Himalayan Cat Vs Persian Cat Price, Personality, Overall Comparison
Contrasting the Himalayan and Persian cats unveils subtle yet significant differences in their characteristics, appearance, and temperament. While both breeds share common ancestry, the Himalayan stands out with its distinct color point fur and eye color. Additionally, variations in pricing, height, and popularity further differentiate the two. Himalayans are often more playful, active, and inquisitive, whereas Persians are known for their laid-back and docile nature. In terms of cost, Himalayans are generally priced slightly lower, ranging from $800 to over $2000, while Persian kittens can exceed $3000.
Himalayan vs Persian: Navigating Feline Contrasts
I. Ancestral Connection:
– Both the Himalayan and Persian cats share a common ancestral background, contributing to certain similarities in their overall characteristics.
II. Distinct Color Point Fur:
– The Himalayan cat is characterized by its distinctive color point fur, featuring darker coloration on the ears, face, paws, and tail. In contrast, the Persian cat exhibits a more uniform coat color.
III. Varied Eye Color:
– Himalayans often have striking blue almond-shaped eyes, while Persians display a variety of eye colors. This difference in eye color contributes to the unique appearance of each breed.

IV. Price Ranges:
– Himalayan cats are generally priced slightly lower than Persian cats. Himalayan kittens can range from $800 to over $2000, while Persian kittens may exceed $3000, reflecting variations in popularity and demand.
V. Height Disparity:
– Himalayans tend to be slightly taller compared to Persians. The difference in height contributes to the distinct physical characteristics of each breed.
VI. Popularity:
– Persian cats are generally more popular than Himalayans, contributing to differences in pricing and demand within the feline community.
VII. Playful Nature of Himalayans:
– Himalayan cats are known for their playful, active, and energetic nature. Their inquisitive behavior sets them apart from the more laid-back and docile temperament of Persian cats.
VIII. Laid-Back Nature of Persians:
– Persian cats are renowned for their laid-back and docile demeanor. They often exhibit a calm and serene disposition, making them suitable for relaxed and indoor environments.

IX. Appreciating Breed Diversity:
– Understanding the unique characteristics of Himalayan and Persian cats allows potential owners to appreciate the diversity within these breeds. Each cat brings its own charm, contributing to the rich tapestry of feline companionship.
*Details of Comparison
| Criteria | Himalayan Cat | Persian Cat |
| Taxonomy | Felidae, Felis, Catus, Felis catus himalayensis |
Felidae, Felis, Catus, Felis catus domesticus
|
| Appearance | Color points, brachycephalic face |
Varied coat colors, “cobby” appearance
|
| Size | Medium to large | Medium to large |
| Weight | 7 to 12 pounds | 7 to 12 pounds |
| Speed | Up to 30 mph (48 km/h) |
Up to 30 mph (48 km/h)
|
| Overall Physical Capacity | Well-rounded for domestic living |
Well-rounded for domestic living
|
| Habitat Preference(s) | Indoor living, controlled environments |
Indoor living, controlled environments
|
| Tracks | Standard feline prints with retractable claws |
Standard feline prints with retractable claws
|
| Relative Price / Cost | Typically more expensive |
Generally high-priced
|
| Grooming Requirements | Daily grooming for long coat |
Intensive grooming for thick fur
|
| Health Concerns | Prone to respiratory issues |
Susceptible to respiratory problems, dental issues, and eye conditions
|
| Personality | Affectionate and social |
Sweet-natured, calm, and laid-back demeanor
|
| Bite Force (PSI) | Data not available |
Data not available
|
| Offensive Advantages | Not bred for offensive traits |
Not bred for offensive traits
|
| Defensive Advantages | Relies on agility |
May use size and posture defensively
|
| Agility | Slightly more agile |
Reasonable agility
|
| Senses | Standard feline senses |
Standard feline senses
|
| Lifespan | 12 to 15 years | 12 to 16 years |
| Natural Feeding | Carnivorous diet | Carnivorous diet |
| Best Food as a Pet | High-quality cat food |
Protein-rich, low-carb diet
|
| Intelligence | Intelligent and trainable |
Average intelligence
|
| Social Behavior | Affectionate and social |
Sociable but more independent
|
| Reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
Sexual reproduction
|
| Parental Behavior | Exhibits maternal instincts |
Displays typical parental behaviors
|
| Proximity to Humans | Adapts well to indoor living |
Prefers indoor environments
|
1. Taxonomy
Himalayan Cat:
Family: Felidae
Genus: Felis
Species: Catus
Subspecies: Felis catus himalayensis
Persian Cat:
Family: Felidae
Genus: Felis
Species: Catus
Subspecies: Felis catus domesticus
2. Appearance
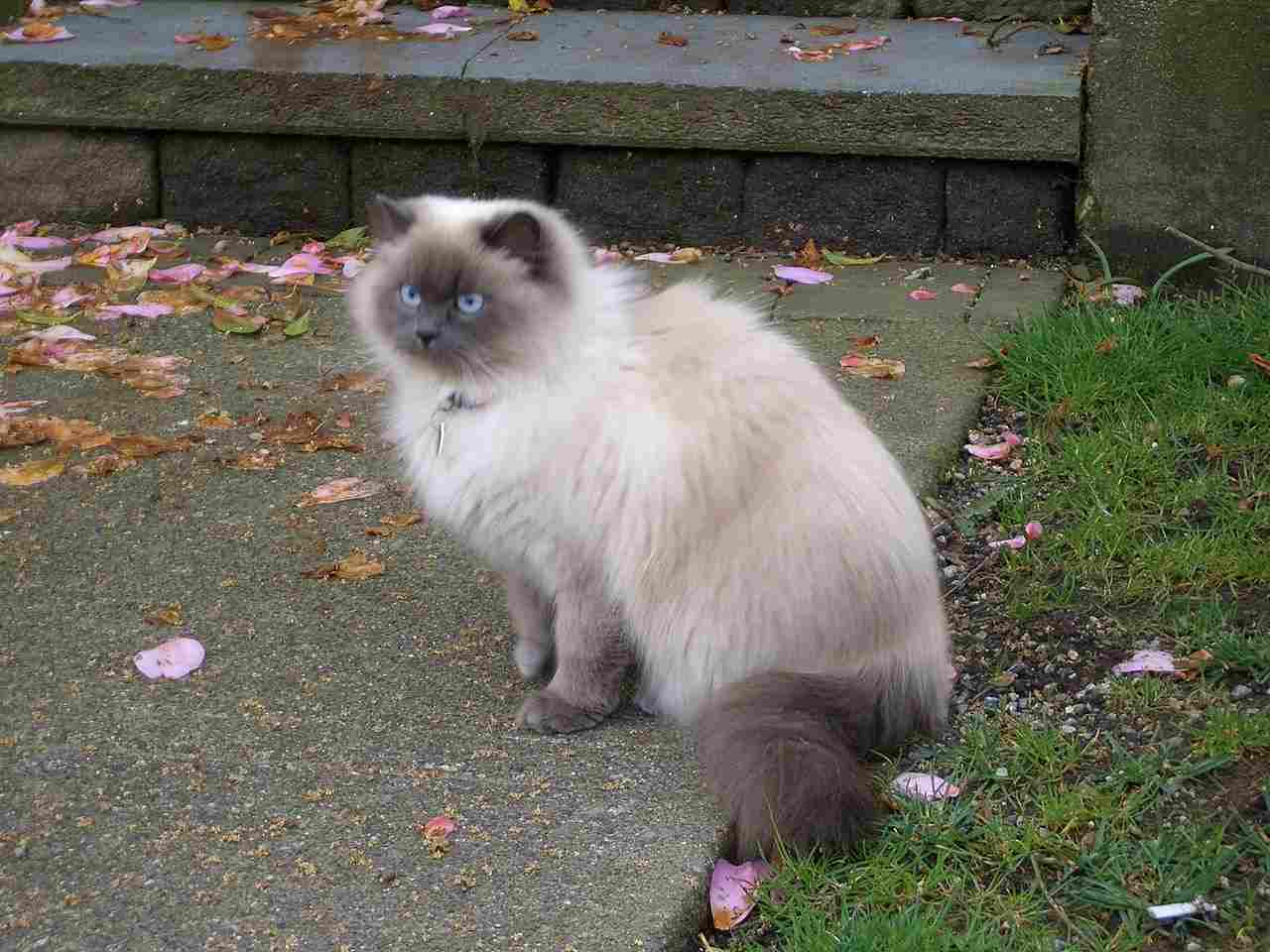

Himalayan Cat:
Distinct color points on a creamy body, with a bushy tail and striking blue almond-shaped eyes.
Short, flat face with a brachycephalic skull structure.
Persian Cat:
Round face with a flat nose, large expressive eyes, and a plush coat in various colors.
Compact, sturdy body with a short nose, giving a distinctive “cobby” appearance.
Comparison: Himalayan cats share a resemblance with Persians due to their common ancestry, but Himalayans exhibit color points similar to Siamese cats, whereas Persians have a broader range of coat colors and patterns.
Ecological Implications: The distinct appearances of Himalayan and Persian cats are primarily a result of selective breeding by humans, which may impact their adaptability in the wild. The flat face in both breeds may pose respiratory challenges, affecting their ecological fitness.
3. Size
Himalayan Cat:
Medium to large size with a well-proportioned body and sturdy build.
Persian Cat:
Medium to large size, characterized by a robust and muscular body structure.
Comparison: Both Himalayan and Persian cats share a similar size range, making them substantial domestic cat breeds.
Ecological Implications: In the wild, their size could affect their predatory success and interactions with other species. Large size may provide advantages in hunting and territory defense.
4. Weight
Himalayan Cat:
Adult weight typically ranges from 7 to 12 pounds.
Persian Cat:
Adult weight typically ranges from 7 to 12 pounds.
Comparison: Himalayan and Persian cats exhibit comparable weight ranges, indicating similar size-related features.
Ecological Implications: Weight considerations are crucial for survival in the wild, influencing factors such as agility, hunting abilities, and energy expenditure.
5. Personality

Himalayan Cat:
Affectionate, calm, and social. Enjoys interactive play and companionship.
Persian Cat:
Sweet-natured, calm, and enjoys a relaxed environment. May exhibit a more laid-back personality.
Comparison: Both breeds share a laid-back and affectionate nature, making them suitable as indoor companions.
Ecological Implications: These personality traits may affect their ability to adapt to wild environments, as they might rely heavily on human interaction and care.
6. Relative Price/Cost
Himalayan Cat:
Typically more expensive due to their distinct color points and selective breeding.
Persian Cat:
Generally high-priced, reflecting the breed’s popularity and elaborate grooming needs.
Comparison: Both Himalayan and Persian cats tend to have high initial costs, with variations based on factors like lineage and breeder reputation.
Ecological Implications: The cost of acquiring these breeds may impact their demand, potentially influencing breeding practices and contributing to overpopulation concerns.
7. Grooming and Maintenance Requirements

Himalayan Cat:
Requires daily grooming due to their long, luxurious coat to prevent matting.
Persian Cat:
Intensive grooming needed, including daily brushing to maintain their thick coat and prevent hairballs.
Comparison: Both breeds demand significant grooming efforts, making them suitable for owners committed to regular care routines.
Ecological Implications: The extensive grooming needs may raise questions about the natural sustainability of these breeds in the wild, as such grooming practices are primarily managed by human caretakers.
8. Health Concerns
Himalayan Cat:
Prone to respiratory issues due to their brachycephalic facial structure.
Persian Cat:
Susceptible to respiratory problems, dental issues, and eye conditions.
Comparison: Both breeds share health concerns associated with their facial features, emphasizing the importance of attentive veterinary care.
Ecological Implications: These health concerns, exacerbated by selective breeding, may impact the ability of these breeds to survive and reproduce in the wild.
9. Bite Force (PSI)

Himalayan Cat:
Bite force information not readily available due to their domestic nature.
Persian Cat:
Bite force information not readily available due to their domestic nature.
Comparison: Insufficient data is available to compare the bite force of Himalayan and Persian cats accurately.
Ecological Implications: In the wild, bite force is crucial for hunting and self-defense; however, domestication has likely altered these characteristics in both breeds.
10. Physical Offensive Advantages
Himalayan Cat:
Typically not bred for physical offensive advantages; their appeal lies more in their appearance and personality.
Persian Cat:
Similarly, Persians are not known for physical offensive capabilities but may use their size for intimidation.
Comparison: Neither Himalayan nor Persian cats are selectively bred for offensive traits, focusing more on their gentle and companionable qualities.
Ecological Implications: In the wild, offensive capabilities would be essential for hunting and territorial disputes, but domestication has shifted these priorities.
11. Physical Defensive Advantages
Himalayan Cat:
Relies on agility and quick reflexes for defensive maneuvers.
Persian Cat:
Defensively uses its size and posture; may rely on hiding due to its calm nature.
Comparison: Both breeds have defensive strategies, with the Himalayan relying on agility, while the Persian may use its size and calm demeanor as a defensive mechanism.
Ecological Implications: Wild counterparts would need robust defensive capabilities against predators, but domestication has altered these needs.
12. Speed (Km/hour or Mile/hour)

Himalayan Cat:
Domestic cats, including Himalayans, can reach speeds up to 30 mph (48 km/h).
Persian Cat:
Persians, like other domestic cats, can achieve speeds up to 30 mph (48 km/h).
Comparison: Similar top speeds are observed in both Himalayan and Persian cats, reflecting typical domestic cat abilities.
Ecological Implications: These speeds would be advantageous for hunting and evading predators in the wild, although domestication may have slightly altered these natural capabilities.
13. Agility
Himalayan Cat:
Exhibits good agility, able to navigate various surfaces with ease.
Persian Cat:
While not as agile as some other cat breeds, Persians still possess reasonable agility.
Comparison: Himalayan cats tend to be slightly more agile, but both breeds display agility suitable for typical domestic environments.
Ecological Implications: Agility is vital for survival in the wild, and while domestication has affected these traits, remnants of natural agility remain in both breeds.
14. Senses

Himalayan Cat:
Exhibits keen senses, particularly sharp hearing and vision, common in domestic cats.
Persian Cat:
Possesses typical cat senses, including acute hearing and vision.
Comparison: Both Himalayan and Persian cats share standard feline senses, with no notable differences.
Ecological Implications: Sharp senses are essential for survival in the wild, but domestication has likely maintained these sensory abilities in both breeds.
15. Overall Physical Capacity
Himalayan Cat:
Well-balanced physical traits, combining agility with a sturdy build.
Persian Cat:
Exhibits a robust physique, with a balance between size and agility.
Comparison: Both Himalayan and Persian cats showcase well-rounded physical capacities, adapted to a domestic lifestyle.
Ecological Implications: While domestication may have altered some physical traits, their overall capacity remains suited for adapting to household environments.
16. Habitat Preference(s)
Himalayan Cat:
Adapts well to indoor living, preferring a calm and controlled environment.
Persian Cat:
Thrives in indoor settings, avoiding extreme temperatures and potential dangers outdoors.
Comparison: Both breeds are well-suited for indoor living, with preferences for controlled environments.
Ecological Implications: Domestication has led to a reliance on human-provided shelter and care, limiting their adaptation to the natural wild habitat.
17. Tracks

Himalayan Cat:
Paw prints exhibit the typical cat-shaped pad with retractable claws.
Persian Cat:
Shows standard feline tracks with retractable claws.
Comparison: Paw prints of Himalayan and Persian cats are similar, reflecting typical domestic cat footprints.
Ecological Implications: Retractable claws are an evolutionary adaptation for hunting and climbing but have limited relevance in domesticated settings.
18. Lifespan
Himalayan Cat:
Average lifespan ranges from 12 to 15 years, with proper care.
Persian Cat:
Typically lives around 12 to 16 years, with health considerations influencing lifespan.
Comparison: Both Himalayan and Persian cats have relatively similar lifespans, influenced by factors like genetics and healthcare.
Ecological Implications: In the wild, lifespan is determined by factors such as predation, disease, and competition for resources, whereas domestication has provided a more secure environment.
19. Natural Mode of Feeding
Himalayan Cat:
Carnivorous, with a diet primarily consisting of meat.
Persian Cat:
Shares a carnivorous diet, requiring high-quality protein sources.
Comparison: Both breeds adhere to the natural carnivorous diet typical for domestic cats.
Ecological Implications: In the wild, hunting for prey is a natural feeding mode, but domestication has shifted this reliance to human-provided cat food.
20. Best Food as a Pet

Himalayan Cat:
High-quality cat food with a balanced mix of protein, fats, and essential nutrients.
Persian Cat:
Requires a diet rich in protein and low in carbohydrates, often relying on specially formulated cat food for long-haired breeds.
Comparison: Both Himalayan and Persian cats benefit from specially formulated cat food to meet their specific nutritional needs.
Ecological Implications: Domestication has altered their feeding habits, as they now rely on human-provided commercial cat food rather than hunting for prey.
21. Intelligence
Himalayan Cat:
Intelligent and trainable, capable of learning commands and tricks.
Persian Cat:
Displays average intelligence, with a calm and relaxed demeanor.
Comparison: While both breeds exhibit intelligence, Himalayan cats may be slightly more trainable compared to the laid-back nature of Persians.
Ecological Implications: Wild counterparts would rely on intelligence for survival, but domestication has allowed these traits to be harnessed for more interactive and trainable behaviors.
22. Social Behavior

Himalayan Cat:
Social and affectionate, forming strong bonds with their owners. May enjoy interaction with other pets.
Persian Cat:
Generally sociable but can be more independent. Enjoys a calm and stable environment.
Comparison: Both breeds exhibit social behavior, but Himalayans are often more overtly affectionate, while Persians may be a bit more independent.
Ecological Implications: Social behavior would impact group dynamics and cooperative efforts in the wild, but domestication has shaped these behaviors to align with human companionship.
23. Mode of Reproduction
Himalayan Cat:
Reproduces through sexual reproduction, with a gestation period of approximately 63 days.
Persian Cat:
Follows sexual reproduction, with a similar gestation period of around 63 days.
Comparison: Both breeds share the same mode of reproduction, characteristic of domestic cats.
Ecological Implications: In the wild, reproduction is essential for species survival, but domestication has led to controlled breeding practices.
24. Parental Behavior
Himalayan Cat:
Exhibits maternal instincts, actively caring for and protecting their kittens.
Persian Cat:
Displays typical parental behaviors, ensuring the well-being of their offspring.
Comparison: Both Himalayan and Persian cats exhibit nurturing parental behaviors, ensuring the survival and well-being of their kittens.
Ecological Implications: In the wild, effective parental behavior contributes to the survival of the species, while domestication has allowed for controlled breeding and care.
25. Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas
Himalayan Cat:
Adapts well to indoor living, thriving in human-inhabited areas.
Persian Cat:
Prefers indoor environments, avoiding exposure to potential dangers outdoors.
Comparison: Both breeds are well-suited for living in close proximity to humans, thriving in indoor settings.
Ecological Implications: Domestication has led to a close association with human-inhabited areas, providing safety and comfort for these breeds.
Summary of Comparison
-Similarities:
Taxonomy:
Both belong to the Felidae family, Felis genus, and Felis catus species.
Size:
Similar medium to large size range.
Weight:
Adult weight typically ranges from 7 to 12 pounds for both breeds.
Speed:
Capable of reaching speeds up to 30 mph (48 km/h).
Overall Physical Capacity:
Well-rounded physical traits suitable for domestic environments.
Habitat Preference(s):
Adapt well to indoor living, preferring controlled environments.
Tracks:
Standard feline paw prints with retractable claws.
-Differences:
Appearance:
Himalayans have color points and a brachycephalic face, while Persians have a more varied coat color range and a “cobby” appearance.
Relative Price/Cost:
Himalayans can be more expensive due to color points; Persians are generally high-priced.
Grooming and Maintenance Requirements:
Himalayans need daily grooming for their long coat; Persians require intensive grooming to manage their thick fur.
Health Concerns:
Himalayans are prone to respiratory issues; Persians are susceptible to respiratory problems, dental issues, and eye conditions.
Personality:
Himalayans are affectionate and social; Persians are sweet-natured and calm, with a more laid-back demeanor.
Bite Force (PSI):
Insufficient data available for both breeds.
Physical Offensive Advantages:
Neither breed is bred for physical offensive traits.
Physical Defensive Advantages:
Himalayans rely on agility; Persians may use size and posture defensively.
Agility:
Himalayans tend to be slightly more agile.
Senses:
Similar standard feline senses.
Lifespan:
Similar lifespan ranges, influenced by genetics and healthcare.
Natural Mode of Feeding:
Both adhere to a carnivorous diet.
Best Food as a Pet:
Both benefit from specially formulated cat food.
Intelligence:
Himalayans are slightly more trainable; Persians exhibit average intelligence.
Social Behavior:
Himalayans are more overtly affectionate; Persians are a bit more independent.
Mode of Reproduction:
Both reproduce through sexual reproduction.
Parental Behavior:
Both exhibit nurturing parental behaviors.
Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Both well-suited for living in close proximity to humans.