Is a Grasshopper A Consumer? Feeding Habits of Grasshoppers Explored
A grasshopper is a consumer in trophic level 2 of the food chain or energy pyramid. This article discusses several queries related to the question; “is a grasshopper a consumer?” as follows;
Is a Grasshopper A Producer?
A grasshopper is not a producer because it lacks the ability to perform photosynthesis. Unlike plants and other producers that have chlorophyll pigments, grasshoppers do not possess the necessary physiological features to produce their own food.
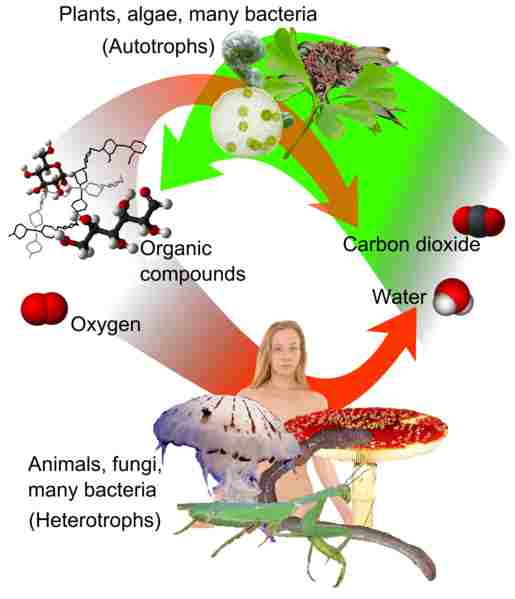
Producers, such as algae, cyanobacteria, and various types of plants, are able to convert solar energy into chemical bioenergy through photosynthesis. This process allows them to synthesize organic compounds, including carbohydrates, which serve as their source of energy.
Grasshoppers, on the other hand, are heterotrophic organisms. They rely on consuming organic matter, particularly plants, as their source of energy. Grasshoppers feed directly on parts of plants, such as leaves and stems, making them primary consumers in the food chain. As primary consumers, they occupy the trophic level above the producers.
While grasshoppers play an important role in the ecosystem as consumers, they do not possess the ability to produce their own food like producers do. Instead, they depend on plants as their main source of energy.
This distinction between producers and consumers highlights the diverse roles and interactions within an ecosystem, with each organism contributing to the overall balance and functioning of the system. Grasshoppers, as consumers, help regulate plant populations and serve as a food source for higher-level consumers, such as birds and reptiles.
Is A Grasshopper a Primary Consumer
A grasshopper is typically a primary consumer because it relies and feeds directly on parts of plants, which are producers. This places it one level above the plants as a primary consumer. As a primary consumer, the grasshopper plays a crucial role in the food chain by consuming plant material and obtaining energy from it.
Grasshoppers have a specialized diet consisting mainly of plant material, such as leaves and stems. They use their strong jaws to chew and consume these plant parts. By feeding on plants, grasshoppers obtain the nutrients and energy they need to survive and reproduce.
Being a primary consumer, the grasshopper occupies the trophic level above the producers. Producers, such as plants, are the foundation of the food chain as they are capable of converting solar energy into chemical energy through photosynthesis. Grasshoppers, as primary consumers, rely on the energy stored in plants to meet their nutritional requirements.
The relationship between grasshoppers and plants is an example of herbivory, where an organism feeds on plant material. This interaction is essential for the transfer of energy and nutrients through the ecosystem. Grasshoppers act as intermediaries, converting the energy stored in plants into a form that can be utilized by higher-level consumers.
By consuming plant material, grasshoppers also play a role in regulating plant populations. They can selectively feed on certain plant species, which can influence the abundance and distribution of these plants in their environment. This, in turn, can have cascading effects on other organisms that depend on the plants for food and/or shelter.
Therefore, a grasshopper is considered a primary consumer because it feeds directly on parts of plants, which are producers. This places it one level above the plants in the food chain.
Grasshoppers play a vital role in energy transfer and nutrient cycling within ecosystems, acting as intermediaries between producers and higher-level consumers. Their feeding habits and interactions with plants contribute to the overall balance and functioning of the ecosystem.
Is A Grasshopper a Secondary Consumer
A grasshopper is not considered a secondary consumer because its primary food sources consist mainly of plant material. Unlike secondary consumers, which are predators that feed on other animals, grasshoppers primarily consume parts of plants, such as leaves and stems. This dietary preference classifies them as primary consumers in the food chain.
As mentioned earlier, primary consumers rely on producers, such as plants, for their energy and nutritional needs. Grasshoppers play a crucial role in the ecosystem by consuming plant material and converting it into usable energy. They use their strong mandibular appendages to chew and consume various parts of plants, extracting the nutrients necessary for their survival and reproduction.
Secondary consumers, on the other hand, occupy a higher trophic level in the food chain. They are predators that feed on other animals, including primary consumers.
These secondary consumers obtain their energy by consuming other organisms, which may include herbivores like grasshoppers. However, grasshoppers themselves do not typically exhibit predatory behavior, making them primary consumers rather than secondary consumers.
The distinction between primary and secondary consumers is important in understanding the flow of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem. Primary consumers like grasshoppers serve as a link between producers and higher-level consumers. They transfer the energy stored in plants to the next trophic level, where it can be utilized by secondary consumers.
Grasshoppers’ feeding habits and interactions with plants also have significant ecological implications. By selectively feeding on certain plant species, they can influence the abundance and distribution of these plants in their environment. This, in turn, can impact other organisms that rely on these plants for food or shelter.
Therefore, a grasshopper is not a secondary consumer because its primary food sources consist mainly of plant material. It is not typically a predator, which classifies it as a primary consumer in the food chain.
Grasshoppers are vital in energy transfer and nutrient cycling within ecosystems, acting as intermediaries between producers and higher-level consumers. Their feeding habits and interactions with plants contribute to the overall balance and functioning of the ecosystem.
Is A Grasshopper a Decomposer?
Grasshoppers are not decomposers, because decomposers are organisms that feed on the remains or wastes of other organisms, breaking them down and facilitating the process of biodegradation. Grasshoppers, on the other hand, have a different dietary preference and do not participate in this process.
Decomposition is a vital part of nutrient cycling in ecosystems. It involves the breakdown of organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into simpler compounds that can be recycled and reused by other organisms. This process is facilitated by various organisms, including bacteria, fungi, earthworms, millipedes, and termites.
Grasshoppers, however, do not feed on organic remains or wastes. Their diet primarily consists of plant material, such as leaves and stems.
They use their strong mandibles to chew and consume these plant parts, extracting the nutrients necessary for their survival and reproduction. Grasshoppers are classified as herbivores, as they rely on plants as their main source of energy and nutrients.
The role of decomposers in the ecosystem is distinct from that of grasshoppers. Decomposers break down complex organic matter into simpler forms, releasing nutrients back into the environment. This process is essential for the recycling of nutrients and the maintenance of a healthy ecosystem. Grasshoppers, on the other hand, contribute to the energy flow within the ecosystem by consuming plant material and transferring the energy stored in plants to higher trophic levels.
It is important to recognize the different ecological functions of decomposers and primary consumers like grasshoppers. While decomposers facilitate the breakdown of organic matter, grasshoppers play a crucial role in energy transfer and nutrient cycling. Both processes are essential for the functioning and balance of ecosystems.
By consuming plant material, grasshoppers indirectly influence the decomposition process. Their feeding habits can impact the abundance and distribution of plant species in their environment. This, in turn, can affect the availability of organic matter for decomposers to break down. Therefore, grasshoppers indirectly contribute to the decomposition process by influencing the availability of organic matter.
This implies that, grasshoppers cannot be called decomposers. They do not feed on the remains or wastes of organisms, and they do not facilitate the process of biodegradation.
Grasshoppers are primary consumers that rely on plants as their main source of energy and nutrients. Their role in the ecosystem is distinct from that of decomposers, but both are essential for the functioning and balance of ecosystems.
Is a Grasshopper a Producer or Consumer
The grasshopper is not a producer but rather a consumer, as we have earlier shown. Unlike producers, such as plants, grasshoppers are not autotrophic and cannot produce their own food. Instead, they rely on external sources for their energy and nutrients.
Grasshoppers are classified as herbivores, which means they primarily feed on plant material. Their diet consists of leaves, stems, and other parts of plants. They use their strong mandibles to chew and consume these plant parts, extracting the nutrients necessary for their survival and reproduction.
One of the reasons why grasshoppers are considered consumers is because they do not have chlorophyll. Chlorophyll is a pigment found in plants that allows them to convert sunlight into energy through the process of photosynthesis. Since grasshoppers lack chlorophyll, they are unable to produce their own food and must obtain it from other sources.
Plants are the main source of energy for grasshoppers. They provide the carbohydrates, proteins, and other essential nutrients that grasshoppers need to survive and thrive. Grasshoppers play an important role in the energy flow within ecosystems by consuming plant material and transferring the energy stored in plants to higher trophic levels.
Another characteristic that distinguishes grasshoppers as consumers is their mode of respiration. Grasshoppers take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide during respiration, just like other animals. This process is necessary for the breakdown of food molecules and the release of energy.
It is important to note that grasshoppers are not decomposers. Decomposers are organisms that feed on the remains or wastes of other organisms, breaking them down and facilitating the process of biodegradation. Grasshoppers, on the other hand, do not participate in this process. They have a different dietary preference and do not feed on organic remains or wastes.
The grasshopper is therefore a consumer rather than a producer. It relies on external sources for its energy and nutrients, primarily feeding on plant material. Grasshoppers are not autotrophic and cannot produce their own food like producers do.
Is A Grasshopper a Producer, Consumer or Decomposer
A grasshopper is neither a producer nor a decomposer, based on all earlier discussions. While we have established that grasshoppers are consumers, it is important to understand why they do not fall into the categories of producers or decomposers.
Firstly, as mentioned before, grasshoppers do not have the ability to produce their own food. Unlike producers, such as plants, they lack chlorophyll, which is necessary for photosynthesis. Without chlorophyll, grasshoppers cannot convert sunlight into energy, making them reliant on external sources for their nutritional needs.
Secondly, grasshoppers do not participate in the process of decomposition. Decomposers are organisms that feed on organic remains or waste matter, breaking them down and facilitating biodegradation. Grasshoppers, on the other hand, have a different dietary preference and primarily feed on plant material. They do not contribute to the breakdown of organic matter in the same way decomposers do.
Instead, grasshoppers play an important role as consumers in the ecosystem. They rely on autotrophs, such as plants, as their primary energy source. By consuming plant material, grasshoppers transfer the energy stored in plants to higher trophic levels. This energy flow is essential for the functioning of the ecosystem and the survival of other organisms.
Furthermore, grasshoppers are heterotrophic, meaning they cannot produce their own food. They depend on the nutrients and energy obtained from consuming plants to meet their metabolic needs. This reliance on external sources further emphasizes their role as consumers rather than producers or decomposers.
In addition, grasshoppers engage in respiration, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. This process is essential for the breakdown of food molecules and the release of energy. It is another characteristic that aligns them with other consumers in the animal kingdom.
To draw from the above, a grasshopper is neither a producer nor a decomposer. It lacks the ability to produce its own food and does not participate in the process of decomposition.
Instead, grasshoppers are consumers that rely on autotrophs for their energy and nutrients. By understanding the role of grasshoppers as consumers, we can appreciate their importance in the ecosystem and the intricate web of energy flow.

Reasons Why the Grasshopper is a Consumer
Grasshoppers are classified as consumers due to several reasons. Firstly, they lack chlorophyll and other characteristics of producers. Unlike plants, which are able to produce their own food through photosynthesis, grasshoppers do not have the ability to convert sunlight into energy. This makes them reliant on external sources for their nutritional needs.
Secondly, grasshoppers are heterotrophic organisms, meaning they cannot produce their own food. Instead, they rely on consuming other organisms for their energy and nutrients. In the case of grasshoppers, their primary energy source comes from autotrophs, such as plants. By feeding on plant material, grasshoppers transfer the energy stored in plants to higher trophic levels, contributing to the flow of energy in the ecosystem.
Unlike decomposers, grasshoppers do not feed on organic remains or waste matter. Decomposers are organisms that break down and facilitate the biodegradation of organic matter. Grasshoppers, on the other hand, have a different dietary preference and primarily feed on plant material. They do not contribute to the breakdown of organic matter in the same way decomposers do.
Additionally, grasshoppers engage in respiration, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. This process is essential for the breakdown of food molecules and the release of energy. It is another characteristic that aligns them with other consumers in the animal kingdom.
To summarize, there are several reasons why grasshoppers are classified as consumers. They lack the ability to produce their own food, relying on external sources for their nutritional needs.
They primarily feed on autotrophs, such as plants, and do not participate in the process of decomposition. Grasshoppers also engage in respiration, further emphasizing their role as consumers in the ecosystem.
By understanding the reasons why grasshoppers are consumers, we can appreciate their importance in the ecosystem and the intricate web of energy flow. Grasshoppers play a vital role in transferring energy from plants to higher trophic levels, contributing to the overall functioning and balance of the ecosystem.
Therefore, grasshoppers are consumers due to their inability to produce their own food, their reliance on autotrophs as an energy source, their preference for plant material, and their participation in respiration. These characteristics distinguish them from producers and decomposers, highlighting their role as important consumers in the ecosystem.
Below is an elaborate discussion of the different reasons why grasshoppers are consumers;
1. Grasshoppers Do Not Have Chlorophyll
Grasshoppers do not have chlorophyll, and this is one of the reasons why they are classified as consumers. Chlorophyll is a pigment found in plants that allows them to carry out photosynthesis and produce their own food. Without chlorophyll, grasshoppers are unable to convert sunlight into energy, making them reliant on external sources for their nutritional needs.
As heterotrophic organisms, grasshoppers must obtain their energy and nutrients by consuming other organisms. They rely on autotrophs, such as plants, as their primary energy source. By feeding on plant material, grasshoppers transfer the energy stored in plants to higher trophic levels, contributing to the flow of energy in the ecosystem.
Unlike decomposers, which break down organic remains and waste matter, grasshoppers have a different dietary preference. They primarily feed on plant material and do not participate in the process of decomposition. This further emphasizes their role as consumers rather than decomposers in the ecosystem.
In addition to their lack of chlorophyll, grasshoppers engage in respiration, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. This process is essential for the breakdown of food molecules and the release of energy. It aligns them with other consumers in the animal kingdom.
Generally, the absence of chlorophyll in grasshoppers is a significant factor that classifies them as consumers. They rely on external sources for their nutritional needs, primarily feeding on autotrophs like plants. This distinguishes them from producers and decomposers, highlighting their role as important consumers in the ecosystem.
2. They are Heterotrophic
Grasshoppers are classified as consumers because they are heterotrophic organisms. This means that they cannot produce their own food and must obtain energy and nutrients by consuming other organisms.
Unlike autotrophs, such as plants, which can convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, grasshoppers rely on external sources for their nutritional needs.
Being heterotrophic is a key characteristic that distinguishes grasshoppers as consumers in the ecosystem. They feed on autotrophs like plants, which serve as their primary source of energy. By consuming plant material, grasshoppers transfer the energy stored in plants to higher trophic levels, contributing to the flow of energy in the food chain.
This dietary preference of grasshoppers further emphasizes their role as consumers rather than producers. While producers, like plants, can synthesize their own food, grasshoppers rely on consuming other organisms to meet their energy requirements. This makes them an important link in the food web, as they help to regulate plant populations and maintain ecosystem balance.
The fact that grasshoppers are heterotrophic organisms highlights their role as consumers in the ecosystem. They rely on external sources, particularly plants, for their energy needs. This distinguishes them from producers and underscores their importance in the flow of energy through the food chain.
3. Plants are The Main Source of Energy for Grasshoppers
Grasshoppers rely on plants as their main source of energy, which indicates their herbivorous nature. This dietary preference clearly establishes grasshoppers as consumers rather than producers in the ecosystem. Unlike producers, such as plants, which can synthesize their own food through photosynthesis, grasshoppers must consume other organisms to meet their energy requirements.
By feeding on plants, grasshoppers transfer the energy stored in plants to higher trophic levels, contributing to the flow of energy in the food chain. This makes them an important link in the ecosystem, as they help regulate plant populations and maintain balance.
The fact that grasshoppers depend on plants for their energy needs further indicates their role as consumers. They cannot produce their own food like autotrophs, and instead rely on external sources. This distinction sets them apart from producers and highlights their significance in the energy flow through the food chain.
Because plants are the main source of energy for grasshoppers indicates their herbivorous nature and establishes them as consumers in the ecosystem.
Grasshoppers play an important role in the food web by consuming plants and transferring energy to higher trophic levels. Their dependence on external sources for energy distinguishes them from producers and underscores their importance in maintaining ecosystem balance.
4. Grasshoppers Do Not Feed On Organic Remains Or Wastes, Like Decomposers
Grasshoppers are not saprophytic or detritivorous like decomposers. Unlike decomposers, which feed on organic remains or wastes, grasshoppers are herbivorous. This means that they primarily consume plants for their energy and nutrient needs.
The fact that grasshoppers do not feed on organic remains or wastes further emphasizes their role as consumers in the ecosystem. While decomposers play a crucial role in breaking down dead organic matter and recycling nutrients back into the environment, grasshoppers rely on living plants as their source of sustenance.
As herbivores, grasshoppers contribute to the energy flow in the food chain by transferring the energy stored in plants to higher trophic levels. They play an important role in regulating plant populations and maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
By consuming plants, grasshoppers also help to disperse seeds and promote plant diversity. Their feeding habits can influence the distribution and abundance of plant species in their habitat.
5. Grasshoppers Take In Oxygen and Release Carbon Dioxide During Respiration
The respiratory exchange patterns of grasshoppers provide further evidence that they are consumers rather than producers. Grasshoppers, like other animals, take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide during respiration. This process is essential for their survival and energy production.
Unlike producers, such as plants, which use photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy-rich molecules, grasshoppers rely on consuming organic matter to obtain the energy they need.
Through respiration, grasshoppers break down the organic molecules they consume, releasing the stored energy and producing carbon dioxide as a waste product.
This respiratory exchange clearly distinguishes grasshoppers as consumers in the ecosystem. They depend on external sources of energy, primarily plants, to fuel their metabolic processes. By consuming plants, grasshoppers play a vital role in transferring energy from the primary producers to higher trophic levels in the food chain.
Furthermore, the respiratory process of grasshoppers highlights their reliance on oxygen, which is obtained from the environment. This dependence on oxygen further reinforces their classification as consumers, as producers like plants generate their own oxygen through photosynthesis.