Leopard Vs Lion Size, Weight, Ecological Comparison
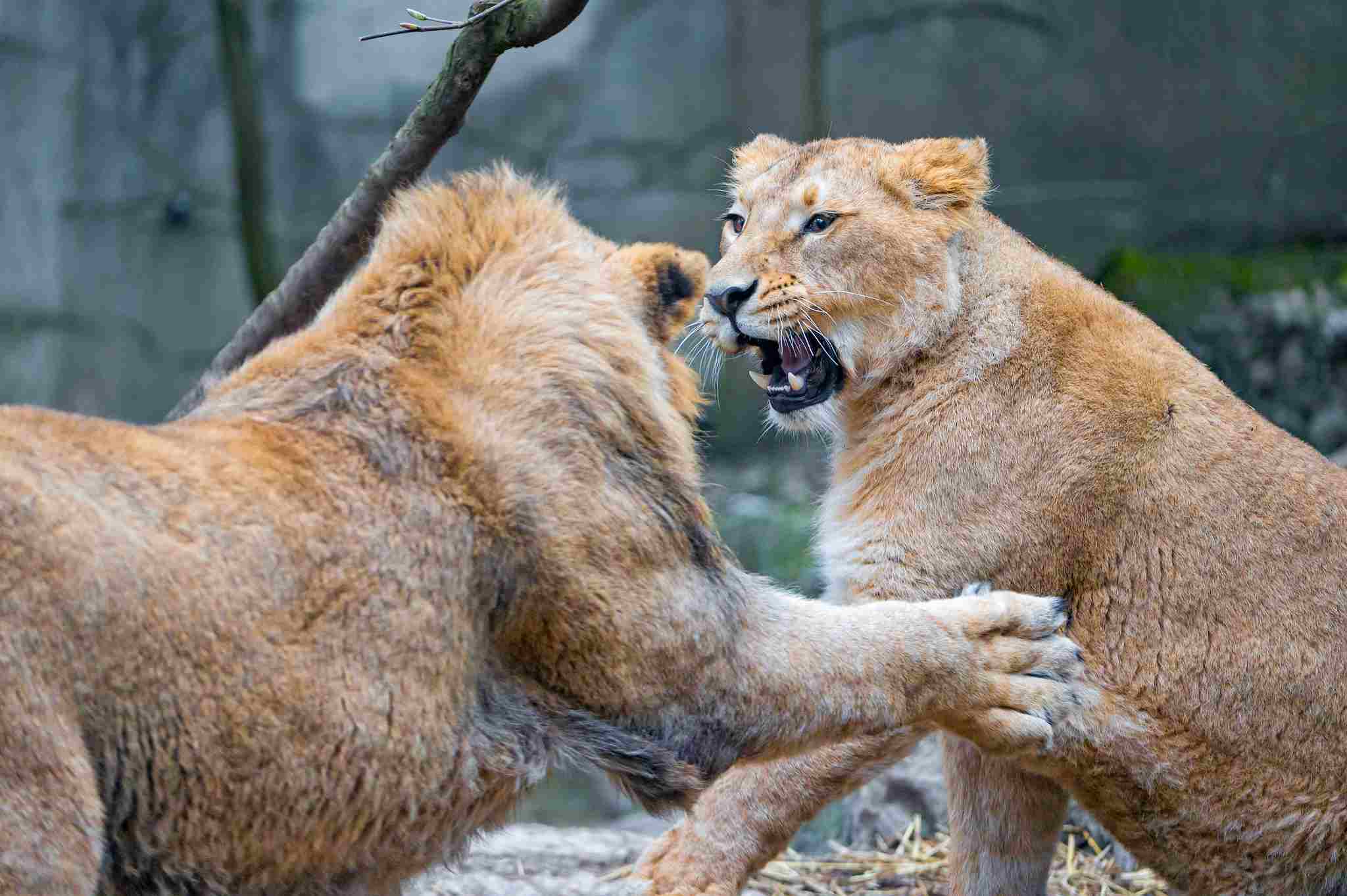
A lion will overpower and kill a leopard in a fight because it is notably larger, heavier, stronger, more aggressive, and generally superior as a predator.
In this article, we will delve into the details of the comparison between these two big cats. We will explore their taxonomy, appearance, size, weight, speed and agility, bite force, overall physical capacity, habitat, lifespan, behavior, reproduction, danger posed to humans, intelligence, tracks, and conservation status. By examining these factors, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of the differences between leopards and lions.
Reasons Why a Lion Will Win a Leopard In a Fight/Physical Confrontation
I). Size and Weight Advantages
One of the main reasons why a lion will win a fight against a leopard is its size and weight advantage. Lions are significantly larger and heavier than leopards, giving them a clear physical advantage in a confrontation. A fully grown male lion can weigh up to 420 pounds, while a male leopard typically weighs around 130 pounds.
This size difference allows lions to overpower leopards with their sheer strength and weight. With their larger size, lions have a greater reach and can deliver more powerful blows, making it difficult for a leopard to defend itself.
II). Lions are More Aggressive Than Leopards
Another reason why a lion will likely win in a fight against a leopard is their difference in aggression levels. Lions are known for their fierce and aggressive nature, especially when it comes to defending their territory or pride.
On the other hand, leopards are more solitary and elusive, preferring to avoid confrontations whenever possible. Lions are more likely to initiate a fight and display dominance, which can intimidate and overpower a leopard.

III). Overall Predatory Superiority
In terms of overall predatory superiority, lions have the advantage over leopards. Lions are apex predators and are skilled hunters, often working together in coordinated attacks to bring down large prey. Their social structure and hunting strategies give them an edge over leopards, who primarily rely on stealth and ambush tactics.
Lions have a higher success rate in hunting and are more experienced in taking down larger prey, which translates to their ability to overpower a leopard in a physical confrontation.
Therefore, the size and weight advantages, along with the more aggressive nature and overall predatory superiority of lions, make them the likely victors in a fight against leopards.
*Details of Comparison
1). Taxonomy
The taxonomy of the leopard and lion reveals interesting insights into their evolutionary history and relationship. The leopard belongs to the genus Panthera, with its scientific name being Panthera pardus. On the other hand, the lion belongs to the same genus Panthera, with its scientific name being Panthera leo.
Both animals are part of the Panthera genus, which also includes other big cats like tigers and jaguars. This classification highlights their shared ancestry and similar physical characteristics. However, it is important to note that despite their taxonomic similarities, leopards and lions are distinct species with unique adaptations and behaviors.
When comparing the taxonomy of these animals, it is fascinating to observe the subtle differences in their genetic makeup and physical traits. These differences contribute to their distinct appearances, sizes, and ecological roles. Understanding the taxonomy of leopards and lions provides a foundation for further exploration into their individual characteristics and the factors that contribute to their success in their respective habitats.
2). Appearance
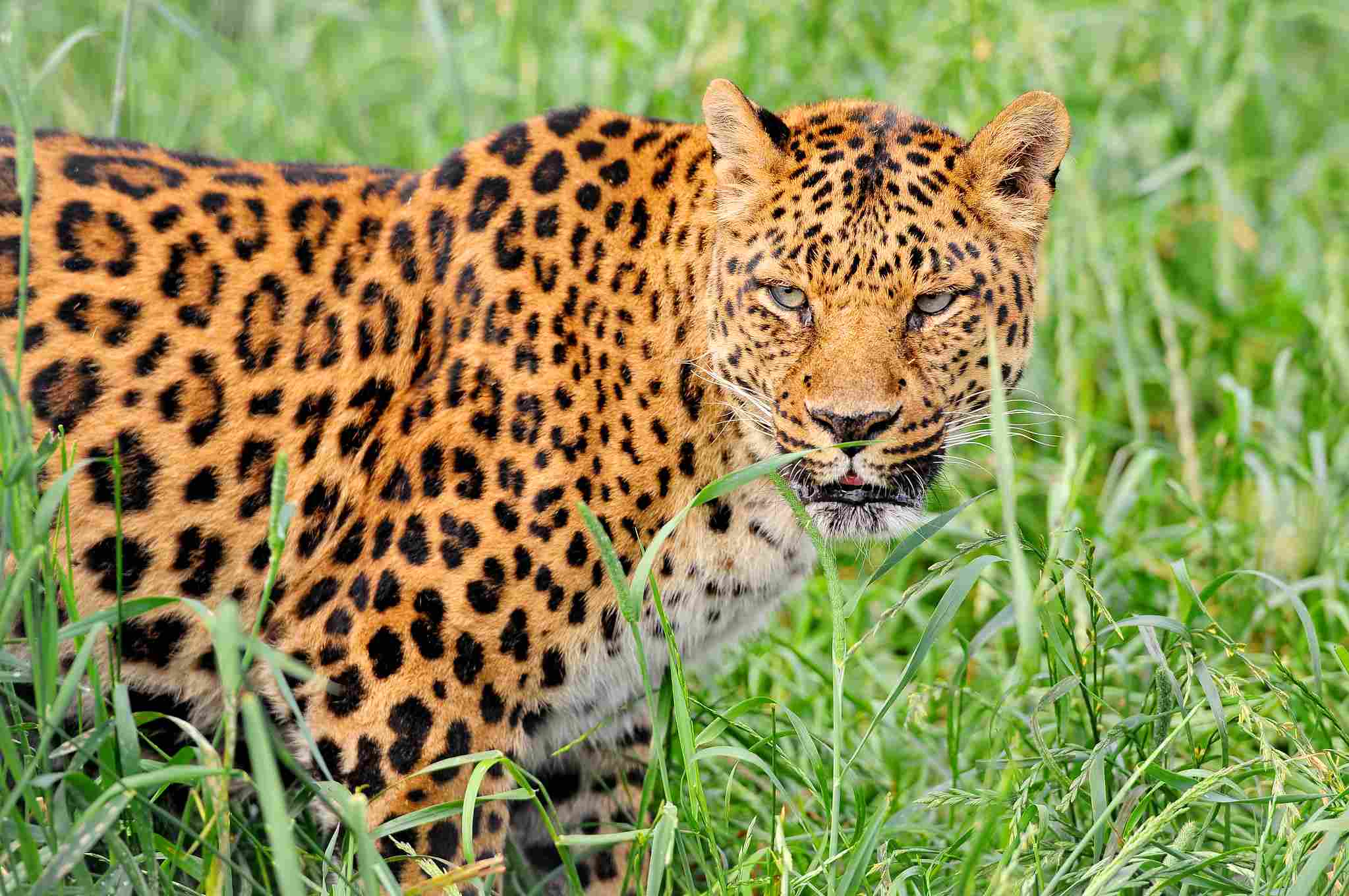
The appearance of both leopards and lions is fascinating and plays a crucial role in their survival and ecological niche. Starting with their coats, both animals have unique fur patterns that aid in their camouflage within their respective habitats.
Leopards have a distinctive rosette pattern on their fur, which helps them blend into the dappled light and shadows of the trees and grasslands. On the other hand, lions have a tawny-colored coat that allows them to blend in with the savannah grasses.
In terms of stature and build, leopards and lions have noticeable differences. Leopards are known for their sleek and agile bodies, designed for stealth and climbing trees. They have a more compact and muscular build, allowing them to navigate through dense vegetation effortlessly. On the contrary, lions have a larger and more robust build, with a muscular frame and a prominent mane in males. This build gives them a more intimidating presence and aids in their social interactions within their pride.
When comparing the appearance of these animals, it is clear that their physical characteristics are adapted to their specific environments and hunting strategies. The unique coat patterns and body structures of leopards and lions contribute to their survival and success in their respective habitats.

3). Size
When comparing the size of leopards and lions, it is important to consider their total body length and height at the shoulders. Leopards typically measure around 4 to 6 feet in length, with an additional 2 to 3 feet for their tail. On the other hand, lions are much larger, with a total body length ranging from 5 to 8 feet, excluding their tail, which adds another 2 to 3 feet. In terms of height at the shoulders, leopards stand at around 2 to 3 feet, while lions can reach heights of 3 to 4 feet.
The size difference between these two big cats is significant, with lions being noticeably larger than leopards. This size advantage gives lions a greater presence and intimidation factor, especially when it comes to defending their territory or competing for resources. However, it is important to note that leopards compensate for their smaller size with their agility and stealth, allowing them to navigate through dense vegetation and climb trees effortlessly.
4). Weight
When comparing the weight of leopards and lions, it is clear that lions are significantly heavier than leopards. Adult male lions can weigh anywhere between 330 to 550 pounds, while adult female lions typically weigh around 265 to 395 pounds. On the other hand, adult male leopards weigh between 80 to 200 pounds, and adult female leopards weigh around 60 to 130 pounds.
The weight difference between these two big cats is substantial, with lions outweighing leopards by a considerable margin. This additional weight gives lions a distinct advantage in terms of strength and power, making them formidable predators. The sheer size and weight of lions enable them to bring down larger prey, such as wildebeests and zebras, which would be more challenging for leopards to tackle.
However, it is important to note that leopards compensate for their smaller size and weight with their agility and hunting techniques. Leopards are known for their ability to climb trees effortlessly, allowing them to ambush their prey from above. This strategy helps them overcome the disadvantage of their lighter weight and ensures their survival in their respective habitats.
5). Speed and Agility
When comparing the speed and agility of leopards and lions, it is evident that both big cats possess impressive physical capabilities. However, there are notable differences between the two.
Leopards are renowned for their exceptional speed and agility. With their slender build and long limbs, they are built for speed. Leopards can reach speeds of up to 36 miles per hour (58 kilometers per hour) in short bursts, allowing them to swiftly chase down their prey. Their agility is equally remarkable, enabling them to navigate through dense vegetation and climb trees effortlessly. This combination of speed and agility gives leopards a distinct advantage when it comes to hunting and evading predators.
On the other hand, while lions may not match the speed and agility of leopards, they possess their own unique strengths. Lions are capable of reaching speeds of up to 50 miles per hour (80 kilometers per hour) in short sprints. Although not as fast as leopards, lions compensate for their slightly slower speed with their sheer power and endurance. Their muscular build and strong legs allow them to bring down larger prey through sheer force and persistence.
6). Bite Force
Leopards have an impressive bite force, with an average psi (pounds per square inch) of around 300. This allows them to deliver a powerful bite that can easily crush the bones and neck of their prey. With their sharp teeth and strong jaw muscles, leopards are able to secure a firm grip on their prey, ensuring a successful kill.
On the other hand, lions possess an even stronger bite force compared to leopards. With an average psi of around 650, lions have one of the most powerful bites among big cats. This immense bite force enables them to take down large prey, such as wildebeests and zebras, by delivering a crushing bite to the throat or neck.
While leopards have a formidable bite force, lions surpass them in terms of sheer power. Lions’ stronger bite force allows them to overpower larger prey and exert dominance in confrontations with other animals.
7). Overall Physical Capacity (Which is Stronger?)
When comparing the overall physical capacity of a lion and a leopard, it becomes evident that the lion holds a significant advantage. This is primarily due to its larger size, greater weight, and superior muscular endurance.
In terms of size, lions are much larger than leopards. Adult male lions can weigh up to 420 pounds, while leopards typically weigh around 130 pounds. This size difference gives lions a clear advantage in terms of strength and power.
Additionally, lions have a higher muscular endurance compared to leopards. This means that they can sustain physical exertion for longer periods of time, making them more formidable in a fight or confrontation.
When it comes to a violent confrontation between a lion and a leopard, the lion’s superior physical capacity is likely to be the determining factor. The lion’s size, weight, and muscular endurance give it the ability to overpower the leopard and ultimately cause its demise.
Therefore, the overall physical capacity of a lion is significantly stronger than that of a leopard.
8). Habitat
Lions are primarily found in grassland savannah habitats, where they can take advantage of the open spaces to hunt their prey. They are known to inhabit areas with a sufficient supply of water, as they require regular access to drinking sources. Lions are social animals and are often found in prides, which consist of multiple females, their offspring, and a few dominant males.
On the other hand, leopards are more adaptable in terms of habitat. They can be found in a variety of ecosystems, including forests, mountains, and even deserts. Leopards are solitary animals and are known for their ability to climb trees, which allows them to escape from predators and store their kills out of reach. Their geographic range is wider compared to lions, as they are found in both Africa and Asia.

9). Lifespan
Leopards have an average lifespan of around 12 to 17 years in the wild, although some individuals have been known to live up to 20 years. On the other hand, lions have a slightly shorter lifespan, with an average of 10 to 14 years in the wild.
Several factors contribute to the difference in lifespan between these two big cats. One key factor is the level of competition and aggression within their respective social structures. Lions, being social animals, often engage in territorial disputes and fights with other prides, which can result in injuries and a higher mortality rate. Leopards, being solitary animals, have less competition and are generally less prone to such conflicts.
Another factor that affects lifespan is the availability of food and resources. Lions, as apex predators, require a large amount of prey to sustain themselves and their prides. This constant need for food can lead to more risks and potential injuries during hunts. Leopards, being more adaptable and opportunistic hunters, can survive on a wider range of prey and are not as dependent on large kills.
While leopards generally have a longer lifespan compared to lions, it is important to consider the various factors that contribute to this difference.
10). Behavior
Leopards and lions exhibit distinct behaviors that reflect their different lifestyles and social structures.
In terms of feeding, both leopards and lions are carnivores, but their hunting strategies differ. Leopards are solitary hunters and rely on stealth and camouflage to ambush their prey. They are known for their ability to drag their kills up trees to protect them from scavengers. On the other hand, lions are social hunters that rely on teamwork and coordination to bring down larger prey. They often engage in group hunts, with the females doing most of the hunting while the males guard the territory.
Aggression is another aspect where the two big cats differ. While both leopards and lions can be aggressive when threatened or during territorial disputes, lions are generally more aggressive due to their social nature. They are known to engage in fierce battles with rival prides to protect their territory and resources. Leopards, being solitary animals, are less prone to aggression and tend to avoid confrontations whenever possible.
Vocalization is an important means of communication for both species. Lions are known for their powerful roars, which can be heard over long distances and serve to communicate with other members of their pride. Leopards, on the other hand, have a wide range of vocalizations, including growls, hisses, and purrs, which they use to communicate with other leopards and mark their territory.
In terms of social behavior, lions are highly social animals that live in prides consisting of multiple females, their offspring, and a few dominant males. They engage in grooming, playing, and resting together, which helps to strengthen social bonds within the pride. Leopards, on the other hand, are solitary animals that prefer to live and hunt alone. They only come together during mating season or when a female is raising her cubs.
11). Reproduction
In terms of reproduction, both leopards and lions are viviparous, meaning they give birth to live young. However, there are differences in their gestation periods and reproductive behaviors.
Leopards have a gestation period of approximately 90 to 105 days. During this time, the female leopard will find a secluded den or cave to give birth to her cubs. A typical litter size ranges from one to six cubs, with two or three being the average. The cubs are born blind and helpless, and the mother will nurse them for several months until they are old enough to accompany her on hunts.
On the other hand, lions have a slightly longer gestation period of around 100 to 110 days. Lionesses give birth to their cubs in a communal den within the pride. A litter usually consists of two to four cubs, and they are born with their eyes open and covered in a spotted coat. The lioness will nurse her cubs and provide them with protection within the pride until they are old enough to join in hunting activities.
Therefore, while both leopards and lions are viviparous and give birth to live young, there are differences in their gestation periods and reproductive behaviors. Leopards have a shorter gestation period and give birth in secluded dens, while lions have a slightly longer gestation period and give birth within the communal den of the pride.
12). Danger Posed to Humans
When it comes to the danger posed to humans, both lions and leopards can be potentially dangerous, but there are some notable differences. Lions, being larger and stronger than leopards, have the potential to cause more harm. They are known to be more aggressive and have been involved in more attacks on humans compared to leopards.
Lions have been known to come close to human settlements, especially in areas where their natural habitat overlaps with human populations. This proximity increases the chances of encounters between lions and humans. In some cases, lions have shown aggression towards humans, especially if they feel threatened or if they perceive humans as a potential source of food.
On the other hand, leopards are generally more elusive and tend to avoid human settlements. While they may occasionally come into contact with humans, they are less likely to show aggression towards them unless provoked or cornered.
In terms of the rate of human deaths caused, lions have been responsible for more fatalities compared to leopards. This is partly due to their larger size and more aggressive nature.
If you happen to encounter a lion or leopard in the wild, it is important to take precautions to ensure your safety. Avoid approaching the animal and give it space to retreat. Make yourself appear larger by raising your arms and making loud noises to deter the animal. It is crucial to remember that these are wild animals and should be treated with caution and respect.
Therefore, while both lions and leopards can pose a danger to humans, lions are generally considered to be more dangerous due to their larger size, strength, and more aggressive behavior.
13). Intelligence
Lions are known for their social structure and cooperative hunting techniques. They live in prides, which are family groups consisting of multiple females, their offspring, and a few adult males. This social structure requires a certain level of intelligence to coordinate hunting strategies, communicate effectively, and maintain social bonds within the pride.
Leopards, on the other hand, are solitary animals and rely more on their individual hunting skills. They are known for their stealth and agility, which require a high level of intelligence to successfully stalk and capture prey. Leopards are also highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of habitats, showcasing their ability to problem-solve and adjust to different environments.
In terms of problem-solving abilities, both lions and leopards have been observed to exhibit intelligence. Lions have been known to strategize during hunts, using tactics such as surrounding prey or ambushing from different angles. Leopards, on the other hand, are skilled climbers and have been observed using their intelligence to navigate trees and escape potential threats.
Overall, it is difficult to determine which animal is more intelligent as their intelligence is specialized for their specific lifestyles and ecological needs. Lions showcase intelligence in their social dynamics, while leopards demonstrate intelligence in their solitary hunting strategies. Both animals have adapted their intelligence to survive and thrive in their respective environments.
14). Tracks
When comparing the tracks of leopards and lions, there are distinct differences that can help identify which animal left the mark. The tracks of a leopard are typically smaller and more compact, with four toes and a distinctive “M” shape at the front. These tracks are often found in areas with dense vegetation, as leopards are skilled climbers and can easily navigate through trees and bushes.
On the other hand, lion tracks are larger and more rounded, with four toes and a prominent pad at the front. These tracks are commonly found in open grasslands and savannas, where lions prefer to roam and hunt. The size and depth of the tracks can also indicate the weight and strength of the animal, with lion tracks being larger and more deeply imprinted due to their larger size and weight.
By analyzing the tracks left behind, researchers and wildlife enthusiasts can gain valuable insights into the presence and behavior of these majestic predators. Tracking can provide information about their movement patterns, hunting strategies, and territorial boundaries. It is an essential tool for studying and conserving these animals in their natural habitats.
15). Conservation Status
When it comes to the conservation status of leopards and lions, both species face significant challenges in the wild. They are both classified as “endangered” or “threatened” due to various factors that threaten their survival.
For leopards, habitat loss and fragmentation are major threats. As human populations expand and encroach upon their natural habitats, leopards are losing their homes and access to prey. Additionally, illegal hunting and poaching for their beautiful fur and body parts further contribute to their declining numbers.
On the other hand, lions also face similar threats, but with some additional factors. Habitat loss, due to human activities such as agriculture and urbanization, is a significant concern for lions. Furthermore, conflicts with humans, including retaliatory killings and trophy hunting, pose a serious threat to their populations.
Both species also suffer from the depletion of their prey base, as well as the impact of climate change on their habitats. These factors, combined with the illegal wildlife trade and inadequate conservation efforts, make it crucial to prioritize the protection and conservation of both leopards and lions.
Efforts are being made to conserve these animals through initiatives such as protected areas, anti-poaching measures, and community-based conservation programs. However, more needs to be done to ensure their long-term survival in the wild.

Conclusion
I). SIMILARITIES
In conclusion, the comparison between leopards and lions reveals several similarities. Both animals face significant threats to their survival, including habitat loss, illegal hunting, and the depletion of their prey base.
They are both classified as “endangered” or “threatened” species, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect them. Additionally, both leopards and lions play crucial roles in their respective ecosystems, contributing to the balance and biodiversity of their habitats.
II). DIFFERENCES
Despite their similarities, there are also notable differences between leopards and lions. In terms of appearance, leopards have a distinct spotted coat, while lions have a tawny coloration with a mane in males.
Size-wise, lions are generally larger and heavier than leopards. Lions also exhibit social behavior, living in prides, whereas leopards are solitary animals. In terms of behavior, lions are known for their roaring, while leopards are more stealthy and elusive.