Robotics Definition, History, Pros/Cons, Examples and Importance
Robotics refers to the description, development and deployment of intelligent machines that are designed to perform tasks traditionally handled by humans. This article discusses robotics definition, history, pros and cons, examples, and importance, as follows;
-Robotics Definition: An Introduction to Robotics and its Major Fields
-Advantages and Disadvantages of Robotics
-Examples of Robotics Applications
Robotics Definition: An Introduction to Robotics and its Major Fields
Robotics is the concept, development and utilization of autonomous machines with human-like locomotive and/or analytic capabilities.
The above is a simple definition of robotics that highlights its most basic details, including the term autonomous; which is based on the tendency of robots to operate without active human control.
Automation-robotics is in fact one of the types of robotics, and focuses on optimizing the autonomous functioning and self-dependency of robotic systems. Other types of robotics are mentioned in the alternative robotics definition below;
Robotics is an engineering field or practice that draws from computer, physical and biological sciences to design and deploy systems called robots to handle human tasks; according to the principles of any of its sub-disciplines like motion planning and control, automation, signal processing, micro and field robotics.
It can be observed above that robotics is linked to multiple fields that include physics, computer science and biological science. Consulting these fields enables robotics engineers to come up with efficient and workable concepts.
In the alternative robotics definition below, some related fields and concepts are highlighted;
Robotics is an innovative discipline that entails the development of human-like, mobile, processing systems, using tools and ideas from mechanical and electrical engineering, artificial intelligence, machine learning, neural network models, locomotive and neurological biology, and Internet of Things (IoT), among other fields [5].
The next robotics definition also highlights some of examples of robotics systems and utilization;
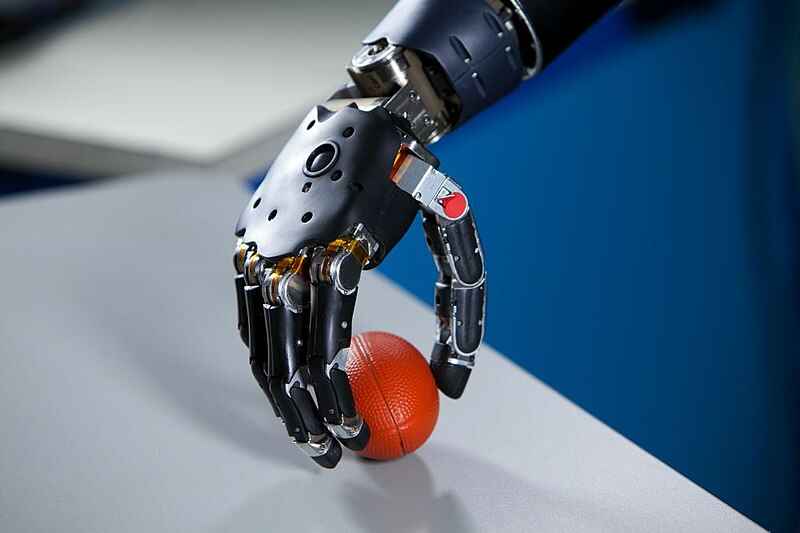
Robotics is the concept, development and use of intelligent autonomous machines, designed to perform human functions. Examples of robotics include the development and deployment of surveillance drones, autonomous sustainable irrigation systems, process-robotics for sustainable manufacturing, self-driving electric cars, and robotic prosthetics in medicine.

The major fields of robotics are;
1). Electrical engineering
2). Programming and deep leaning
3). Bioengineering
4). Language modeling
5). Data management
History of Robotics
The history of robotics as a concept, can be traced back to the work of Ancient Greek mathematician Archytas of Tarentum; who around 350 B. C. built a steam-driven mechanical contraption called "The Pigeon", and having the geometry of a bird, which was almost entirely autonomous in its locomotion [2].
Modern efforts to make robotic ls a working concept began mainly in the early nineteenth century, as a result of the introduction, widespread acceptance and rapid growth of the factory system of production, that used machines and a large workforce to achieve mass production.
While no actual robot was developed at this time, the efforts to automate aspects of labor, facilitated the advent and improvement of several important technologies, such as the steam turbine.
Next came the coining of the terms; robot and robotics.
The word robot was first used by Czech writer Karel Capek in 1920, in a play titled Rossum's Universal Robots (R.U.R), which described a fictional scenario where humanoids where manufactured to handle human labor [4].
American author and biochemist Isaac Asimov invented robotics as a fictional term in a story titled Liar!, which was published in 1941 [3].
The earliest working, modern robot was built by American Inventor George C. Devol, and took the form of an industrial robotic arm called Universal-Automation (Unimate) robot; for which he filed a patent in 1954 [1].
Industrial robots in manufacturing and construction have mostly been derived from the Unimate concept.
Twenty-first century advancements in the field of robotics have been mostly concerned with optimizing functionality, while improving autonomy, artificial intelligence and environmental sustainability, of robots.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Robotics
Benefits or advantages of robotics are;
1). Increase in productivity and accuracy
2). Improvement of work safety and efficiency by handling hazardous and repetitive tasks
3). Lower labor costs
4). Improvement of output-quality
5). Multi-purpose applicability
Disadvantages of robotics are;
1). High capital costs
2). Potential loss of human jobs
3). High technical expertise required for maintenance
4). Limited working creativity
5). Limited operational-flexibility
6). High energy demand
7). Risk of damage and malfunctioning
Examples of Robotics Applications
Examples of robotics applications are;
1). Surveillance drone deployment
2). Autonomous sustainable irrigation systems
3). Process-robotics for sustainable manufacturing
4). Self-driving vehicles
5). Robotic prosthetic devices
Importance of Robotics
The main purpose of robots is to improve the productivity and efficiency of the economy and society, by performing traditionally-human tasks with more speed, consistency and accuracy.
Importance of robotics is based on its role in developing robots that can be used in various sectors to boost economic growth rates, reduce product costs through cheaper mass production, improve product quality, and optimize worker safety by handling arduous and dangerous tasks.
Conclusion
Robotics is the combined application of engineering and science to develop autonomous, intelligent systems that can handle various human tasks.
Major fields of robotics are; electrical engineering, programming and deep learning, bioengineering, language modeling, and data management.
Advantages of robotics are; increase in productivity and accuracy, improved work safety, lower labor cost, high output quality, and multipurpose applicability.
Disadvantages of robotics are; high capital costs, human job loss, technical expertise requirement, limited creativity and flexibility, high energy demand, and risk of malfunctioning.
Examples of robotics applications are; development and deployment of surveillance drones, autonomous sustainable irrigation systems, process-robotics for sustainable manufacturing, self-driving electric cars, and robotic prosthetics in medicine.
References
1). Corke, P. (2017). "Introduction." In: Robotics, Vision and Control. Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, vol 118. Springer, Cham. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54413-7_1. (Accessed 26 March 2023).
2). Domela, L. (2012). "The first robot, created in 400 BCE, was a steam-powered pigeon." Available at: https://www.eejournal.com/fresh_bytes/the-first-robot-created-in-400-bce-was-a-steam-powered-pigeon/. (Accessed 26 March 2023).
3). Lupu-Onet, R. (2017). "Isaac Asimov’s fictional world: humanity and robots between fear and faith." Isaac Asimov’s fictional world: humanity and robots between fear and faith." GASG -2017, Stockholm Conference. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321159303_Isaac_Asimov's_fictional_world_humanity_and_robots_between_fear_and_faith. (Accessed 26 March 2023).
4). Moran, M. E. (2007). "Rossum's universal robots: not the machines." J Endourol. 2007 Dec;21(12):1399-402. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2007.0104. (Accessed 26 March 2023).
5). Samara, G.; Hussein, A.; Matarneh, I. A.; Alrefai, M.; Al-Safarini, M. Y. (2021). "Internet of Robotic Things: Current Technologies and Applications." 2021 22nd International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT), Muscat, Oman, 2021, pp. 1-6. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACIT53391.2021.9677407. (Accessed 26 March 2023).