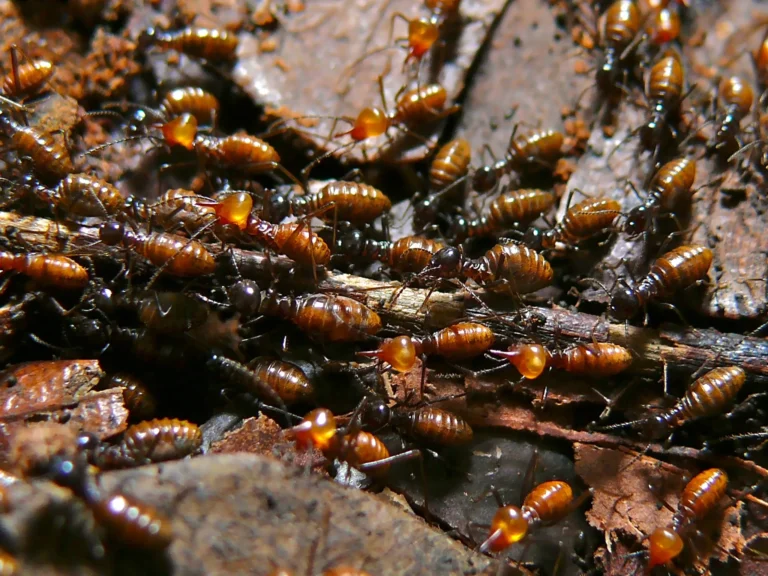
Why are Decomposers Important? Ecological Importance of Decomposers Discussed
Decomposers are important because they play a crucial role in nutrient cycling within ecosystems. They release nutrients from organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, and make them available for primary producers to utilize. This nutrient recycling process is essential for the growth and survival of plants and other organisms in the food web.
Additionally, decomposers help to remove organic waste from the environment, preventing the accumulation of harmful substances. They also contribute to soil conservation and enrichment by breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients into the soil. Furthermore, decomposers facilitate energy transfer within ecosystems by breaking down complex organic compounds into simpler products that can be utilized by other organisms.
Reasons Why Decomposers are Important
1). They Breakdown Complex Organic Compounds into Simpler Products
Decomposers play a crucial role in ecosystems by breaking down complex organic compounds into simpler products. This process is essential for the recycling of nutrients and the overall functioning of the ecosystem.
One of the main reasons why decomposers are important is their ability to break down complex organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into simpler forms. This breakdown process, known as decomposition, involves the release of enzymes by decomposers, which break down the complex molecules into smaller, more manageable compounds. These compounds can then be utilized by other organisms in the ecosystem.
By breaking down complex organic compounds, decomposers help release nutrients for primary consumers. When plants and animals die, their organic matter contains valuable nutrients that can be recycled back into the ecosystem. Decomposers break down this organic matter and release nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon back into the soil or water. These nutrients are then taken up by primary consumers, such as plants, and used for growth and development.
Furthermore, the breakdown of complex organic compounds by decomposers facilitates energy transfer within the ecosystem. Energy is stored in the chemical bonds of organic matter, and decomposers play a vital role in releasing this energy. Through the process of decomposition, decomposers convert the stored energy in organic matter into a form that can be utilized by other organisms. This energy transfer is essential for the functioning of the food web and the overall energy flow within the ecosystem.
2). Decomposers Help Release Nutrients for Primary Consumers
Decomposers play a vital role in ecosystems by helping to release nutrients for primary consumers. This is another reason why decomposers are important in maintaining the balance of an ecosystem.
When plants and animals die, their organic matter contains valuable nutrients that can be recycled back into the environment. Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down this organic matter through the process of decomposition. They release enzymes that break down complex organic compounds into simpler forms, releasing nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon back into the soil or water.
These released nutrients are then available for primary consumers, such as plants, to utilize for their growth and development. Primary consumers rely on these nutrients to obtain the energy they need to survive. Without decomposers, the nutrients locked within dead organic matter would remain inaccessible, leading to nutrient depletion and a disruption in the food chain.
In addition to releasing nutrients, decomposers also help to break down and recycle waste materials in the environment. They play a crucial role in the decomposition of dead plants and animals, as well as other organic waste materials. By breaking down these waste materials, decomposers help to maintain a clean and healthy environment.
3). Facilitation of Energy Transfer
Decomposers play a crucial role in the facilitation of energy transfer within ecosystems. This is another reason why decomposers are important in maintaining the balance of an ecosystem.
When organisms die, their organic matter becomes a valuable source of energy. Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down this organic matter through the process of decomposition. They release enzymes that break down complex organic compounds into simpler forms, releasing energy in the process.
This energy is then transferred to other organisms in the ecosystem. Primary consumers, such as herbivores, feed on plants and obtain energy from the nutrients released by decomposers. Secondary consumers, such as carnivores, then feed on the primary consumers, transferring the energy further up the food chain.
By facilitating energy transfer, decomposers ensure that energy flows through the ecosystem, sustaining the various organisms within it. Without decomposers, the energy locked within dead organic matter would remain trapped and unavailable for other organisms to utilize, leading to a disruption in the energy flow and the overall functioning of the ecosystem.
4). Role in Soil Conservation and Enrichment
Decomposers play a crucial role in soil conservation and enrichment, making them an essential component of ecosystems. Their importance lies in their ability to break down organic matter and release nutrients that are vital for the growth and health of plants.
One of the key reasons why decomposers are important in soil conservation is their role in the decomposition of dead plant and animal material. When plants and animals die, their remains accumulate on the soil surface. Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down these organic materials into simpler forms through the process of decomposition. This breakdown releases essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, into the soil. These nutrients are then made available for uptake by plants, promoting their growth and overall health.
In addition to nutrient release, decomposers also contribute to soil enrichment through the formation of humus. Humus is a dark, organic material that is rich in nutrients and acts as a natural fertilizer. It improves soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient retention. Decomposers break down organic matter and convert it into humus, which helps to maintain soil fertility and productivity.
Furthermore, decomposers play a vital role in the cycling of organic matter in the soil. They break down complex organic compounds, such as cellulose and lignin, into simpler forms that can be readily utilized by plants. This process not only releases nutrients but also helps to improve soil structure and aeration. By breaking down organic matter, decomposers contribute to the formation of stable soil aggregates, which enhance soil porosity and water infiltration.
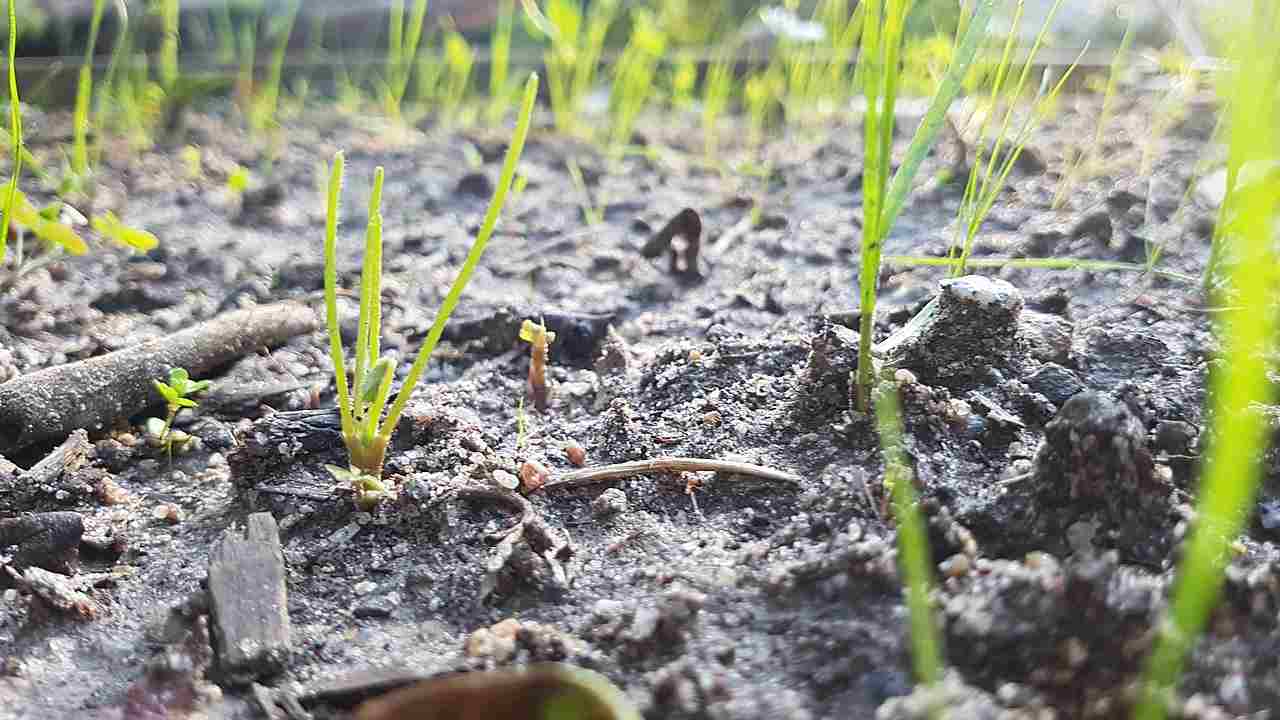

5). Decomposers Remove Wastes from The Environment
Decomposers play a crucial role in removing wastes from the environment, making them an important component of ecosystems. One reason why decomposers are essential is their ability to break down dead organic matter and convert it into simpler forms. When plants and animals die, their remains accumulate in the environment, leading to the buildup of waste material. Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, break down these organic wastes through the process of decomposition. This breakdown not only helps to clean up the environment but also releases essential nutrients back into the ecosystem.
By breaking down organic wastes, decomposers prevent the accumulation of dead material, which can lead to the release of harmful substances and the growth of pathogens. They help to maintain a healthy and balanced ecosystem by recycling nutrients and reducing the risk of pollution. Additionally, decomposers contribute to the overall cleanliness of the environment by breaking down organic matter that would otherwise contribute to unpleasant odors and unsightly waste piles.
Why are Decomposers Important to the Food Web?
Decomposers play a crucial role in the food web by contributing to the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism or species to another. They break down dead organic matter into simpler inorganic materials, making nutrients available to primary producers. This process helps to recycle nutrients within the ecosystem, ensuring that they are continuously available for other organisms.
By breaking down organic matter, decomposers sustain the food web by strengthening the interconnections between organisms. They support the producers, which are the basis of the food web, by releasing essential nutrients that they can utilize for growth and reproduction. Without decomposers, the nutrients locked within dead organisms would remain trapped and unavailable for other organisms to use.
Furthermore, decomposers help to maintain the balance and stability of the food web. They prevent the accumulation of dead material, which can lead to the release of harmful substances and the growth of pathogens. By breaking down organic matter, decomposers also contribute to the overall cleanliness of the environment, reducing the risk of pollution and the presence of unpleasant odors and waste piles.
Why are Decomposers Important to the Food Chain?
Decomposers play a critical role in the flow of energy through an ecosystem. They break apart dead organisms into simpler inorganic materials, making nutrients available to primary producers. This process of breaking down organic matter is essential for the functioning of the food chain.
One of the main reasons why decomposers are important to the food chain is their ability to breakdown organic matter. When plants and animals die, their bodies are decomposed by various organisms such as bacteria, fungi, and insects. These decomposers break down the complex organic compounds present in dead organisms into simpler products. This breakdown process releases essential nutrients that were locked within the dead organisms.
By breaking down organic matter, decomposers help recycle nutrients within the ecosystem. The nutrients released during decomposition are then available for primary producers, such as plants, to utilize. This recycling of nutrients ensures that they are continuously available for other organisms in the food chain. Without decomposers, the nutrients would remain trapped within dead organisms and unavailable for other organisms to use.
In addition to nutrient recycling, decomposers also facilitate the flow of energy from one trophic level to another in the food chain. When decomposers break down organic matter, they release energy that is stored within the dead organisms. This energy can then be transferred to other organisms in the food chain. For example, decomposers break down a dead plant, releasing energy that can be consumed by herbivores. The herbivores, in turn, become a food source for carnivores, and so on. Without decomposers, the energy stored in dead organisms would not be available for other organisms to utilize.
Why are Decomposers Important to Ecosystems?
Decomposers play a vital ecological role in ecosystems due to their ability to break down organic matter and release nutrients for primary consumers. This process is essential for the functioning and sustainability of ecosystems.
One of the key reasons why decomposers are important to ecosystems is their role in breaking down organic matter. When plants and animals die, decomposers such as bacteria, fungi, and insects break down their bodies into simpler inorganic materials. This breakdown process releases essential nutrients that were locked within the dead organisms. These nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, are then made available for primary consumers, such as herbivores, to utilize.
By releasing nutrients through the decomposition process, decomposers provide a continuous supply of essential elements for primary producers, such as plants. These primary producers rely on these nutrients to carry out photosynthesis and produce energy-rich organic compounds. Without decomposers, the nutrients would remain trapped within dead organisms, leading to nutrient depletion and limiting the growth and productivity of primary producers.
Furthermore, decomposers contribute to the overall sustainability of ecosystems. By breaking down organic matter, they prevent the accumulation of dead biomass, which could otherwise lead to the depletion of organic resources. Decomposers ensure that the energy and nutrients stored in dead organisms are recycled back into the ecosystem, making them available for other organisms to utilize. This recycling process helps to maintain the balance and functioning of the ecosystem.
Why are Decomposers an Essential Part of Ecosystems?
Decomposers are an essential part of ecosystems due to their crucial role in preventing the depletion of organic resources and sustaining the overall balance and functioning of the ecosystem. By breaking down and recycling biomass, decomposers ensure that the energy and nutrients stored within dead organisms are made available for other organisms to utilize.
One of the key reasons why decomposers are essential in ecosystems is their ability to break down and recycle organic matter. When plants and animals die, decomposers such as bacteria, fungi, and insects play a vital role in breaking down their bodies into simpler inorganic materials. This breakdown process releases essential nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, which were previously locked within the dead organisms. These nutrients are then made available for primary producers, such as plants, to utilize for growth and energy production.
By recycling nutrients through decomposition, decomposers provide a continuous supply of essential elements for primary producers. This is crucial for the sustainability of ecosystems as primary producers rely on these nutrients to carry out photosynthesis and produce energy-rich organic compounds. Without decomposers, the nutrients would remain trapped within dead organisms, leading to nutrient depletion and limiting the growth and productivity of primary producers.
Furthermore, decomposers play a vital role in preventing the accumulation of dead biomass in ecosystems. If dead organisms were not broken down and recycled, organic resources would become depleted over time. Decomposers ensure that the energy and nutrients stored in dead organisms are released and made available for other organisms to utilize. This recycling process helps to maintain the balance and functioning of the ecosystem by ensuring a continuous supply of nutrients and preventing the buildup of organic waste.
Why are Decomposers Important to Energy Transfer Within an Ecosystem?
Decomposers play a fundamental role in energy transfer within an ecosystem by releasing nutrients and recycling essential resources. This process is crucial for sustaining the flow of energy through the different trophic levels and ensuring the overall functioning and balance of the ecosystem.
One of the key ways decomposers contribute to energy transfer is through the breakdown of organic matter. When plants and animals die, decomposers such as bacteria, fungi, and insects break down their bodies into simpler inorganic materials. This decomposition process releases nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, which were previously locked within the dead organisms. These nutrients are then made available for other organisms to utilize, including primary producers.
Primary producers, such as plants, rely on these nutrients to carry out photosynthesis and produce energy-rich organic compounds. By recycling nutrients through decomposition, decomposers provide a continuous supply of essential elements for primary producers. This allows energy to flow from the lower trophic levels to the higher trophic levels, as primary producers are consumed by herbivores, which are then consumed by carnivores. Without decomposers, the energy stored within dead organisms would remain trapped, leading to a disruption in energy transfer and limiting the productivity of the ecosystem.
In addition to nutrient recycling, decomposers also contribute to energy transfer through the breakdown of organic waste. Dead plant and animal material, as well as feces and other organic waste, are decomposed by decomposers. This process not only releases nutrients but also converts organic matter into energy-rich compounds that can be utilized by other organisms. By breaking down organic waste, decomposers ensure that energy is not wasted and is instead made available for other organisms to utilize.
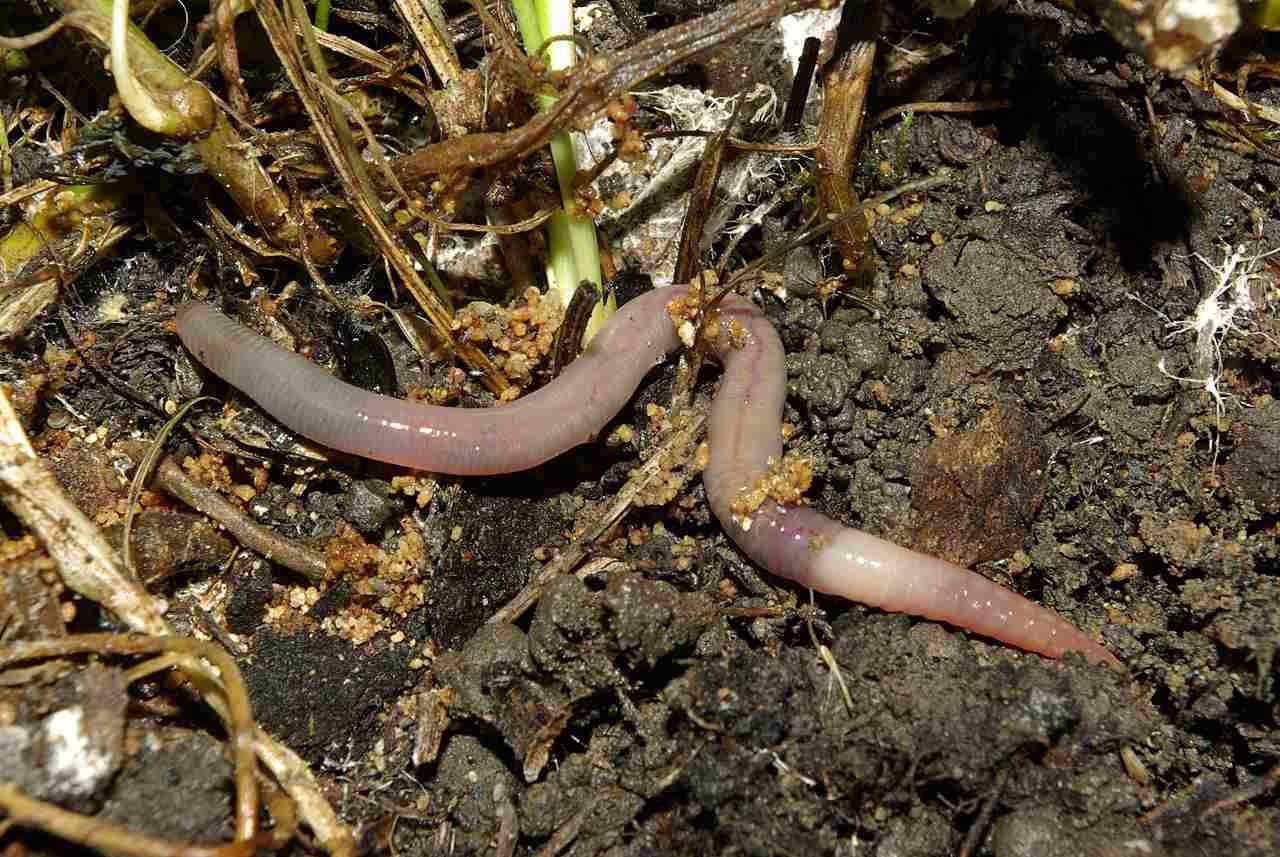

Are Decomposers Consumers or Producers?
Decomposers are classified as consumers rather than producers because they are heterotrophic organisms that rely on consuming biomass from other organisms, such as plants or animals, for their energy and nutrients. Unlike autotrophic organisms, which can produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, decomposers lack the ability to synthesize organic compounds from inorganic sources.
Instead, decomposers play a crucial role in breaking down complex organic matter into simpler compounds through the process of decomposition. This breakdown releases nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, that were previously locked within the dead organisms. These nutrients are then made available for other organisms, including primary producers, to utilize.
By consuming and breaking down organic matter, decomposers facilitate the recycling of nutrients within ecosystems. They release these nutrients back into the environment, allowing them to be utilized by other organisms in the food web. This nutrient recycling is essential for the overall functioning and balance of ecosystems.
Why Decomposers are Classified as Consumers and Not Producers
1). Lack of Autotrophic Capabilities
Most decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, lack the ability to synthesize biomass or produce their own food through photosynthesis. This is a key characteristic that distinguishes them from producers, such as plants and algae. Instead, decomposers rely on consuming organic matter from dead organisms or waste materials as their source of energy and nutrients. They break down complex organic compounds into simpler products through the process of decomposition.
By consuming and breaking down organic matter, decomposers play a crucial role in nutrient cycling within ecosystems. They release essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, back into the environment, making them available for uptake by primary producers. This nutrient recycling is vital for the growth and productivity of plants and other primary consumers in the food web.
Furthermore, the lack of autotrophic capabilities in decomposers means that they must obtain their energy from other organisms. They actively feed on dead organic matter, breaking it down into smaller particles that can be further decomposed by other decomposers. This process of decomposition not only helps to recycle nutrients but also facilitates the release of energy stored in organic matter, contributing to the overall energy flow within an ecosystem.
2). Heterotrophic Mode of Feeding
Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungi, exhibit a heterotrophic mode of feeding, which means they must consume biomass from other organisms to obtain their energy and nutrients. This mode of feeding is in stark contrast to autotrophs, like plants, which can produce their own food through photosynthesis. By relying on organic matter from dead organisms or waste materials, decomposers play a crucial role in the recycling of nutrients within ecosystems.
The consumption and breakdown of organic matter by decomposers result in the release of essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, back into the environment. These nutrients become available for uptake by primary producers, such as plants, enabling their growth and productivity. This nutrient recycling is vital for the overall functioning of the food web and the sustainability of ecosystems.
Furthermore, the heterotrophic mode of feeding in decomposers allows them to actively break down dead organic matter into smaller particles. This process of decomposition not only facilitates nutrient recycling but also contributes to the release of stored energy within organic matter. The energy released during decomposition becomes available for other organisms in the ecosystem, supporting the flow of energy through the food web.
3). Decomposers Release Nutrients for Producers to Utilize
Decomposers play a crucial role in the nutrient cycling within ecosystems. One of the key reasons why decomposers are important is that they release nutrients for producers to utilize. Unlike autotrophs, decomposers do not have the ability to produce their own food through photosynthesis. Instead, they rely on consuming organic matter from dead organisms or waste materials. By breaking down this organic matter, decomposers release essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, back into the environment.
These released nutrients become available for uptake by primary producers, such as plants, which utilize them for growth and productivity. This nutrient recycling is vital for the overall functioning of the food web and the sustainability of ecosystems. Without decomposers releasing these nutrients, the availability of essential elements for producers would be limited, hindering their growth and the productivity of the entire ecosystem.
Conclusion
* Decomposers play a crucial role in ecosystems by breaking down complex organic compounds into simpler products. This process releases essential nutrients for primary consumers and facilitates energy transfer within the food web.
* Additionally, decomposers contribute to soil conservation and enrichment, as they break down organic matter and release nutrients that can be utilized by plants. They also help remove wastes from the environment, ensuring the overall health and balance of ecosystems.
* Their role in breaking down organic matter and releasing nutrients is vital for the growth and productivity of primary producers, as well as the sustainability of the entire food web. Without decomposers, ecosystems would struggle to maintain the necessary nutrient levels and would be unable to support the diverse array of organisms that rely on them.
FAQs
1). Why do We Need Decomposers?
Decomposers play a crucial role in ecosystems, serving several important functions. Firstly, they help to sustain plants and other producers by breaking down complex organic compounds into simpler products. This breakdown process releases essential nutrients that can be absorbed by plants, promoting their growth and productivity. Secondly, decomposers recycle organic matter, ensuring that nutrients are continuously cycled through the ecosystem. This recycling process is vital for maintaining the overall health and balance of the ecosystem.
Additionally, decomposers contribute to the cleanup of the ecological environment. They remove organic waste in the form of excrement and remains, preventing the accumulation of harmful substances and reducing the risk of disease transmission. By efficiently decomposing organic matter, decomposers also help to prevent the release of greenhouse gases, contributing to the mitigation of climate change.
2). Why are Decomposers Important to the Environment?
Decomposers play a vital role in maintaining the health and balance of the environment. One key reason is their ability to help cleanup by removing organic waste in the form of excrement and remains. By efficiently decomposing these materials, decomposers prevent the accumulation of harmful substances and reduce the risk of disease transmission. This is particularly important in natural ecosystems where the buildup of waste can have detrimental effects on the overall ecosystem health.
Furthermore, decomposers contribute to the overall nutrient cycling in the environment. As they break down organic matter, they release essential nutrients back into the ecosystem, making them available for other organisms to utilize. This recycling process ensures that nutrients are continuously cycled through the environment, promoting the growth and productivity of plants and other organisms.
3). Why are Decomposers and Detritivores Essential Parts of All Food Webs
Decomposers and detritivores are essential parts of all food webs because they play a crucial role in the release of nutrients that are necessary for the functioning and existence of the food web.
When organisms die or produce waste, decomposers and detritivores break down their remains and excrement, releasing nutrients back into the environment. These nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are then made available for other organisms to utilize. Without decomposers and detritivores, organic matter would accumulate, and the nutrients within it would remain locked away, limiting the availability of resources for other organisms in the food web.
Additionally, decomposers and detritivores help to break down complex organic compounds into simpler forms, making them more accessible for other organisms to consume. This process of decomposition and nutrient recycling ensures the continuous flow of energy and nutrients throughout the food web, supporting the growth and survival of all organisms within the ecosystem.
4). What are The Importance of Decomposers?
What are the importance of decomposers? Decomposers play a vital role in ecosystems by breaking down organic matter and recycling nutrients. They are responsible for the decomposition of dead plants, animals, and other organic materials, returning essential nutrients back into the environment. This nutrient recycling is crucial for the functioning of ecosystems as it allows for the continuous availability of resources for other organisms.
One importance of decomposers is their role in nutrient cycling. When decomposers break down organic matter, they release nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon back into the soil or water. These nutrients are then taken up by plants and used for growth. Without decomposers, these nutrients would remain locked away in dead organisms, limiting their availability for other organisms in the ecosystem.
Another importance of decomposers is their contribution to soil conservation and enrichment. By breaking down organic matter, decomposers help to improve soil structure and fertility. They enhance the nutrient content of the soil, making it more suitable for plant growth. This is particularly important in agricultural systems where decomposers play a crucial role in maintaining soil health and productivity.
5). What are the Most Important Decomposers?
When it comes to decomposers, there are several key players that are considered the most important in the process of breaking down organic matter. One group of decomposers that stands out are the saprophytes. Saprophytes are organisms that obtain their nutrients by feeding on dead and decaying organic matter. They play a crucial role in decomposition because they have the ability to break down complex organic compounds into simpler products.
Fungi, for example, are one of the most important saprophytic decomposers. They secrete enzymes that break down organic matter, allowing them to absorb the nutrients they need for growth and reproduction. Bacteria are also important decomposers, as they have the ability to break down a wide range of organic materials.
It’s important to note that the most important decomposers can vary depending on the specific ecosystem and the type of organic matter present. Factors such as temperature, moisture, and nutrient availability can influence the composition and activity of decomposer communities. Nonetheless, saprophytes like fungi and bacteria are generally recognized as key players in the decomposition process.

6). Why is Decomposition Important?
Decomposition is important because it plays a vital role in recycling organic matter, energy, and nutrients within ecosystems. When organisms die or produce waste, decomposers break down their remains into simpler forms, releasing nutrients back into the environment. This nutrient recycling is crucial for the growth and survival of other organisms, including plants and primary consumers.
Moreover, decomposition helps to break down complex organic compounds, making them available for other organisms to utilize. Without decomposition, organic matter would accumulate, and nutrients would become locked away, limiting the productivity and sustainability of ecosystems. Therefore, decomposition is essential for maintaining the balance and functioning of ecosystems, ensuring their long-term health and stability.
7). Why are Decomposers Important to Humans?
Decomposers play a crucial role in sustaining the producers, such as plants, which we rely on for food, energy, and nutrients. They are an essential part of the food chain that supports all our sources of sustenance.
Firstly, decomposers break down organic matter, including dead plants and animals, into simpler forms. This decomposition process releases nutrients back into the soil, which are then absorbed by plants. As a result, decomposers contribute to the fertility of agricultural lands, ensuring healthy crop growth and higher yields.
Secondly, decomposers help in waste management. They break down organic waste, such as food scraps and dead organisms, preventing the accumulation of harmful substances and reducing the risk of disease transmission.
8). Why are Decomposers Important in The Carbon Cycle?
Decomposers play a vital role in the carbon cycle, making them important in maintaining the balance of carbon in ecosystems. They recycle organic carbon present in the biomass of dead plants and animals, breaking it down into simpler forms. This process releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere, contributing to carbon sequestration and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
When decomposers break down organic matter, they release carbon back into the environment, allowing it to be reused by other organisms. This recycling of carbon ensures that it remains in circulation within the ecosystem, rather than being locked away in dead organic material.
Furthermore, decomposers help regulate carbon emissions by preventing the buildup of organic waste. By breaking down dead organisms and organic matter, they reduce the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases that would occur if the waste were left to decompose anaerobically.
9). What are Two Importance of Decomposers?
Decomposers play a crucial role in ecosystems by serving two important functions. Firstly, they are responsible for recycling ecological resources. When decomposers break down dead plants and animals, they release nutrients back into the environment. These nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, are essential for the growth and survival of other organisms in the ecosystem. By recycling these resources, decomposers ensure that they are continuously available for use by primary producers and other consumers.
Secondly, decomposers are responsible for the removal of waste from the environment. They break down organic matter, including dead plants and animals, and convert them into simpler forms. This process helps to prevent the accumulation of organic waste, which can be harmful to the ecosystem. By removing waste, decomposers contribute to the overall cleanliness and health of the environment.
10). Why Decomposition is a Very Important Stage for Any Food Chain?
Decomposition is a vital stage for any food chain due to its crucial role in nutrient recycling and energy flow. During decomposition, organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, is broken down by decomposers into simpler forms. This process releases essential nutrients back into the environment, including nitrogen and phosphorus, which are then available for use by primary producers and other organisms in the food chain.
Furthermore, decomposition plays a key role in energy transfer within the food chain. As decomposers break down organic matter, they release energy that is stored within it. This energy is then transferred to other organisms as they consume the decomposers or feed on the products of decomposition. Without decomposition, the flow of nutrients and energy through the food chain would be disrupted, leading to imbalances and potential ecosystem collapse. Therefore, decomposition is a critical stage that ensures the sustainability and functioning of food chains in ecosystems.
11). What is The Importance of Detritivores and Decomposers in The Food Chain?
Detritivores and decomposers play a crucial role in the food chain by recycling organic matter and providing essential nutrients to sustain the ecosystem. While they have similar functions, there are some key differences between the two.
Detritivores, such as earthworms and millipedes, primarily feed on dead organic material, breaking it down into smaller particles. They physically break down the organic matter, increasing its surface area for decomposition by decomposers. Decomposers, on the other hand, are microorganisms like bacteria and fungi that chemically break down the organic matter into simpler forms.
The importance of detritivores and decomposers in the food chain lies in their ability to release nutrients from dead organic matter. These nutrients, including nitrogen and phosphorus, are then made available for primary producers, such as plants, to utilize for growth. Without detritivores and decomposers, organic matter would accumulate, and nutrients would become locked away, leading to nutrient imbalances and the inability of primary producers to thrive.
12). Why are Fungal Decomposers Important to The Environment?
Fungal decomposers play a vital role in the environment due to their ability to break down organic matter and facilitate nutrient recycling. They are essential for the decomposition process, breaking down complex organic compounds into simpler forms. This breakdown releases nutrients back into the ecosystem, making them available for other organisms to utilize.
Fungi also help in the decomposition of dead plant and animal material, contributing to the overall health of the environment. Without fungi, organic matter would accumulate, leading to nutrient imbalances and the inability of other organisms to access essential nutrients.
13). What is The Importance of Heterotrophs and Decomposers in an Ecosystem?
Heterotrophs and decomposers play a crucial role in an ecosystem by contributing to energy flow and nutrient cycling. While all decomposers are heterotrophs, not all heterotrophs are decomposers. Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, break down organic matter into simpler forms, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem.
This process allows other organisms, including primary consumers and producers, to utilize these nutrients for growth and survival. Heterotrophs, including herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores, obtain their energy by consuming other organisms. Together, heterotrophs and decomposers ensure the efficient transfer of energy and the recycling of nutrients within an ecosystem.
14). Why is Decomposition Important in an Ecosystem?
Decomposition is an essential process in an ecosystem, playing a vital role in the recycling and sustainability of nutrients. It serves as the medium by which organic matter is broken down into simpler forms, allowing for the release of valuable nutrients back into the environment.
One key reason why decomposition is important in an ecosystem is nutrient cycling. When organisms die or produce waste, decomposers such as bacteria and fungi break down their remains, releasing nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon back into the soil or water. These nutrients are then available for uptake by plants and other organisms, ensuring the continuous flow of energy and nutrients throughout the ecosystem.
Another reason for the significance of decomposition is the removal of dead organic matter. Without decomposers, dead plants and animals would accumulate, leading to the buildup of waste and the potential for disease and pollution. Decomposers play a crucial role in breaking down and removing these wastes, maintaining the overall health and balance of the ecosystem.
15). What are Two Reasons to Show that the Existence of Decomposers is Essential in an Ecosystem?
The existence of decomposers is essential in an ecosystem for two reasons: nutrient recycling and maintaining a healthy environment.
Firstly, decomposers play a crucial role in nutrient recycling. When organisms die or produce waste, decomposers break down their remains and release valuable nutrients back into the environment. This process ensures that essential elements like nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon are continuously cycled through the ecosystem. Without decomposers, these nutrients would remain locked in dead organic matter, limiting their availability to other organisms and disrupting the flow of energy and nutrients.
Secondly, decomposers help maintain a healthy environment by removing dead organic matter. If not decomposed, dead plants and animals would accumulate, leading to the buildup of waste and the potential for disease and pollution. Decomposers break down and remove these wastes, preventing their accumulation and ensuring the overall health and balance of the ecosystem.
16). What are The Most Important Decomposers in an Ecosystem Typically?
Typically, the most important decomposers in an ecosystem are microscopic saprophytes like bacteria and fungi. These organisms play a vital role in breaking down dead organic matter, such as fallen leaves, dead animals, and plant debris. Bacteria and fungi secrete enzymes that break down complex organic compounds into simpler products, facilitating the release of nutrients back into the environment.
They are responsible for the initial stages of decomposition and are crucial for nutrient recycling in ecosystems. However, it’s important to note that the specific decomposers present in an ecosystem may vary depending on factors such as climate, habitat, and the type of organic material available.