially stronger build of the Savannah Cat could give it a practical advantage over the Bengal Cat, highlighting how physical attributes contribute to potential outcomes in feline confrontations.
VII. Tailoring Companionship:
– Prospective cat owners must carefully consider the distinct personalities, expenses, and care requirements of Savannah and Bengal Cats to tailor their choice of feline companion to their preferences and lifestyle, fostering a fulfilling and harmonious companionship.
*Details of Comparison
| Criteria | Savannah Cat | Bengal Cat |
| Taxonomy | Felis catus x serval |
Panthera bengalensis x Felis catus
|
| Appearance | Spotted coat, tall, lean build |
Spotted or marbled coat, muscular
|
| Size | Generally larger, especially F1s |
Moderate to large, influenced by generation
|
| Weight | Heavier, especially in early generations |
Generally lighter but larger than most domestic cats
|
| Bite Force (PSI) | Within typical domestic cat range |
Within typical domestic cat range
|
| Offensive Advantages | Agility, climbing skills, hunting abilities |
Agility, climbing skills, hunting abilities
|
| Defensive Advantages | Camouflage, agility, sharp claws |
Camouflage, agility, sharp claws
|
| Speed | Faster, around 30 mph |
Quick bursts, around 25 mph
|
| Agility | Exceptional, especially in jumping |
Highly agile with quick and precise movements
|
| Senses | Keen sight, hearing, night vision |
Keen sight, hearing, night vision
|
| Physical Capacity | Robust build, adapted for an active lifestyle |
Robust build, adapted for an active lifestyle
|
| Habitat Preference | Diverse environments |
Prefer lush, vegetated habitats
|
| Tracks | Feline characteristics, slight variations |
Feline characteristics, slight variations
|
| Lifespan | Generally longer, 12 to 20 years |
Typically 10 to 16 years
|
| Mode of Feeding | Carnivorous diet, domestic feeding practices |
Carnivorous diet, domestic feeding practices
|
| Intelligence | Highly intelligent, problem-solving skills |
Highly intelligent, problem-solving skills
|
| Social Behavior | Social, strong bonds with owners and other pets |
Social, strong bonds with owners and other pets
|
| Reproduction | Follow standard domestic cat reproductive patterns |
Follow standard domestic cat reproductive patterns
|
| Parental Behavior | Nurturing and protective maternal instincts |
Nurturing and protective maternal instincts
|
| Proximity to Humans | Well-suited for living in human-inhabited areas |
Well-suited for living in human-inhabited areas
|
| Behavior Toward Humans | Affectionate, seeking companionship and interactive play |
Affectionate, seeking companionship and interactive play
|
| Danger Posed to Humans | Generally non-threatening when properly socialized |
Generally non-threatening when properly socialized
|
| Associated Precautions | Require precautions for high energy levels and mental stimulation |
Require precautions for high energy levels and mental stimulation
|
| Conservation Status | Domestic, not subject to specific conservation concerns |
Domestic, not subject to specific conservation concerns
|
Key Points
- Both breeds share a wild appearance, high intelligence, and social behavior as domesticated hybrids.
- Savannahs tend to be larger, with longer legs, and potentially faster.
- Bengals have a distinctive “glitter” effect on their coat and may prefer lush habitats.
- Lifespan varies, with Savannahs generally having a longer potential lifespan.
- Both cats exhibit typical feline behaviors, requiring precautions for high energy levels and mental stimulation.
- Conservation efforts for Bengals focus on preserving the natural habitat of the wild leopard cat.
1. Taxonomy
Savannah Cat:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Felidae
Genus: Felis
Species: F. catus (domestic cat) x serval (wild African cat)
Bengal Cat:
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Felidae
Genus: Panthera
Species: P. bengalensis (wild Asian leopard cat) x F. catus (domestic cat)
2. Appearance
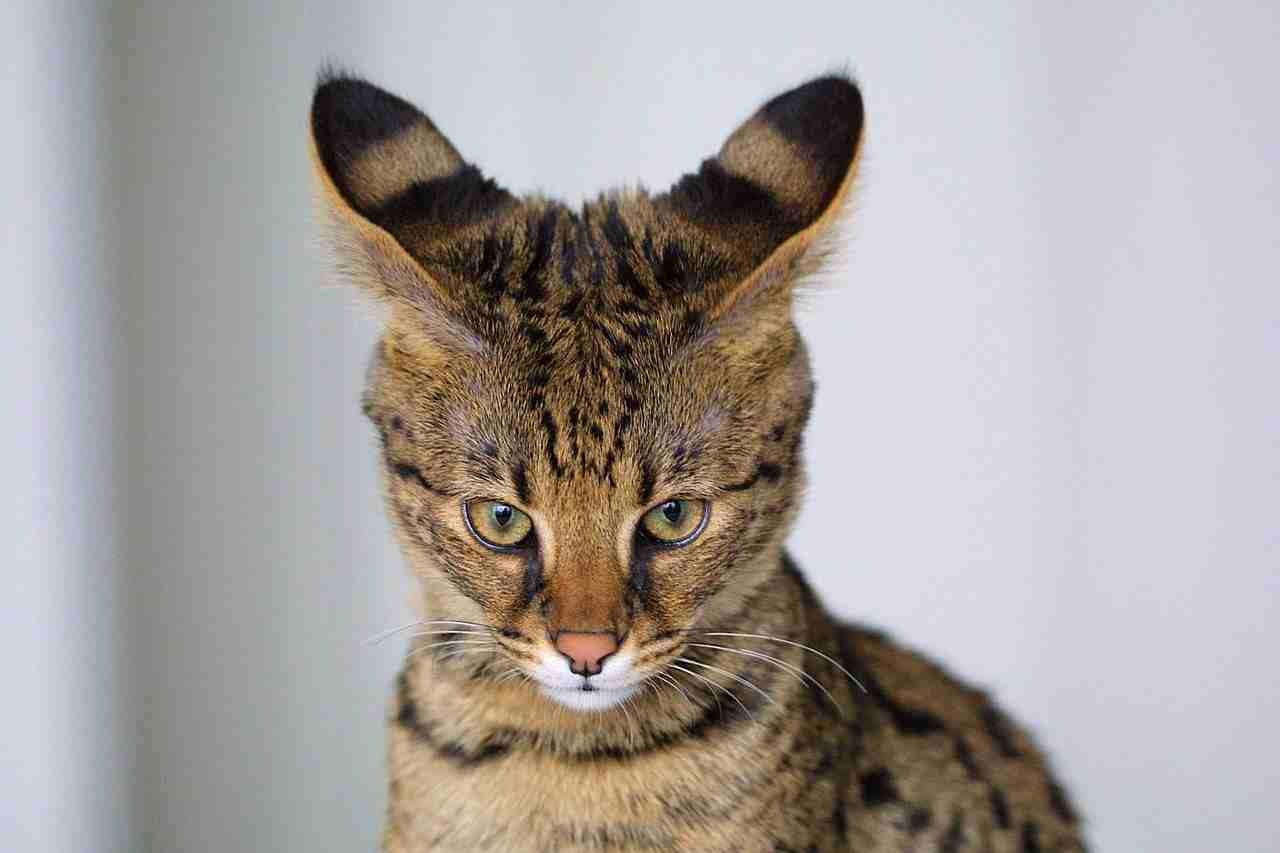

Savannah Cat:
Exhibits a distinctive spotted coat pattern reminiscent of its serval ancestry.
Taller, leaner build with long legs, large ears, and a short to medium-length tail.
Coat colors vary, often with a golden or tawny background.
Bengal Cat:
Known for its spotted or marbled coat resembling that of a wild leopard.
Muscular and sleek body, with a distinctive “glitter” effect on the fur.
Coat colors range from golden, brown, silver, to snow (with a white background).
Comparison:
Both breeds share a striking resemblance to wild big cats, owing to their hybridization with wild species.
Differences lie in the specific coat patterns, color variations, and the presence of the glitter effect in Bengals.
3. Size
Savannah Cat:
Generally larger than the average domestic cat.
Size can range from medium to large, with F1 (first-generation) Savannahs being the largest.
Bengal Cat:
Moderate to large in size, with males typically larger than females.
Size influenced by generation (F1 to later generations).
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit larger sizes compared to typical domestic cats.
Savannahs, especially F1s, tend to be larger overall compared to Bengals.
4. Weight
Savannah Cat:
Weights vary based on generation, with F1s weighing between 12 to 25 pounds.
Later generations (F2 and beyond) generally weigh less.
Bengal Cat:
Adult Bengals typically weigh between 8 to 15 pounds.
Males are usually larger than females.
Comparison:
Savannahs tend to be heavier, particularly in the early generations.
Bengals are generally lighter but still larger than most domestic cats.
5. Bite Force (PSI)
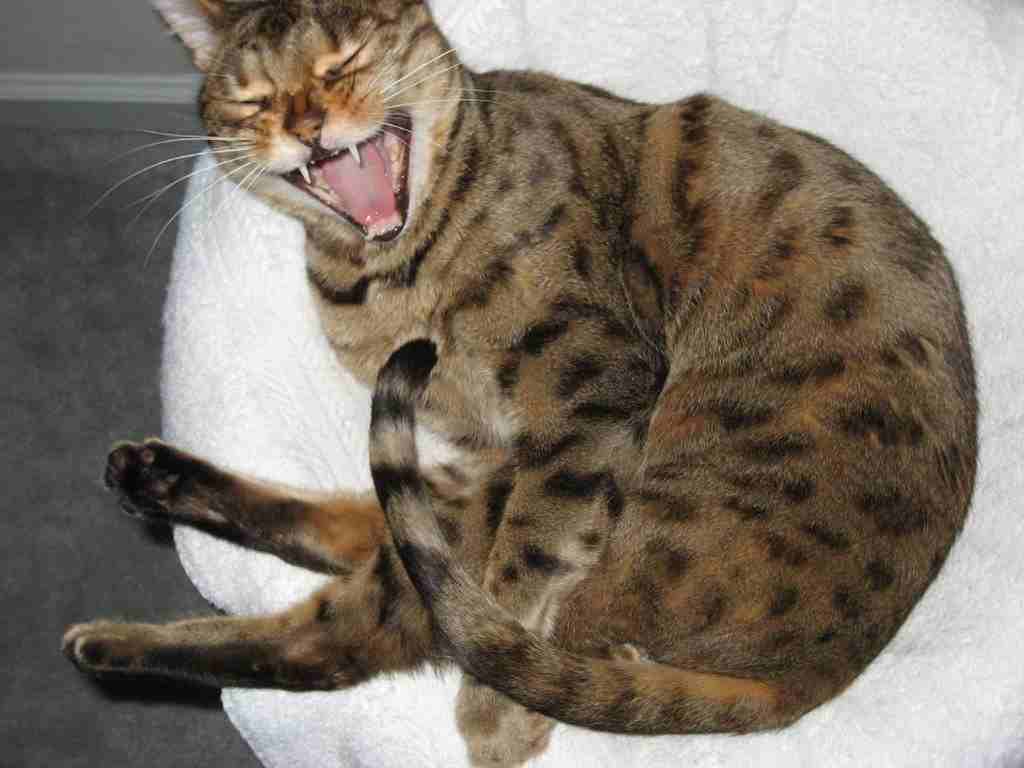

Savannah Cat:
Limited data available; estimated to have a bite force comparable to domestic cats.
Bengal Cat:
Domestic cat average bite force, around 200 to 300 PSI.
Not known for an exceptionally strong bite compared to some wild cat species.
Comparison:
Both breeds possess bite forces within the typical range for domestic cats.
Lack the jaw strength of larger wild cat species, mitigating potential ecological impact.
6. Physical Offensive Advantages
Savannah Cat:
Long legs provide enhanced jumping ability.
Agile and adept at climbing, offering advantages in hunting and exploration.
Bengal Cat:
Muscular build and agility contribute to efficient hunting and play.
Sharp claws and powerful hind legs aid in capturing prey.
Comparison:
Both breeds possess physical traits advantageous for hunting and exploring.
Savannahs may have a slight advantage in jumping due to their longer legs.
7. Physical Defensive Advantages
Savannah Cat:
Camouflage coat aids in blending into natural environments.
Quick reflexes and agility serve as defensive mechanisms.
Bengal Cat:
Spotted coat provides a degree of camouflage in certain environments.
Sharp claws and a strong, agile body offer defensive capabilities.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit defensive traits, relying on agility and camouflage.
The effectiveness may vary based on the specific environment.
8. Speed (Km/hour or Mile/hour)
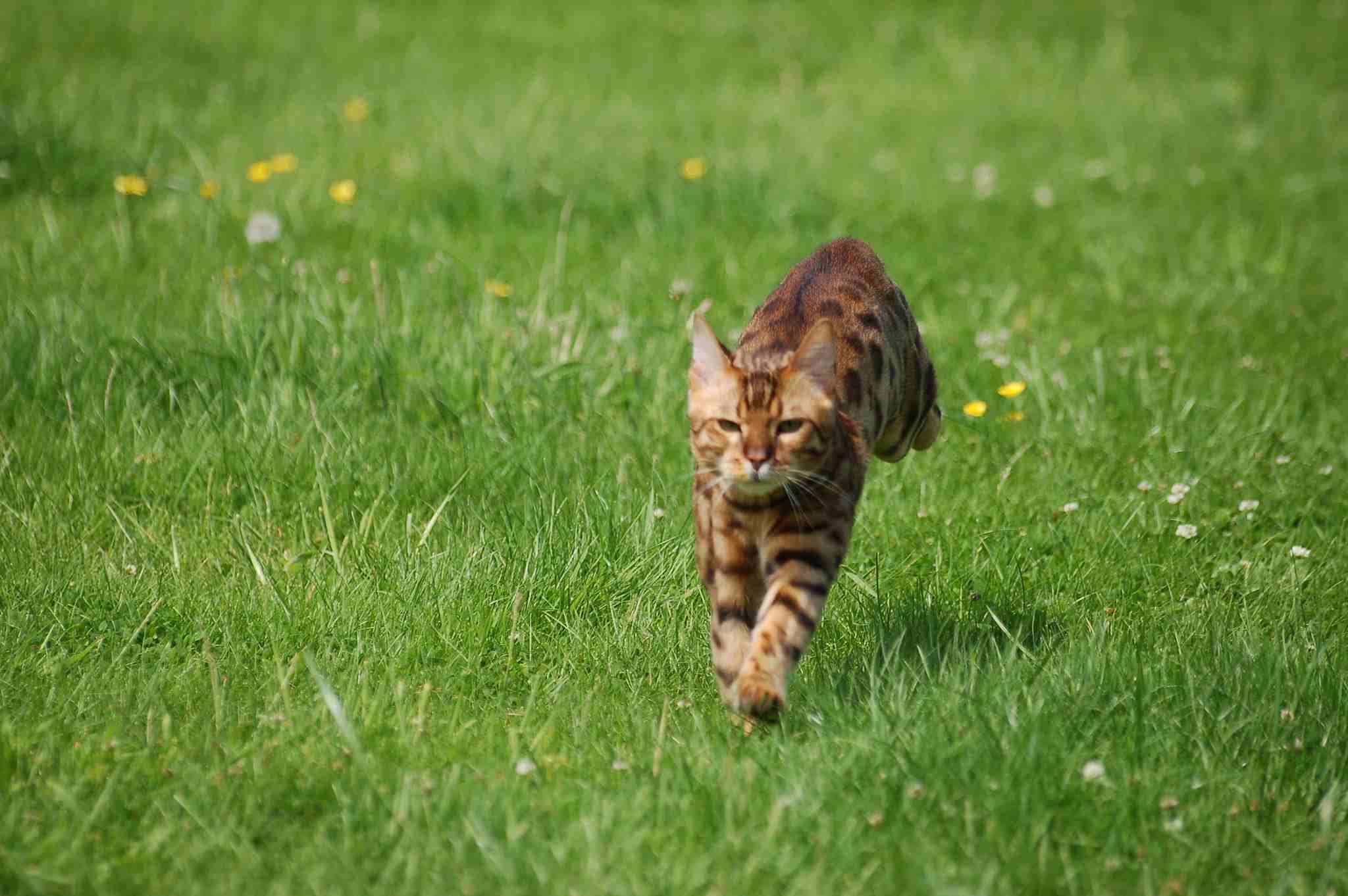

Savannah Cat:
Capable of reaching speeds around 30 miles per hour (48 km/h).
Long legs contribute to swift movements.
Bengal Cat:
Agility allows for bursts of speed, reaching around 25 miles per hour (40 km/h).
Quick acceleration and sharp turns are characteristic.
Comparison:
Savannahs generally have a slight speed advantage due to their longer legs.
Bengals, while fast, may excel in quick bursts and agility.
9. Agility
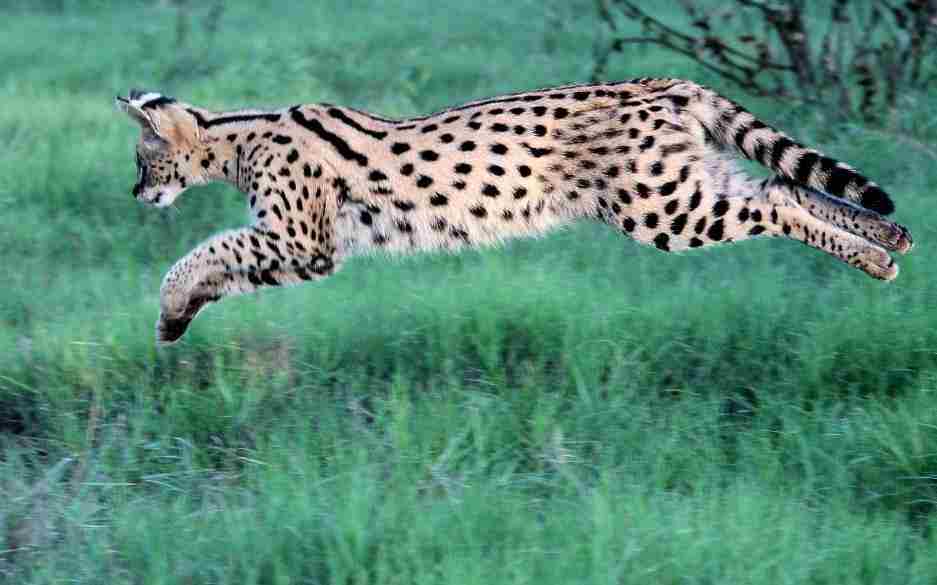

Savannah Cat:
Exceptionally agile, able to navigate obstacles with ease.
High jumping ability and keen coordination contribute to agility.
Bengal Cat:
Highly agile, capable of quick and precise movements.
Excellent climbers, utilizing their agility for hunting and exploration.
Comparison:
Both breeds showcase remarkable agility, a characteristic inherited from their wild ancestors.
Savannahs may exhibit slightly superior agility, especially in jumping.
10. Senses
Savannah Cat:
Keen senses of sight and hearing, crucial for hunting in varied environments.
Exceptional night vision inherited from the serval ancestry.
Bengal Cat:
Sharp senses of sight and hearing, adapted for detecting prey.
Good night vision, a trait inherited from the wild leopard cat.
Comparison:
Both breeds share heightened senses, an adaptation for their hunting instincts.
Savannahs may have a slight advantage in night vision due to serval genes.
11. Overall Physical Capacity
Savannah Cat:
Robust build, combining strength and agility for versatile physical capabilities.
Well-adapted for an active and dynamic lifestyle.
Bengal Cat:
Muscular physique and agility contribute to overall physical prowess.
Suited for hunting, climbing, and various physical activities.
Comparison:
Both breeds excel in overall physical capacity, adapted for an active lifestyle.
Slight differences may exist based on specific traits inherited from wild ancestors.
12. Habitat Preference(s)
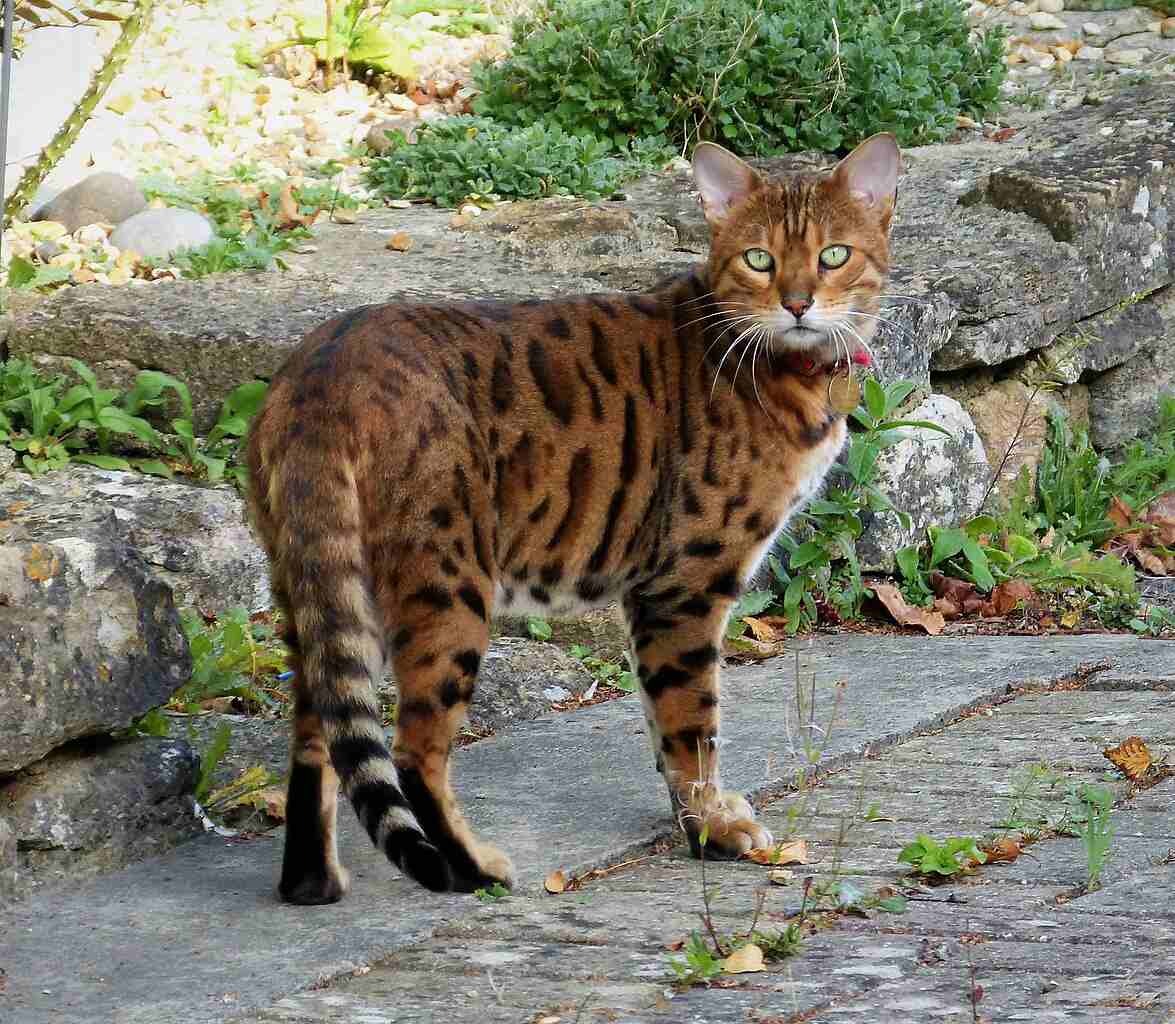

Savannah Cat:
Thrives in diverse environments, from grasslands to wooded areas.
Well-adapted to varying landscapes due to serval ancestry.
Bengal Cat:
Prefers habitats with dense vegetation, reflecting the natural habitat of the leopard cat.
Often found in tropical forests and jungle-like settings.
Comparison:
While both cats are adaptable, Savannahs may exhibit a broader range of habitat preferences.
Bengals show a preference for lush, vegetated environments.
13. Tracks
Savannah Cat:
Tracks display a combination of domestic cat and serval characteristics.
Distinctive elongated shape with visible toe prints.
Bengal Cat:
Tracks resemble those of domestic cats, with clear toe prints and retractable claw marks.
Size may vary based on individual cat size.
Comparison:
Tracks provide insights into the cat’s size and gait but may not clearly distinguish between the two breeds.
Savannah tracks may show more elongation due to serval ancestry.
14. Lifespan
Savannah Cat:
Generally has a lifespan of 12 to 20 years, with proper care.
Longevity influenced by factors such as genetics and healthcare.
Bengal Cat:
Typically lives 10 to 16 years, although some may live longer.
Health, diet, and genetics impact overall lifespan.
Comparison:
Savannahs tend to have a slightly longer potential lifespan compared to Bengals.
Both breeds benefit from attentive healthcare for optimal longevity.
15. Mode of Feeding
Savannah Cat:
Carnivorous diet, similar to domestic cats, with a preference for meat-based foods.
May have a more varied diet due to potential hunting instincts.
Bengal Cat:
Carnivorous diet, with commercial cat food supplemented by protein-rich treats.
Retains hunting instincts but often relies on provided meals.
Comparison:
Both breeds share a carnivorous diet, with Savannahs potentially exhibiting more hunting behaviors.
Domestic feeding practices mitigate ecological impacts compared to wild counterparts.
16. Intelligence

Savannah Cat:
Highly intelligent, known for problem-solving and interactive play.
May learn tricks and exhibit a curiosity resembling wild ancestors.
Bengal Cat:
Intelligent and curious, quick learners with a playful nature.
Thrives on mental stimulation and interactive activities.
Comparison:
Both breeds demonstrate high intelligence, a reflection of their wild ancestry.
Savannahs may have a slight edge in problem-solving abilities.
17. Social Behavior
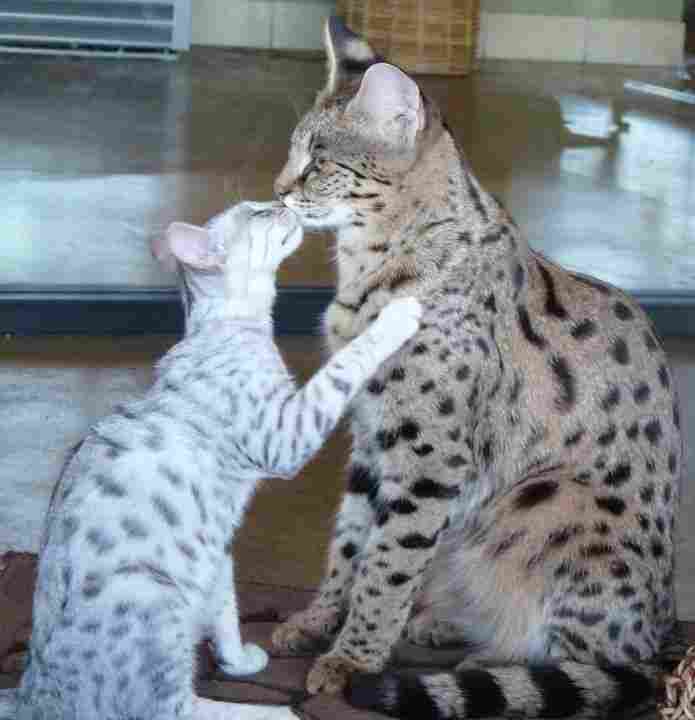

Savannah Cat:
Social and may form strong bonds with owners.
Tends to get along with other pets, including dogs, if introduced properly.
Bengal Cat:
Social and enjoys interaction, forming close bonds with owners.
May have territorial tendencies, especially with other cats.
Comparison:
Both breeds are social and affectionate, forming strong connections with their human companions.
Proper socialization is key to harmonious interactions with other pets, with individual variations.
18. Mode of Reproduction
Savannah Cat:
Reproduces through traditional domestic cat mating.
Gestation period and kitten-rearing behaviors are similar to other domestic cats.
Bengal Cat:
Reproduces through traditional domestic cat mating.
Exhibits typical feline reproductive behaviors during mating, gestation, and raising kittens.
Comparison:
Both breeds follow standard domestic cat reproductive patterns.
No notable differences in the mode of reproduction.
19. Parental Behavior
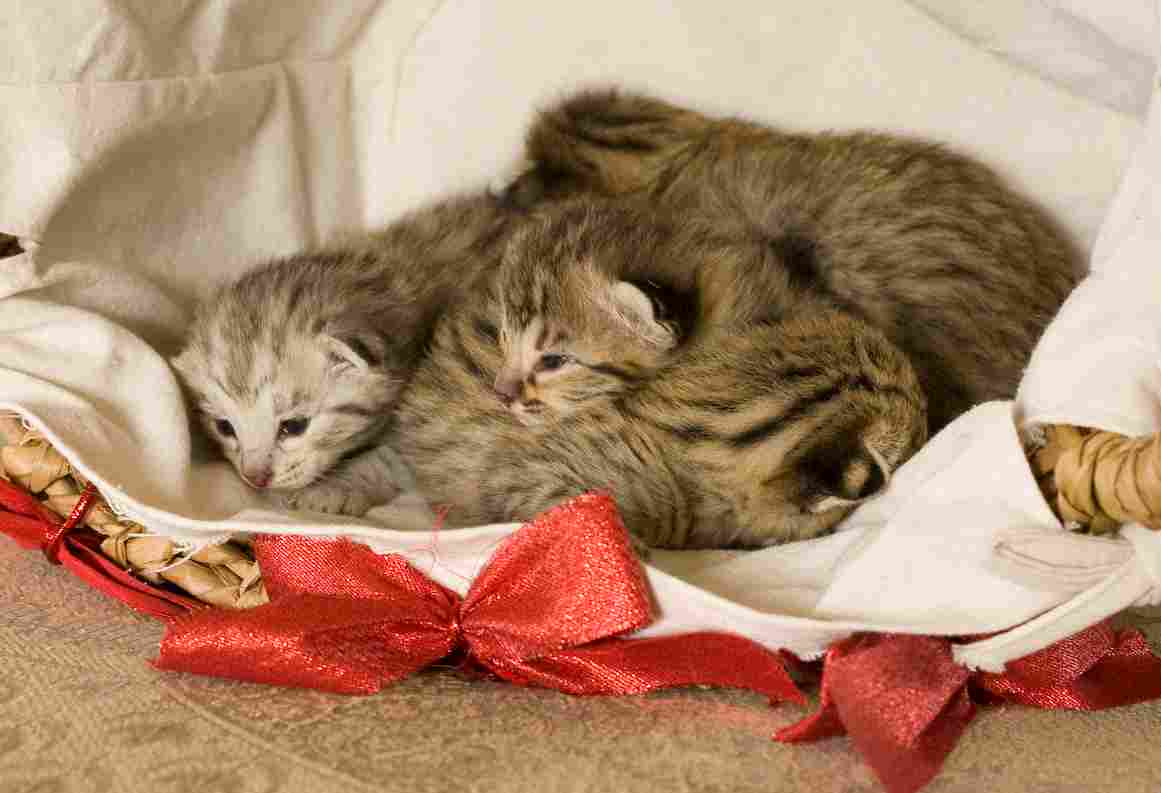

Savannah Cat:
Displays maternal instincts, caring for and nurturing kittens.
May exhibit some hunting behaviors to teach kittens.
Bengal Cat:
Shows maternal care, grooming and protecting kittens.
May teach hunting skills through play with offspring.
Comparison:
Similar parental behaviors in both breeds, reflecting typical domestic cat nurturing instincts.
Varied hunting behaviors may be observed in both Savannahs and Bengals.
20. Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas
Savannah Cat:
Comfortable living in human-inhabited areas, forming close bonds with owners.
Requires mental stimulation and interactive play.
Bengal Cat:
Adapts well to human-inhabited environments, forming strong connections with owners.
Requires mental and physical engagement for overall well-being.
Comparison:
Both breeds are well-suited for living in human-inhabited areas.
Human interaction and environmental enrichment are crucial for their contentment.
21. Behavior Toward Humans
Savannah Cat:
Affectionate and social, often forming strong bonds with owners.
May seek attention and enjoy interactive play.
Bengal Cat:
Affectionate and interactive, forming close relationships with owners.
Enjoys playtime and may have a vocal nature to communicate needs.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit affectionate behavior toward humans, seeking companionship and interaction.
Individual personalities may vary, but a generally sociable nature is common to both.
22. Danger Posed to Humans
Savannah Cat:
Generally poses no significant danger to humans when properly socialized and cared for.
May exhibit playful behaviors, but aggression is rare with adequate training.
Bengal Cat:
Generally poses no substantial danger when raised in a domestic environment.
Playful behavior may involve scratching or biting during play, but aggression is uncommon.
Comparison:
Both breeds, when properly socialized, are not known to pose substantial danger to humans.
Consistent training and care are essential for managing their behavior.
23. Associated Precautions
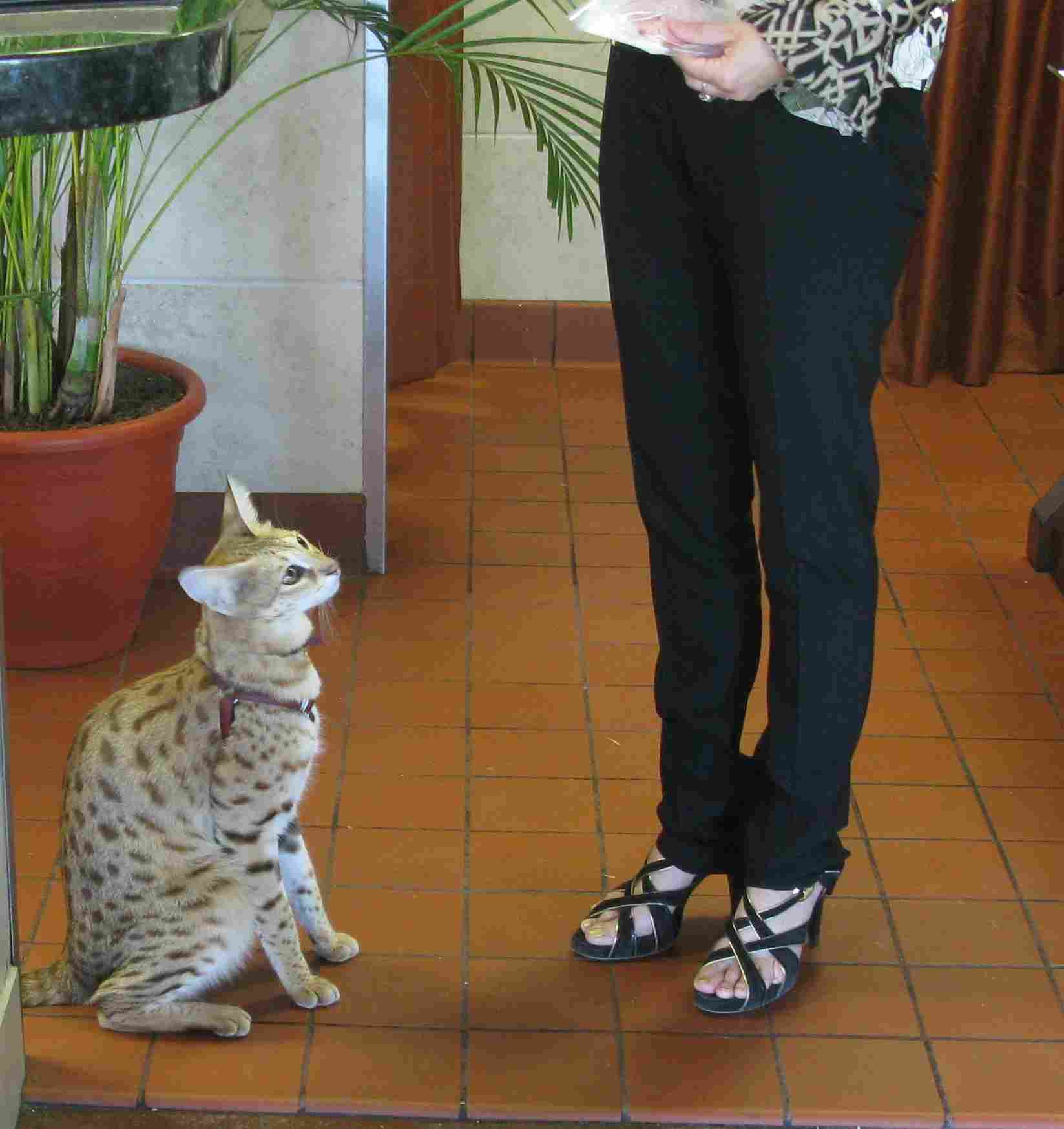

Savannah Cat:
Owners should be aware of the potential for high energy levels and provide sufficient mental stimulation.
Secure enclosures or supervised outdoor access may be needed to prevent escape.
Bengal Cat:
Regular play and mental stimulation are crucial to prevent boredom-related behaviors.
Ensuring a safe and stimulating environment helps mitigate potential issues.
Comparison:
Both breeds require precautions to address their high energy levels and need for mental stimulation.
Owners must take measures to create safe and engaging surroundings.
24. Conservation Status
Savannah Cat:
Not considered a wild species; conservation status is not applicable.
Managed by domestic cat breeding standards and regulations.
Bengal Cat:
Not a separate species, but the wild ancestor (Asian leopard cat) is near threatened due to habitat loss.
Conservation efforts focus on preserving the natural habitat of the wild leopard cat.
Comparison:
Both breeds are domestic and not subject to specific conservation concerns.
Conservation efforts for Bengals center on their wild ancestor’s natural habitat.
Summary of Comparison
Taxonomy:
Savannah: Felis catus x serval
Bengal: Panthera bengalensis x Felis catus
Appearance:
Savannah: Spotted coat, tall, lean build
Bengal: Spotted or marbled coat, muscular and sleek
Size:
Savannah: Generally larger, especially F1s
Bengal: Moderate to large, influenced by generation
Weight:
Savannah: Heavier, especially in early generations
Bengal: Generally lighter but larger than most domestic cats
Bite Force (PSI):
Both: Within typical domestic cat range, lack the strength of larger wild cats
Physical Offensive Advantages:
Both: Agility, climbing skills, and hunting abilities
Physical Defensive Advantages:
Both: Camouflage, agility, and sharp claws
Speed:
Savannah: Faster, around 30 mph
Bengal: Quick bursts, around 25 mph
Agility:
Savannah: Exceptional agility, especially in jumping
Bengal: Highly agile with quick and precise movements
Senses:
Both: Keen sight, hearing, and night vision
Overall Physical Capacity:
Both: Robust build, adapted for an active lifestyle
Habitat Preference(s):
Savannah: Diverse environments
Bengal: Prefer lush, vegetated habitats
Tracks:
Both: Tracks show feline characteristics, with slight variations
Lifespan:
Savannah: Generally longer, 12 to 20 years
Bengal: Typically 10 to 16 years
Mode of Feeding:
Both: Carnivorous diet, domestic feeding practices
Intelligence:
Both: Highly intelligent, exhibiting problem-solving skills
Social Behavior:
Both: Social, forming strong bonds with owners, and with proper introduction, other pets
Mode of Reproduction:
Both: Follow standard domestic cat reproductive patterns
Parental Behavior:
Both: Nurturing and protective maternal instincts
Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Both: Well-suited for living in human-inhabited areas, requiring human interaction
Behavior Toward Humans:
Both: Affectionate, seeking companionship and interactive play
Danger Posed to Humans:
Both: Generally non-threatening when properly socialized
Associated Precautions:
Both: Require precautions for high energy levels and mental stimulation
Conservation Status:
Both: Domestic and not subject to specific conservation concerns
Conclusion
-Similarities:
Both Savannah and Bengal cats share a wild appearance, high intelligence, and social behavior.
Domesticated hybrids with unique coat patterns resembling wild big cats.
-Differences:
Savannahs are generally larger and may have longer legs, contributing to increased agility.
Bengals exhibit the distinctive “glitter” effect on their coat and may have a preference for lush habitats.
Slight variations in lifespan, energy levels, and potential physical capabilities.



