Is Algae a Producer? Algae Food Chain Position and Role
Algae, encompassing a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms, are indeed primary producers within ecosystems. They possess chlorophyll and other pigments that enable them to utilize sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce organic compounds through photosynthesis. As such, algae form the foundation of many aquatic and terrestrial food chains by converting solar energy into chemical energy, which is then consumed by other organisms. Their ability to generate energy from sunlight makes them essential contributors to the Earth’s ecosystems, positioning them firmly as producers.
Reasons Why Algae are Primary Producers

-
Photosynthetic Capability: Algae possess chlorophyll and other pigments that facilitate photosynthesis, enabling them to convert sunlight into chemical energy.
-
Carbon Fixation: Through photosynthesis, algae absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere or water and incorporate it into organic molecules, such as carbohydrates, essential for sustaining life.
-
Oxygen Production: As a byproduct of photosynthesis, algae release oxygen into the environment, contributing significantly to the oxygen levels in the atmosphere and aquatic ecosystems.
-
Basis of Food Chains: Algae serve as the primary food source for various organisms, including zooplankton, small fish, and invertebrates, forming the basis of aquatic food chains.
-
Support Ecosystems: Algae play crucial roles in supporting marine and freshwater ecosystems by providing food and habitat for a wide range of organisms, from microorganisms to larger marine animals.
-
Nutrient Cycling: Algae participate in nutrient cycling by absorbing nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus from their surroundings, and upon their death and decomposition, returning these nutrients back into the ecosystem for reuse by other organisms.
Is Algae a Producer or Consumer?

Algae primarily function as producers within ecosystems due to their ability to perform photosynthesis and generate energy from sunlight. As producers, they produce organic compounds from inorganic substances, such as carbon dioxide and water. This process forms the basis of the food chain, as the energy-rich compounds produced by algae are consumed by other organisms. However, under certain conditions, some algae species can also act as consumers by obtaining nutrients from their environment through methods such as absorption or ingestion. Despite this, their primary role as producers remains fundamental to ecosystem dynamics.
Reasons Why Algae are Not Consumers
-
Photosynthetic Nature: Algae primarily obtain energy through photosynthesis rather than consuming organic matter from other organisms.
-
Autotrophic Nutrition: Algae are autotrophic organisms, meaning they can synthesize their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water, without relying on consuming other organisms.
-
Primary Production: Algae play a vital role in primary production within ecosystems by converting solar energy into chemical energy, which is then utilized by consumers higher up in the food chain.
-
Lack of Specialized Organs: Unlike consumers, algae lack specialized structures for capturing and ingesting food, further emphasizing their role as primary producers.
-
Importance in Food Chains: Algae serve as the base of various food chains, providing energy and nutrients to consumers, highlighting their primary producer status in ecosystems.
Are Algae Decomposers?
Algae are not typically considered decomposers in the traditional sense. While some species of algae may contribute to the decomposition process under specific conditions, their primary role lies in photosynthesis and primary production. Decomposers are organisms that break down organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into simpler substances, aiding in nutrient recycling. Algae, on the other hand, are more commonly associated with producing organic matter through photosynthesis rather than decomposing it. However, in certain situations, algae may contribute to the breakdown of organic matter through the release of enzymes or by providing a substrate for microbial decomposition. Nonetheless, their primary function in ecosystems revolves around energy production rather than decomposition.
Are Algae Consumers?
Algae are not typically classified as consumers in ecosystems. While they primarily function as producers through photosynthesis, some algae species may exhibit heterotrophic behavior under certain conditions. Heterotrophic algae can obtain nutrients by consuming organic matter or by absorbing dissolved nutrients from their environment. However, the majority of algae are autotrophic, meaning they produce their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. Thus, while some algae may display consumer-like behaviors, their overarching role in ecosystems is that of primary producers.
Is Algae A Producer Or Consumer Or Decomposer?

Algae primarily function as producers in ecosystems, utilizing photosynthesis to convert sunlight into chemical energy. This process allows them to produce organic compounds from inorganic substances like carbon dioxide and water. While some algae species may exhibit consumer-like behaviors under specific conditions, such as heterotrophic feeding, their primary role remains that of producers. As producers, they form the base of food chains, providing energy and nutrients to other organisms. Generally, algae are not considered decomposers, as their main function is not to break down organic matter but rather to generate energy through photosynthesis.
Is Green Algae A Producer?
Yes, green algae are producers within ecosystems. Like other algae, they possess chlorophyll and other pigments necessary for photosynthesis, enabling them to convert sunlight into chemical energy. Green algae play a crucial role in primary production by synthesizing organic compounds from carbon dioxide and water, thus forming the foundation of various food chains. Their ability to generate energy from sunlight categorizes them as primary producers in ecosystems.
Features of Green Algae That Help With Primary Production
-
Chlorophyll Pigments: Green algae contain chlorophyll a and b pigments, allowing them to capture light energy from the sun for photosynthesis.
-
Photosynthetic Structures: Green algae have specialized structures, such as chloroplasts, where photosynthesis takes place, facilitating the conversion of light energy into chemical energy.
-
Adaptability: Green algae exhibit a wide range of adaptations to different environments, enabling them to thrive in various aquatic and terrestrial habitats and maximize their contribution to primary production.
-
Carbon Fixation: Green algae efficiently fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere or water, incorporating it into organic molecules essential for sustaining life and supporting food webs.
-
Reproductive Strategies: Green algae employ diverse reproductive strategies, including asexual and sexual reproduction, allowing them to proliferate and maintain their population size, thus ensuring continuous primary production.
-
Nutrient Utilization: Green algae have mechanisms for efficiently utilizing nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, to support their growth and photosynthetic activities, further enhancing their role as primary producers.
Is Red Algae A Consumer?
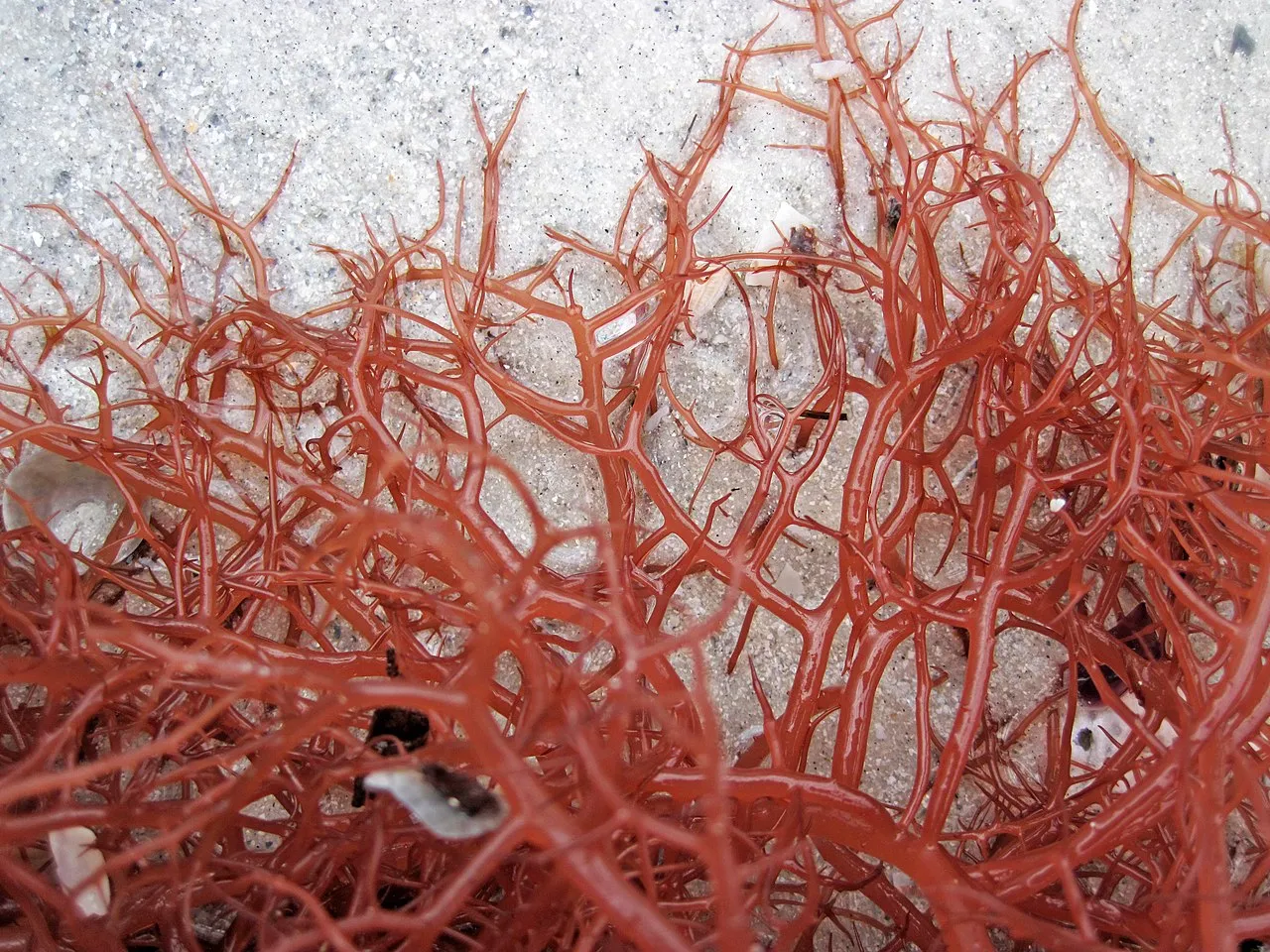

Red algae are primarily producers within ecosystems, similar to other algae species. They possess chlorophyll and other pigments necessary for photosynthesis, enabling them to convert sunlight into chemical energy. While some red algae may exhibit heterotrophic behavior under specific conditions, such as consuming organic matter or absorbing dissolved nutrients, their overarching role remains that of producers. As producers, red algae contribute to primary production by synthesizing organic compounds from inorganic substances like carbon dioxide and water, thus forming the foundation of various food chains.
Reasons Why Red Algae are Not Consumers
-
Photosynthetic Capability: Red algae possess chlorophyll and other pigments necessary for photosynthesis, allowing them to produce their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water.
-
Autotrophic Nutrition: Red algae are primarily autotrophic organisms, meaning they can synthesize organic compounds from inorganic substances without relying on consuming other organisms.
-
Role in Primary Production: Red algae play a crucial role in primary production within ecosystems by converting solar energy into chemical energy, which is then utilized by other organisms in the food chain.
-
Absence of Specialized Feeding Structures: Unlike consumers, red algae lack specialized structures for capturing and ingesting food, further emphasizing their role as primary producers.
-
Importance in Food Chains: Red algae serve as the base of various food chains, providing energy and nutrients to consumers, highlighting their primary producer status in ecosystems.
Is Red Algae A Producer Or Consumer?
Red algae primarily function as producers within ecosystems. Their ability to perform photosynthesis, facilitated by chlorophyll and other pigments, enables them to convert sunlight into chemical energy. As producers, red algae synthesize organic compounds from inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide and water, playing a foundational role in primary production. While some red algae species may exhibit heterotrophic behavior under certain conditions, their overarching role remains that of producers. They contribute significantly to the energy and nutrient flow within ecosystems, serving as vital components of various food chains.
Are Algae And Fungi Producers?

While algae are primarily producers due to their ability to perform photosynthesis, fungi, on the other hand, are not considered producers. Fungi are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they obtain their nutrients by decomposing organic matter or by parasitizing other organisms. Unlike algae, fungi cannot photosynthesize to produce their own food. Instead, they play crucial roles as decomposers, breaking down organic material and returning nutrients to the soil. Therefore, while algae are producers, fungi are not; they function primarily as decomposers or consumers within ecosystems.
Algae Food Chain Position and Role
Algae occupy a crucial position in various food chains within ecosystems, serving as primary producers. As the base of the food chain, algae convert solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis, synthesizing organic compounds from inorganic substances. These compounds serve as food for herbivores and primary consumers, such as zooplankton and small fish, which then become prey for higher trophic levels. Thus, algae form the foundation of aquatic and terrestrial food webs, supporting the entire ecosystem by providing energy and nutrients to organisms at different trophic levels. Additionally, algae play a vital role in nutrient cycling by absorbing and releasing essential nutrients, further contributing to ecosystem stability and productivity.
Conclusion
Algae, as primary producers, play a fundamental role in sustaining life within ecosystems. Through photosynthesis, they harness sunlight to produce organic compounds, serving as the foundation of food chains. Their ability to convert solar energy into chemical energy provides vital nutrients and energy to various organisms, from microscopic plankton to large marine mammals. Additionally, algae contribute to nutrient cycling and ecosystem stability, further emphasizing their significance. Understanding the role of algae in ecosystems is essential for conservation efforts and maintaining the balance of natural habitats. As such, preserving and protecting algae populations is crucial for the health and sustainability of ecosystems worldwide.
*Summary
| Aspect | Summary |
| Role in Ecosystems |
– Primary producers
|
|
– Convert sunlight into chemical energy through photosynthesis
|
|
|
– Synthesize organic compounds from inorganic substances like carbon dioxide and water
|
|
|
– Form the foundation of food chains
|
|
| Consumer-like Behavior |
– Some species may exhibit consumer-like behaviors under specific conditions
|
| Contributions to Ecosystems |
– Contribute to nutrient cycling
|
|
– Enhance ecosystem stability
|
|
|
– Provide vital energy and nutrients to organisms at different trophic levels
|
|
| Importance for Conservation |
– Understanding algae’s role is crucial for conservation efforts
|
|
– Preserving and protecting algae populations is essential for maintaining ecosystem balance
|
FAQs about Algae:
- What are the different types of algae?
- Algae encompass a diverse group of photosynthetic organisms, including green algae, red algae, brown algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates.
- Where do algae live?
- Algae can be found in various aquatic environments, including oceans, lakes, rivers, and ponds. Some species also thrive in terrestrial habitats such as soil, rocks, and tree bark.
- Do algae only exist in water?
- While many algae species are aquatic, some can also live in terrestrial environments, including moist soil, rocks, and even symbiotically with other organisms like fungi in lichens.
- Are algae harmful?
- While many algae species are harmless and play essential roles in ecosystems, some algae blooms can produce toxins harmful to humans and other animals. These harmful algal blooms (HABs) can lead to water contamination and pose risks to aquatic life and human health.
- Can algae be used for biofuel production?
- Yes, certain algae species, such as microalgae, have high lipid content and can be cultivated for biofuel production. Algae-based biofuels are considered a promising renewable energy source due to their high productivity and potential for carbon dioxide sequestration.
- What is the importance of algae in the environment?
- Algae are vital for ecosystem health and function. They produce oxygen, serve as food for various organisms, contribute to nutrient cycling, and support biodiversity. Additionally, algae play roles in water purification and carbon sequestration.
- How do algae reproduce?
- Algae reproduce through both sexual and asexual methods. Asexual reproduction typically involves cell division or fragmentation, while sexual reproduction involves the fusion of gametes from different individuals.
- What are the economic uses of algae?
- Algae have numerous economic uses, including food supplements (e.g., Spirulina), agar production, wastewater treatment, biofuel production, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.








