Sun Bear Vs Sloth Bear Size, Weight, Overall Comparison
In a hypothetical showdown between a sun bear and a sloth bear, both members of the Ursidae family, we explore the potential dynamics of this confrontation, emphasizing the significant differences in size, weight, and aggression between these two bear species. This analysis aims to elucidate why a sloth bear might emerge victorious in a physical encounter with a sun bear, given its larger size, heavier build, and more aggressive nature.
Sun Bear vs Sloth Bear: Analyzing the Likely Victor in a Clash
In a theoretical confrontation involving a sun bear and a sloth bear, the outcome of a fight hinges on the substantial variations in size, weight, and aggression within the Ursidae family. While both are formidable bears, the sloth bear’s larger size, heavier build, and more aggressive demeanor could tip the scales in its favor.
I). Size, Weight, and Aggression Disparities:
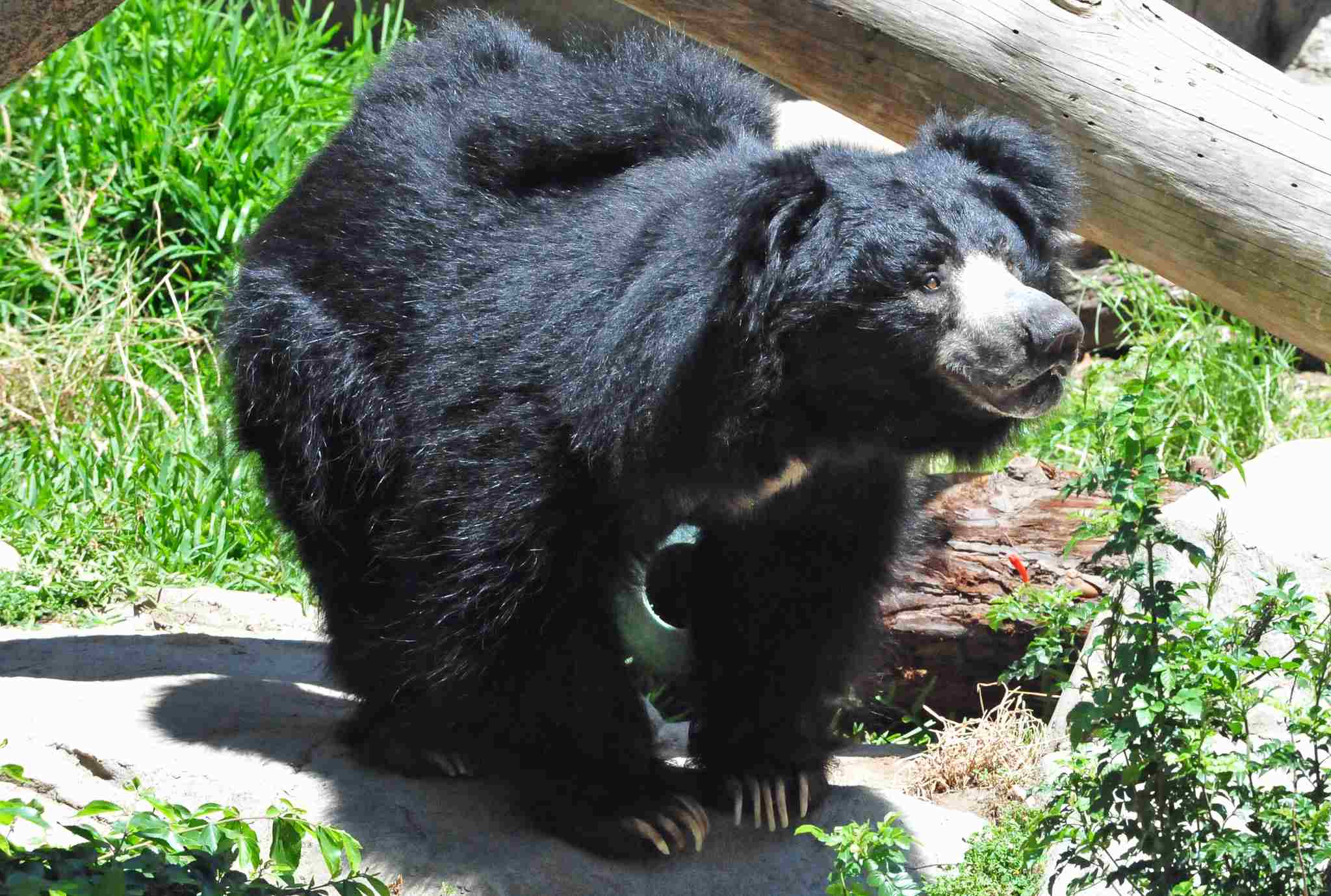
– Bears within the Ursidae family exhibit notable differences in size, weight, and aggression. Sun bears, being the smallest bear species, typically weigh between 27 to 80 kg, while sloth bears, renowned for their size and aggression, can weigh between 55 to 145 kg. These considerable disparities underscore the diversity within the bear family.

II). Individual and Species-Specific Traits:
– Individual and species-specific traits play a decisive role in shaping the outcome of a confrontation between a sun bear and a sloth bear. The sloth bear’s larger size, heavier build, and more aggressive nature collectively contribute to its potential advantage in a physical altercation.
III). Sloth Bear’s Dominant Physical Attributes:
– Sloth bears, characterized by their substantial size, robust build, and notable aggression, possess dominant physical attributes compared to sun bears. The sloth bear’s larger size, heavier weight, and aggressive demeanor collectively enhance its overall strength, providing a distinct edge in a physical clash.
IV). Potential Strategies of the Sun Bear:
– Sun bears, although smaller in size, may employ their agility and climbing abilities as potential strategies in a confrontation. However, the sloth bear’s larger size, greater weight, and aggression could pose challenges for the sun bear to effectively counter.
V). Overall Dynamics:
– In this hypothetical scenario, the sloth bear is likely to emerge victorious in a fight against a sun bear due to its larger size, heavier build, and more aggressive nature. While the sun bear may attempt strategic maneuvers, the overall dynamics favor the sloth bear in this hypothetical confrontation.
*Details of Comparison
| Criteria | Sun Bear | Sloth Bear |
| Taxonomy | Ursidae, Helarctos malayanus |
Ursidae, Melursus ursinus
|
| Appearance | Sleek with short fur, crescent chest |
Shaggy fur, V-shaped chest mark, distinctive facial features
|
| Size | Similar, sun bears possibly larger | Similar |
| Weight | 27–80 kg | 55–95 kg |
| Bite Force (PSI) | ~650 PSI |
Limited information
|
| Physical Offensive Advantages | Sharp claws, powerful jaws |
Long, powerful claws for digging
|
| Physical Defensive Advantages | Climbing abilities, agility |
Aggression, standing on hind legs
|
| Speed | 40 km/h (25 mph) |
Limited information
|
| Agility | Agile climbers |
Agile on ground and in trees
|
| Overall Physical Capacity | Well-adapted for climbing, strong bite |
Adapted for ground and tree-based foraging
|
| Habitat Preference(s) | Dense tropical forests |
Various habitats including grasslands and forests
|
| Tracks | Smaller with prominent claw marks |
Distinctive footprint with long claws
|
| Lifespan | 20–25 years |
About 20–30 years
|
| Mode of Feeding | Omnivores |
Mainly insectivores
|
| Intelligence | Considered intelligent |
Limited studies, general cognitive abilities
|
| Social Behavior | Generally solitary | Typically solitary |
| Mode of Reproduction | Solitary, brief mating associations |
Solitary, brief mating associations
|
| Parental Behavior | Females raise cubs independently |
Females build nests, actively involved in care
|
| Proximity to Human Areas | Can be found near human settlements |
Occurs in areas with human populations
|
| Behavior Toward Humans | Generally shy |
Can be aggressive, potential for conflicts
|
| Danger Posed to Humans | Rarely poses significant threat |
Can be dangerous if threatened, potential for attacks
|
| Associated Precautions | Habitat protection, minimizing conflicts |
Conservation strategies include awareness and habitat protection
|
| Conservation Status | Vulnerable | Vulnerable |
1. Taxonomy
Sun Bear (Helarctos malayanus):
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Ursidae
Genus: Helarctos
Species: malayanus
Sloth Bear (Melursus ursinus):
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Family: Ursidae
Genus: Melursus
Species: ursinus
2. Appearance
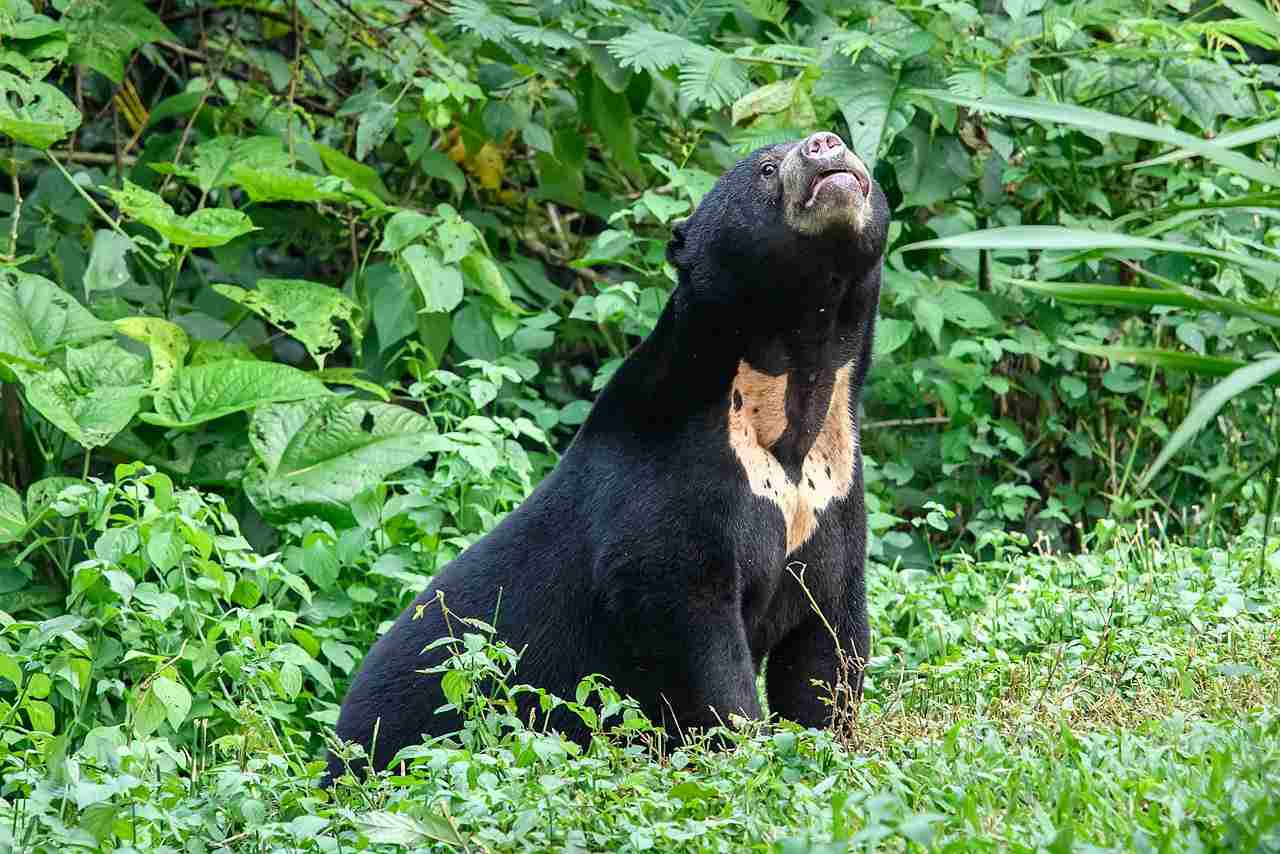

Sun Bear:
Short fur, sleek body, and a distinctive, crescent-shaped chest marking.
Rounded ears, small eyes, and a short snout.
Sloth Bear:
Shaggy, long fur with a distinct V-shaped mark on the chest.
Long, flexible snout, large lips, and large, round ears.
Comparison: Sun bears have a sleeker appearance, while sloth bears exhibit shaggier fur and distinctive facial features.
Ecological Implications: The appearance of each species may be adapted to their specific habitats and lifestyles, influencing factors like thermoregulation and camouflage.
3. Size
Sun Bear:
Length: 120–150 cm (47–59 in)
Shoulder Height: 70 cm (28 in)
Sloth Bear:
Length: 120–150 cm (47–59 in)
Shoulder Height: 60–90 cm (24–35 in)
Comparison: Both species share similar sizes, with sun bears possibly having a slightly larger shoulder height.
Ecological Implications: Size can impact resource requirements and niche occupation within their respective habitats.
4. Weight
Sun Bear:
Average: 27–80 kg (60–176 lbs)
Sloth Bear:
Average: 55–95 kg (121–209 lbs)
Comparison: Sloth bears generally weigh more than sun bears.
Ecological Implications: Variances in weight may influence feeding behaviors, energy expenditure, and competition for resources.
5. Bite Force (PSI)
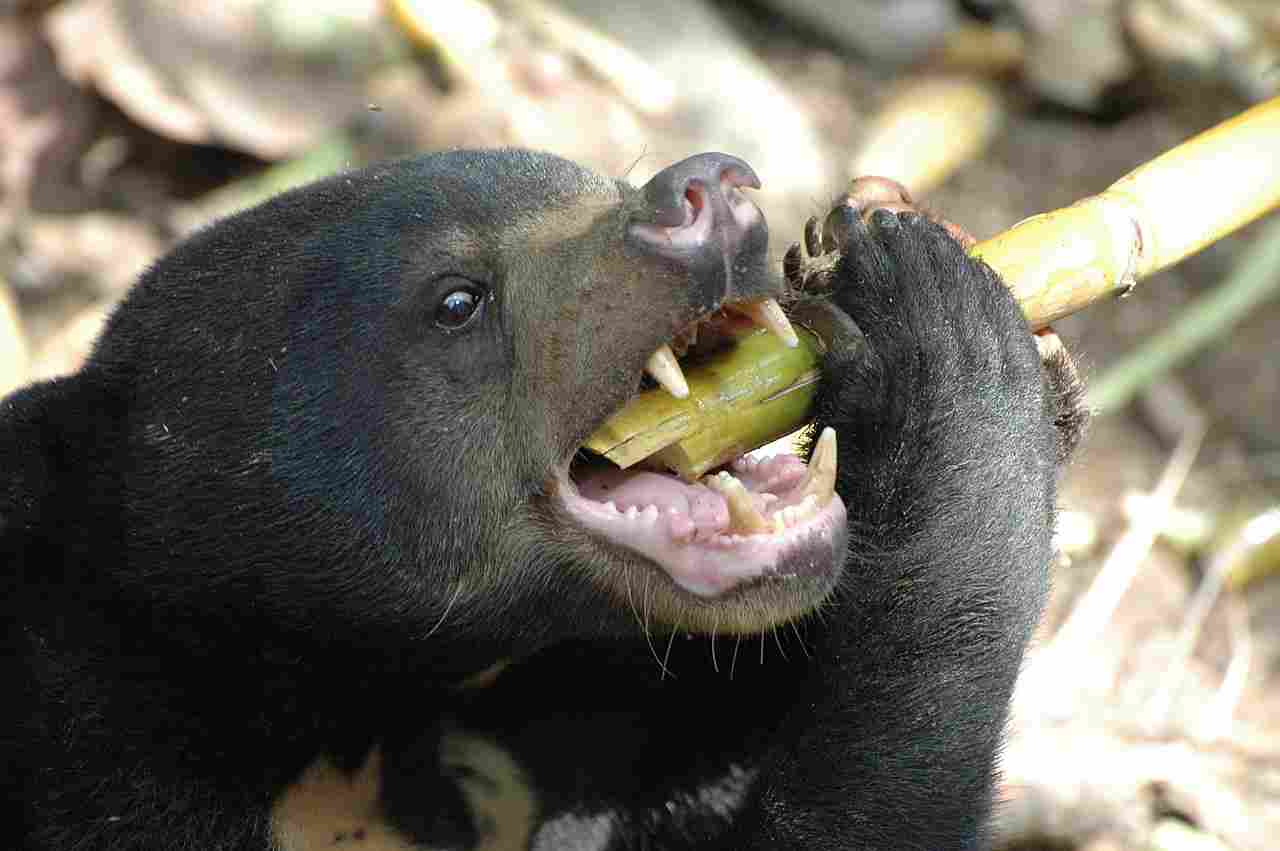

Sun Bear:
Estimated at around 650 PSI.
Sloth Bear:
Bite force not well-documented, but bears generally have powerful jaws.
Comparison: Sun bears have a documented bite force, while sloth bear information is limited.
Ecological Implications: Bite force relates to feeding habits and hunting capabilities, impacting the ecological roles each species plays in their environments.
6. Physical Offensive Advantages
Sun Bear:
Sharp claws and powerful jaws aid in hunting small vertebrates and insects.
Sloth Bear:
Long, powerful claws for digging termite mounds and ant nests.
Comparison: Sun bears use their offensive capabilities for hunting, while sloth bears employ theirs for extracting insects.
Ecological Implications: Offensive adaptations contribute to their roles in controlling insect populations within their ecosystems.
7. Physical Defensive Advantages
Sun Bear:
Climbing abilities, agility, and powerful forelimbs for self-defense.
Sloth Bear:
Slightly more aggressive temperament, and the ability to stand on hind legs for intimidation.
Comparison: Sun bears rely on agility, while sloth bears use aggression and intimidation as defensive strategies.
Ecological Implications: Defensive mechanisms impact interactions with predators and other species, influencing their roles in the ecosystem.
8. Speed (Km/hour or Mile/hour)
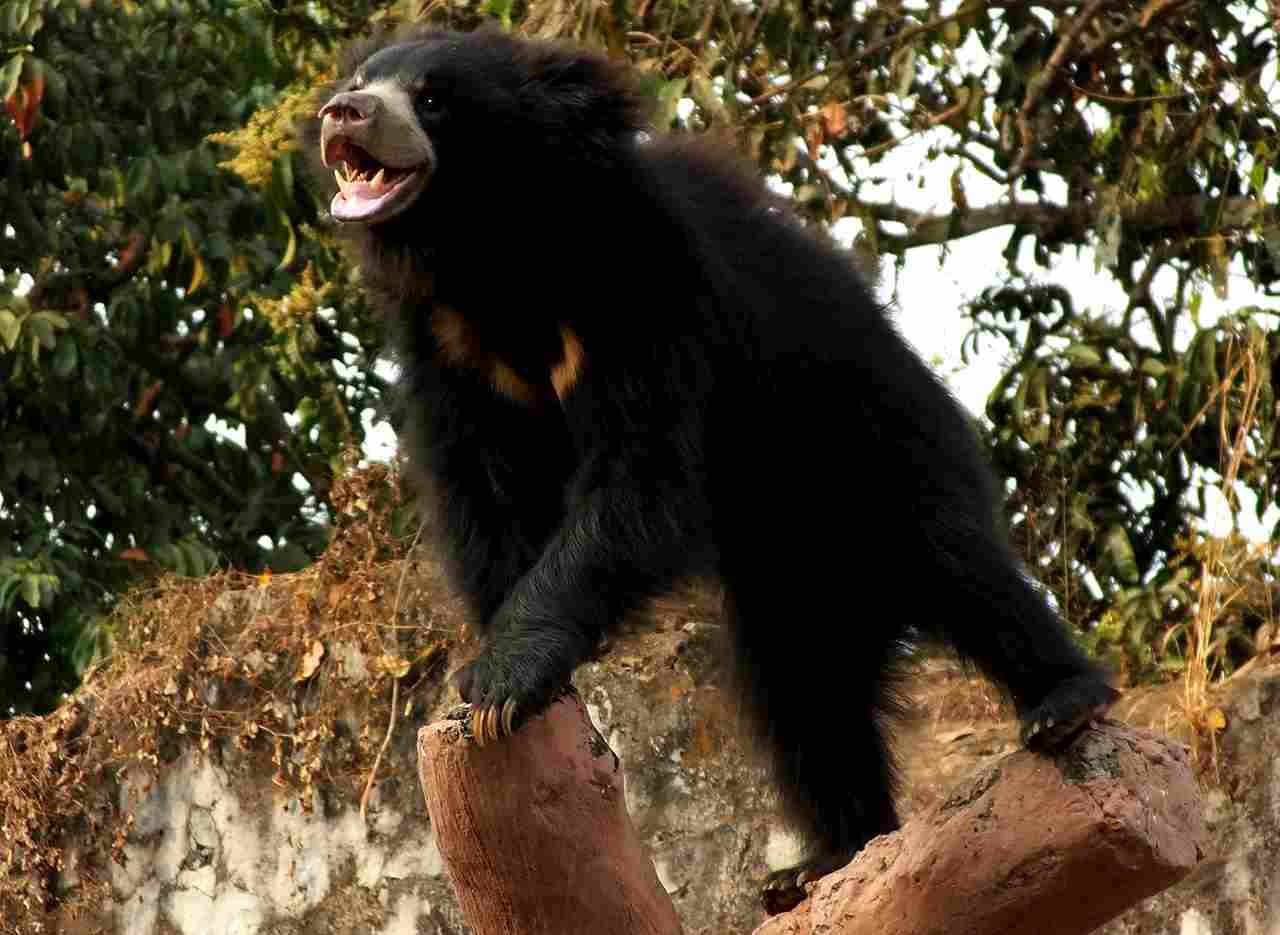

Sun Bear:
Estimated speed of 40 km/h (25 mph).
Sloth Bear:
Limited information, but bears generally are not known for high-speed pursuits.
Comparison: Sun bears are known to be faster runners than sloth bears.
Ecological Implications: Speed can influence hunting success, evasion of predators, and overall mobility within their habitats.
9. Agility
Sun Bear:
Agile climbers with strong limbs and sharp claws.
Sloth Bear:
Agile on the ground, adept at climbing trees.
Comparison: Sun bears exhibit agility in trees, while sloth bears display agility both on the ground and in trees.
Ecological Implications: Agility impacts their ability to access different parts of their habitats, find food, and avoid threats.
10. Overall Physical Capacity
Sun Bear:
Well-adapted for climbing and have a strong bite for hunting.
Sloth Bear:
Adapted for ground and tree-based foraging, with powerful claws and jaws.
Comparison: Sun bears emphasize climbing, while sloth bears are adapted for both ground and tree activities.
Ecological Implications: Their overall physical capacity shapes their roles in the ecosystem, affecting prey selection and habitat use.
11. Habitat Preference(s)
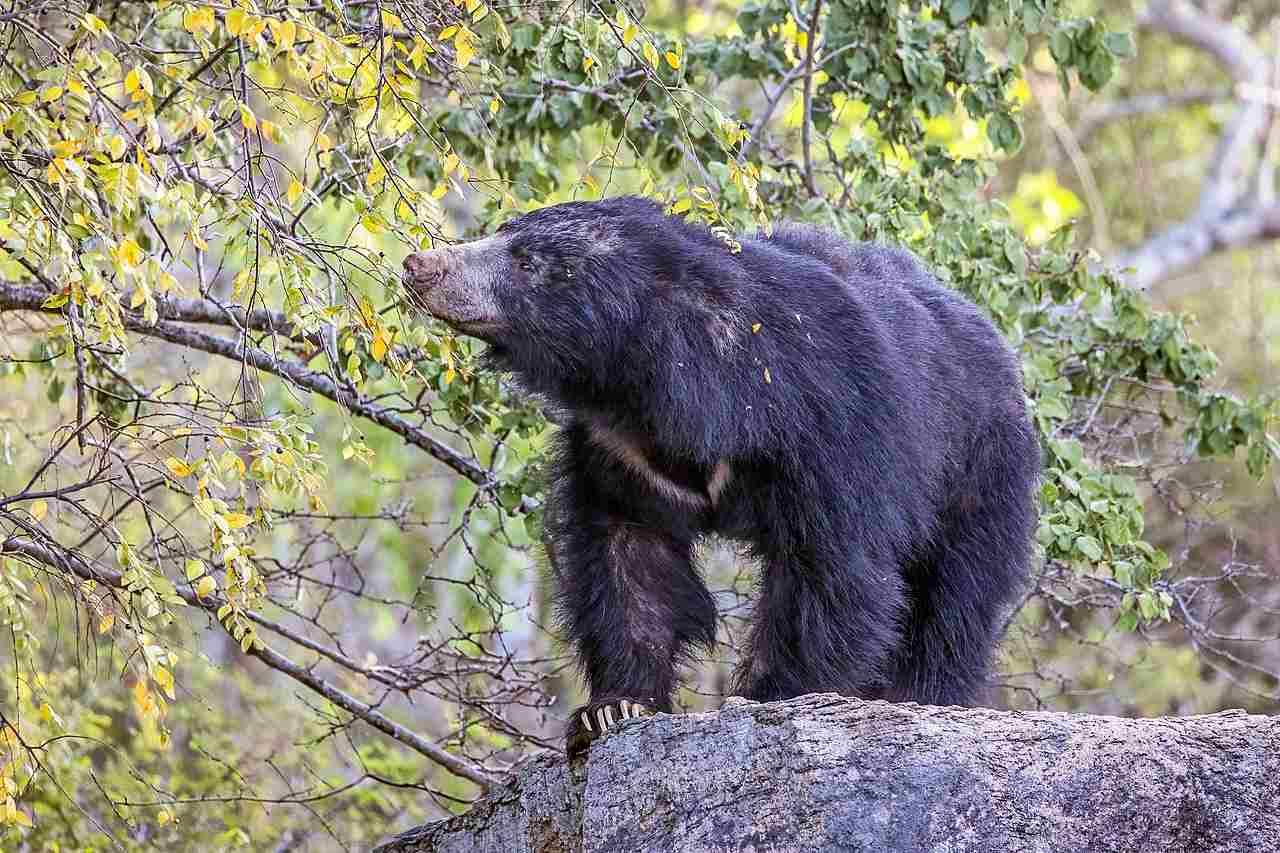

Sun Bear:
Dense tropical forests, but they can also be found in other habitats.
Sloth Bear:
Various habitats, including grasslands, scrublands, and forests.
Comparison: While both occupy forests, sloth bears have a broader habitat range.
Ecological Implications: Habitat preferences influence their interactions with other species and their ecological impact.
12. Tracks
Sun Bear:
Smaller, compact tracks with prominent claw marks.
Sloth Bear:
Distinctive footprint with long claws, especially the middle two toes.
Comparison: Track features differ, with sloth bear tracks often showing more pronounced claw marks.
Ecological Implications: Tracking can aid in studying their movement patterns and understanding their presence in different habitats.
13. Lifespan
Sun Bear:
Typically 20–25 years in the wild.
Sloth Bear:
About 20–30 years in the wild.
Comparison: Similar lifespans, with some variation.
Ecological Implications: Lifespan affects population dynamics and their contributions to ecosystem processes over time.
14. Mode of Feeding
Sun Bear:
Omnivores with a diet consisting of fruits, insects, small vertebrates, and honey.
Sloth Bear:
Mainly insectivores, with termites and ants forming a significant part of their diet.
Comparison: Sun bears have a broader omnivorous diet, while sloth bears specialize in insectivory.
Ecological Implications: Differences in feeding modes contribute to their ecological roles, impacting local fauna and flora.
15. Intelligence

Sun Bear:
Considered intelligent, displaying problem-solving skills.
Sloth Bear:
Limited studies on intelligence, but bears, in general, show cognitive abilities.
Comparison: Both species exhibit intelligence, but detailed studies on sloth bear intelligence are scarce.
Ecological Implications: Intelligence influences their adaptability and resource utilization within their environments.
16. Social Behavior
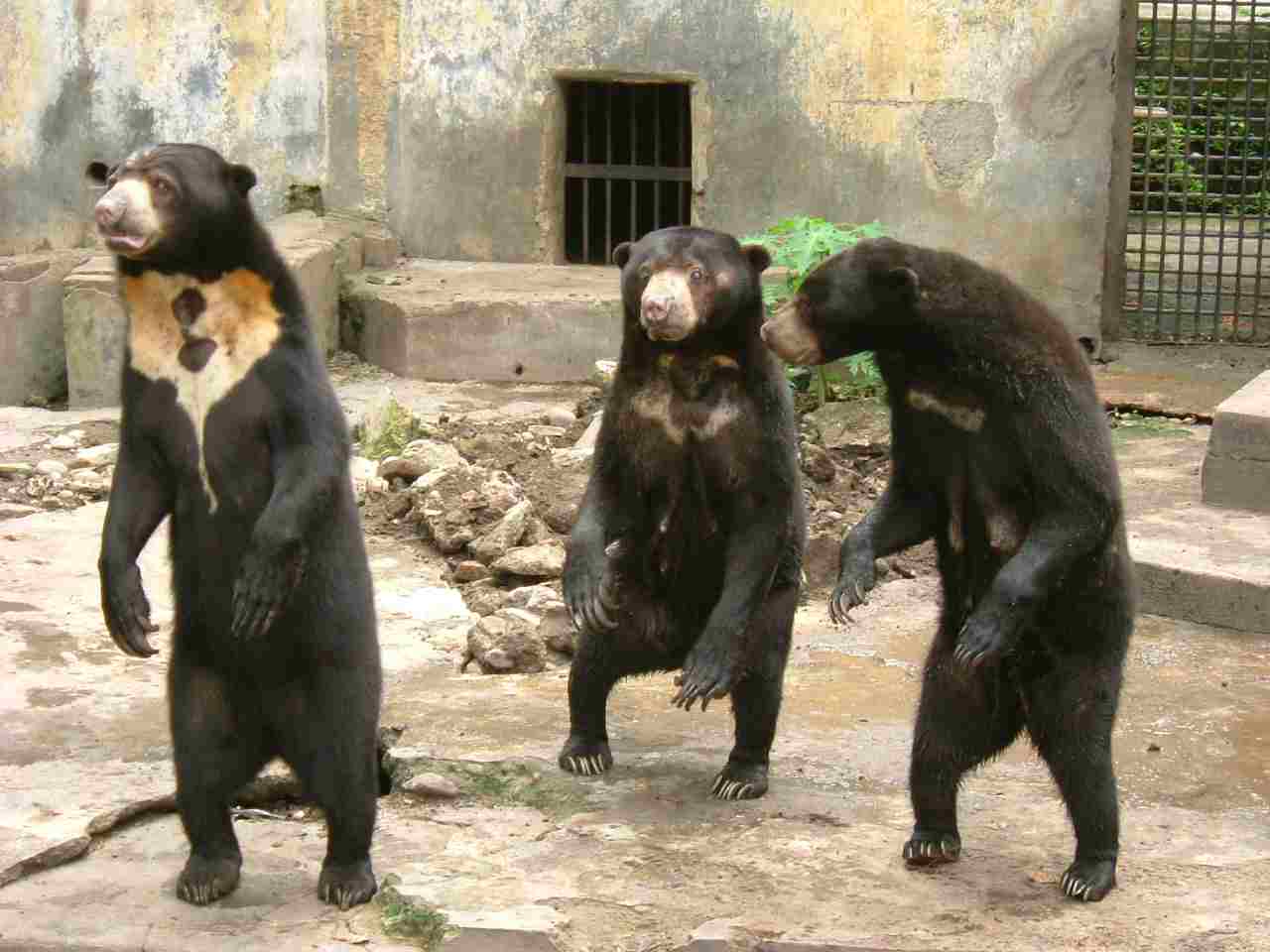

Sun Bear:
Generally solitary, except during mating or when raising cubs.
Sloth Bear:
Typically solitary, but they may tolerate other bears during feeding on termite mounds.
Comparison: Both species are predominantly solitary.
Ecological Implications: Solitary behavior affects competition for resources and population dynamics.
17. Mode of Reproduction
Sun Bear:
Typically solitary, with mating pairs coming together for a brief period.
Sloth Bear:
Solitary, with mating pairs forming temporarily.
Comparison: Similar reproductive strategies, involving brief associations for mating.
Ecological Implications: Reproductive behaviors impact population dynamics and genetic diversity within their habitats.
18. Parental Behavior
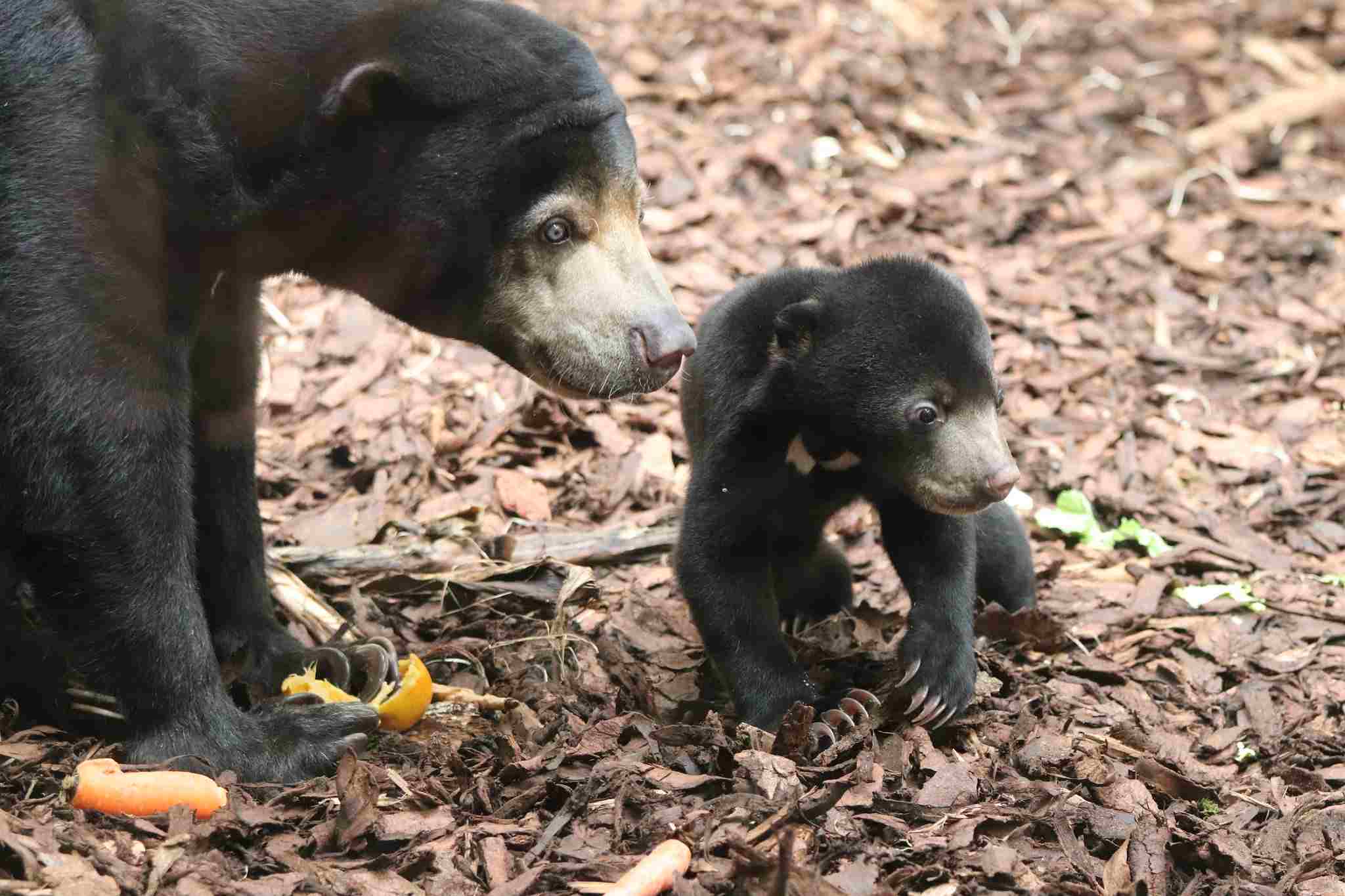

Sun Bear:
Females are responsible for raising cubs independently.
Sloth Bear:
Females build nests for cubs, and they are actively involved in their care.
Comparison: While both species exhibit maternal care, sloth bears show more active involvement in cub care.
Ecological Implications: Parental behaviors influence cub survival rates and population dynamics.
19. Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas
Sun Bear:
Can be found in proximity to human settlements, especially if suitable habitats are fragmented.
Sloth Bear:
Occurs in areas with human populations, sometimes leading to human-bear conflicts.
Comparison: Both species may come into contact with humans, posing challenges for conservation and safety.
Ecological Implications: Human interactions can impact their behavior, habitats, and survival.
20. Behavior Toward Humans
Sun Bear:
Generally shy and avoids confrontations with humans.
Sloth Bear:
Can be aggressive if threatened, leading to conflicts in human-dominated landscapes.
Comparison: Sun bears tend to be less aggressive towards humans compared to sloth bears.
Ecological Implications: Behavioral responses influence their coexistence or conflicts with human communities.
21. Danger Posed to Humans
Sun Bear:
Rarely poses a significant threat to humans.
Sloth Bear:
Can be dangerous if cornered or feels threatened, potentially leading to attacks.
Comparison: Sloth bears may pose a higher risk to humans than sun bears.
Ecological Implications: Perceived danger affects human attitudes towards conservation efforts and coexistence strategies.
22. Associated Precautions
Sun Bear:
Conservation efforts often focus on habitat protection and minimizing human-bear conflicts.
Sloth Bear:
Conservation strategies include raising awareness, managing conflicts, and protecting habitats.
Comparison: Both species require conservation measures, but specific precautions vary based on their behaviors and interactions with humans.
Ecological Implications: Conservation efforts play a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance and preserving these bear species.
23. Conservation Status

Sun Bear:
Classified as “Vulnerable” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Sloth Bear:
Classified as “Vulnerable” by the IUCN.
Comparison: Both sun bears and sloth bears share a vulnerable conservation status.
Ecological Implications: Conservation status reflects the need for urgent measures to protect their populations and habitats.
Summary of Comparison
Taxonomy:
Both belong to the Ursidae family but differ in genus and species.
Appearance:
Sun bears have a sleeker appearance with short fur and a distinctive chest marking.
Sloth bears exhibit shaggier fur, a V-shaped chest mark, and distinctive facial features.
Size:
Similar sizes, with sun bears possibly having a slightly larger shoulder height.
Weight:
Sloth bears generally weigh more than sun bears.
Bite Force (PSI):
Sun bears have an estimated bite force of around 650 PSI; limited information for sloth bears.
Physical Offensive Advantages:
Sun bears use sharp claws and powerful jaws for hunting.
Sloth bears have long, powerful claws for digging termite mounds.
Physical Defensive Advantages:
Sun bears rely on climbing abilities and agility.
Sloth bears use aggression and standing on hind legs for defense.
Speed:
Sun bears are faster runners than sloth bears.
Agility:
Sun bears are agile climbers.
Sloth bears are agile on the ground and in trees.
Overall Physical Capacity:
Sun bears are well-adapted for climbing and have a strong bite.
Sloth bears are adapted for ground and tree-based foraging with powerful claws and jaws.
Habitat Preference(s):
Both occupy forests, but sloth bears have a broader habitat range.
Tracks:
Sun bear tracks are smaller with prominent claw marks.
Sloth bear tracks show a distinctive footprint with long claws.
Lifespan:
Similar lifespans, with some variation.
Mode of Feeding:
Sun bears are omnivores with a broad diet.
Sloth bears are mainly insectivores, focusing on termites and ants.
Intelligence:
Both exhibit intelligence, with detailed studies more common for sun bears.
Social Behavior:
Both are predominantly solitary.
Mode of Reproduction:
Both species have similar reproductive strategies with brief mating associations.
Parental Behavior:
Sun bear females raise cubs independently.
Sloth bear females actively build nests and care for cubs.
Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Both can be found near human settlements, potentially leading to conflicts.
Behavior Toward Humans:
Sun bears are generally shy.
Sloth bears can be more aggressive, especially if threatened.
Danger Posed to Humans:
Sloth bears may pose a higher risk to humans than sun bears.
Associated Precautions:
Conservation efforts focus on habitat protection and minimizing conflicts for both.
Conservation Status:
Both are classified as “Vulnerable” by the IUCN.
Conclusion
I. Similarities
Both sun bears and sloth bears belong to the Ursidae family and share a “Vulnerable” conservation status.
II. Differences
Sun bears tend to be less aggressive toward humans and have a broader omnivorous diet, while sloth bears can be more aggressive and specialize in insectivory. The differences in their appearances, habitats, and parenting behaviors contribute to their unique ecological roles.