What Is The Role Of Scavengers In An Ecosystem? Discussed
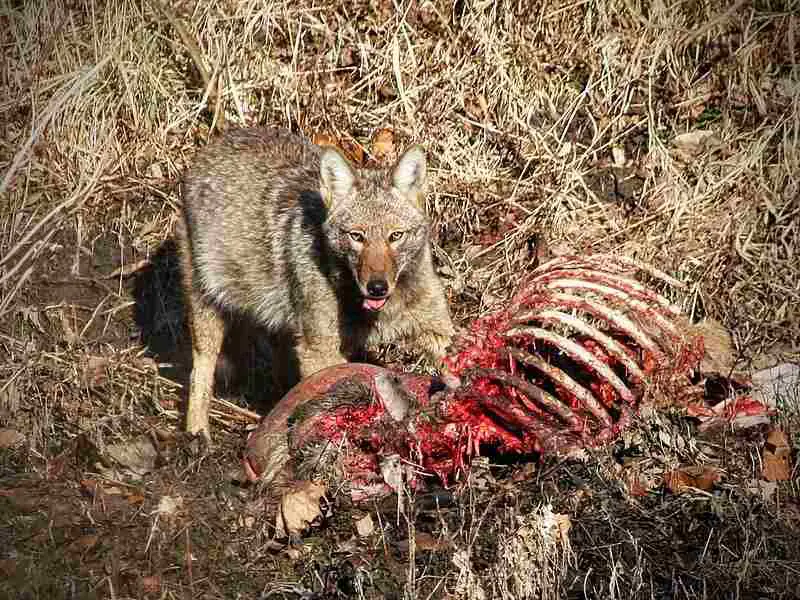
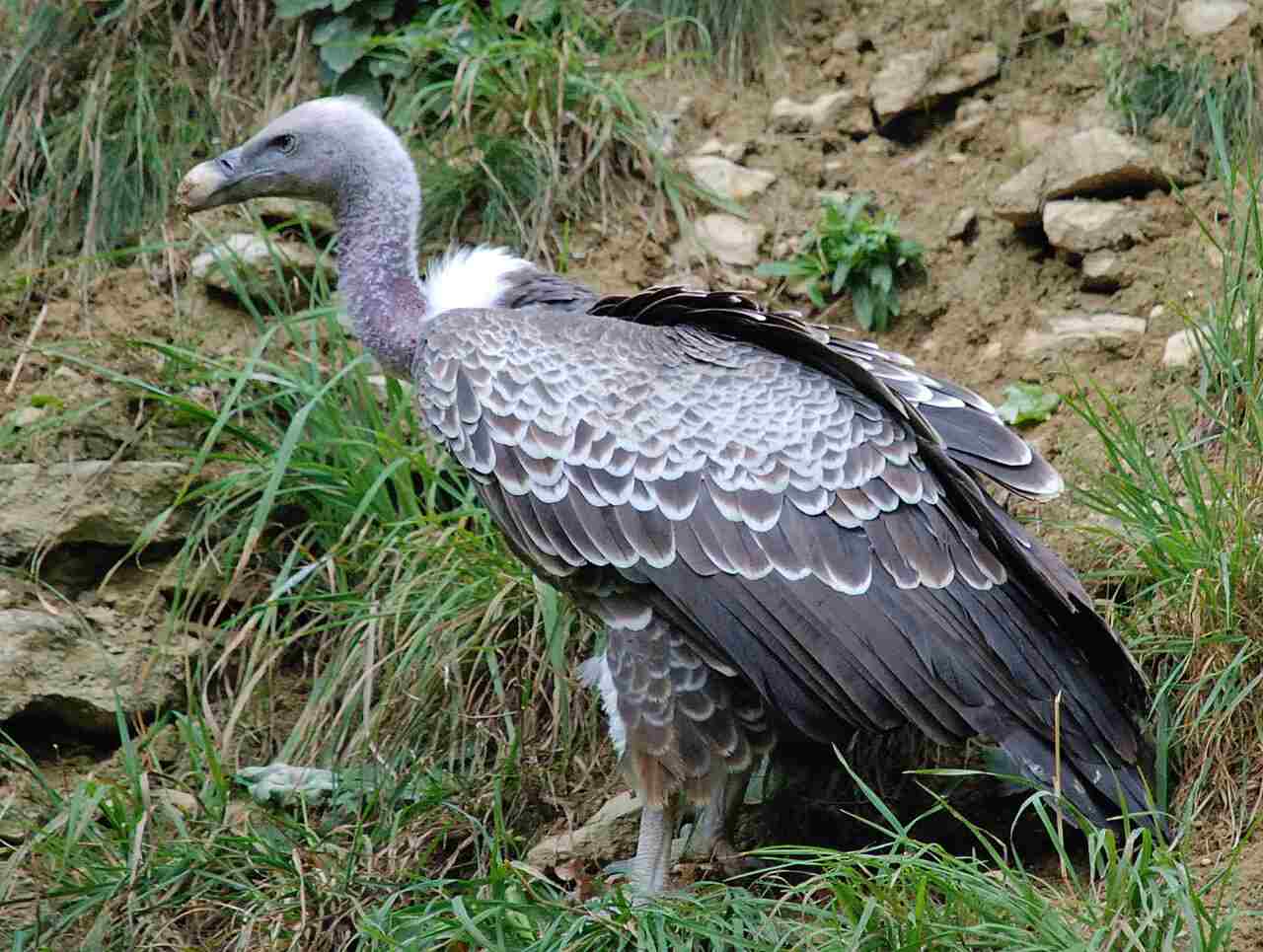
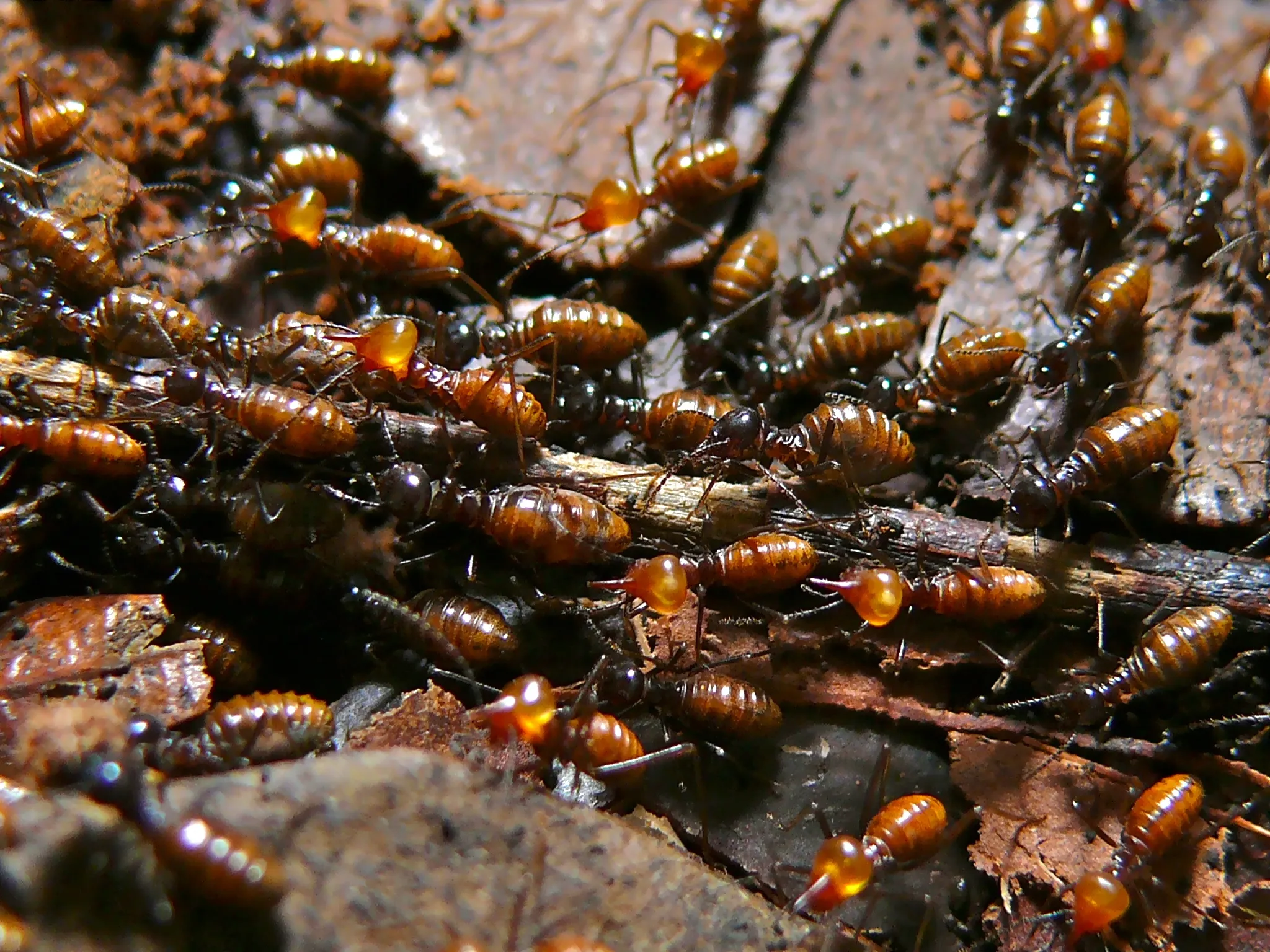
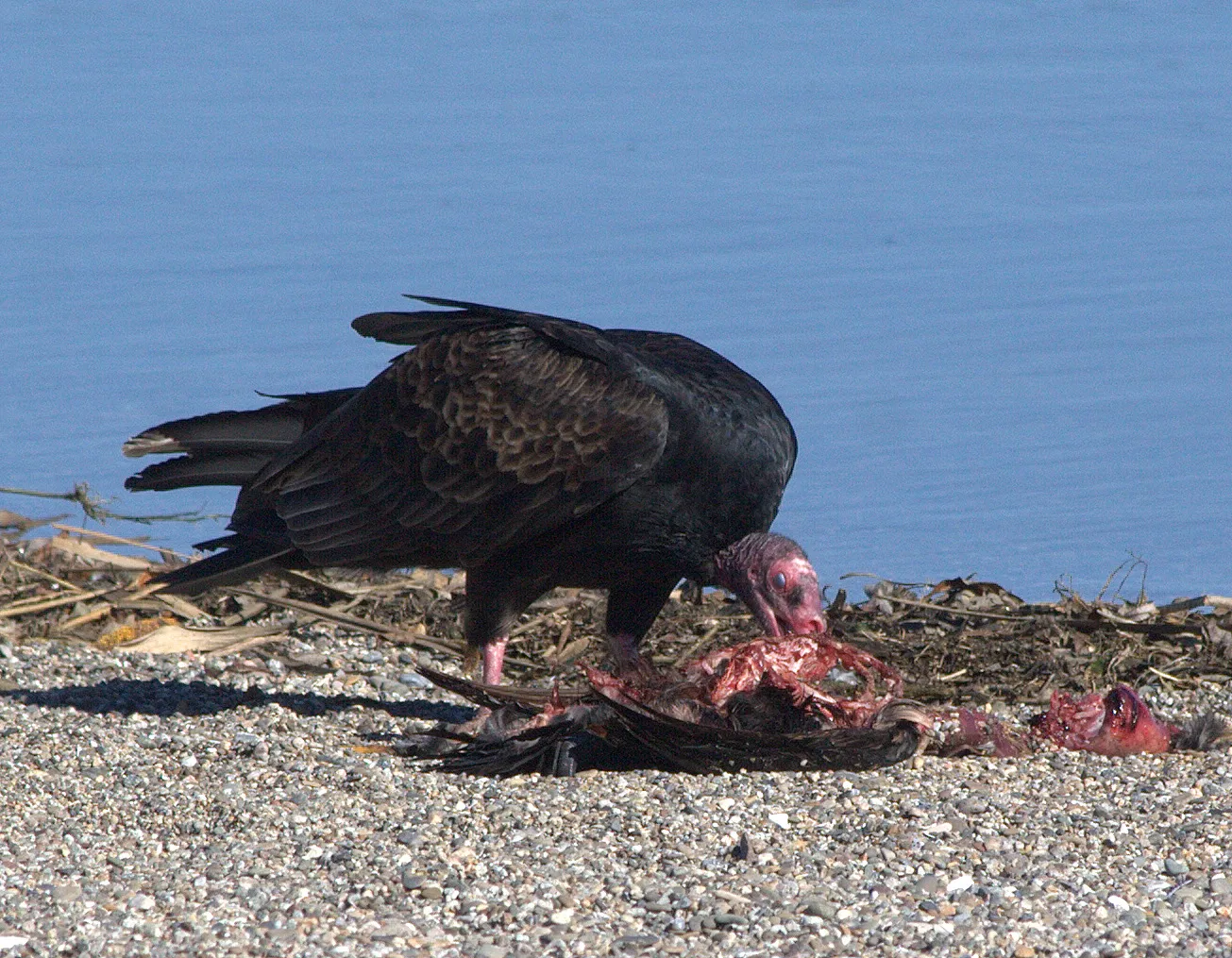
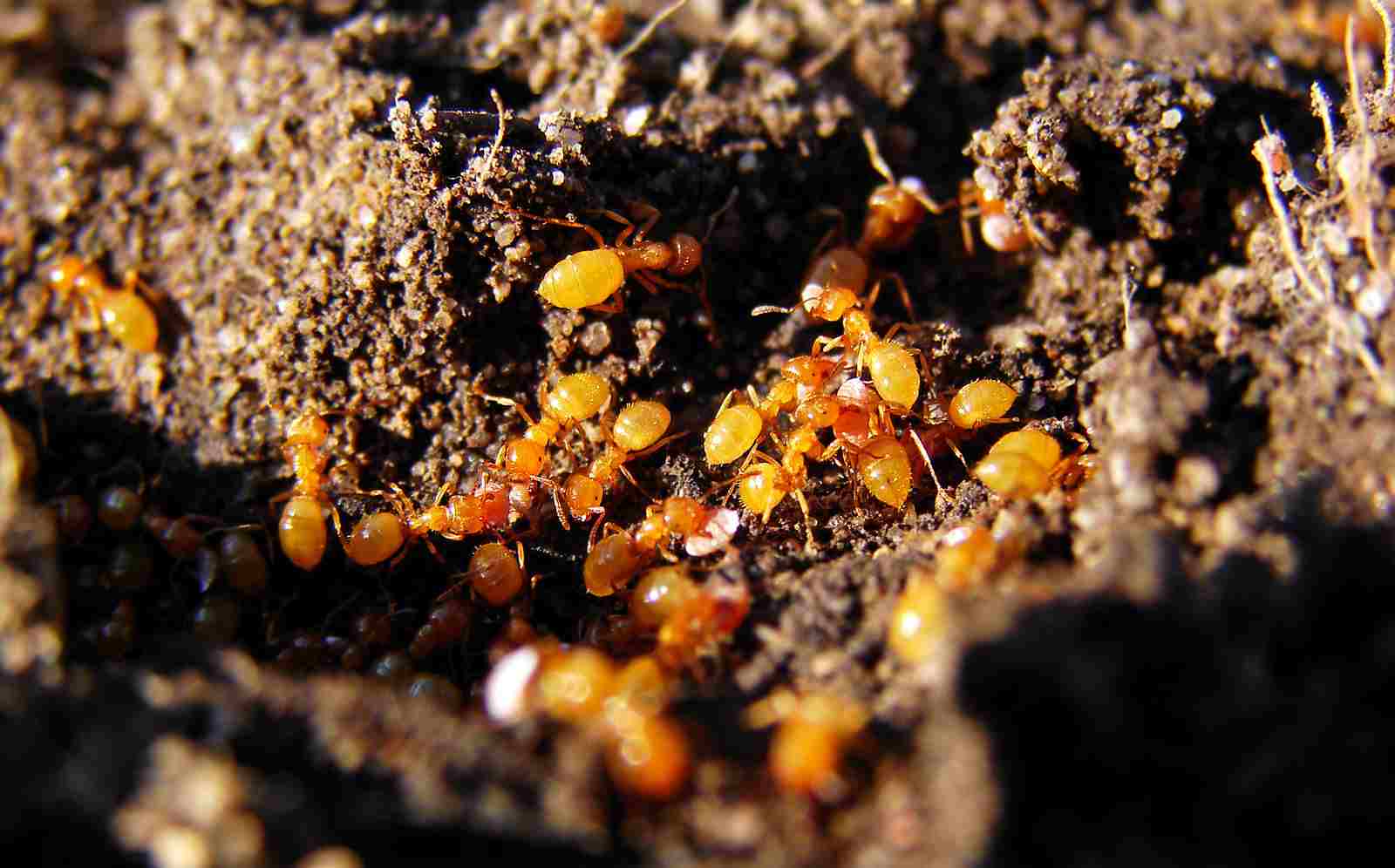
The role of scavengers in an ecosystem comprises of consuming dead plants and animals, breaking down organic material, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem, and aiding in maintaining food and energy levels. Scavengers like hyenas, vultures, and termites play a crucial role in removing decaying organisms, promoting energy transfer between trophic levels, and contributing to the overall functioning and balance of the ecosystem. Their scavenging activities help conserve energy and nutrients, disperse them throughout the ecosystem, and reduce diseases associated with decomposition, highlighting their essential role in ecosystem health and sustainability.
Why Are Scavengers Important To The Ecosystem?
Scavengers are important to ecosystems because they help remove dead and decaying organic matter, preventing the buildup of harmful substances and the spread of disease. By consuming carrion, scavengers eliminate potential sources of disease and pathogens that could otherwise infect other animals or even humans. This helps maintain the overall health and stability of the ecosystem. Additionally, scavengers play a crucial role in the nutrient cycling process. As they consume dead animals and plants, they break down the organic matter and release the nutrients back into the soil and water, making them available for other organisms to use.
This recycling of nutrients is essential for the continued growth and productivity of the ecosystem. Scavengers also help prevent the overpopulation of certain species by removing their dead bodies, which can otherwise lead to imbalances in the food web. By regulating the population of decomposing organisms, scavengers ensure that the ecosystem remains in a state of dynamic equilibrium. Furthermore, the presence of scavengers can indicate the overall health of an ecosystem.
The diversity and abundance of scavenger species can serve as a valuable indicator of the ecosystem’s well-being, as changes in their populations can reflect broader environmental changes or disturbances. In summary, scavengers are essential components of healthy ecosystems, playing a vital role in disease prevention, nutrient cycling, population regulation, and ecosystem monitoring. Their importance cannot be overstated, as the loss or decline of scavenger species can have far-reaching and detrimental consequences for the entire ecosystem.
Examples Of Scavengers In An Ecosystem
Scavengers in an ecosystem encompass a diverse range of species that play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance. Some common examples of scavengers include:
-
Vultures: These birds are well-known scavengers that feed on carrion, helping to clean up dead animals and prevent the spread of disease.
-
Coyotes: These mammals are opportunistic scavengers that consume a variety of food sources, including carrion.
-
Crows and Ravens: These intelligent birds are adept scavengers, feeding on a wide range of organic matter, including dead animals.
-
Hyenas and Jackals: These carnivores are known for their scavenging behavior, often feeding on carrion left behind by other predators.
-
Burying Beetles and Blowflies: Invertebrates like burying beetles and blowflies are obligate scavengers that play a vital role in decomposing dead animal material.
-
Termites: Termites are important scavengers of dead plant material, contributing to nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
These examples highlight the diversity of scavengers in ecosystems and their essential role in recycling nutrients, preventing disease, and maintaining ecosystem health.
What Ecosystem Service Do Scavengers Provide?
Scavengers provide a vital ecosystem service by removing dead and decaying organic matter from the environment. This process serves several important functions:
-
Disease prevention: By consuming carrion, scavengers eliminate potential sources of disease and pathogens that could otherwise infect other animals or even humans. This helps maintain the overall health and stability of the ecosystem.
-
Nutrient cycling: As scavengers consume dead animals and plants, they break down the organic matter and release the nutrients back into the soil and water, making them available for other organisms to use. This recycling of nutrients is essential for the continued growth and productivity of the ecosystem.
-
Population regulation: Scavengers help prevent the overpopulation of certain species by removing their dead bodies, which can otherwise lead to imbalances in the food web. By regulating the population of decomposing organisms, scavengers ensure that the ecosystem remains in a state of dynamic equilibrium.
-
Ecosystem monitoring: The presence and diversity of scavenger species can serve as a valuable indicator of the ecosystem’s overall health. Changes in scavenger populations can reflect broader environmental changes or disturbances, making them important for ecosystem monitoring and assessment.
What Are The Benefits Of Scavengers?
The benefits of scavengers to ecosystems are numerous:
-
Maintaining ecosystem balance: Scavengers play a crucial role in preventing the buildup of dead organic matter, which can lead to the spread of disease and disruption of nutrient cycling.
-
Nutrient recycling: By breaking down and consuming carrion, scavengers return essential nutrients to the soil and water, supporting the growth and productivity of other organisms.
-
Disease control: Scavengers help control the spread of diseases by removing potential sources of infection, such as dead animals.
-
Ecosystem stability: The presence of a diverse community of scavengers helps maintain the overall stability and resilience of the ecosystem, as they can adapt to changes in food availability.
-
Indicator species: Monitoring the health and abundance of scavenger populations can provide valuable insights into the overall condition of the ecosystem.
-
Evolutionary adaptations: Scavengers have evolved unique adaptations, such as strong digestive systems and keen senses, that allow them to thrive in their ecological niche.
In summary, scavengers are essential components of healthy ecosystems, providing a range of critical services that support the overall balance and functioning of the natural world.
What Is The Role Of Scavengers And Decomposers?
Scavengers and decomposers work together to break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem. Scavengers consume dead and decaying organic matter, while decomposers break down the organic matter further, releasing the nutrients back into the soil and water.
Summary in Tabular Format
| Column 1: Topic |
Column 2: Description
|
| Importance of Scavengers |
Scavengers play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance by removing dead and decaying organic matter, preventing the buildup of harmful substances, and controlling the spread of disease.
|
| Examples of Scavengers |
Examples of scavengers include vultures, coyotes, crows and ravens, hyenas and jackals, burying beetles, blowflies, and termites.
|
| Ecosystem Services |
Scavengers provide ecosystem services such as nutrient cycling, population regulation, and disease control.
|
| Benefits of Scavengers |
The benefits of scavengers include maintaining ecosystem balance, recycling nutrients, controlling disease, and contributing to ecosystem stability.
|
| Role of Scavengers and Decomposers |
Scavengers and decomposers work together to break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
|
| Ecological Functions |
Scavengers promote food web complexity, provide routes for resource sequestration, and subsidize populations during food-limited times.
|
| Urban Ecosystems |
Vertebrate scavengers play a key role in urban ecosystems, providing energy transfer between trophic levels and sanitary benefits.
|
| Legacy of Scavengers |
The decline of scavengers can have significant impacts on ecosystem health, human health, and the economy, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts.
|
FAQs and Answers
Q: What is the role of scavengers in an ecosystem?
A: Scavengers play a crucial role in maintaining ecosystem balance by removing dead and decaying organic matter, preventing the buildup of harmful substances, and controlling the spread of disease.
Q: What are some examples of scavengers?
A: Examples of scavengers include vultures, coyotes, crows and ravens, hyenas and jackals, burying beetles, blowflies, and termites.
Q: What ecosystem services do scavengers provide?
A: Scavengers provide ecosystem services such as nutrient cycling, population regulation, and disease control.
Q: What are the benefits of scavengers?
A: The benefits of scavengers include maintaining ecosystem balance, recycling nutrients, controlling disease, and contributing to ecosystem stability.
Q: How do scavengers and decomposers work together?
A: Scavengers and decomposers work together to break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
Q: What is the ecological function of vertebrate scavenging?
A: Vertebrate scavenging promotes food web complexity, provides routes for resource sequestration, and subsidizes populations during food-limited times.
Q: What is the role of scavengers in urban ecosystems?
A: Vertebrate scavengers play a key role in urban ecosystems, providing energy transfer between trophic levels and sanitary benefits.
Q: What is the legacy of scavengers?
A: The decline of scavengers can have significant impacts on ecosystem health, human health, and the economy, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts.