Prevention of Corrosion : 5 Applicable Measures Discussed
Prevention of corrosion can be achieved through; appropriate storage, protective coating (painting and galvanization), greasing and oiling, alloying, and use of drying agents.
This article discusses measures for the prevention of corrosion, as follows;
1). Appropriate Storage (as one of the Measures for Prevention of Corrosion)
One of the ways to prevent corrosion is appropriate storage of metallic materials.
The environment in which metals are stored should have low moisture and moderate temperature characteristics. This reduces the tendency and intensity of oxidation reactions, which are required for corrosion and deterioration of the metal to occur.
Acidic characteristics of the environment must also be low, as low pH (high-acidity) conditions are closely associated with faster rates and higher severity of corrosion [3].
By controlling the conditions of storage, the lifespan and structural integrity of metals can be extended and preserved.
The same principles of storage are also useful in transport of metal products, especially when such transport is occurring in large scale.
Appropriate storage must be combined with other corrosion-preventive measures like galvanization, greasing and oiling.

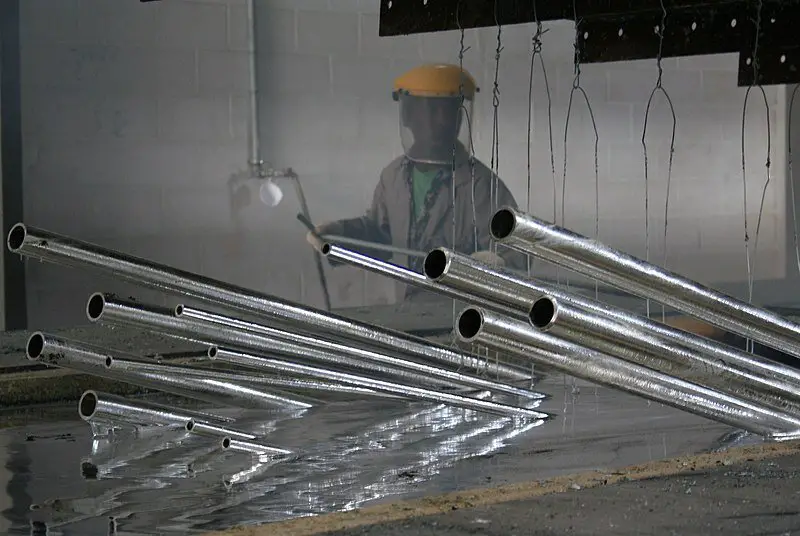
2). Protective Coating
Protective coating to prevent corrosion is the application of an extra layer of covering to the surface of a metal in order to reduce its susceptibility to corrosive deterioration.
It may also be described as anti-corrosion coating, especially when the coating material is carefully selected for corrosion resistance.
Regardless of the material used, protective coating reduces the susceptibility of metals to corrosion, because it limits exposure of these metals to corrosive agents, which may come in contact with the coating material instead.
There are multiple forms which protective coating of metals can take, as there are multiple materials that can be used to 'coat' metals for corrosion prevention. These include; paint, powder, plastic, tar, bitumen and pitch, any of which may be selected based on situational factors and needs.
The two most common forms of protective coating for prevention of corrosion are; painting and galvanization.
Painting results in a thin layer of extra material over the metal surface. The best corrosion prevention is offered by water-proof paint coating, which protects metals from moisture or high humidity (a prominent cause of corrosion) [2].
Most paints wear off within a relatively short period of time.
On the contrary, galvanization can protect metals from corrosion for significant time periods, if done appropriately.
Basically, galvanization of metals is the addition of an extra layer of metallic coating, to provide protection from chemical attack. The difference between galvanization and alloying is that galvanization allows the two metals to remain chemically distinct while being in electrical and physical contact; while alloying involves a complete mixing or combination of metals.
It must be noted that the effectiveness of corrosion prevention achieved through galvanization depends on the manner in which it is done; in terms of both materials and methods.
An effective method like hot-dip galvanization using corrosion-resistant metal like zinc can yield good results for corrosion-prone metals like iron [1].

3). Greasing and Oiling (as one of the Measures for Prevention of Corrosion)
Greasing and oiling can be used to prevent corrosion, in a similar manner as painting and galvanization.
This is because an extra layer of oil or grease reduces the exposure and reactivity of metals. It protects metal surfaces from moisture and acidic media.
Oiling is especially known for preventing rusting of iron. Due to its fluid state; it can be spread evenly over metal surfaces, and can even enter into crevices and grooves to prevent these from becoming micro-cells for localized corrosion.
The inert, impervious nature of grease and oils can reduce the impact of chemical processes like oxidation that cause metals to corrode.
Compared to other methods, however, greasing and oiling have a very temporary effect in the prevention of corrosion. They are most recommendable where there is need for and immediate protective measure, and must be supported with other, more-permanent measures like galvanization, for long-term protection.
4). Alloying
Alloying is the mixture of two or more metals to produce a new metallurgical material with desired properties. One of the common desired properties of alloys is corrosion resistance.
Alloying is effective for preventing corrosion, because the new metallic materials formed can combine multiple physical and chemical properties of different native metals, so that it becomes highly advanced in resilience and resistance to deterioration..
Examples of alloys that are less-prone to corrosion are; chromium, carbon and nickel-enriched steel respectively [4].
Alloying is one of the most effective measures for prevention of corrosion because it leads to an overall fortification of the metal. This differs from galvanization, which provides only surficial protection by coating the susceptible metal to reduce exposure to the environment.

5). Use of Drying Agents (as one of the Measures for Prevention of Corrosion)
Drying agents or desiccants can be used to prevent corrosion especially in enclosed spaces.
This is because such materials can adsorb moisture through a mechanism of chemical hydration and capillary condensation.
Metallic systems that can benefit from the use of drying agents for corrosion prevention include conduits and containers.
Examples of drying agents that can be used to prevent corrosion are; calcium hydride (CaH2), lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4), and phosphorus pentoxide (P4O10). These materials are able to absorb water because they are hydrophilic, and are able to incorporate water molecules into their chemical structure without reacting with the metal.
It is recommendable for drying agents to be used in combination with other corrosion-preventive measures like appropriate storage and protective coating.
Conclusion
Measures for the prevention of corrosion are;
1. Appropriate Storage
2. Protective Coating (painting and galvanization)
3. Greasing and Oiling
4. Alloying
5. Use of Drying Agents
References
1). Hegyi, A.; Dico, C.; Constantinescu, H.; Barea, C. (2017). "Influence of Hot-dip Galvanizing of Reinforcement on the Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Corrosion Process in Concrete." Procedia Engineering 181:226-233. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.02.380. (Accessed 15 May 2023).
2). Korde, N. (2015). "EFFECT OF CATHODIC PROTECTION ON COATING STEEL PIPELINE IN SALINE ENVIRONMENT." Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339750147_EFFECT_OF_CATHODIC_PROTECTION_ON_COATING_STEEL_PIPELINE_IN_SALINE_ENVIRONMENT. (Accessed 15 May 2023).
3). Tang, D.; Du, Y.; Lu, M.-X.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, Z.-T.; Dong, L. (2015). "Effect of pH value on corrosion of carbon steel under an applied alternating current." Materials and Corrosion 66(12):n/a-n/a. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1002/maco.201508365. (Accessed 15 May 2023).
4). Xie, W.; Ding, J.; Wei, X.; Wang, W.; Xia, G.; Xing, J. (2019). "Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steel and Pure Metal in Ternary Molten Nitrate for Thermal Energy Storage." Energy Procedia 158:4897-4902. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2019.01.703. (Accessed 15 May 2023).