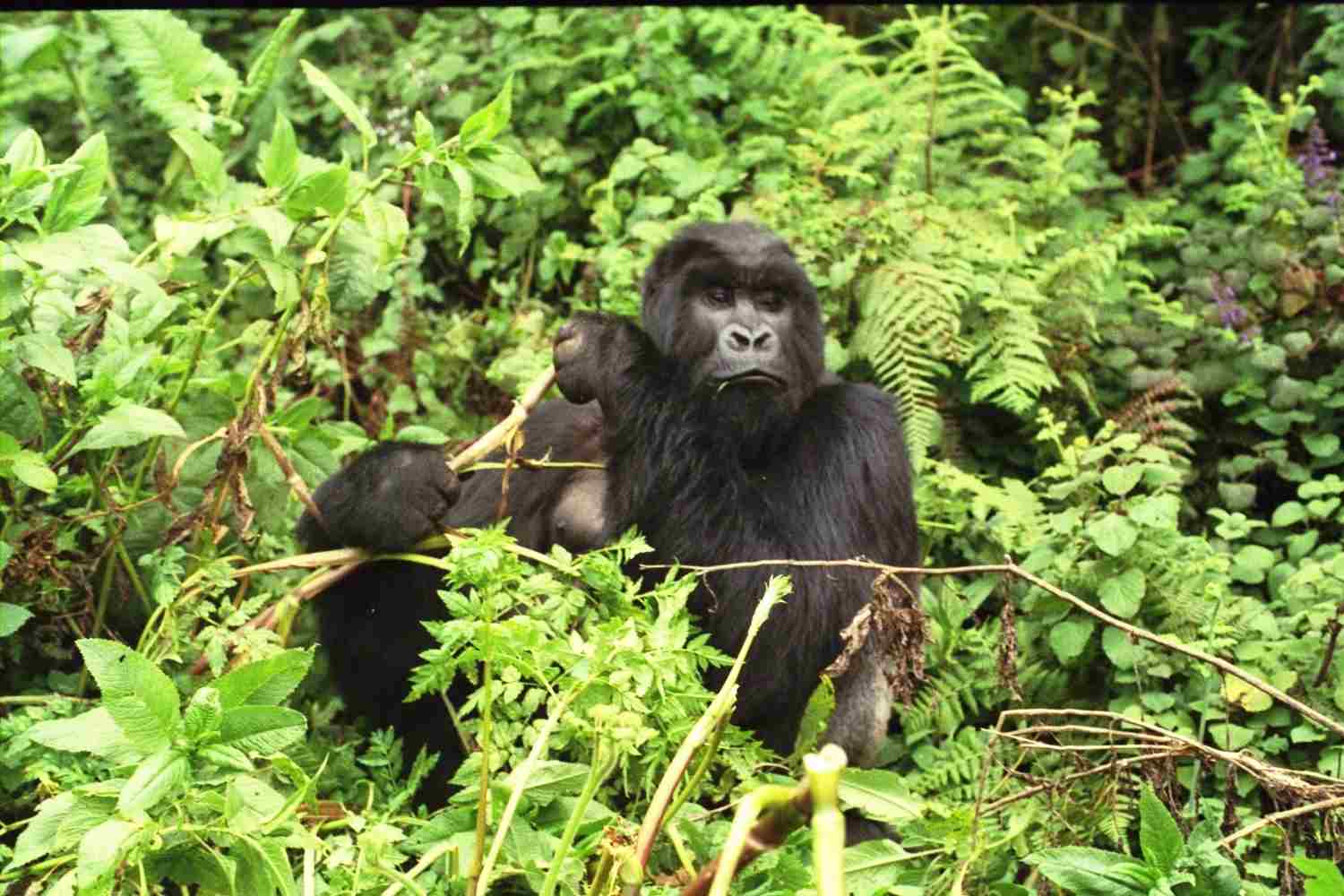
Silverback Gorilla Vs Grizzly Bear Size, Weight, Overall Comparison
The silverback gorilla and grizzly bear can be compared to each other based on factors like size, weight, and behavior. These comparisons can help us understand and predict the potential outcomes of interactions between them.
Key Outcomes of Comparison
A) Size:
When comparing the size of silverback gorillas and grizzly bears, it is evident that both species are formidable in their own right. However, the silverback gorilla is generally smaller, with males weighing up to 400 pounds and standing at a height of around 5.6 feet. In contrast, grizzly bears can reach weights of up to 1,500 pounds and stand at a height of approximately 7 feet.
B) Weight:
In terms of weight, grizzly bears clearly outweigh silverback gorillas. Grizzly bears can reach weights of up to 1,500 pounds, while silverback gorillas typically weigh around 400 pounds.
C) Taxonomic Classification:
Silverback gorillas belong to the family Hominidae, while grizzly bears belong to the family Ursidae. This distinction places silverback gorillas closer to humans in terms of taxonomic classification.
D) Hypothetical Interaction:
In a hypothetical confrontation between a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear, it is difficult to determine a clear winner. Both species possess immense strength and formidable physical attributes. However, due to their larger size and powerful bite force, the grizzly bear may have a slight advantage in such an encounter.
*Physical Comparison
1). Size
When comparing the size of a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear, several factors come into play. The average height and total body length are key measurements to consider.
A silverback gorilla typically stands at an average height of around 5.6 to 5.9 feet (1.7 to 1.8 meters) when standing upright. In terms of total body length, they can reach up to 5.6 to 5.9 feet (1.7 to 1.8 meters) as well.
On the other hand, a grizzly bear can grow to be much larger. They can stand at an average height of 6.5 to 8 feet (2 to 2.4 meters) when standing on their hind legs. In terms of total body length, they can reach up to 6.5 to 8 feet (2 to 2.4 meters) as well.
In comparison, the grizzly bear is generally larger than the silverback gorilla in terms of both height and total body length. However, it’s important to note that individual variations can occur within each species, and there may be exceptions to these average measurements.
2). Weight
When comparing the weight of a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear, it is important to consider the average weight of both males and females.
On average, a male silverback gorilla weighs between 300 to 400 pounds (136 to 181 kilograms). In comparison, a female silverback gorilla weighs around 200 to 300 pounds (91 to 136 kilograms).
In contrast, a male grizzly bear can weigh anywhere between 600 to 1,500 pounds (272 to 680 kilograms), while a female grizzly bear typically weighs around 300 to 800 pounds (136 to 363 kilograms).
Based on these averages, it is clear that grizzly bears are generally heavier than silverback gorillas, regardless of gender. However, it is important to note that individual variations can occur within each species, and there may be exceptions to these average weights.
The weight of an animal plays a significant role in its overall strength and physical capabilities. In the case of a hypothetical encounter between a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear, the weight difference could potentially impact the outcome of the interaction.
3). Skeletal Anatomy
The skeletal anatomy of a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear reveals significant differences in their bone structure and density.
The skeletal structure of a silverback gorilla is adapted for their arboreal lifestyle, with long arms and a robust chest. Their bones are dense and strong, providing support for their large muscles and allowing them to climb trees with ease. The gorilla’s skull is also characterized by a prominent sagittal crest, which serves as an attachment point for powerful jaw muscles.
On the other hand, the skeletal structure of a grizzly bear is designed for their terrestrial lifestyle. Their bones are larger and more robust than those of a gorilla, providing support for their massive size and strength. The bear’s skull is characterized by a broad and powerful snout, which houses strong teeth and jaws capable of crushing bones and tearing through tough prey.
In terms of bone density, grizzly bears have denser bones compared to silverback gorillas. This increased bone density contributes to the bear’s overall strength and endurance, allowing them to withstand the rigors of their environment and engage in powerful physical activities such as digging and hunting.
These differences in skeletal anatomy and bone density reflect the unique adaptations of each species to their respective habitats and lifestyles.
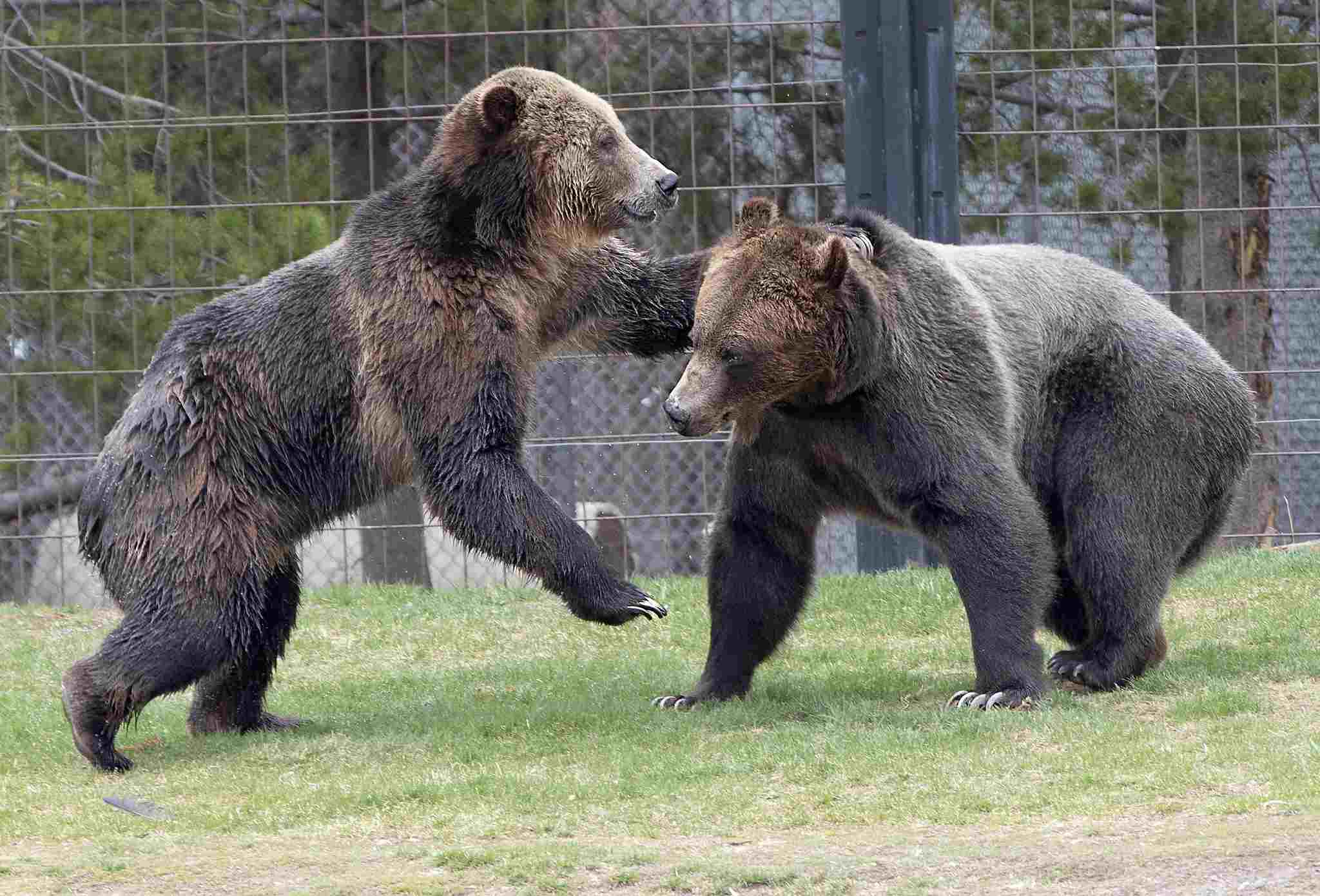

4). Mode of Locomotion
The mode of locomotion differs significantly between a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear.
Silverback gorillas primarily rely on their powerful arms and legs to move through their environment. They are adept climbers, using their long arms to swing from tree branches and their strong legs to leap between them. While they are not built for speed, gorillas can run on all fours when necessary, reaching speeds of up to 20 miles per hour. However, their preferred method of locomotion is climbing and walking on the ground.
On the other hand, grizzly bears are well-adapted for terrestrial movement. They are capable of running at impressive speeds, reaching up to 35 miles per hour for short distances. Bears have a distinctive lumbering gait, with their front legs slightly shorter than their hind legs, which gives them stability and power when walking or running. While they are not natural climbers like gorillas, grizzly bears are proficient swimmers and can cover long distances in water.
Generally, silverback gorillas excel in climbing and walking, utilizing their strong arms and legs, while grizzly bears are more versatile in their locomotion, with the ability to run, swim, and cover long distances on land.
5). Speed
When comparing the speed of a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear, it is important to consider their average speeds and determine which animal is faster.
The average speed of a silverback gorilla is around 20 miles per hour. While they are not known for their speed, gorillas can run on all fours when necessary, reaching this impressive speed. However, their preferred method of locomotion is climbing and walking on the ground, where they excel due to their strong arms and legs.
On the other hand, grizzly bears are capable of running at speeds of up to 35 miles per hour for short distances. This makes them faster than silverback gorillas. Bears have a distinctive lumbering gait, with their front legs slightly shorter than their hind legs, which gives them stability and power when walking or running.
In terms of speed, grizzly bears have the advantage over silverback gorillas. While gorillas can reach speeds of up to 20 miles per hour, grizzly bears can run at speeds of up to 35 miles per hour, making them faster in comparison. However, it is important to note that speed is just one aspect of their overall comparison, and other factors such as strength and agility also play a significant role in determining their capabilities.
6). Agility
When comparing the agility of a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear, it is important to consider their speed and mode of locomotion. Agility refers to the ability to move quickly and easily, change direction, and navigate different terrains.
In terms of speed, grizzly bears have the advantage over silverback gorillas. Bears can run at speeds of up to 35 miles per hour, while gorillas can reach speeds of up to 20 miles per hour. This higher speed gives grizzly bears an edge in terms of agility, as they can cover more ground and react faster in different situations.
However, when it comes to mode of locomotion, gorillas have their own unique agility. Gorillas are primarily climbers and walkers, excelling in their ability to navigate through trees and dense vegetation. Their strong arms and legs allow them to swing from branches and move with ease in their natural habitat. This agility enables them to quickly adapt to their surroundings and escape potential threats.

7). Relative Strength and Endurance
When comparing the relative strength and endurance of a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear, several factors need to be considered, including muscular endurance, size, weight, and agility.
In terms of muscular endurance, both the silverback gorilla and the grizzly bear possess impressive strength. However, due to their larger size and weight, grizzly bears are generally considered to be stronger. Their massive muscles and powerful build give them an advantage in terms of raw strength.
Size and weight play a significant role in determining relative strength. Grizzly bears can weigh up to 1,500 pounds, while silverback gorillas typically weigh around 400 pounds. The sheer size and weight of grizzly bears contribute to their overall strength and ability to overpower their opponents.
Although grizzly bears have the advantage in terms of strength, silverback gorillas possess their own unique form of endurance. Gorillas are known for their ability to sustain physical exertion for extended periods. Their muscular build and stamina allow them to engage in intense activities such as climbing, foraging, and defending their territory.
8). Bite force
When comparing the bite force of a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear, it is important to consider their average bite force and determine which animal has a higher bite force.
The average bite force of a silverback gorilla is estimated to be around 1,300 pounds per square inch (psi). This powerful bite allows them to crush and tear through tough vegetation, such as bamboo shoots and tree bark, as well as defend themselves against potential threats.
On the other hand, the grizzly bear possesses an even more formidable bite force. With an average bite force of approximately 1,200 psi, the grizzly bear’s bite is incredibly strong. This enables them to easily break through bones and tough hides of their prey, including fish, small mammals, and even larger animals like moose and elk.
In terms of bite force, the grizzly bear has a slightly higher bite force compared to the silverback gorilla. However, it is important to note that bite force is just one aspect of an animal’s overall strength and hunting ability.
9). Attack and Defense Method(s)
When it comes to attack and defense methods, both the silverback gorilla and the grizzly bear have their own unique strategies.
The silverback gorilla primarily relies on its physical strength and intimidating presence as a means of defense. With their massive size and muscular build, they are capable of delivering powerful blows and using their long arms to grab and restrain potential threats. In terms of attack, gorillas have been observed using their sharp canine teeth and strong jaws to bite and intimidate rivals or predators. However, their main defense mechanism is to display dominance through aggressive posturing, vocalizations, and chest-beating displays.
On the other hand, the grizzly bear utilizes a combination of physical strength, speed, and sharp claws as its primary defense and attack methods. When threatened, grizzly bears can stand on their hind legs to appear larger and more intimidating. They also have the ability to deliver powerful swipes with their long claws, which can cause significant damage to potential threats. In terms of attack, grizzly bears are known to use their strength and speed to overpower their prey, delivering powerful bites and using their claws to immobilize and kill.
Comparing the efficiency of attack and defense methods between the silverback gorilla and the grizzly bear is challenging, as they have evolved different strategies based on their unique environments and social structures.
*Hypothetical Interaction
Grizzly bears are likely to overpower and kill silverback gorillas, due to reasons like their superior size, weight, strength, and predatory features.
In a hypothetical conflict between a silverback gorilla and a grizzly bear, the outcome of a fight would likely be influenced by their respective size and weight. The grizzly bear, being larger and heavier than the silverback gorilla, would have a significant advantage in terms of physical strength and power. With its massive size and muscular build, the grizzly bear would be capable of delivering powerful blows and using its sharp claws to inflict serious damage.
However, it is important to note that a hypothetical interaction between these two animals would be highly unlikely in the wild. Silverback gorillas are primarily herbivores and are not known to be aggressive towards other animals unless provoked. Grizzly bears, on the other hand, are solitary animals and tend to avoid confrontations with other large predators.
*Behavioral Comparison
10). Feeding/Predation Habits
Feeding habits play a crucial role in understanding the behavior and survival strategies of animals. When comparing the feeding/predation habits of the Silverback Gorilla and the Grizzly Bear, it is important to consider their dietary preferences and hunting techniques.
The Silverback Gorilla is primarily an herbivore, with a diet consisting mainly of leaves, stems, fruits, and shoots. They are known to be selective feeders, carefully choosing the most nutritious parts of plants. Additionally, they may occasionally consume insects and small vertebrates. Gorillas are not known for their predatory behavior and do not actively hunt for prey.
On the other hand, the Grizzly Bear is an omnivore, with a diet that includes both plant matter and animal protein. Their food sources vary depending on the season and availability, but they commonly feed on berries, nuts, roots, fish, small mammals, and carrion. Grizzly Bears are opportunistic predators and have been observed hunting large mammals such as elk and moose.
In terms of predation, the Silverback Gorilla relies on its sheer size and strength to intimidate potential threats rather than actively hunting for prey. They are more likely to engage in territorial disputes or display dominance within their social groups. In contrast, the Grizzly Bear uses its powerful jaws and claws to capture and kill prey. They are skilled hunters and can employ various hunting techniques, including stalking, ambushing, and scavenging.
11). Social Behavior
The social behavior of animals provides valuable insights into their interactions and relationships within their species. When comparing the social behavior of the Silverback Gorilla and the Grizzly Bear, it is evident that they have distinct social structures and behaviors.
The Silverback Gorilla is known for its highly social nature. They live in cohesive groups called troops, which are led by a dominant male known as the silverback. These troops typically consist of multiple adult females, their offspring, and a few subordinate males. The silverback plays a crucial role in maintaining order within the group, protecting its members, and resolving conflicts. The troop members engage in various social activities, including grooming, playing, and communicating through vocalizations and body language.
In contrast, the Grizzly Bear is primarily a solitary animal. They are known to be territorial and establish large home ranges that they defend against intruders. Adult males have larger territories that may overlap with the territories of several females. However, the interactions between Grizzly Bears are typically limited to mating or territorial disputes. They do not form cohesive social groups like gorillas.
When it comes to parental relations, both species exhibit different behaviors. Silverback Gorillas show strong parental care, with the silverback playing a protective role towards the young gorillas. Female gorillas also play an active role in nurturing and raising their offspring. In contrast, Grizzly Bears have a more independent parenting style. Female bears raise their cubs on their own, providing them with the necessary skills for survival before they eventually separate.

12). Aggressive Tendency
When comparing the aggressive tendencies of the Silverback Gorilla and the Grizzly Bear, it is important to consider their natural behaviors and the conditions that can trigger aggression in each species.
The Silverback Gorilla, despite its imposing size and strength, is generally not an aggressive animal. However, they can display aggression in certain situations. One of the main triggers for aggression in gorillas is the protection of their troop or family members. If they perceive a threat to their group, they may exhibit aggressive behaviors such as charging, chest-beating, or vocalizing loudly. Another factor that can lead to aggression in gorillas is competition for resources, such as food or mates.
On the other hand, the Grizzly Bear is known for its aggressive nature, especially when it feels threatened or its territory is invaded. Grizzly Bears have a strong sense of territoriality and will defend their home ranges vigorously. They may display aggressive behaviors such as growling, roaring, or even charging when they perceive a threat. Additionally, female Grizzly Bears with cubs can be particularly aggressive when it comes to protecting their offspring.
It is important to note that aggression in both species is not a constant behavior but rather a response to specific circumstances.
13). Danger to Humans (and Pets)
When considering the danger posed by the Silverback Gorilla and the Grizzly Bear to humans and pets, it is important to take into account their respective behaviors and physical attributes. While both animals have the potential to cause harm, the Grizzly Bear is generally considered to be more dangerous than the silverback gorilla due to its sheer strength, ferocious behavior, and larger size.
Grizzly Bears have been known to attack humans in certain situations, particularly when they feel threatened or their territory is invaded. These attacks can result in serious injuries or even fatalities. Additionally, female Grizzly Bears with cubs can be particularly aggressive when it comes to protecting their offspring, posing an increased risk to humans and pets.
On the other hand, Silverback Gorillas are not typically aggressive towards humans unless provoked or if they perceive a threat to their troop or family members. While they have the strength to cause harm, instances of gorillas attacking humans are rare. However, it is important to exercise caution and maintain a safe distance when encountering gorillas in the wild to avoid any potential risks.
13a). Likelihood of Interaction (With Humans)
When considering the likelihood of interaction between Silverback Gorillas and Grizzly Bears with humans, it is important to examine their behaviors and habitats.
Silverback Gorillas primarily inhabit dense forests and mountainous regions in Central and East Africa, far away from human settlements. Their natural habitat and shy nature make it unlikely for them to come into direct contact with humans. However, as human populations expand and encroach upon gorilla habitats, the chances of accidental encounters may increase.
On the other hand, Grizzly Bears are found in various habitats across North America, including forests, mountains, and even near human settlements. Due to their wide distribution and adaptability, the likelihood of interaction between Grizzly Bears and humans is higher compared to Silverback Gorillas.
It is important to note that both animals generally avoid human contact and prefer to retreat when they sense human presence. However, if a human unknowingly enters their territory or threatens their young, both Silverback Gorillas and Grizzly Bears have the potential to become defensive or aggressive.
To minimize the likelihood of negative interactions, it is crucial for humans to respect the natural habitats of these animals, follow guidelines for wildlife encounters, and take necessary precautions when visiting areas where these animals are known to reside.
13b). Precautionary Measure(s)
If you find yourself in a situation where you encounter either a Silverback Gorilla or a Grizzly Bear, it is important to remember some precautionary measures to ensure your safety.
When encountering a Silverback Gorilla, it is crucial to remain calm and avoid any sudden movements. Keep a safe distance and do not make direct eye contact, as this can be seen as a threat. Slowly back away while facing the gorilla, and give it space to retreat if it feels threatened.
In the case of a Grizzly Bear encounter, it is important to stay calm and avoid running, as this may trigger the bear’s predatory instincts. Make yourself appear larger by raising your arms and standing tall. Back away slowly, avoiding direct eye contact. If the bear charges, use bear spray if available, aiming for the face.
*Ecological Comparison
14). Taxonomic Classification
The taxonomic classification of the silverback gorilla and grizzly bear reveals their evolutionary relationship and genetic similarities. The silverback gorilla belongs to the genus Gorilla and the species Gorilla beringei or Gorilla gorilla, depending on the specific subspecies. On the other hand, the grizzly bear is classified under the genus Ursus and the species Ursus arctos horribilis.
The taxonomic classification also highlights the close relationship between these two powerful creatures and their shared characteristics. Both the silverback gorilla and grizzly bear are large, formidable animals that have adapted to their respective habitats. They are apex predators in their ecosystems and play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of their environments.
15). Skin/Coat Texture, Camouflage
The skin and coat texture of the silverback gorilla and grizzly bear are distinct and serve different purposes. The silverback gorilla has coarse, black hair covering its body, which provides protection against the elements and helps to regulate body temperature. The hair on their back appears silver, hence the name “silverback.” This unique coloration acts as a form of camouflage in their natural habitat, allowing them to blend in with the surrounding vegetation and making it easier for them to move stealthily through the dense forests.
On the other hand, the grizzly bear has a thick, shaggy coat that varies in color from light brown to dark brown. This fur provides insulation during colder months and helps them to stay warm in their mountainous habitats. The grizzly bear’s coat also acts as a form of camouflage, allowing them to blend in with their surroundings, such as the rocky terrain or dense forests, making it easier for them to hunt or avoid potential threats.
Both the silverback gorilla and grizzly bear have adapted their skin and coat textures to suit their respective environments. While the silverback gorilla’s black and silver hair provides camouflage in the dense forests, the grizzly bear’s brown fur helps it blend in with its mountainous surroundings.
16). Reproduction
The silverback gorilla and grizzly bear have different modes of reproduction. Silverback gorillas are viviparous, meaning they give birth to live young. The gestation period for a silverback gorilla is approximately 8.5 months. Female gorillas usually give birth to one baby at a time, although twins can occur rarely. The newborn gorilla is completely dependent on its mother for care and protection.
On the other hand, grizzly bears are also viviparous, giving birth to live cubs. The gestation period for a grizzly bear is around 6-8 months. Female grizzly bears typically give birth to two or three cubs at a time. The cubs are born blind and hairless, and they rely on their mother for warmth and nourishment.
Reproduction is an essential aspect of the life cycle for both silverback gorillas and grizzly bears. It ensures the continuation of their species and contributes to the overall biodiversity of their respective habitats. The reproductive strategies of these animals have evolved to suit their specific environments and ensure the survival of their offspring.
17). Lifespan
The lifespan of silverback gorillas and grizzly bears varies depending on their environment and whether they are in the wild or in captivity. In the wild, silverback gorillas have an average lifespan of around 35-40 years. However, some individuals have been known to live up to 50 years. In captivity, where they receive proper care and nutrition, silverback gorillas can live even longer, with some reaching their late 50s or early 60s.
Grizzly bears, on the other hand, have a slightly shorter lifespan in the wild, averaging around 20-25 years. However, in captivity, where they are protected from natural predators and have access to a controlled diet, grizzly bears can live significantly longer. Some captive grizzly bears have been known to live into their 30s or even 40s.
The lifespan of both species is influenced by various factors, including genetics, diet, habitat quality, and overall health. It is important to note that these are average lifespans, and individual animals may live shorter or longer lives depending on their specific circumstances.
18). Habitat
The habitat of silverback gorillas and grizzly bears plays a crucial role in their survival and overall well-being. Silverback gorillas are primarily found in the dense forests of central and eastern Africa, including countries such as Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. These forests provide the gorillas with ample vegetation for foraging, as well as cover and shelter from predators.
Grizzly bears, on the other hand, inhabit a variety of habitats across North America, including forests, mountains, and tundra regions. They can be found in areas such as Alaska, western Canada, and parts of the United States. Grizzly bears are highly adaptable and can thrive in different ecosystems, from coastal areas to inland forests.
Both species rely on their habitats for food, water, and shelter. Silverback gorillas primarily feed on vegetation, including leaves, fruits, and shoots, which are abundant in their forest habitats. Grizzly bears have a more varied diet, including berries, nuts, fish, and even small mammals. Their habitats provide them with access to these food sources, as well as suitable denning sites for hibernation during the winter months.
19). Geographic Range
The geographic range of silverback gorillas and grizzly bears is quite distinct, with minimal chances of them crossing paths in nature. Silverback gorillas are native to the dense forests of central and eastern Africa, specifically in countries such as Uganda, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. These regions provide the ideal habitat for gorillas, with abundant vegetation and suitable cover from predators.
On the other hand, grizzly bears inhabit various habitats across North America. They can be found in areas such as Alaska, western Canada, and parts of the United States. Grizzly bears are highly adaptable and can thrive in different ecosystems, including forests, mountains, and tundra regions.
Due to the vast geographical separation between their respective ranges, the chances of silverback gorillas and grizzly bears encountering each other in the wild are extremely low. The continents of Africa and North America are separated by vast oceans and thousands of miles, making it highly unlikely for these two species to interact naturally.
20). Ecologic Importance
The ecologic importance of silverback gorillas and grizzly bears cannot be overstated. Both species play crucial roles in their respective ecosystems, contributing to the overall balance and health of their habitats.
Silverback gorillas are considered keystone species in the forests of central and eastern Africa. As herbivores, they play a vital role in seed dispersal, helping to maintain the diversity and regeneration of plant species. Gorillas consume a wide variety of fruits, leaves, and stems, and their waste acts as natural fertilizer, enriching the soil and promoting the growth of new vegetation.
Similarly, grizzly bears have a significant impact on the ecosystems they inhabit in North America. As omnivores, they have a diverse diet that includes berries, nuts, fish, and small mammals. Their foraging behavior helps to control populations of prey species, preventing overgrazing and maintaining a healthy balance in the food chain. Additionally, grizzly bears are known to create “bear beds” by digging depressions in the ground, which can provide habitat for other species such as ground-nesting birds.
The presence of both silverback gorillas and grizzly bears in their respective habitats is essential for maintaining the overall biodiversity and functioning of these ecosystems. Their interactions with other species, as well as their roles as seed dispersers and regulators of prey populations, contribute to the stability and resilience of the natural environment.
21). Conservation Status
The conservation status of silverback gorillas and grizzly bears is a matter of great concern. Both species are currently threatened or endangered, facing numerous challenges to their survival.
Silverback gorillas, classified as critically endangered by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), are under significant threat due to habitat loss, poaching, and disease. Deforestation and human encroachment have resulted in the destruction of their natural habitats, leaving them with limited areas to roam and find food. Additionally, the illegal wildlife trade continues to pose a grave danger, as gorillas are hunted for their meat and body parts. Diseases, such as Ebola, also pose a significant risk to their populations.
Grizzly bears, listed as a species of special concern in some regions, face similar threats. Habitat loss and fragmentation due to human activities, including urban development and agriculture, have greatly reduced their range. This loss of habitat limits their access to food sources and disrupts their natural behaviors. Additionally, conflicts with humans, such as bear-human encounters and poaching, further endanger their populations.
Conservation efforts are crucial for the survival of both species. Organizations and governments are working to protect and restore their habitats, implement anti-poaching measures, and raise awareness about the importance of these iconic animals. Collaborative initiatives involving local communities, scientists, and policymakers are essential to ensure the long-term survival of silverback gorillas and grizzly bears in their respective ecosystems.

22). Main Threats to Survival
The main threats to the survival of silverback gorillas and grizzly bears are multifaceted and pose significant challenges to their populations.
For silverback gorillas, habitat loss is a major concern. Deforestation and human encroachment have resulted in the destruction of their natural habitats, leaving them with limited areas to roam and find food. This loss of habitat not only disrupts their feeding patterns but also isolates populations, making it difficult for them to find mates and maintain genetic diversity. Additionally, the illegal wildlife trade poses a grave danger, as gorillas are hunted for their meat and body parts. Diseases, such as Ebola, also pose a significant risk to their populations, as they can decimate entire groups.
Grizzly bears face similar threats, with habitat loss and fragmentation being a primary concern. Human activities, including urban development and agriculture, have greatly reduced their range, limiting their access to food sources and disrupting their natural behaviors. This loss of habitat also increases the likelihood of conflicts with humans, such as bear-human encounters and poaching, which further endanger their populations.
Conclusion
-Similarities
When comparing the silverback gorilla and the grizzly bear, there are several similarities that can be observed. Firstly, both species are known for their impressive size and weight. They are among the largest land-dwelling mammals, with the silverback gorilla being the largest primate and the grizzly bear being one of the largest bear species.
Additionally, both animals possess incredible strength and endurance, allowing them to dominate their respective habitats. Both the silverback gorilla and the grizzly bear are also highly intelligent creatures, capable of problem-solving and exhibiting complex social behaviors. Lastly, both species play important ecological roles within their ecosystems, contributing to the balance and diversity of their habitats.
-Differences
The most significant difference between the silverback gorilla and the grizzly bear is their mode of locomotion. While the gorilla primarily moves on all fours, using its long arms and knuckles for support, the grizzly bear is a proficient biped, capable of walking and running on its hind legs. This fundamental difference in locomotion affects their overall movement and agility.
The gorilla’s quadrupedal stance provides stability and allows it to navigate through dense vegetation, while the bear’s bipedalism gives it an advantage in terms of speed and maneuverability.
-Hypothesis
Based on the physical attributes and behavior of both species, the hypothesis is that the grizzly bear would emerge victorious in a violent confrontation. The grizzly bear’s size, strength, and aggressive tendencies give it an advantage over the silverback gorilla. Additionally, the bear’s powerful bite force and attack methods make it a formidable opponent.