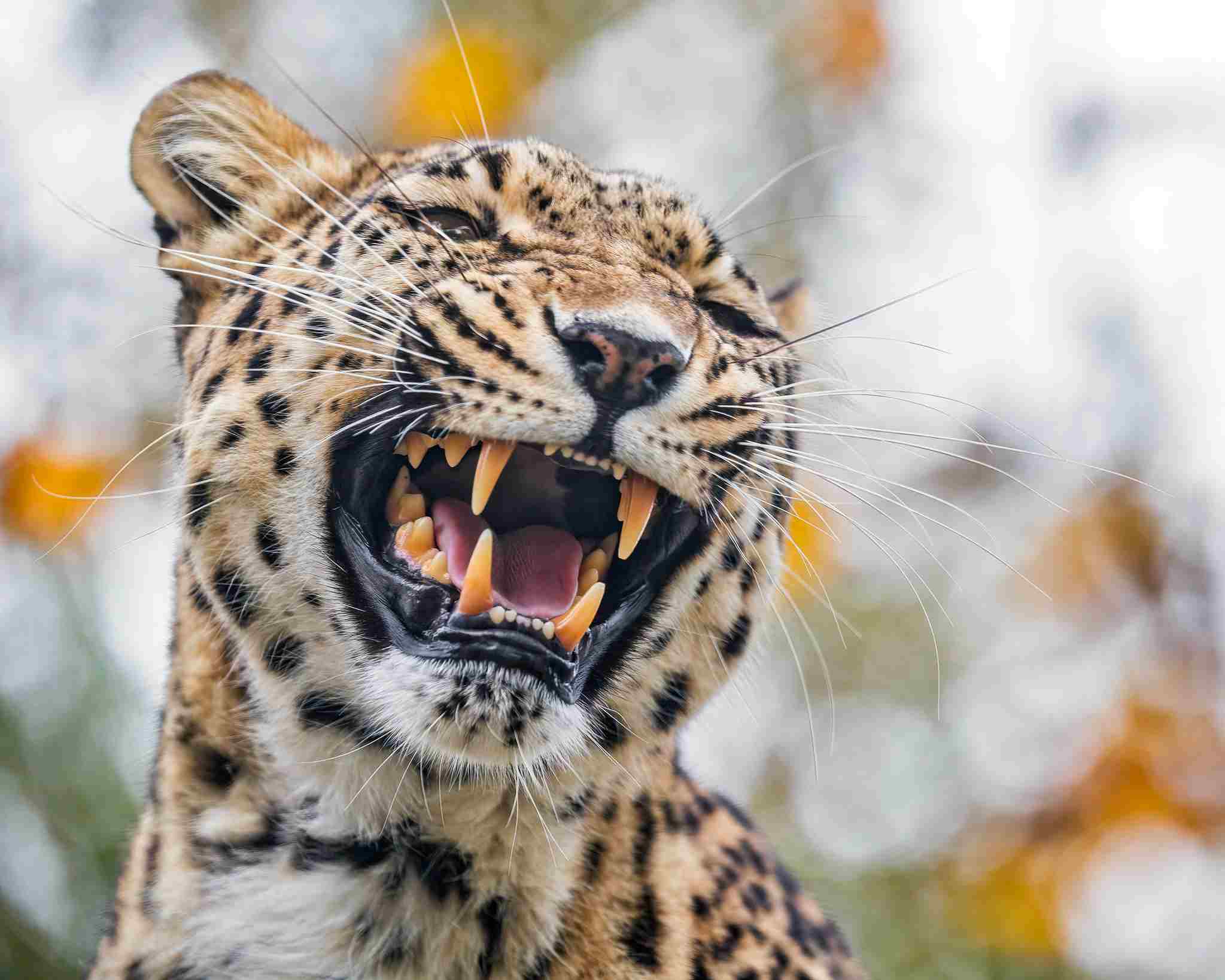
Leopard Vs Gorilla Size, Weight, Ecological Comparison
Leopards have the advantage in a fight against a gorilla due to their speed and unpredictability. Their predatory nature gives them an edge. While gorillas are stronger, other factors like size, weight, and overall physical capacity are used to compare them in this article. The leopard’s agility and quick reflexes make it a formidable opponent. Additionally, its bite force is another factor that contributes to its ability to overpower a gorilla. These characteristics make the leopard a formidable predator in the animal kingdom.
Reasons Why a Leopard Will Win a Gorilla In a Fight/Physical Confrontation
I). Leopards are Fast and Unpredictable
Leopards possess remarkable speed and agility, making them formidable opponents in a fight against a gorilla. With their sleek and muscular bodies, leopards can reach speeds of up to 60 kilometers per hour (37 mph) in short bursts. This incredible speed allows them to quickly close the distance between themselves and their prey, making it difficult for a gorilla to escape their pursuit.
Furthermore, leopards are known for their unpredictable nature. They are stealthy hunters, capable of stalking their prey silently and pouncing with lightning-fast reflexes. This element of surprise gives them a significant advantage in a physical confrontation with a gorilla, as the gorilla may struggle to anticipate the leopard’s movements.
II). Possession of Predatory Features
Leopards possess a range of predatory features that contribute to their ability to overpower a gorilla. Their sharp retractable claws enable them to climb trees effortlessly, giving them an advantage in terms of height and maneuverability. This allows leopards to attack from above, catching their prey off guard.
Additionally, leopards have powerful jaws and sharp teeth, which they use to deliver a lethal bite. Their bite force is incredibly strong, enabling them to immobilize their prey quickly. In a fight against a gorilla, this bite force can cause significant damage and potentially incapacitate the gorilla.
Therefore, the combination of speed, unpredictability, and predatory features makes the leopard a formidable opponent in a fight against a gorilla. Its ability to quickly close the distance, deliver a powerful bite, and utilize its agility and stealth gives it a significant advantage in a physical confrontation.

*Details of Comparison
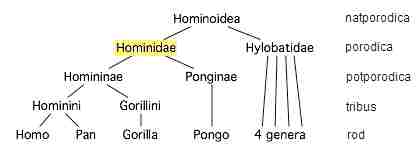
1). Taxonomy
The taxonomy of the leopard and gorilla reveals interesting insights into their evolutionary history and genetic relationships. The leopard belongs to the genus Panthera and the species Panthera pardus, while the gorilla belongs to the genus Gorilla and the species Gorilla gorilla.
These two animals are classified under different taxonomic families, with the leopard belonging to the Felidae family and the gorilla belonging to the Hominidae family. Despite their distinct taxonomic classifications, both the leopard and gorilla share common ancestry with other members of their respective families.
The leopard is closely related to other big cats such as lions, tigers, and jaguars, while the gorilla is closely related to other great apes including chimpanzees, bonobos, and orangutans. This shared ancestry is reflected in their physical and behavioral similarities.
While the leopard and gorilla may seem vastly different in appearance and behavior, their taxonomy highlights the interconnectedness of the animal kingdom. Understanding their taxonomic classifications allows us to appreciate the diversity and complexity of life on Earth.
2). Appearance
The appearance of both the leopard and gorilla is distinct and well-adapted to their respective environments. Starting with their coats, the leopard has a beautiful spotted fur pattern that provides excellent camouflage in its natural habitat. This allows the leopard to blend seamlessly into the dappled light and shadows of the forest or grasslands where it resides. On the other hand, the gorilla has a coarse and dark-colored fur that helps it blend in with the dense vegetation of the rainforest.
In terms of stature and build, the leopard is known for its sleek and agile physique. It has a long and muscular body, with strong legs and a flexible spine that enables it to climb trees and pounce on its prey with precision. In contrast, the gorilla has a robust and muscular build, with broad shoulders and a barrel-shaped chest. This physique is well-suited for its arboreal lifestyle, as it allows the gorilla to navigate through the trees and use its strength for various activities such as foraging and defending its territory.
When comparing the appearance of these two animals, it is clear that they have evolved distinct physical characteristics that enable them to thrive in their respective habitats. The leopard’s spotted coat provides effective camouflage for hunting, while the gorilla’s muscular build and dark fur help it navigate and survive in the dense rainforest. These adaptations showcase the remarkable diversity and adaptability of nature.
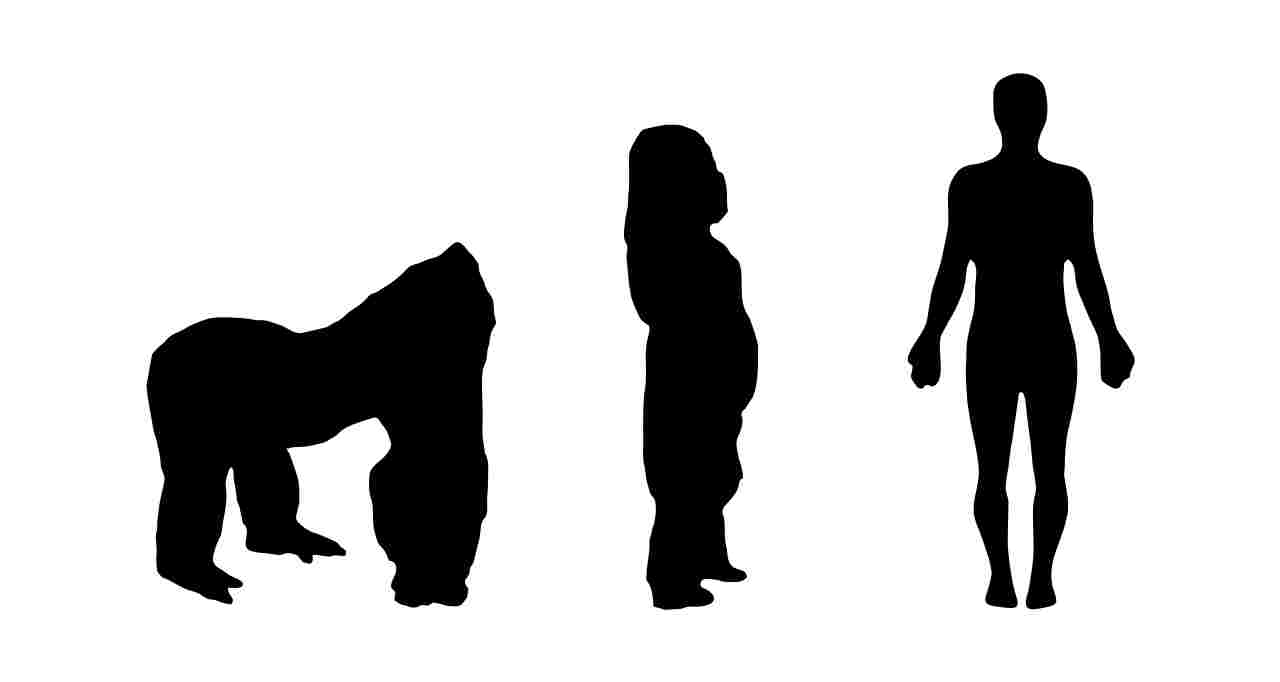
3). Size
When comparing the size of a leopard and a gorilla, it is important to consider their total body length and height at the shoulders. The leopard typically measures around 4 to 6 feet in length, with an additional 2 to 3 feet for its tail. In terms of height, leopards stand at approximately 2 to 2.5 feet at the shoulders. On the other hand, gorillas are much larger in size. Adult male gorillas can reach heights of up to 5.6 feet when standing upright, while females are slightly smaller at around 4.6 feet. In terms of total body length, gorillas measure around 4 to 6 feet.
The significant size difference between leopards and gorillas is due to their different evolutionary adaptations and lifestyles. Leopards are solitary hunters that rely on their agility and stealth to capture prey, while gorillas are social animals that primarily feed on vegetation. The larger size of gorillas is advantageous for their herbivorous diet and for competing with other males for dominance within their social groups.
4). Weight
When comparing the weight of a leopard and a gorilla, it is evident that gorillas are significantly heavier than leopards. Adult male gorillas can weigh anywhere between 300 to 450 pounds, while females typically weigh around 150 to 250 pounds. In contrast, leopards are much lighter, with males weighing around 80 to 200 pounds and females weighing between 50 to 130 pounds.
The difference in weight between these two animals is due to their distinct lifestyles and dietary preferences. Gorillas are herbivores, consuming a large quantity of vegetation to meet their nutritional needs. Their bulky bodies and muscular build are essential for their herbivorous diet and for competing with other males for dominance within their social groups.
Leopards, on the other hand, are carnivores and rely on their agility and stealth to hunt and capture prey. Their lighter weight allows them to move swiftly through their natural habitats, such as forests and grasslands, making them efficient hunters. The combination of their muscular bodies and lighter weight gives leopards the advantage in terms of speed and agility, allowing them to pursue and capture their prey effectively.
Therefore, while gorillas outweigh leopards significantly, the difference in weight is a result of their distinct evolutionary adaptations and dietary preferences. Gorillas’ larger size and weight are advantageous for their herbivorous lifestyle and social dynamics, while leopards’ lighter weight contributes to their speed and agility in hunting.
5). Speed and Agility
Leopards and gorillas differ significantly in terms of speed and agility. Leopards are known for their exceptional speed and agility, allowing them to navigate their natural habitats with ease. With their muscular bodies and lighter weight, leopards can swiftly move through various terrains, including forests and grasslands, making them highly efficient hunters. Their ability to accelerate quickly and change direction rapidly gives them an advantage when pursuing and capturing prey.
On the other hand, gorillas are not known for their speed and agility. Due to their larger size and heavier weight, gorillas have a more limited range of movement and are not as agile as leopards. Their bulkier bodies are better suited for their herbivorous lifestyle and for competing with other males within their social groups. While gorillas may possess strength and power, their slower movements make them less adept at chasing down prey or evading predators.
Therefore, leopards excel in terms of speed and agility, thanks to their lighter weight and muscular build. Gorillas, on the other hand, prioritize strength and power over speed and agility due to their larger size and herbivorous diet.
6). Bite Force
Leopards and gorillas have distinct differences in terms of bite force. The bite force of an animal is a measure of its jaw strength and can be an important factor in determining its hunting or defensive capabilities.
Leopards possess a powerful bite force, with an average psi (pounds per square inch) ranging from 300 to 500. This allows them to deliver a crushing bite to their prey, effectively immobilizing or killing it. Their sharp teeth and strong jaw muscles enable them to penetrate through tough hides and bones, making them formidable predators.
On the other hand, gorillas, despite their immense size and strength, do not possess the same level of bite force as leopards. Their bite force is estimated to be around 1,300 psi, which is significantly lower than that of leopards. This is because gorillas primarily rely on their herbivorous diet, which consists of plant material that does not require the same level of biting force as carnivorous predators.
7). Overall Physical Capacity (Which is Stronger?)
While a full-grown gorilla is undeniably stronger than a leopard in terms of sheer size and muscle mass, determining which animal is stronger in a violent confrontation requires a deeper analysis.
In terms of raw strength, a gorilla’s immense size and muscular build give it a clear advantage over a leopard. Gorillas have the ability to exert tremendous force, allowing them to overpower most predators. However, leopards possess other physical attributes that contribute to their overall capacity.
Leopards are known for their speed and agility, which enables them to swiftly maneuver and strike with precision. Their powerful bite force, ranging from 300 to 500 psi, allows them to immobilize or kill their prey effectively. Additionally, their sharp teeth and strong jaw muscles enable them to penetrate through tough hides and bones.
While a gorilla may have the advantage in terms of raw strength, a leopard’s combination of speed, agility, and bite force makes it a formidable predator in its own right. In a violent confrontation between the two, the outcome would depend on various factors such as the element of surprise, the environment, and the specific circumstances of the encounter.
8). Habitat
Leopards are highly adaptable and can be found in a wide range of habitats, including forests, grasslands, mountains, and even urban areas. They have a vast geographic range that spans across Africa and parts of Asia. This adaptability allows leopards to thrive in various environments and take advantage of different food sources.
On the other hand, gorillas are primarily found in the dense forests of Central Africa. They inhabit tropical rainforests, montane forests, and swamp forests. Gorillas are highly dependent on these forest habitats for their survival, as they rely on the abundance of vegetation for food and shelter.
When comparing the habitats of leopards and gorillas, it is evident that leopards have a broader range and can adapt to a wider variety of environments. This adaptability gives leopards an advantage in terms of their ability to find food and avoid competition. Gorillas, on the other hand, are more specialized in their habitat requirements and are limited to specific forest ecosystems.

9). Lifespan
Leopards typically have a lifespan of around 12 to 17 years in the wild, although some individuals have been known to live up to 20 years. On the other hand, gorillas have a longer lifespan, with males living an average of 35 to 40 years and females living up to 50 years.
The shorter lifespan of leopards can be attributed to various factors, including predation, competition for resources, and the risks associated with their solitary lifestyle. Leopards face threats from larger predators such as lions and hyenas, which can significantly impact their survival. Additionally, their solitary nature means they have to constantly defend their territory and hunt for food, which can be physically demanding and risky.
Gorillas, on the other hand, benefit from living in social groups and having a more herbivorous diet. Their social structure provides protection against predators and allows for cooperative behaviors that enhance their chances of survival. The herbivorous diet of gorillas also reduces the risks associated with hunting and predation.
10). Behavior
Leopards and gorillas exhibit distinct behaviors that reflect their different lifestyles and social structures. When it comes to feeding, leopards are solitary hunters, relying on their stealth and agility to ambush and capture their prey. They are known for their ability to adapt to various habitats and can feed on a wide range of animals, including small mammals, birds, and even larger prey like antelope. On the other hand, gorillas are herbivores, primarily feeding on leaves, stems, fruits, and other plant matter. They are known to spend a significant amount of time foraging for food, as their diet requires them to consume large quantities of vegetation to meet their nutritional needs.
In terms of aggression, both leopards and gorillas can display aggressive behaviors, but for different reasons. Leopards are territorial animals and will fiercely defend their hunting grounds from intruders. They are known to be solitary and secretive, avoiding confrontations whenever possible. Gorillas, on the other hand, live in social groups led by a dominant silverback male. Aggression within gorilla groups is usually related to establishing dominance or protecting the group from external threats.
Vocalization is another aspect of behavior where leopards and gorillas differ. Leopards are generally silent animals, relying on their stealth to avoid detection. However, they can produce a range of vocalizations, including growls, hisses, and roars, especially during mating or territorial disputes. Gorillas, on the other hand, are known for their distinct vocalizations, including grunts, hoots, and chest-beating displays. These vocalizations play a crucial role in communication within the group and can convey various messages, such as warning signals or social bonding.
When it comes to social behavior, leopards are solitary animals, with minimal social interactions outside of mating. They establish and defend their territories, avoiding encounters with other leopards except during mating season. Gorillas, on the other hand, live in cohesive social groups, led by a dominant silverback male. They engage in complex social interactions, including grooming, playing, and vocal communication, which help maintain group cohesion and social bonds.
In terms of parenting, leopards are typically solitary parents, with females raising their cubs alone. The mother leopard provides care, protection, and teaches her cubs essential hunting skills until they are independent. Gorillas, on the other hand, exhibit cooperative parenting within the group. The dominant silverback male plays a crucial role in protecting and guiding the young gorillas, while other females in the group also contribute to their care and upbringing.
11). Reproduction
Leopards are viviparous, meaning they give birth to live young. After a gestation period of approximately 90 to 105 days, female leopards will typically give birth to a litter of two to three cubs. The cubs are born blind and helpless, relying on their mother for nourishment and protection. The mother leopard will nurse her cubs for several months before gradually introducing them to solid food and teaching them essential hunting skills. This period of maternal care and guidance is crucial for the cubs’ survival and development.
Gorillas, on the other hand, are also viviparous and give birth to live young. The gestation period for gorillas is longer, lasting approximately 8.5 to 9 months. Female gorillas will typically give birth to a single infant, although twins can occur rarely. The newborn gorilla is completely dependent on its mother for care and nourishment. The mother gorilla will nurse her infant for several years, gradually introducing solid food as the infant grows. The bond between mother and infant is strong, and the mother provides constant protection and guidance to her offspring.
When comparing the reproduction of leopards and gorillas, it is evident that both species invest significant time and energy in raising their young. However, the reproductive strategies differ due to the solitary nature of leopards and the social structure of gorillas. While leopards raise their cubs alone, gorillas benefit from cooperative parenting within the social group, with multiple individuals contributing to the care and upbringing of the young. This cooperative parenting ensures the survival and well-being of the gorilla offspring.
12). Danger Posed to Humans
While leopards are predators and have been known to attack humans, gorillas are generally peaceful and rarely exhibit aggression towards humans.
Leopards, being solitary animals, are more likely to come close to human settlements in search of food, especially in areas where their natural prey is scarce. This proximity increases the chances of human encounters with leopards. In some cases, when leopards feel threatened or cornered, they may exhibit aggressive behavior towards humans. However, it is important to note that such incidents are relatively rare.
On the other hand, gorillas, being herbivores, do not pose a direct threat to humans. They typically inhabit dense forests and are less likely to come into contact with human settlements. Gorillas are known to be shy and peaceful animals, and they usually avoid confrontations with humans.
In terms of human deaths caused, leopards have been responsible for a higher number of fatalities compared to gorillas. This is mainly due to the predatory nature of leopards and their ability to overpower humans if they feel threatened or if they mistake a person for prey.
If one encounters a leopard or gorilla in the wild, it is important to exercise caution and follow certain precautions. For leopards, it is advisable to maintain a safe distance, avoid sudden movements, and make oneself appear larger by raising arms or jackets. In the case of gorillas, it is crucial to respect their space, avoid direct eye contact, and follow the guidance of experienced guides or park rangers.
Therefore, while leopards can be more dangerous to humans due to their predatory nature and potential for aggression, gorillas are generally peaceful and pose minimal threat.
13). Intelligence
Leopards are known for their cunning and adaptability. They are skilled hunters and have the ability to strategize and plan their attacks. Their intelligence is evident in their hunting techniques, such as stalking their prey and using stealth to their advantage. Leopards also display problem-solving skills when faced with obstacles or challenges in their environment.
On the other hand, gorillas are highly intelligent primates. They exhibit complex social behaviors and have been observed using tools in the wild. Gorillas have the ability to communicate through a variety of vocalizations and gestures, indicating a level of cognitive understanding. They also display emotional intelligence, forming strong bonds within their social groups and showing empathy towards other gorillas.
In terms of which animal is more intelligent, it is difficult to determine as their intelligence is specialized for their respective lifestyles. Leopards’ intelligence is focused on hunting and survival in their solitary existence, while gorillas’ intelligence is centered around their social interactions and adaptation to their forest environment.
Generally, both leopards and gorillas demonstrate intelligence in their own unique ways. While leopards showcase their intelligence through hunting strategies and problem-solving, gorillas exhibit intelligence through their complex social behaviors and tool usage.
14). Tracks
Leopards and gorillas leave distinct tracks that can be used to identify their presence in an area. When comparing the tracks of these animals, there are noticeable differences.
Leopard tracks are characterized by their large size and distinct paw prints. Their tracks typically show four toes and a prominent pad, which helps to distribute their weight and provide stability while walking or running. The size of the tracks can vary depending on the age and sex of the leopard, with adult males leaving larger prints than females or younger individuals. These tracks are often found in areas where leopards hunt or traverse, such as near water sources or along game trails.
On the other hand, gorilla tracks are quite different. Gorillas have hands and feet that are adapted for climbing and grasping, which is reflected in their tracks. Their tracks show five toes and the imprint of their hands, which can be distinguished by the presence of opposable thumbs. Gorilla tracks are typically found in forested areas where they move through the vegetation and climb trees.
By examining the tracks left behind by leopards and gorillas, researchers and wildlife enthusiasts can gain valuable insights into their presence and behavior in a particular habitat. These tracks serve as important indicators of their movements, feeding patterns, and territorial boundaries.
15). Conservation Status
When it comes to the conservation status of leopards and gorillas, both species face significant challenges in the wild. They are both classified as “endangered” or “threatened” due to various factors that pose a threat to their survival.
For leopards, the main threats to their population include habitat loss, poaching for their fur and body parts, and conflicts with humans. As their natural habitats continue to be destroyed or fragmented, leopards struggle to find suitable territories and prey. Additionally, illegal hunting and trade of leopard skins and bones contribute to their declining numbers. Human activities, such as encroachment into their habitats and retaliatory killings, also impact leopard populations.
Gorillas, on the other hand, face similar challenges. Habitat destruction, primarily through deforestation and land conversion for agriculture, is a major threat to their survival. Gorillas rely on dense forests for food, shelter, and protection, and as these forests disappear, their populations decline. Illegal hunting and poaching for bushmeat and the capture of infant gorillas for the illegal pet trade further exacerbate their vulnerability.
Therefore, both leopards and gorillas are facing significant conservation challenges. Protecting their habitats, combating illegal hunting and trade, and promoting sustainable practices are crucial for their long-term survival.

Conclusion
I). SIMILARITIES
When comparing leopards and gorillas, it is evident that these two animals share some similarities. Both species face significant conservation challenges and are classified as “endangered” or “threatened.” Habitat loss, illegal hunting, and conflicts with humans pose threats to the survival of both leopards and gorillas. Protecting their habitats, combating illegal activities, and promoting sustainable practices are crucial for the long-term survival of these magnificent creatures.
II). DIFFERENCES
Despite their similarities, leopards and gorillas also have distinct differences. In terms of taxonomy, leopards belong to the Felidae family, while gorillas are part of the Hominidae family. In terms of appearance, leopards have a sleek and spotted coat, while gorillas have a robust and muscular build. When it comes to size, leopards are smaller and more agile, while gorillas are larger and more powerful.
Therefore, while leopards and gorillas may share some similarities in terms of conservation challenges, they also have notable differences in their taxonomy, appearance, and physical characteristics.










