Smart House Meaning, Mechanism, Components and Examples
A smart house is a building that is equipped to be self-sustaining, through a network of artificial intelligence devices. This article discusses smart house meaning, mechanism, components and examples.
Things in a smart house include devices like smartphones, televisions, LED bulbs, thermostats, cameras, auto alerts, door locks, laptop computers, and tablets; which are seamlessly connected to each other through a central management system.
This article discusses the concept of the smart house and its components, based on the following outline;
-Smart House Meaning: 5 Ways to Define A Smart House
–How does a Smart House Work? Mechanism and Technological Architecture of Smart Buildings
Smart House Meaning: 5 Ways to Define a Smart House
A smart house, smart home or smart building, is a house that is equipped with interconnected devices, which enable automation and end-to-end control, of the house.
What makes a smart building ‘smart ‘ s the seamless integration of its components, such that it can carry out most of its functions through the use of data sharing, machine learning and automation.
When describing a smart house, some factors that must be put into consideration include;
1). The house
2). Components of the house (like doors, water-supply systems and windows)
3). The smart devices in the house
4). Integration of the central management system with the components of the house
5). Integration of the central management system with the smart devices
6). The integration of the smart devices with each other
7). The integration of the smart devices with the components of the house
8). Wireless network, which enables these components (devices, central management system, and building) to connect seamlessly to each other
The above list can help to understand how the smart house is designed, based on the connections between its components.
In most cases, the wireless network is internet-based. This knowledge can be used to create another definition of a smart house, as follows;
A smart house is a house which uses internet-connections to integrate its components and devices together, such that they function seamlessly as a unit.
The terms; smart house, smart home, and smart building, are all interchangeable and can be used in place of each other, for such definitions. A smart house can also be described based on electronics and technology, as follows;
A smart house is a house which uses the latest computer technologies and electronics, to automate or control a variety of devices and functions [3].
The word ‘latest’ used in the above definition, indicates that the concept of a smart house is often discussed within the context of recent technological developments.
Another definition of a smart house can be derived based on the concepts of sustainability and sustainable development;
A smart house is a building that is designed to achieve sustainability in terms of control, technological integration, data management, and energy consumption.
As is obvious in the above definition, energy, is yet another factor to consider, for smart houses. Based on this knowledge, an alternative definition can be provided as follows;
A smart house is a house whose functionalities are structured so as to combine modern technology with energy efficiency, energy conservation and renewable energy usage.
All the definitions given so far, can help to identify the attributes or features of a smart house.
Features of a smart house are; smart devices, seamless integration, end-to-end control, energy conservation and efficiency, modern technology, data management, and automation.
However, in real-life scenarios, a smart house may not have all the features mentioned in the given definitions.
The most unique and typical characteristic of a smart house is the presence of a central point of connection and control, which links the smart, internet-enabled devices and parts of the house.
Data management is the main purpose of the interconnections which make up a smart house. Through effective data transfer and management, functions can be carried out with efficiency and effectiveness.
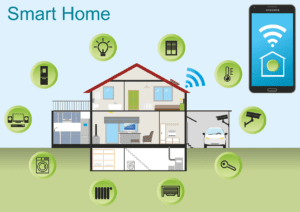
How does a Smart House Work? Mechanism and Technological Architecture of Smart Buildings
A smart house works based on three main functions, which are; data collection, data transfer and data utilization.
Data collection is done by any of the smart devices in the house, such as a camera or thermostat.
The type of data collected may vary from physicochemical data (light, temperature, motion) to digital and virtual data (time and date, digital files). These data are used for monitoring and control.
Data transfer is done using the wireless network connection. The data which has been collected can then be shared with other devices and components through the central management system.
In data utilization, the transferred data is used to make real-time decisions, based on which functions are executed. This may be as simple as the sounding of an alarm, or the dimming of light bulbs, or the opening/closing of windows and doors.
The final product of all three functions of a smart house, is end-to-end control, which can be observed in the form of automation.
Devices in a smart house are interconnected to each other, through the central management system.
This central management system may be in the form of an energy management software, which can be controlled using a laptop, tablet, or smart phone, among other devices.
It is the central management system that gives the house owner or user; end-to-end control of the smart house.
Some ways by which the user may gain control of the house include scheduling, energy saving, motion control, internal temperature regulation, and appliance operation.
In terms of energy-saving and appliance operation; a smart house provides functionalities that can help to regulate the use of energy; such as the switch to critical energy components when power from the utility grid is cut-off, and the house switches over to rely on solar panels.
Appliance-operation may involve regulating the operation of devices and electronics like water filters, refrigerators, laptops, doorbells, security cameras, smart locks, thermostats, water supply systems, and kitchen appliances.
In a smart house, wireless or hardwired connections may be used [2].
Wireless connections provide a relatively simple means of connecting building appliances, components and devices. However, hardwired connections are often more reliable, stable and less-likely to be compromised.
The technology behind a smart house is called Domotics; a term derived from the Latin word “Domus” which means Home [4].
Domotics is itself an aspect of Internet of Things (IoT) technology; which is concerned with the seamless connection or integration of devices and systems.
What Is in A Smart House?
Things in a smart house include smart devices like cameras, thermostats, speakers, electric kettles, laptops, refrigerators, auto alerts, smart phones, tablet phones, motion-sensitive lights, and smart clocks.
1). Smart Camera
A smart camera is a monitoring tool, that uses image-sensing technology to collect visual data from its surroundings, which it transfers via wireless network or hardwired connections, to a retrieval and storage system.
By collecting visual data, a smart camera tracks the surroundings of its installation point. The data can be analyzed from the storage system to which it is transferred.
In a smart house, cameras record surveillance footage from within and outside the house, which is transferred to the central management system through wireless or hardwired network.
Smart cameras may be installed indoor or outdoor.
Features which make a good smart camera are;
-Easy Installation
-Variable connection options
-Inbuilt data storage
-Cloud storage
-Easy to integrate with multiple devices
-Efficient image sensing and capture capability
-Wi-fi enablement
-Night Vision
2). Smart Thermostat as one of the Devices in a Smart House
A smart thermostat is a connective device equipped with sensors that monitor the physical conditions like temperature and humidity, of its environs.
Smart thermostats are important because they can help regulate the internal conditions of a smart house.
They can be used to determine the schedule of operation of the heating and cooling system of the house, as well as to detect problems like fire outbreaks.
Features of a good smart thermostat are;
-Easy installation
-Wireless connection enablement
-Compatibility with various integration systems
-Efficient temperature and humidity sensors
-Proximity sensor
-Integrated and easy-to-use control tool
3). Smart Speaker
A smart speaker is a sound-sensitive, connective device, which is usually equipped with voice-control capabilities, and may function as a virtual assistant.
While smart speakers can perform most of the functions of conventional speakers, they are capable of carrying out even more tasks.
As a virtual assistant, a smart speaker can be used to control other devices and components of a smart house, by issuing audio prompts that facilitate the execution of a function.
Smart speakers may control wireless lighting and audio systems, motion sensors, thermostats and other appliances.
In some smart houses, a smart speaker can serve as a tool for boosting energy efficiency, and achieving energy conservation; by regulating the operations of devices.
Some smart speakers can be used for scheduling; simply by programming time-based functions in these speakers.
4). Smart Electric Kettles
A smart kettle has basically the same functionalities as a conventional electric kettle. However, it is usually equipped with wire connection capabilities and can be controlled remotely, often using a software on a laptop or smart phone.
In a smart house, this appliance can be integrated into the interconnected network, and may be automated on a schedule basis by the central management system.
5). Laptops
A laptop is a portable personal computer which is powered by a rechargeable battery, and us equipped with an alphanumeric keyboard and a screen [1].
In a smart house, a laptop can play a very important role, of operating the software tools that are used to control the various interconnected devices.
6). Smart Refrigerators
A smart refrigerator is a refrigerator that is equipped with modern technology, that enables it to perform enhanced functions like automated internal temperature regulation, operation-scheduling, and data sharing.
A smart refrigerator may be integrated with the other devices in a smart house, through a wireless network. Some smart refrigerators can regulate their cooling temperature based on the items stored in them.
7). Smart Phones and Tablets
Like laptop computers, smart phones and tablets are capable of coordinating the interconnected devices in a smart house, mainly using software tools and wireless servers.
They provide a more portable and simple means of operating smart devices and sharing relevant data.
8). Motion-Sensitive Lights
Motion-sensitive lights are lights which operate based on the detection of motion within their surroundings.
In a smart house, these appliances may be integrated with the central management system, which would enable the user to have more control over their operations.
9) Smart Clock as one of the Devices in a Smart House
A smart clock is time data-equipped, however, it is usually capable of carrying out other functions like wireless connection, data sharing and automation.
In a smart house, a smart clock may be used for scheduling, music, and data accessing, among other functions.
Smart House Examples
Basically, any house which comprises of interconnected devices is a smart house.
Some examples of a smart house or smart building are;
- The Frasers Tower in Singapore
- Glumac in China
- Duke Energy Center, North Carolina
- DPR Construction, California
- Fulton East, Chicago
- Oakland City Center
- Vodaphone Group Global Headquarters, England
- The Crystal Building, England

- U.S. Green Building Council Headquarters
Conclusion
A smart house, smart building, smart home or intelligent building, is a building that is equipped with technological components and devices that are connected seamlessly to each other, such that they can share data, and carry out functions through automation and machine learning.
The technology of smart house development is known as Domotics, and it is an aspect of IoT technology.
Components that make up a smart house include;
1. Smart Camera
2. Smart Thermostat
3. Smart Speaker
4. Smart Electric Kettles
5. Laptops
6. Smart Refrigerators
7. Smart Phones and Tablets
8. Motion-Sensitive Lights
9. Smart Clock
For a smart house to be efficient, all the above devices and appliances must be seamlessly connected to each other through a central management system, such that they can share data and execute functions collaboratively.
What makes up a smart house or smart home are the integrated components, the control systems, and the automated processes.
Examples of smart houses are;
- The Frasers Tower in Singapore
- Glumac in China
- Duke Energy Center. North Carolina
- DPR Construction, California
- Fulton East, Chicago
- Oakland City Center
- Vodaphone Group Global Headquarters, England
- The Crystal Building, England
- U.S. Green Building Council Headquarters
References
1). Atkinson, P. (2005). “Man in a Briefcase: The Social Construction of the Laptop Computer and the Emergence of a Type Form.” Journal of Design History, Vol. 18, No. 2 (Summer, 2005), pp. 191-205. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/3527036. (Accessed 27 March 2022).
2). Laurenson, C. (2021). “Smart Home Choices Wired vs. Wireless.” Available at: https://www.tltechsmart.com/2020/08/19/smart-home-choices-wired-vs-wireless/. (Accessed 27 March 2022).
3). Shea, S. (2020). “Smart Home or Building (home automation or domotics).” Available at: https://internetofthingsagenda.techtarget.com/definition/smart-home-or-building. (Accessed 27 March 2022).
4). Simonet, A. C.; Noyce, A. J. (2021). “Domotics, Smart Homes, and Parkinson’s Disease.” Journal of Parkinson’s Disease 11(s1):1-9. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3233/JPD-202398. (Accessed 27 March 2022).
