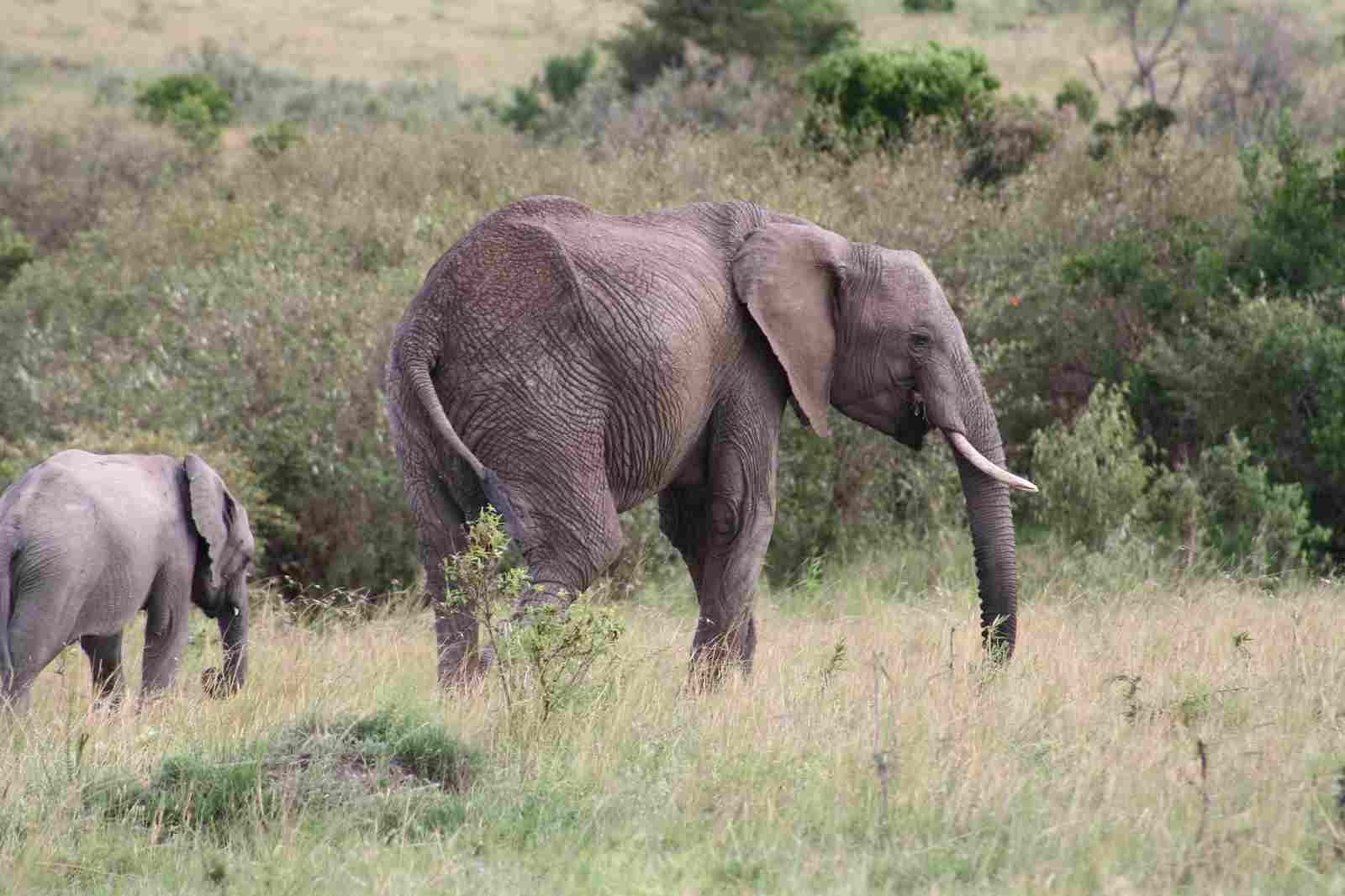
African Elephant Vs Asian Elephant Size, Weight, Ecological Comparison
African elephants have the advantage over Asian elephants in terms of size and weight, as well as possessing prominent tusks. Size and weight are important factors to consider when comparing these two species. African elephants are generally larger and heavier than Asian elephants, which can affect their physical capabilities, including bite force and overall strength. Furthermore, their habitat, behavior, and conservation status also differ, highlighting the unique characteristics of each species.
Key Outcomes
*Biological Comparison
The African elephant and the Asian elephant are both part of the Elephantidae family, but they belong to different genera and species. The African elephant is classified as Loxodonta africana, while the Asian elephant is known as Elephas maximus. Despite their biological differences, these majestic creatures share some similarities in terms of their physical characteristics and behaviors.
*Size and Weight Comparison
The size and weight of African and Asian elephants are notable points of comparison. In terms of size, African elephants are generally larger than their Asian counterparts. African elephants can reach heights of up to 13 feet at the shoulder, while Asian elephants typically reach heights of around 10 feet.
When it comes to weight, African elephants also outweigh Asian elephants. Adult African elephants can weigh between 5,000 to 14,000 pounds, whereas adult Asian elephants weigh between 4,000 to 11,000 pounds. These differences in size and weight contribute to variations in physical capabilities and behaviors between the two species.
*Physical Capability Comparison
African elephants are slightly stronger than Asian elephants, on average. While both elephants possess immense strength, it is important to note that strength alone does not determine which species can overpower and cause the death of the other.
African elephants are known for their larger size and weight compared to Asian elephants. This size advantage gives African elephants a greater physical presence and potentially more power in confrontations.
1). Taxonomy
The taxonomy of African and Asian elephants is an interesting subject to explore. Both species belong to the same genus, Loxodonta, but they are classified as different species. The African elephant is scientifically known as Loxodonta africana, while the Asian elephant is classified as Elephas maximus.
When comparing the taxonomy of these two species, it is important to note that they share some similarities but also have distinct differences. Both African and Asian elephants are part of the family Elephantidae, which includes all elephants. However, they are further classified into different subfamilies. African elephants belong to the subfamily Elephantinae, while Asian elephants belong to the subfamily Stegodontinae.
In terms of their genetic makeup, African and Asian elephants have some variations. Genetic studies have revealed that African elephants have a higher level of genetic diversity compared to Asian elephants. This could be attributed to the historical range and population size differences between the two species.
2). Appearance
The appearance of African and Asian elephants is distinct and can be attributed to various factors such as their coat, stature, and build.
In terms of their coat, both African and Asian elephants have different characteristics. African elephants have a sparse covering of hair on their bodies, while Asian elephants have a thicker coat of hair that covers their bodies. This difference in fur density is believed to be an adaptation to their respective habitats. African elephants, living in warmer climates, have less hair to help regulate their body temperature, while Asian elephants, inhabiting cooler regions, have a thicker coat for insulation.
Another aspect of their appearance is their stature and build. African elephants are generally larger and taller than their Asian counterparts. They have a robust and muscular build, with long, straight tusks that can reach impressive lengths. On the other hand, Asian elephants have a more compact and rounded body shape, with shorter and often curved tusks.
These differences in appearance between African and Asian elephants are not only fascinating but also play a role in their adaptation to their respective environments. The variations in their coat, stature, and build are a result of their evolutionary history and the unique challenges they face in their habitats.
3). Size
When comparing the size of African and Asian elephants, two key measurements are often considered: total body length and height at the shoulders.
African elephants are known for their impressive size. They are the largest land animals, with males reaching lengths of up to 23 feet and standing at a shoulder height of around 10 to 13 feet. In comparison, Asian elephants are slightly smaller. They typically measure between 19 and 21 feet in length and have a shoulder height of about 8 to 10 feet.
The difference in size between the two species can be attributed to various factors, including their evolutionary history and the availability of resources in their respective habitats. African elephants, with their larger size, have adapted to thrive in the vast savannas and forests of Africa, where they require more energy and strength to navigate and survive. Asian elephants, on the other hand, have adapted to the dense forests and grasslands of Asia, where their smaller size allows for easier movement and access to food sources.
4). Weight
When comparing the weight of African and Asian elephants, it is clear that African elephants are significantly heavier. African elephants are known for their massive size and weight, with males weighing between 5,000 and 14,000 kilograms (11,000 to 31,000 pounds). In contrast, Asian elephants are relatively lighter, with males weighing between 2,700 and 6,000 kilograms (6,000 to 13,000 pounds).
The difference in weight between the two species can be attributed to their distinct evolutionary paths and the environments they inhabit. African elephants, with their larger size and weight, have adapted to the more open and resource-rich habitats of Africa, where they require greater strength and bulk to survive and thrive. On the other hand, Asian elephants have adapted to the dense forests and grasslands of Asia, where their relatively lighter weight allows for easier movement and navigation through the vegetation.
The weight of elephants plays a crucial role in their overall physical capabilities and behaviors. The sheer mass of African elephants gives them an advantage in terms of dominance and intimidation, while the lighter weight of Asian elephants allows them to be more agile and maneuverable in their forested habitats.

5). Bite Force
When comparing the bite force of African and Asian elephants, it is important to consider the immense power behind their jaws. The bite force of an animal is a measure of its jaw strength and can provide insights into its feeding habits and overall physical capabilities.
African elephants, with their larger size and weight, possess a formidable bite force. Studies have estimated that the bite force of an African elephant can reach up to 6,000 pounds per square inch (psi). This immense pressure allows them to tear through vegetation, strip bark from trees, and even break branches.
On the other hand, Asian elephants, although smaller in size, still possess a significant bite force. While specific measurements are not as readily available, it is estimated that Asian elephants have a bite force of around 2,000 psi. This is still a considerable amount of force, allowing them to consume a variety of plant material.
The difference in bite force between the two species can be attributed to their distinct feeding habits and the types of vegetation they consume. African elephants, with their larger size and need for more food, have evolved to have a stronger bite force to handle tougher vegetation. Asian elephants, on the other hand, have adapted to a diet that includes softer plants and grasses, requiring a slightly lower bite force.
While African elephants have a higher bite force compared to Asian elephants, both species possess impressive jaw strength that enables them to feed on their respective diets and survive in their habitats.
6). Overall Physical Capacity (Which is Stronger?)
When comparing the overall physical capacity of African and Asian elephants, it is clear that the African elephant is stronger based on the factors we have evaluated and compared. While both species possess impressive physical capabilities, the African elephant’s larger size and weight give it an advantage in terms of strength.
In a violent confrontation between the two species, the African elephant’s size and strength would likely cause the demise of the Asian elephant. The African elephant’s formidable bite force, estimated to reach up to 6,000 pounds per square inch (psi), allows it to tear through vegetation, strip bark from trees, and even break branches. This immense power demonstrates the African elephant’s ability to exert force and overcome obstacles.
Although Asian elephants are smaller in size, they still possess significant physical capabilities. However, their bite force is estimated to be around 2,000 psi, which is lower than that of African elephants. This difference in bite force can be attributed to their distinct feeding habits and the types of vegetation they consume.
While both African and Asian elephants possess impressive physical capacities, the African elephant’s larger size, heavier weight, and stronger bite force give it the edge in terms of overall strength.
7). Habitat
African elephants are primarily found in sub-Saharan Africa, where they occupy a wide range of habitats, including savannas, grasslands, forests, and wetlands. They are adaptable and can thrive in diverse environments, from arid deserts to lush rainforests. This versatility allows them to access a variety of food sources and water, ensuring their survival even in challenging conditions.
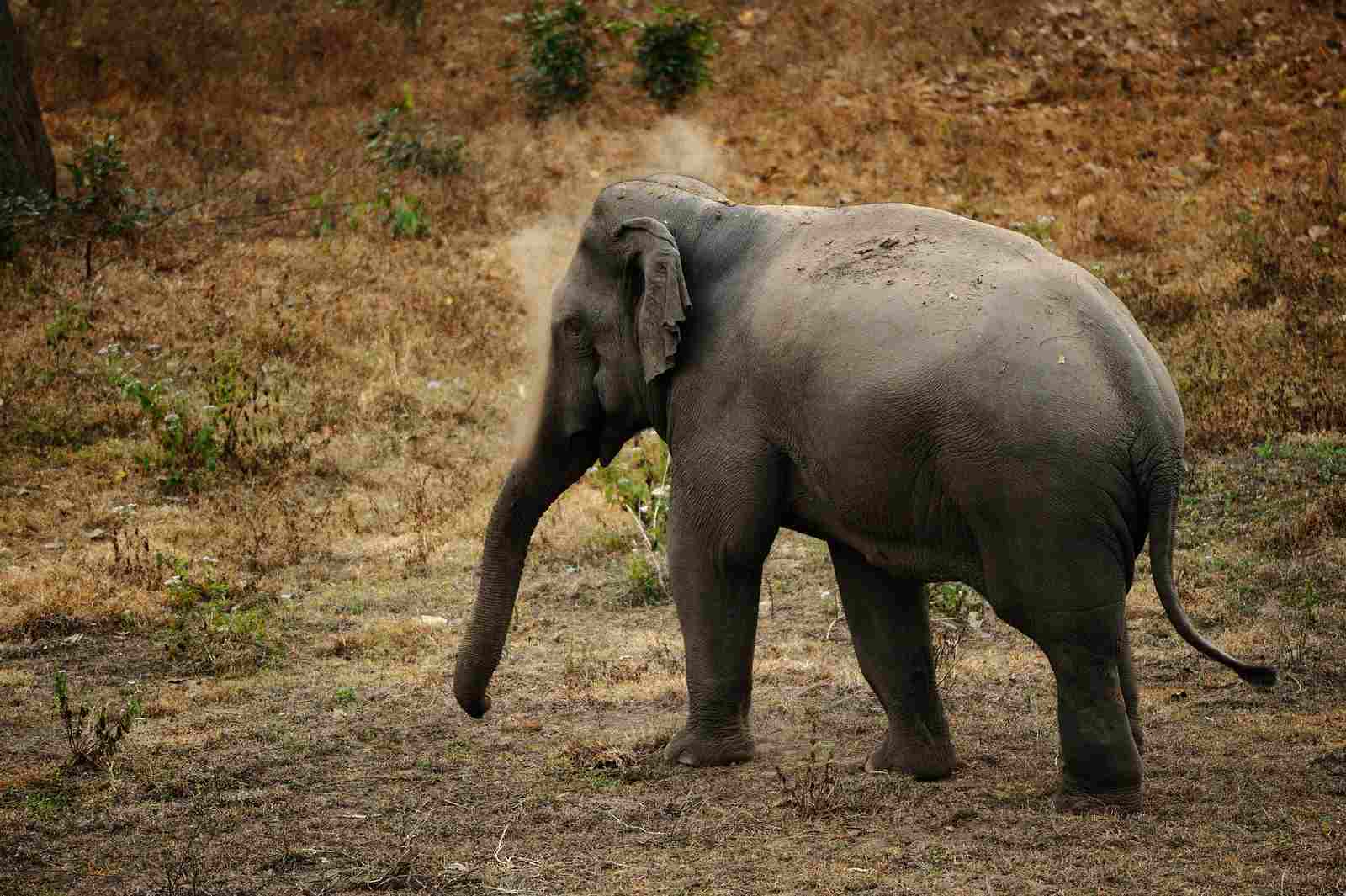
On the other hand, Asian elephants are native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia. They inhabit a range of habitats, including tropical rainforests, dry deciduous forests, and grasslands. However, their geographic range is more limited compared to African elephants. Asian elephants face habitat fragmentation and loss due to human activities such as deforestation and urbanization, which poses a significant threat to their survival.
The contrasting habitats of African and Asian elephants contribute to differences in their behavior and feeding patterns. African elephants, with access to a wider range of vegetation, are known to be more generalist feeders, consuming a variety of grasses, leaves, bark, and fruits. In contrast, Asian elephants have a more specialized diet, primarily feeding on grasses, bamboo, and a variety of plant species.
8). Lifespan
When comparing the lifespan of African elephants and Asian elephants, there are notable differences between the two species. African elephants have an average lifespan of around 60 to 70 years in the wild, although some individuals have been known to live into their 80s. On the other hand, Asian elephants have a slightly shorter lifespan, with an average of 50 to 60 years in the wild.
Several factors contribute to the difference in lifespan between the two species. One key factor is the size difference, with African elephants being larger and heavier than their Asian counterparts. Generally, larger animals tend to have longer lifespans. Additionally, African elephants have a more diverse diet, which may provide them with a greater range of nutrients and contribute to their longevity.
Another factor that affects the lifespan of both species is human impact. Both African and Asian elephants face threats from habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. These factors can significantly impact their survival and reduce their lifespan.
9). Behavior
When comparing the behavior of African elephants and Asian elephants, there are several notable differences between the two species.
In terms of feeding behavior, both African and Asian elephants are herbivores and primarily feed on vegetation such as grasses, leaves, and bark. However, African elephants have a more varied diet and are known to consume a wider range of plant species compared to Asian elephants. This difference in diet may be attributed to the availability of resources in their respective habitats.
Aggression is another aspect of behavior that differs between the two species. African elephants are generally considered to be more aggressive than Asian elephants. This aggression can be seen in their interactions with other elephants, as well as with other animals. African elephants are known to be more territorial and may exhibit aggressive behavior when defending their territory or resources.
Vocalization is another behavior that varies between African and Asian elephants. African elephants are known for their low-frequency rumbling calls, which can travel long distances and are used for communication within the herd. On the other hand, Asian elephants produce higher-pitched vocalizations that are often described as trumpeting sounds.
Social behavior is an important aspect of both African and Asian elephants. Both species live in matriarchal societies, where the females form tight-knit family groups led by an older, experienced female. These family groups are essential for social bonding, protection, and sharing of resources.
In terms of parenting behavior, both African and Asian elephants exhibit strong maternal instincts and care for their young. Female elephants play a crucial role in raising and protecting their offspring, providing them with guidance and teaching them essential survival skills.

10). Reproduction
When comparing the reproduction of African elephants and Asian elephants, there are several notable differences between the two species.
In terms of reproductive strategy, both African and Asian elephants are viviparous, meaning they give birth to live young. However, there is a difference in the gestation period between the two species. African elephants have a longer gestation period, lasting approximately 22 months, while Asian elephants have a gestation period of around 18 to 22 months. This difference in gestation period may be attributed to various factors, including genetic differences and environmental conditions.
Another aspect to consider is the comparison of the animals in terms of their reproductive behavior. African elephants are known to have a more complex social structure, which includes a dominance hierarchy among males. This hierarchy plays a role in the mating behavior of African elephants, as dominant males have greater access to females for breeding. In contrast, Asian elephants have a less pronounced dominance hierarchy, and mating behavior is less influenced by male dominance.
It is important to note that both African and Asian elephants face reproductive challenges due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. These factors can disrupt their natural reproductive patterns and impact population growth.
11). Danger Posed to Humans
Generally, both African and Asian elephants do not pose significant danger to humans unless threatened or provoked.
When considering the danger posed to humans by African and Asian elephants, there are several factors to take into account. Firstly, both species have the potential to come close to human settlements, especially when their natural habitats overlap with human-populated areas. However, it is important to note that aggression towards humans is relatively rare for both African and Asian elephants.
In terms of the rate of human deaths caused by these elephants, there is a notable difference between the two species. African elephants have been responsible for a higher number of human deaths compared to Asian elephants. This can be attributed to their larger size and more aggressive behavior in certain situations.
If you happen to encounter an elephant in the wild, it is crucial to take precautions to ensure your safety. It is recommended to maintain a safe distance and avoid any sudden movements or loud noises that may startle the animal. Additionally, it is important to respect their space and not approach or provoke them in any way.
When comparing the danger posed to humans by African and Asian elephants, it is evident that African elephants have a higher potential for aggression and have caused more human deaths. However, it is essential to remember that these incidents are relatively rare and most interactions between humans and elephants occur without any harm.

12). Conservation Status
The conservation status of African and Asian elephants is a matter of concern due to the main threats to their survival in the wild. Both species are classified as endangered or threatened, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts.
For African elephants, the main threats to their population include habitat loss and fragmentation, as well as poaching for ivory. The demand for ivory products continues to drive illegal hunting, leading to a decline in their numbers. Additionally, human-wildlife conflict poses a significant challenge, especially in areas where elephants come into contact with agricultural lands.
Asian elephants face similar threats, including habitat loss due to deforestation and conversion of land for agriculture. The fragmentation of their habitats restricts their movement and access to resources, further endangering their survival. Poaching for ivory and the capture of elephants for the entertainment industry also contribute to their declining numbers.
Conservation efforts for both species focus on protecting their habitats, implementing anti-poaching measures, and promoting sustainable practices that minimize human-elephant conflict. International organizations, governments, and local communities play a crucial role in these conservation initiatives.

Conclusion
I). SIMILARITIES
In comparing African and Asian elephants, several similarities can be observed. Both species belong to the same taxonomic family, Elephantidae, and share similar appearances, characterized by their large size, long trunks, and distinctive tusks. Additionally, both African and Asian elephants exhibit social behavior, living in matriarchal herds and displaying complex communication patterns.
Both species face significant threats to their survival, including habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. Conservation efforts for African and Asian elephants aim to address these common challenges and protect their populations in the wild.
II). DIFFERENCES
Despite their similarities, African and Asian elephants also have notable differences. One of the most apparent differences is their size. African elephants are generally larger, with males reaching heights of up to 13 feet and weighing around 12,000 pounds, while Asian elephants are smaller, with males averaging heights of 9 feet and weighing around 6,000 pounds.
Another significant difference lies in their habitats. African elephants inhabit a range of diverse ecosystems, including savannas, forests, and grasslands, while Asian elephants are primarily found in forested areas, including tropical rainforests and dry deciduous forests.
Furthermore, African and Asian elephants have distinct behaviors. African elephants are slightly more aggressive nature, while Asian elephants tend to be more docile. This difference in behavior is influenced by various factors, including their social structure and environmental conditions.