Himalayan Cat Vs Ragdoll Size, Weight, Overall Comparison
Himalayan and Ragdoll cats share similar fur coloration with striking points on ears, face, paws, and tail, contributing to their distinct appearance. However, Himalayans are generally smaller with thicker coats, displaying playful and energetic behavior. Both breeds are affectionate, but Himalayans may stand out for their engaging interactive activities. Ragdolls tend to have a gentler demeanor. Pricing distinctions show Ragdolls generally cost slightly more. Recognizing these unique traits allows potential owners to appreciate the diverse qualities each breed brings to feline companionship.
I. Fur Coloration:
– Himalayan cats and Ragdoll cats share similar fur coloration, often exhibiting striking points with darker color on their ears, face, paws, and tail. The contrast between their body color and points contributes to their distinctive appearance.
II. Size and Coat Thickness:
– Himalayan cats are generally smaller in size, characterized by a petite build. They also boast thicker coats, providing them with a plush and luxurious appearance. In contrast, Ragdoll cats typically have a larger and more substantial frame with a semi-longhair coat.
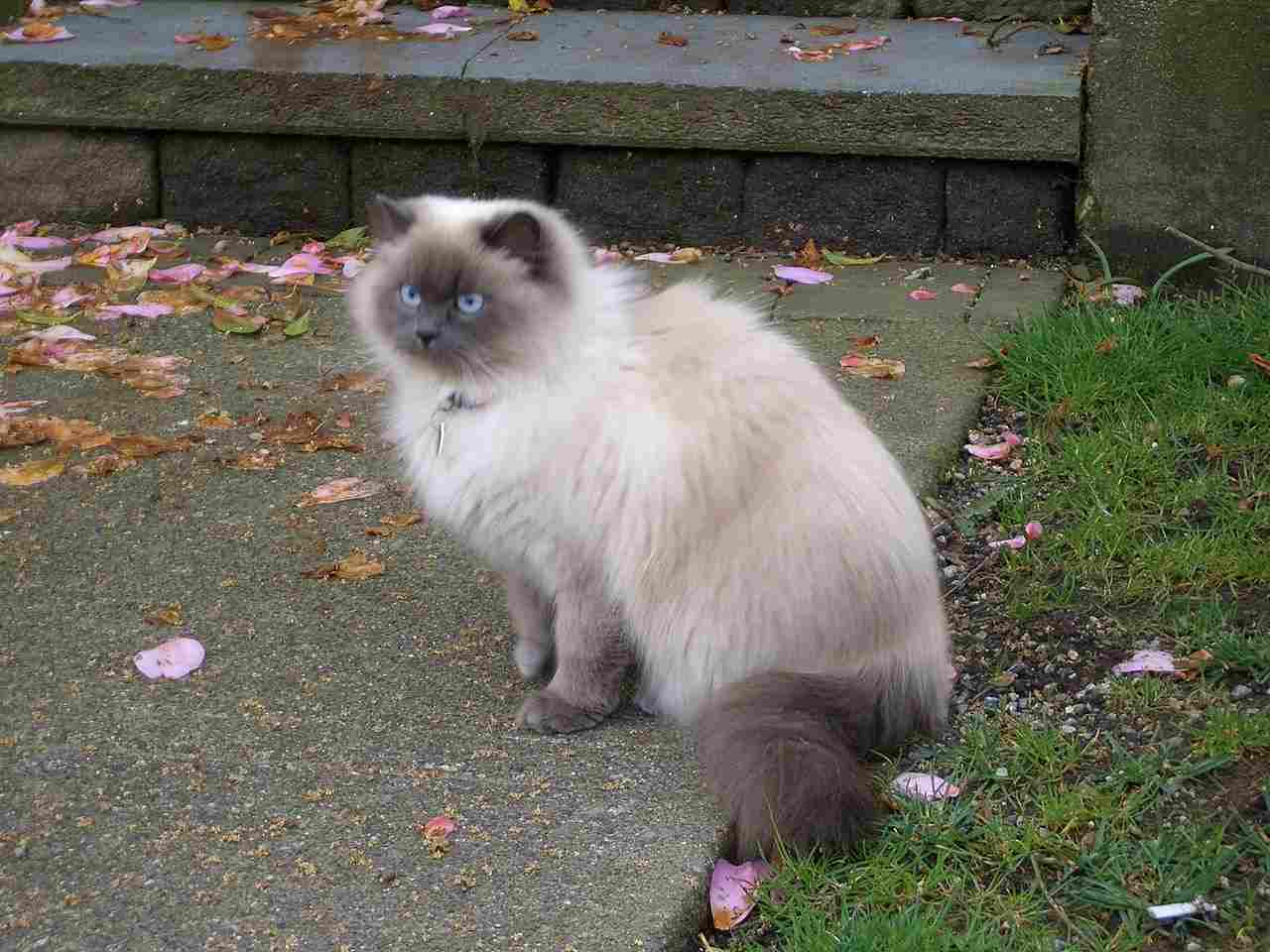

III. Playful and Energetic Himalayan:
– Himalayan cats stand out for their more playful and energetic nature compared to Ragdoll cats. Their lively demeanor adds an extra layer of dynamism to the relationship with their owners, making them a delightful and entertaining pet.
IV. Affectionate Traits:
– Both Himalayan and Ragdoll cats share a commonality in being affectionate as pets. They enjoy spending time with their owners, offering companionship and warmth. However, the Himalayan’s playful energy may make them particularly engaging in interactive activities.
V. Pricing Distinctions:
– Ragdoll cats typically come with a slightly higher price tag, ranging from $800 to $2000. In contrast, Himalayan cats are generally priced between $800 and $1500, providing a more accessible option for those considering these affectionate and beautiful feline companions.
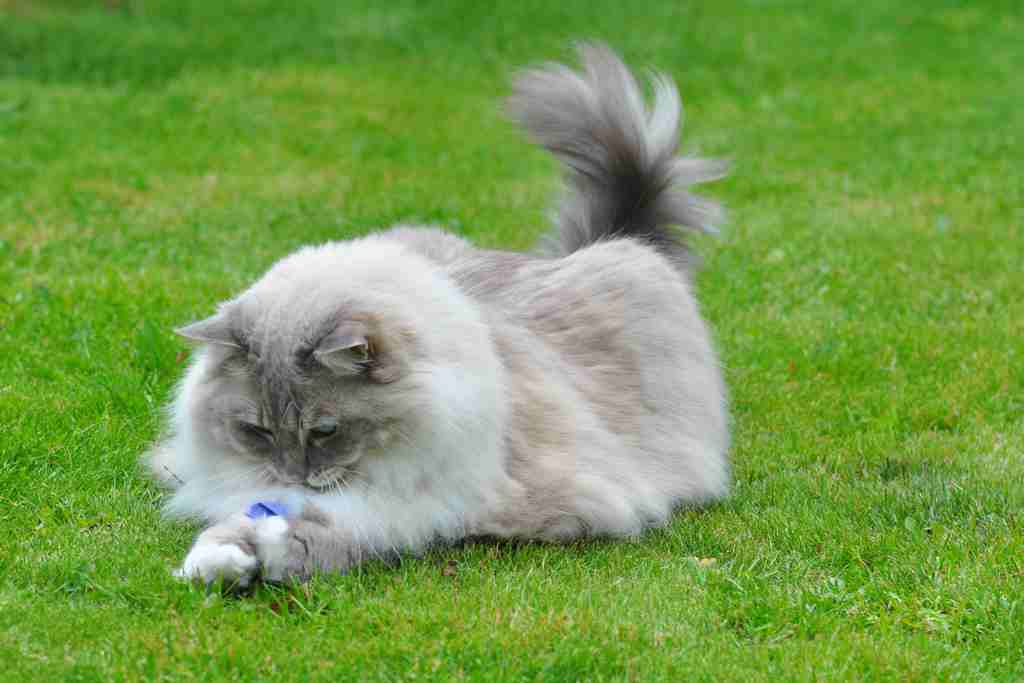

VI. Appreciating Breed Diversity:
– Recognizing the unique traits of Himalayan and Ragdoll cats allows potential owners to appreciate the diversity within these breeds. Whether it’s the energetic playfulness of the Himalayan or the gentle demeanor of the Ragdoll, each cat brings its own set of qualities to enhance the experience of feline companionship.
*Details of Comparison
| Criteria | Himalayan Cat | Ragdoll |
| Taxonomy | Felidae, Felis, Catus |
Felidae, Felis, Catus
|
| Appearance | Color point pattern, compact build |
Color point pattern, larger and robust
|
| Size | Medium |
Larger (medium to large)
|
| Weight | 7-12 pounds | 10-20 pounds |
| Personality | Gentle, sociable | Gentle, sociable |
| Relative Price/Cost | $500-$1,500 | $800-$2,500 |
| Grooming Requirements | Regular grooming for long coat |
Regular grooming for long coat
|
| Health Concerns | Respiratory issues |
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)
|
| Bite Force (PSI) | Average cat bite force |
Average cat bite force
|
| Offensive Advantages | Sharp claws and teeth |
Sharp claws and teeth
|
| Defensive Advantages | Agility for Himalayans; Size for Ragdoll | Size for defense |
| Speed | Average cat speed |
Average cat speed
|
| Agility | Excelling in climbing |
Good agility in play
|
| Senses | Heightened senses for environment |
Heightened senses for environment
|
| Physical Capacity | Climbing for Himalayans; Balanced for Ragdolls |
Balanced physique
|
| Habitat Preference(s) | Mountainous regions | Versatile |
| Tracks | Compact prints with retractable claws |
Retractable claws, larger prints
|
| Lifespan | 12-15 years | 12-17 years |
| Natural Mode of Feeding | Carnivorous | Carnivorous |
| Best Food as a Pet | Protein-rich diet |
Balanced diet with proteins
|
| Intelligence | Intelligent; Problem-solving for Himalayans |
Intelligent, less problem-solving
|
| Social Behavior | Sociable; Forms bonds with owners |
Highly social; Strong bonds
|
| Reproduction | Sexual reproduction, live kittens |
Sexual reproduction, live kittens
|
| Parental Behavior | Maternal instincts |
Maternal instincts
|
| Proximity to Humans | Comfortable indoors, bonds with humans |
Adapts well to indoor living
|
| Behavior Toward Humans | Affectionate | Extremely docile |
| Danger Posed to Humans | Minimal danger | Minimal danger |
| Associated Precautions | Regular veterinary check-ups |
Monitor for heart conditions
|
| Conservation Status | Not a conservation priority |
Not a conservation priority
|
1. Taxonomy:
Himalayan Cat:
Family: Felidae
Genus: Felis
Species: Catus
Ragdoll:
Family: Felidae
Genus: Felis
Species: Catus
2. Appearance:
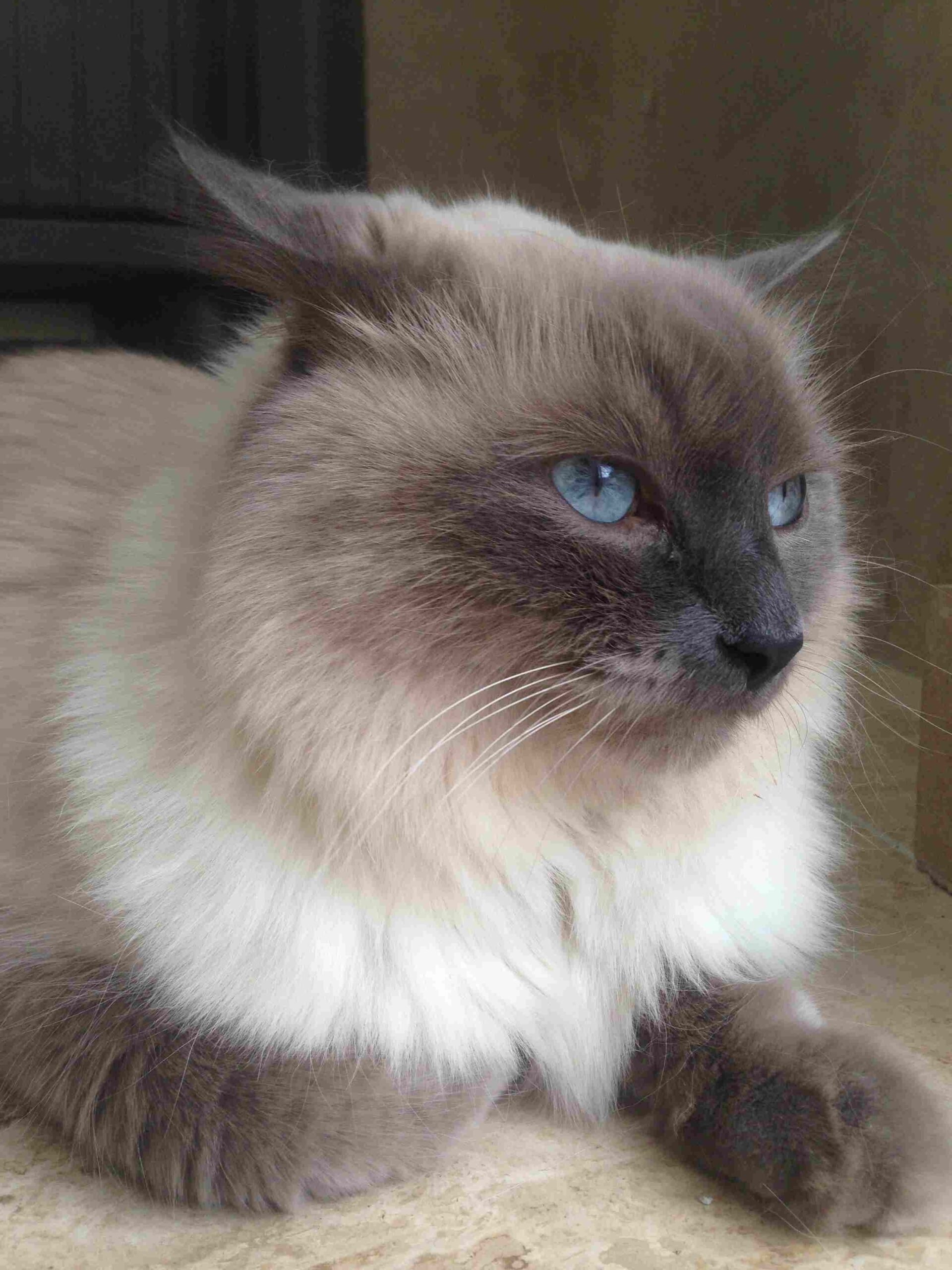


Himalayan Cat:
Features a distinct color point pattern with a silky, long coat.
Large, expressive blue almond-shaped eyes.
Short, rounded body with a bushy tail.
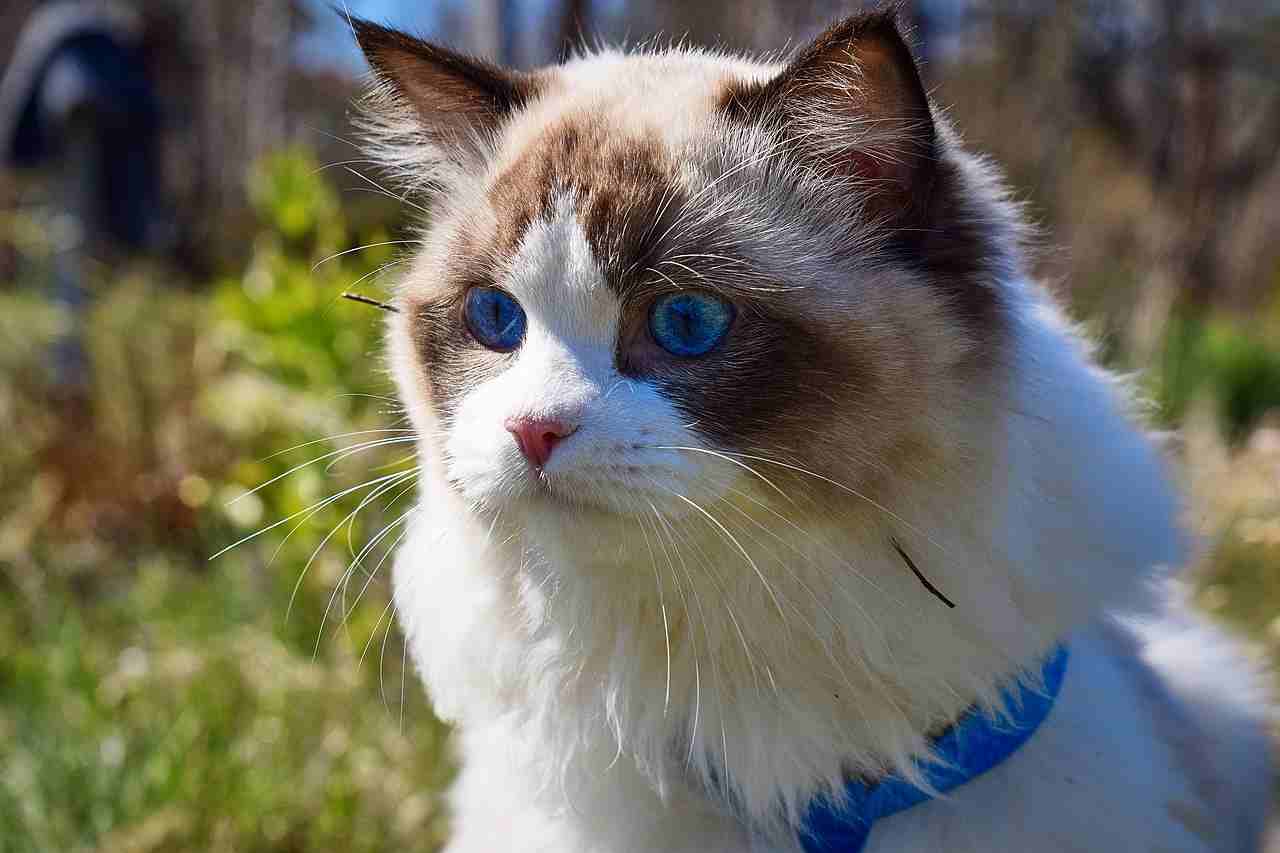
Ragdoll:
Semi-longhair coat with color points similar to the Himalayan.
Striking blue eyes, often described as ‘oval.’
Sturdy, medium to large-sized body with a semi-cobby build.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit color point patterns.
Himalayans have a more compact build, while Ragdolls are larger and more robust.
Ecological Implications:
The long, thick coats of both breeds might provide insulation in colder climates, potentially influencing their habitat preferences.
3. Size:
Himalayan Cat:
Medium-sized breed with a more compact build.
Ragdoll:
Larger than the Himalayan, with a medium to large size.
Comparison:
Ragdolls tend to be notably larger than Himalayans.
Ecological Implications:
The larger size of Ragdolls may offer advantages in colder habitats, providing better insulation against harsh weather conditions.
4. Weight:
Himalayan Cat:
Typically weighs between 7 to 12 pounds.
Ragdoll:
Generally heavier, ranging from 10 to 20 pounds.
Comparison:
Ragdolls have a significantly higher average weight than Himalayans.
Ecological Implications:
The increased weight in Ragdolls might impact their hunting and climbing abilities, potentially influencing their role in the ecosystem.
5. Personality:
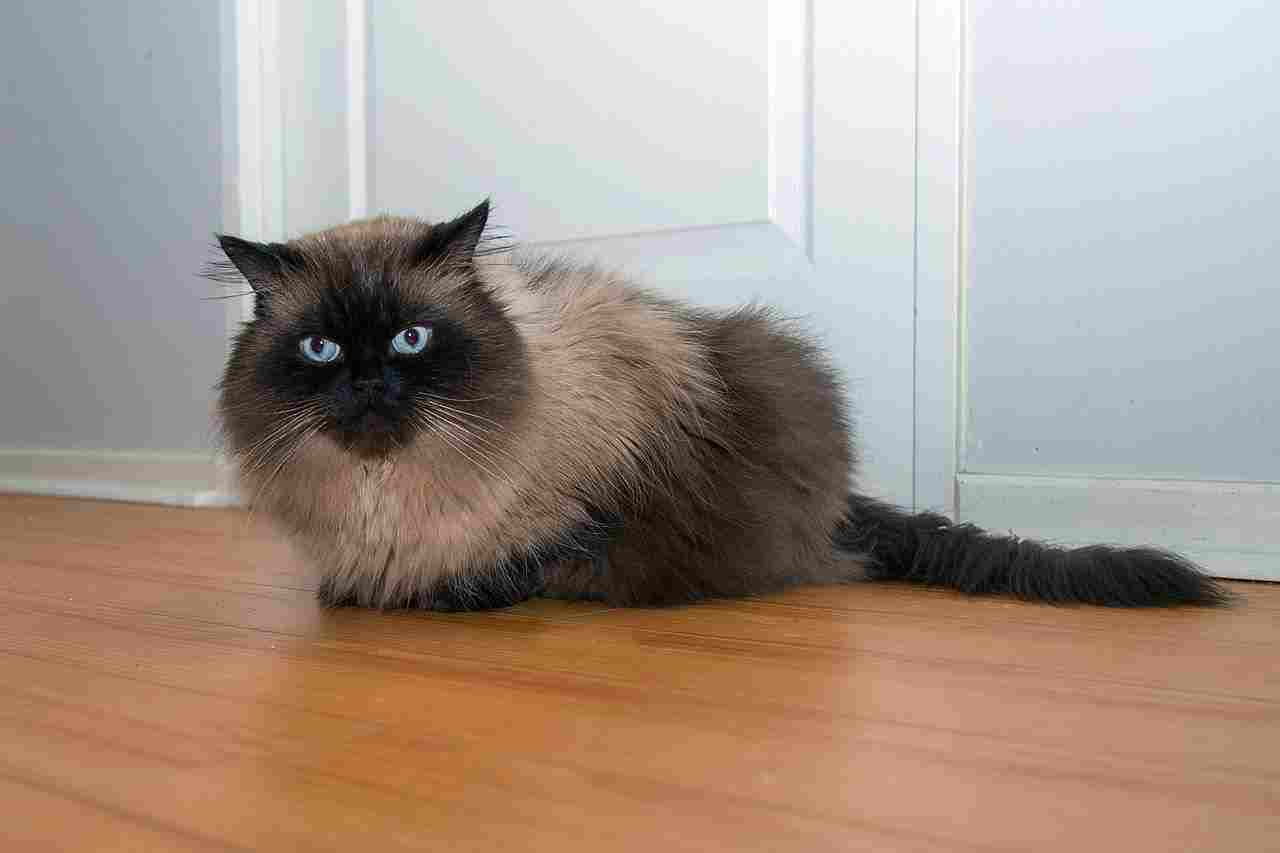

Himalayan Cat:
Affectionate, calm, and gentle.
Enjoys lounging and being pampered.
Ragdoll:
Known for a docile temperament.
Often goes limp when picked up, hence the name “Ragdoll.”
Comparison:
Both breeds are characterized by their gentle and sociable nature.
Ecological Implications:
The friendly disposition of both breeds could influence their interactions with other species in their natural habitat.
6. Relative Price/Cost:
Himalayan Cat:
Generally priced between $500 to $1,500.
Ragdoll:
Typically falls within the range of $800 to $2,500.
Comparison:
Ragdolls are generally more expensive than Himalayans.
Ecological Implications:
The economic value of these breeds in the pet market may affect breeding practices and conservation efforts.
7. Grooming and Maintenance Requirements:
Himalayan Cat:
Requires regular grooming due to its long, silky coat.
Ragdoll:
Also needs regular grooming, especially during shedding seasons.
Comparison:
Both breeds demand consistent grooming to maintain their coat health.
Ecological Implications:
The grooming needs may impact their natural behavior in the wild, influencing how they allocate time for self-grooming and other activities.
8. Health Concerns:

Himalayan Cat:
Prone to respiratory issues due to their brachycephalic facial structure.
Ragdoll:
Can be susceptible to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), a heart condition common in larger cat breeds.
Comparison:
Each breed has its specific health vulnerabilities.
Ecological Implications:
Understanding these health concerns is crucial for conservationists to address potential threats to wild populations.
9. Bite Force (PSI):
Himalayan Cat:
Average cat bite force, around 50 to 60 PSI.
Ragdoll:
Similar average cat bite force.
Comparison:
Both breeds possess a typical cat bite force.
Ecological Implications:
Bite force is essential for hunting and self-defense, and understanding these forces contributes to ecological studies on predation and inter-species interactions in their habitats.
10. Physical Offensive Advantages:
Himalayan Cat:
Sharp claws and teeth for hunting small prey.
Ragdoll:
Strong and agile, with effective predatory instincts.
Comparison:
Both breeds have physical attributes advantageous for hunting.
Ecological Implications:
These offensive advantages are crucial for survival in the wild, affecting their role in the ecosystem.
11. Physical Defensive Advantages:
Himalayan Cat:
Agility and the ability to climb for escaping predators.
Ragdoll:
Their larger size can be a defensive advantage against smaller predators.
Comparison:
Defensive strategies vary, with Himalayans relying on agility and Ragdolls on size.
Ecological Implications:
Understanding defensive mechanisms aids in assessing their interactions with predators and their overall impact on the food chain.
12. Speed (Km/hour or Mile/hour):

Himalayan Cat:
Average cat speed, around 30 mph (48 km/h).
Ragdoll:
Similar average cat speed.
Comparison:
Both breeds share a typical feline running speed.
Ecological Implications:
Speed is crucial for hunting and evading threats, contributing to their ecological niche.
13. Agility:
Himalayan Cat:
Agile climbers with a penchant for high places.
Ragdoll:
Despite their larger size, they maintain good agility, particularly in play.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit agility, though Himalayans may excel in climbing.
Ecological Implications:
Agility is essential for navigating their habitat, avoiding predators, and accessing resources.
14. Senses:

Himalayan Cat:
Excellent vision in low light conditions.
Sensitive whiskers for spatial awareness.
Ragdoll:
Strong sense of hearing and keen eyesight.
Comparison:
Both breeds have heightened senses tailored for their respective environments.
Ecological Implications:
Understanding their sensory capabilities provides insights into their hunting strategies and interactions with their surroundings.
15. Overall Physical Capacity:
Himalayan Cat:
Well-suited for agile movements and climbing.
Ragdoll:
Balanced physique with strength and agility.
Comparison:
Himalayans may excel in climbing, while Ragdolls possess a combination of strength and agility.
Ecological Implications:
Assessing overall physical capacity aids in understanding their adaptability to diverse habitats.
16. Habitat Preference(s):

Himalayan Cat:
Originally adapted to mountainous regions, preferring elevated spaces.
Ragdoll:
No specific habitat preference, adaptable to various environments.
Comparison:
Himalayans show a preference for mountainous habitats, while Ragdolls are more versatile.
Ecological Implications:
Understanding habitat preferences helps in designing effective conservation strategies.
17. Tracks:

Himalayan Cat:
Compact paw prints with retractable claws visible.
Ragdoll:
Similar retractable claws, with larger prints due to their bigger size.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit retractable claws in their tracks.
Ecological Implications:
Identifying tracks aids in studying their movement patterns and presence in specific areas.
18. Lifespan:
Himalayan Cat:
Average lifespan of 12 to 15 years.
Ragdoll:
Generally lives around 12 to 17 years.
Comparison:
Ragdolls tend to have a slightly longer average lifespan compared to Himalayans.
Ecological Implications:
Lifespan influences population dynamics, reproductive rates, and overall ecological roles in their habitats.
19. Natural Mode of Feeding:
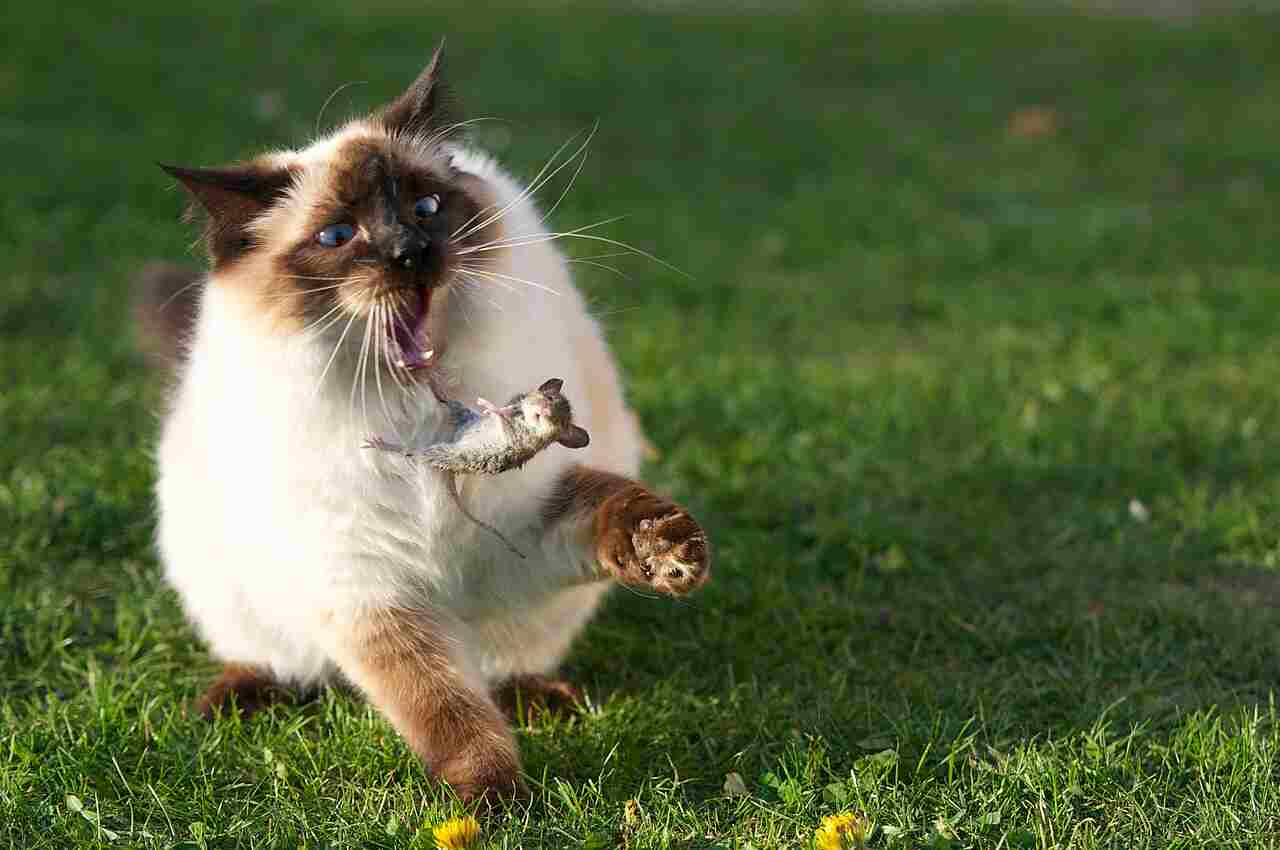

Himalayan Cat:
Carnivorous, primarily hunting small prey.
Ragdoll:
Carnivorous, with a preference for meat-based diets.
Comparison:
Both breeds share a natural inclination for a carnivorous diet.
Ecological Implications:
Studying their feeding habits contributes to understanding their role in the food chain and potential impact on local fauna.
20. Best Food as a Pet:
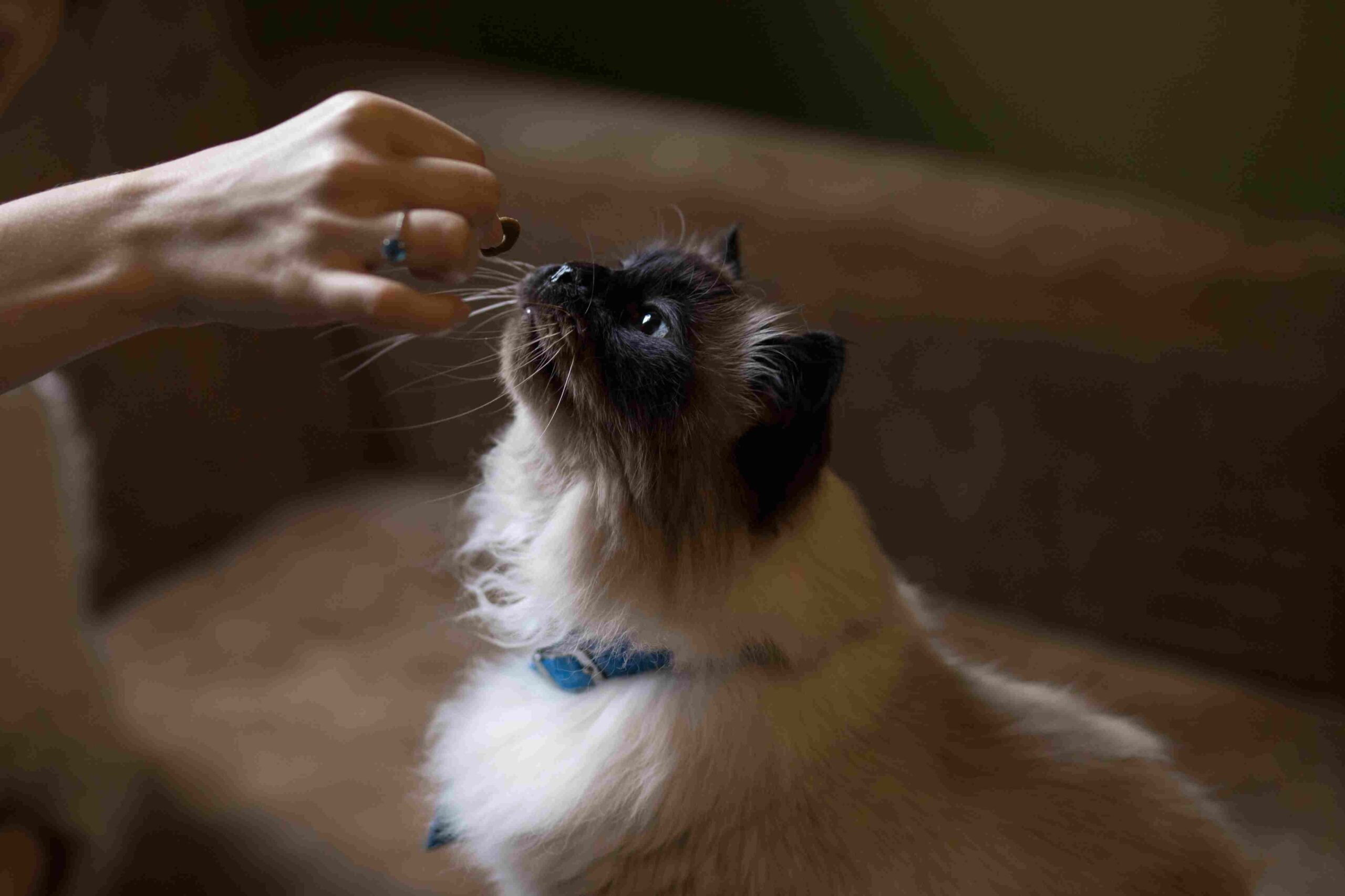

Himalayan Cat:
High-quality cat food with a focus on protein.
Ragdoll:
Balanced diet with a mix of proteins and essential nutrients.
Comparison:
Both breeds benefit from a diet rich in protein and nutrients.
Ecological Implications:
Examining dietary needs aids in understanding their nutritional requirements for survival in the wild.
21. Intelligence:
Himalayan Cat:
Intelligent and can learn tricks.
Ragdoll:
Known for their gentle nature but may not exhibit high problem-solving skills.
Comparison:
While both breeds are intelligent, Himalayans may demonstrate more problem-solving abilities.
Ecological Implications:
Intelligence affects adaptability and learning in response to environmental changes.
22. Social Behavior:
Himalayan Cat:
Generally sociable and enjoys human interaction.
Ragdoll:
Highly social, often forming strong bonds with their owners.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit social behavior, with Ragdolls known for forming particularly strong connections.
Ecological Implications:
Social behavior influences group dynamics and interactions within their habitats, affecting their role in the ecosystem.
23. Mode of Reproduction:
Himalayan Cat:
Reproduces through sexual reproduction, giving birth to live kittens.
Ragdoll:
Same mode of reproduction as Himalayans.
Comparison:
Both breeds reproduce through sexual reproduction, like most domestic cats.
Ecological Implications:
Understanding reproductive strategies contributes to population dynamics and conservation planning.
24. Parental Behavior:
Himalayan Cat:
Exhibits typical maternal behaviors, caring for and protecting kittens.
Ragdoll:
Also displays nurturing parental instincts.
Comparison:
Similar maternal behaviors observed in both breeds.
Ecological Implications:
Parental behavior influences the survival rates of offspring, impacting population stability.
25. Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
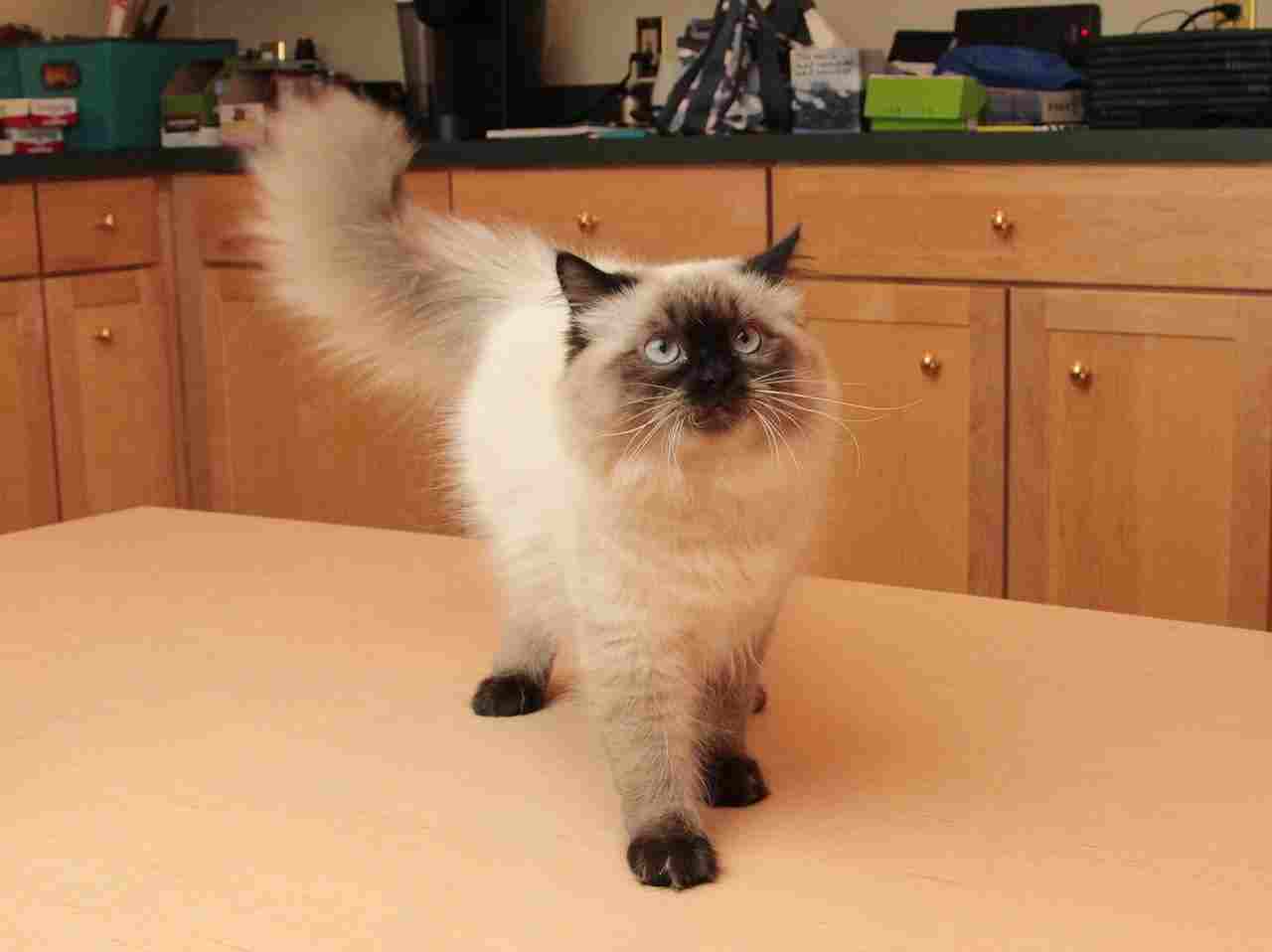

Himalayan Cat:
Often comfortable in indoor settings, forming strong bonds with owners.
Ragdoll:
Adapts well to indoor living, thriving in human companionship.
Comparison:
Both breeds are well-suited for cohabitation with humans.
Ecological Implications:
The ability to thrive in proximity to human-inhabited areas may influence their exposure to various environmental factors and potential conflicts.
26. Behavior Toward Humans:
Himalayan Cat:
Affectionate and enjoys human attention, forming strong bonds with owners.
Ragdoll:
Extremely docile, often going limp when picked up, displaying a relaxed demeanor.
Comparison:
Both breeds are known for their friendly and affectionate behavior towards humans.
Ecological Implications:
Friendliness towards humans might impact their interactions in domestic or urban environments, potentially affecting their roles in local ecosystems.
27. Danger Posed to Humans:
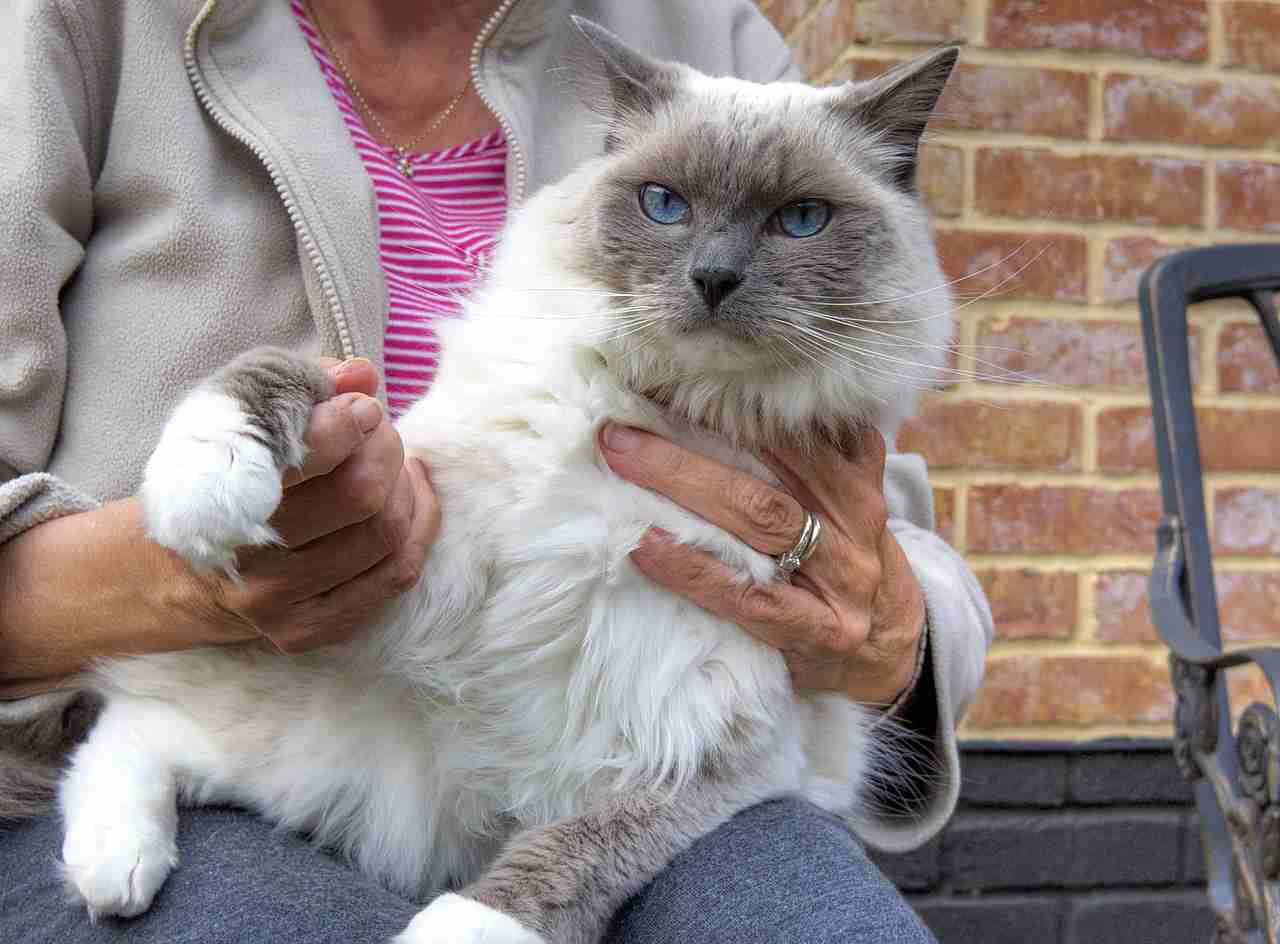

Himalayan Cat:
Generally poses no significant danger to humans.
Ragdoll:
Non-aggressive, with minimal danger to humans.
Comparison:
Neither breed is known for posing a significant danger to humans.
Ecological Implications:
Limited danger to humans may contribute to positive human-wildlife interactions in areas where these cats are found.
28. Associated Precautions:
Himalayan Cat:
Regular veterinary check-ups for respiratory health.
Ragdoll:
Monitoring for heart conditions, especially hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM).
Comparison:
Both breeds require specific health precautions, emphasizing the importance of regular veterinary care.
Ecological Implications:
Implementing precautions in domestic settings aids in the well-being of individual cats, potentially influencing their contribution to local ecosystems if introduced.
29. Conservation Status:
Himalayan Cat:
Not listed as a separate conservation concern; however, various wild cat species in their region may face conservation challenges.
Ragdoll:
Not considered a wild species, so no specific conservation status.
Comparison:
Neither breed is classified as a conservation priority.
Ecological Implications:
Conservation efforts should primarily focus on preserving the natural habitats of wild cat species.
*Summary of Comparison
Taxonomy:
Both belong to the Felidae family, Felis genus, and Catus species.
Appearance:
Himalayans have a color point pattern, while Ragdolls share a similar pattern.
Himalayans have a more compact build; Ragdolls are larger and more robust.
Size:
Himalayans are medium-sized.
Ragdolls are larger than Himalayans, with a medium to large size.
Weight:
Himalayans weigh between 7 to 12 pounds.
Ragdolls are generally heavier, ranging from 10 to 20 pounds.
Personality:
Both breeds are gentle and sociable.
Relative Price/Cost:
Ragdolls are generally more expensive than Himalayans.
Grooming and Maintenance Requirements:
Both demand regular grooming due to their long coats.
Health Concerns:
Himalayans are prone to respiratory issues; Ragdolls may face hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Bite Force (PSI):
Similar average cat bite force for both breeds.
Physical Offensive Advantages:
Both breeds have sharp claws and teeth for hunting.
Physical Defensive Advantages:
Himalayans rely on agility; Ragdolls use their larger size.
Speed:
Similar average cat speed for both breeds.
Agility:
Himalayans excel in climbing; Ragdolls maintain good agility.
Senses:
Both breeds have heightened senses suitable for their environments.
Overall Physical Capacity:
Himalayans excel in climbing; Ragdolls have a balanced physique.
Habitat Preference(s):
Himalayans prefer mountainous regions; Ragdolls are versatile.
Tracks:
Similar retractable claws in tracks for both breeds.
Lifespan:
Ragdolls tend to have a slightly longer average lifespan.
Natural Mode of Feeding:
Both are carnivorous with a preference for meat-based diets.
Best Food as a Pet:
Both benefit from a diet rich in protein and nutrients.
Intelligence:
Himalayans may demonstrate more problem-solving abilities.
Social Behavior:
Both breeds are sociable; Ragdolls form strong bonds.
Mode of Reproduction:
Both reproduce through sexual reproduction.
Parental Behavior:
Similar maternal behaviors observed in both breeds.
Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Both are well-suited for cohabitation with humans.
Behavior Toward Humans:
Both are known for their friendly and affectionate behavior towards humans.
Danger Posed to Humans:
Neither breed is known for posing a significant danger to humans.
Associated Precautions:
Both require specific health precautions.
Conservation Status:
Neither breed is classified as a conservation priority.
Conclusion:
-Similarities:
Both breeds share a carnivorous diet, reproductive strategies, and sociable behavior towards humans.
-Differences:
Divergent in size, lifespan, habitat preferences, and potential ecological implications based on their distinct characteristics.