Komodo Dragon Vs Gila Monster Venom, Size, Weight, Overall Comparison
Comparing the Komodo dragon and the Gila monster reveals fascinating taxonomic and physical similarities as venomous reptiles with carnivorous feeding behavior. Both belong to the order Squamata and share venomous secretions, contributing to their roles as formidable predators. However, in a real-life confrontation, the Komodo dragon’s considerable size, weight, and strength would likely give it the upper hand over the Gila monster.
Komodo dragons’ venom is far more lethal than that of the Gila monster (which is hardly associate with any known human fatalities) as it can have severe and life a threatening effects like hypothermia and retarded blood-clothing. Gila monsters also release their venom in much smaller quantities than Komodo dragons.
I. Komodo Dragon vs Gila Monster: Venomous Reptiles with Shared Characteristics:
– The Komodo dragon and Gila monster, both belonging to the order Squamata, share taxonomic and physical similarities as venomous reptiles with carnivorous feeding behavior.
II. Taxonomic and Physical Similarities:
– Both the Komodo dragon and Gila monster fall under the order Squamata, emphasizing their shared taxonomic classification. Physically, they exhibit venomous secretions and carnivorous feeding habits, highlighting commonalities in their predatory roles.
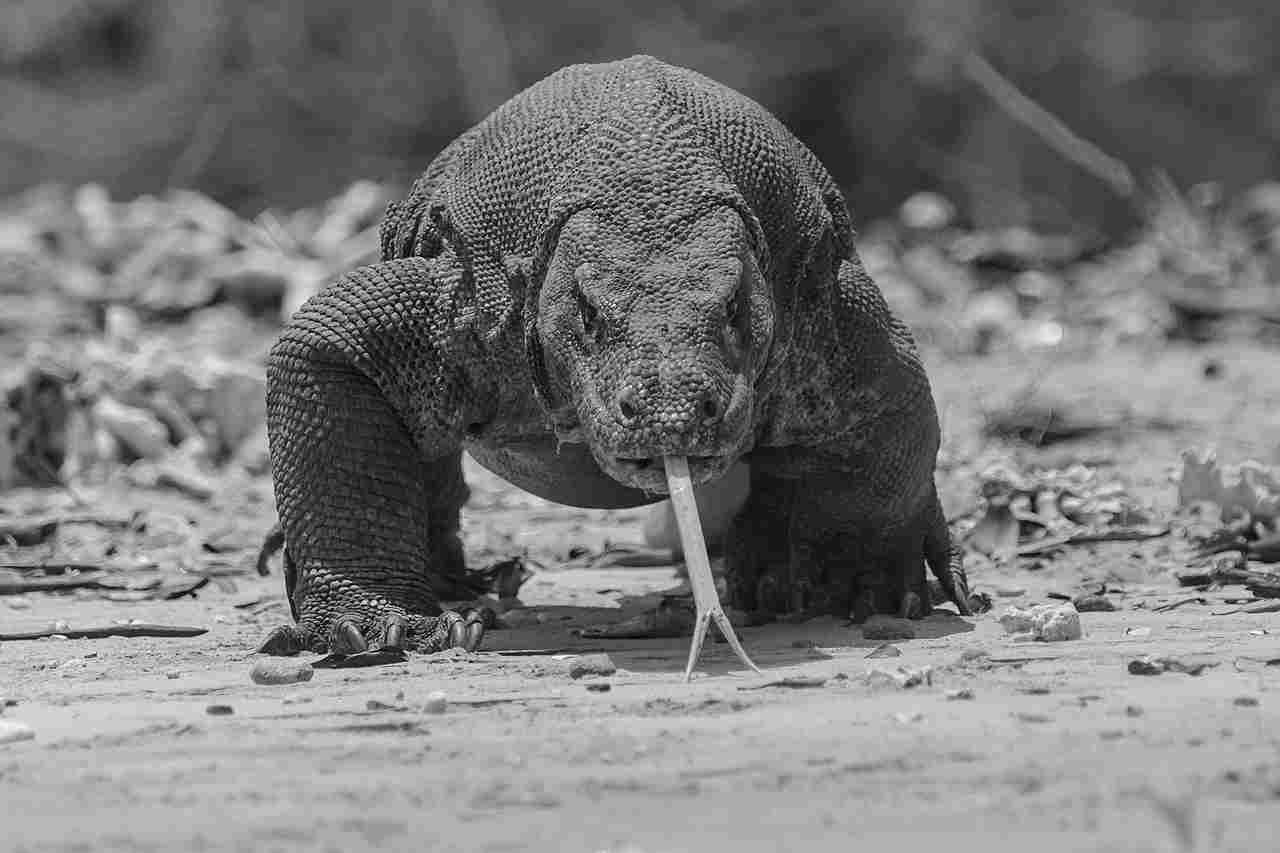

III. Venomous Capabilities:
– Both species utilize venom as a tool for subduing prey. The venomous secretions of the Komodo dragon and Gila monster play pivotal roles in their respective hunting strategies, aiding in immobilizing and consuming their prey.
IV. Size and Strength Disparities:
– Despite their shared venomous characteristics, the Komodo dragon holds a significant advantage in a physical confrontation due to its much larger size, greater weight, and superior strength. These attributes provide the Komodo dragon with a decisive edge over the Gila monster.
V. Jaws and Predatory Adaptations:
– The Komodo dragon’s larger and stronger jaws, coupled with its overall physical superiority, contribute to its effectiveness as a predator. In a fight, the Komodo dragon’s size and strength would likely overpower the Gila monster.
VI. Real-life Predator Superiority:
– In a real-life encounter between a Komodo dragon and a Gila monster, the Komodo dragon’s considerable size, weight, and strength would likely lead to its victory. While both are venomous, the physical advantages of the Komodo dragon in terms of size and strength are decisive in determining the outcome of a confrontation.
VII. Conservation Significance:
– Recognizing the unique attributes of both Komodo dragons and Gila monsters is crucial for conservation efforts. Tailoring strategies to protect these venomous reptiles contributes to the preservation of biodiversity and ecosystem balance in their respective habitats.

*Details of Comparison
| Criteria | Komodo Dragon | Gila Monster |
| Taxonomy | Varanidae, Squamata, Reptilia, Varanus komodoensis |
Helodermatidae, Squamata, Reptilia, Heloderma suspectum
|
| Appearance | Robust, variable coloration, up to 10 feet |
Stocky, black and pink/orange patterns, around 20 inches
|
| Size | Up to 10 feet |
Around 20 inches
|
| Weight | Up to 200 pounds | 1 to 2 pounds |
| Bite Force (PSI) | Around 600 PSI |
Less powerful compared to Komodo Dragon
|
| Offensive Advantages | Powerful bite with venom | Venomous bite |
| Defensive Advantages | Thick skin and scales |
Stout build and robust scales
|
| Speed | Up to 20 km/h |
Less than 5 km/h
|
| Agility | Relatively agile | Limited agility |
| Senses | Excellent smell, vision, and hearing |
Well-developed smell and vision
|
| Physical Capacity | Robust with powerful limbs |
Stocky build adapted to its environment
|
| Habitat & Region | Tropical savannas and forests, Komodo Island |
Deserts, southwestern U.S., and northwestern Mexico
|
| Tracks | Distinctive claw marks, large tracks |
Short, wide tracks with claw imprints
|
| Lifespan | Up to 30 years | Around 20 years |
| Feeding | Carnivorous, large prey |
Carnivorous, small mammals, birds, and eggs
|
| Intelligence | Problem-solving and social intelligence |
Basic cognitive functions
|
| Social Behavior | Complex social behaviors, including cooperation | Primarily solitary |
| Reproduction | Oviparous, no parental care after laying |
Oviparous, females guard the nest until hatching
|
| Parental Behavior | Minimal parental involvement |
Females guard the nest until eggs hatch
|
| Proximity to Humans | Remote islands, minimal human presence |
Near deserts, encounters with humans possible
|
| Behavior Toward Humans | Generally avoids, aggressive if provoked |
Prefers to avoid, may bite if provoked
|
| Danger Posed to Humans | Potentially lethal bites |
Bites are not lethal but painful due to venom
|
| Precautions | Caution and avoidance recommended |
Caution and avoidance recommended, seek professional help if bitten
|
| Conservation Status | Vulnerable | Near-threatened |
1. Taxonomy:
Komodo Dragon (Varanus komodoensis):
Family: Varanidae
Order: Squamata
Class: Reptilia
Genus: Varanus
Species: komodoensis
Gila Monster (Heloderma suspectum):
Family: Helodermatidae
Order: Squamata
Class: Reptilia
Genus: Heloderma
Species: suspectum
2. Appearance:
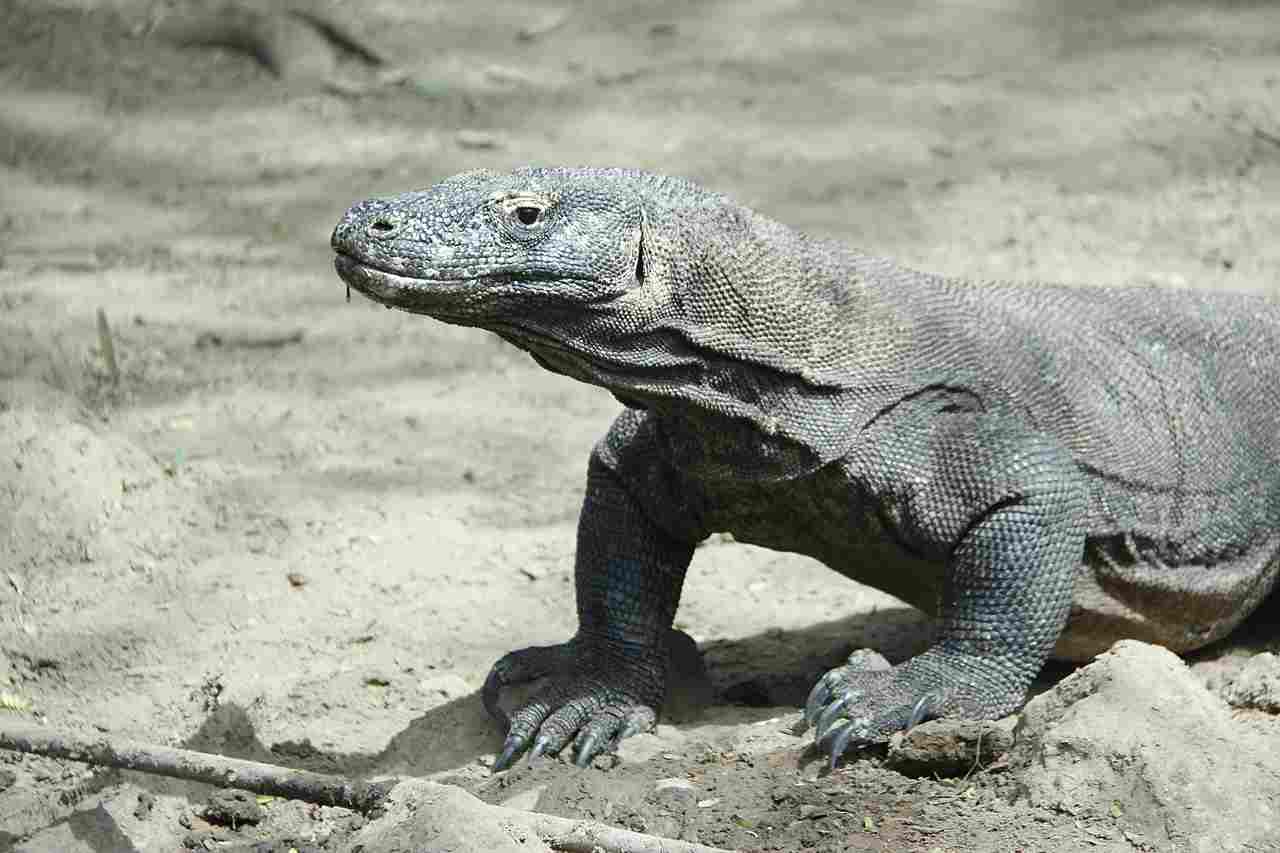
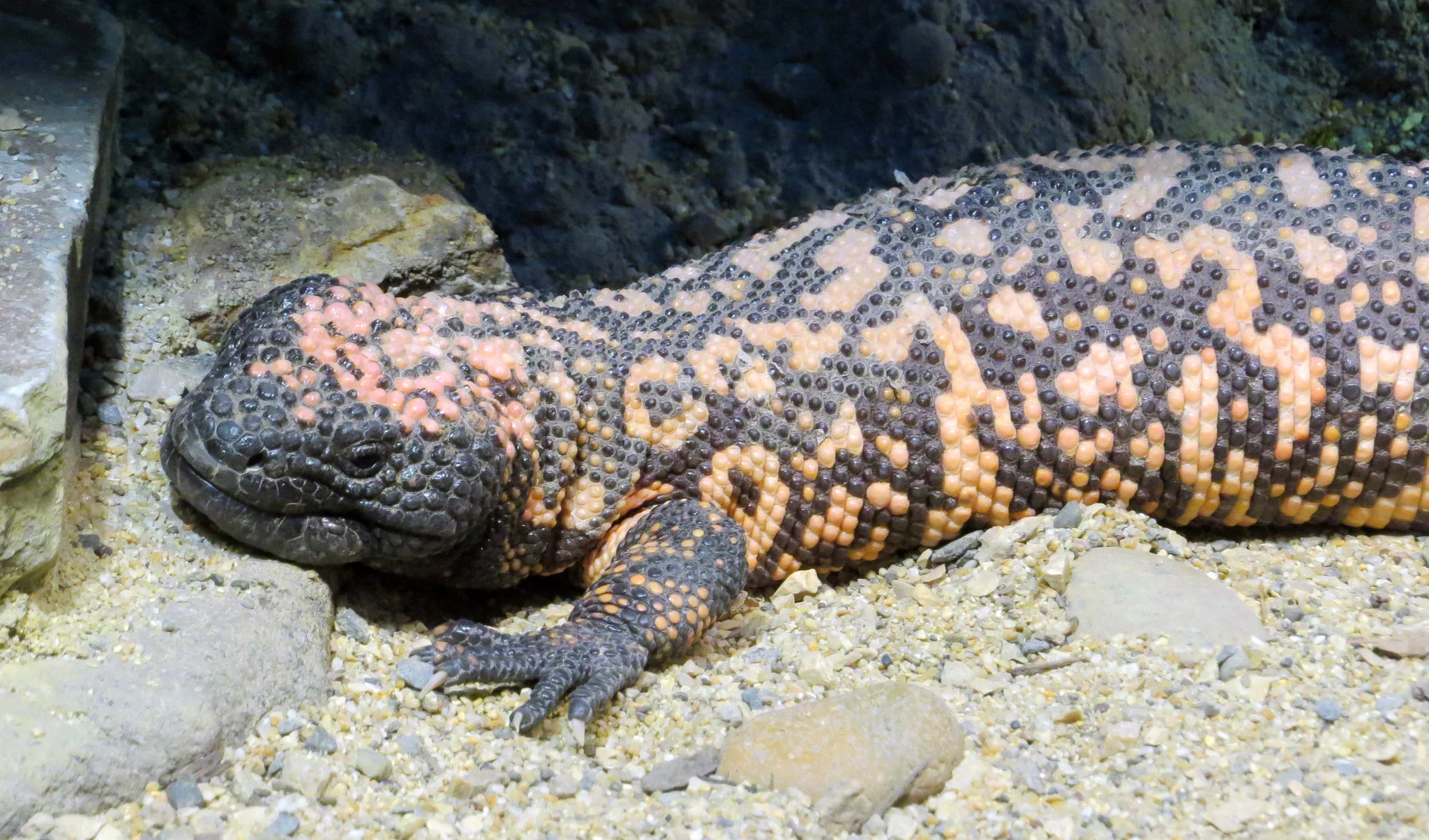


Komodo Dragon:
Stout, robust build with rough, scaly skin.
Varied coloration, ranging from gray to brown, providing effective camouflage.
Can grow up to 10 feet in length.
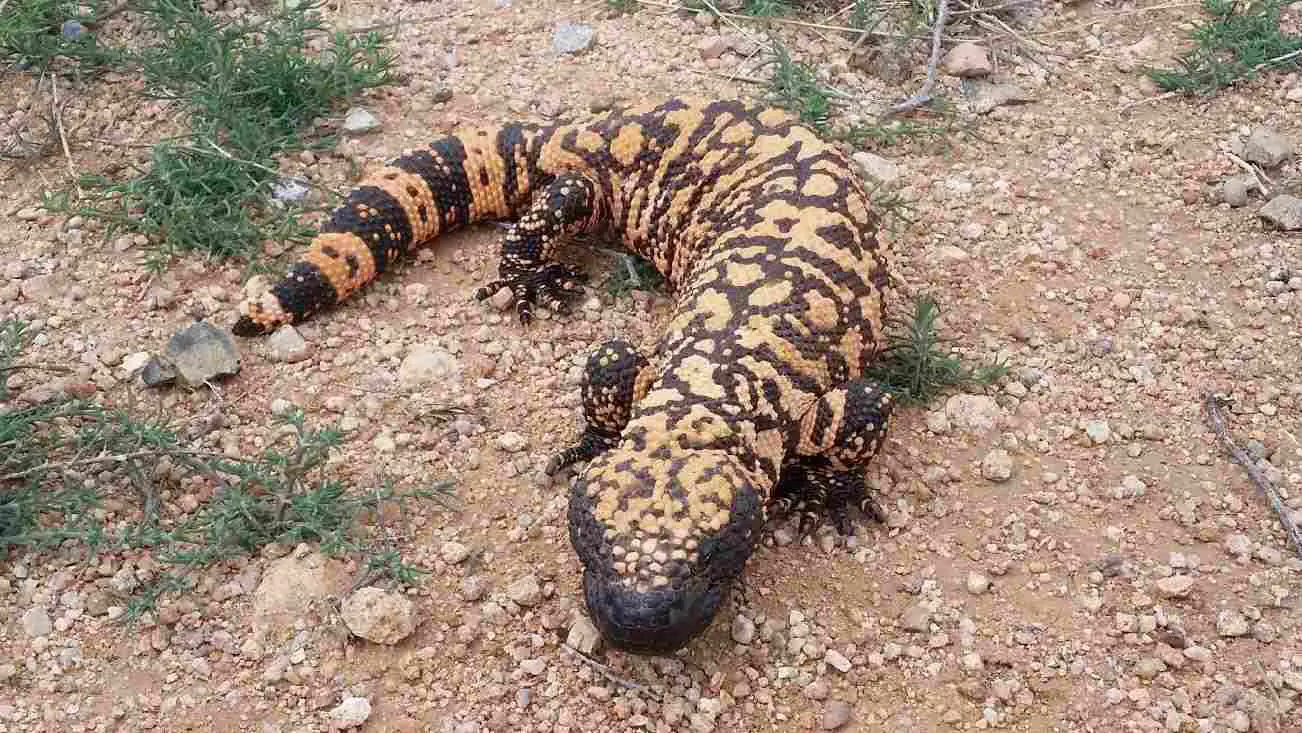
Gila Monster:
Stocky body, covered in distinctive bead-like scales.
Bold black and pink or orange coloration in patterns, serving as a warning signal.
Smaller than the Komodo Dragon, typically reaching lengths of around 20 inches.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon exhibits a larger and more variable size, while the Gila Monster is smaller and characterized by distinct color patterns.
Ecological Implications:
The Komodo Dragon’s coloration aids in its ambush hunting strategy, while the Gila Monster’s bright colors act as a warning to predators.
3. Size:
Komodo Dragon:
Adults can reach lengths of up to 10 feet.
Gila Monster:
Significantly smaller, with typical lengths around 20 inches.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon is substantially larger than the Gila Monster.
Ecological Implications:
Size affects their position in the food chain and impacts their respective roles within their ecosystems.
4. Weight:
Komodo Dragon:
Adults can weigh up to 200 pounds.
Gila Monster:
Weighs considerably less, with adults ranging from 1 to 2 pounds.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon is much heavier than the Gila Monster.
Ecological Implications:
Weight influences factors such as prey selection, hunting strategies, and energy expenditure in their environments.
5. Bite Force (PSI – Pounds per Square Inch):
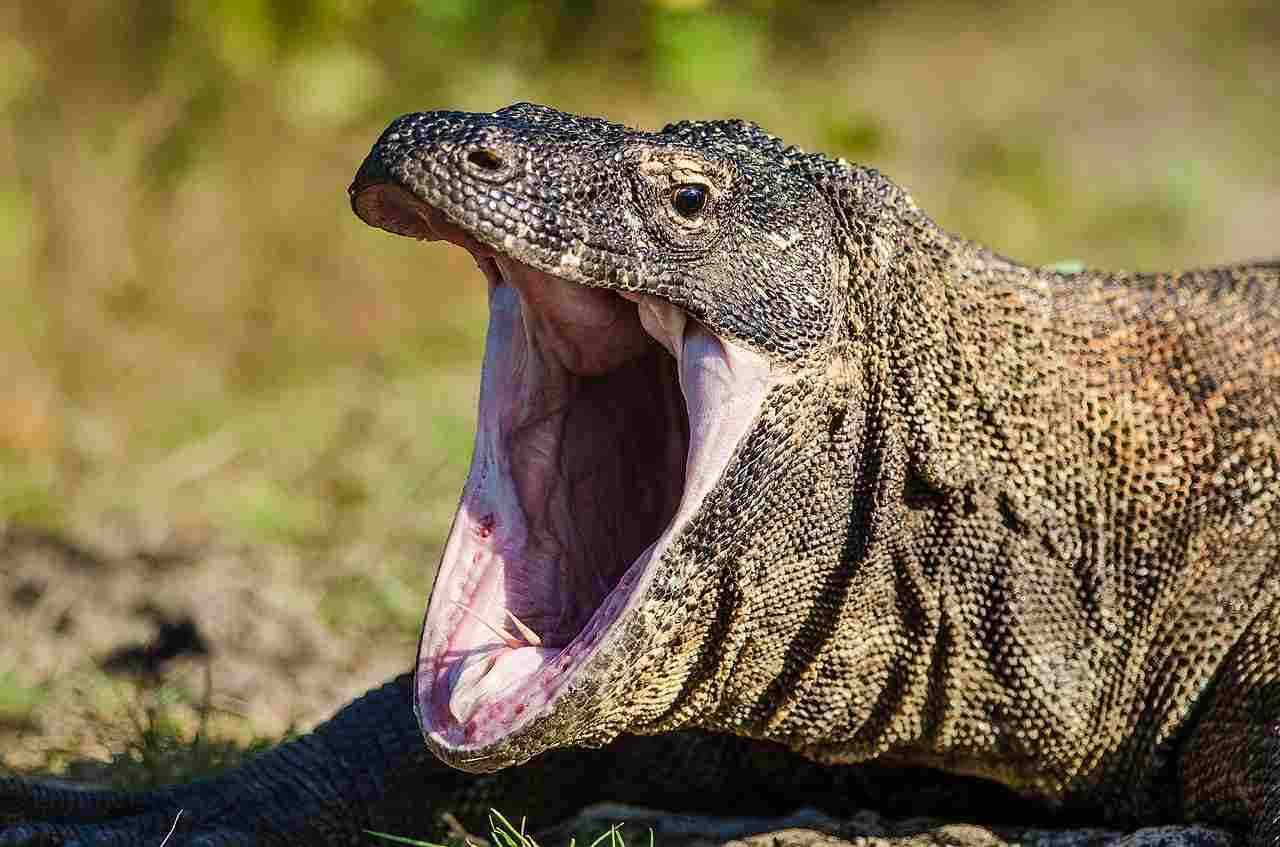

Komodo Dragon:
Bite force estimated around 600 PSI.
Gila Monster:
Bite force is not as powerful compared to the Komodo Dragon.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon possesses a significantly stronger bite force.
Ecological Implications:
Bite force is crucial for hunting and defense, impacting their interactions with prey and potential predators in their ecosystems.
6. Physical Offensive Advantages:
Komodo Dragon:
Strong jaws and sharp teeth, coupled with a powerful bite.
Enhanced by potent venom that aids in subduing prey.
Gila Monster:
Venomous bite, delivering a potent neurotoxin.
Comparison:
Both species rely on venomous bites for offense, with the Komodo Dragon having the added advantage of a powerful bite force.
Ecological Implications:
These offensive features impact prey selection and the overall balance of their respective ecosystems.
7. Physical Defensive Advantages:
Komodo Dragon:
Thick, tough skin and scales provide a degree of protection.
Gila Monster:
Stout build and robust scales offer a defensive layer.
Comparison:
Both species exhibit physical defenses through their skin and scales.
Ecological Implications:
Defense mechanisms influence their survival against potential threats, shaping their roles in the ecosystems they inhabit.
8. Speed (Km/hour or Mile/hour):

Komodo Dragon:
Capable of reaching speeds up to 20 km/h (12 mph).
Gila Monster:
Moves at a slower pace, typically less than 5 km/h (3 mph).
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon is significantly faster than the Gila Monster.
Ecological Implications:
Speed impacts their hunting efficiency and ability to navigate their environments.
9. Agility:
Komodo Dragon:
Relatively agile, especially during hunting or confrontations.
Gila Monster:
Exhibits limited agility due to its stocky build.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon displays greater agility compared to the Gila Monster.
Ecological Implications:
Agility affects their ability to capture prey and evade predators, influencing their ecological roles.
10. Senses:
Komodo Dragon:
Excellent sense of smell, acute vision, and hearing.
Gila Monster:
Well-developed sense of smell and keen vision.
Comparison:
Both species rely on a combination of senses for hunting and navigation.
Ecological Implications:
Their sensory capabilities impact their hunting success and overall ecological interactions.
11. Overall Physical Capacity:

Komodo Dragon:
Robust build, powerful limbs, and versatile physical capabilities.
Gila Monster:
Stocky build with adapted features for its environment.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon generally possesses a more versatile physical capacity.
Ecological Implications:
Physical capacity influences their ability to adapt to different environmental challenges and niches.
12. Habitat Preference(s) and Geographic Region:
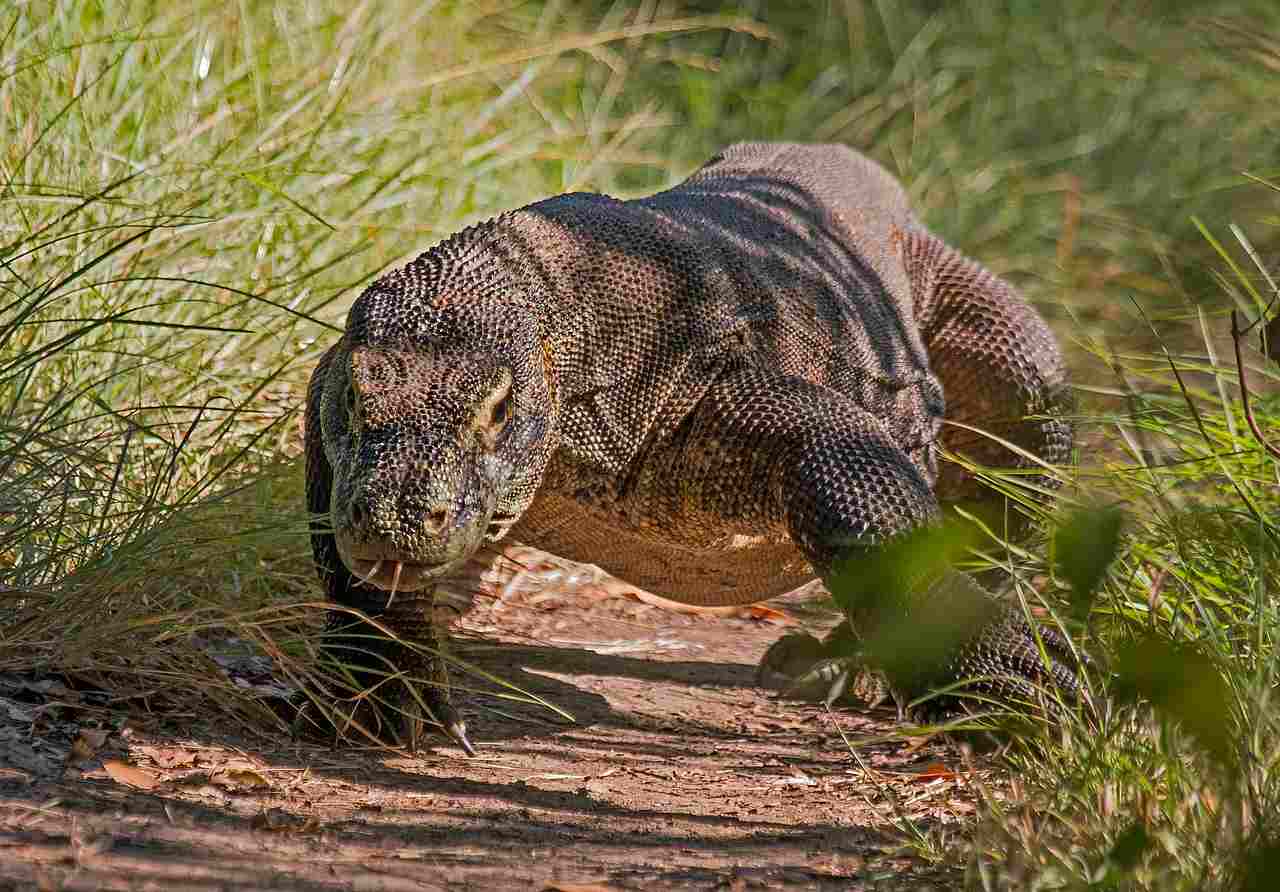
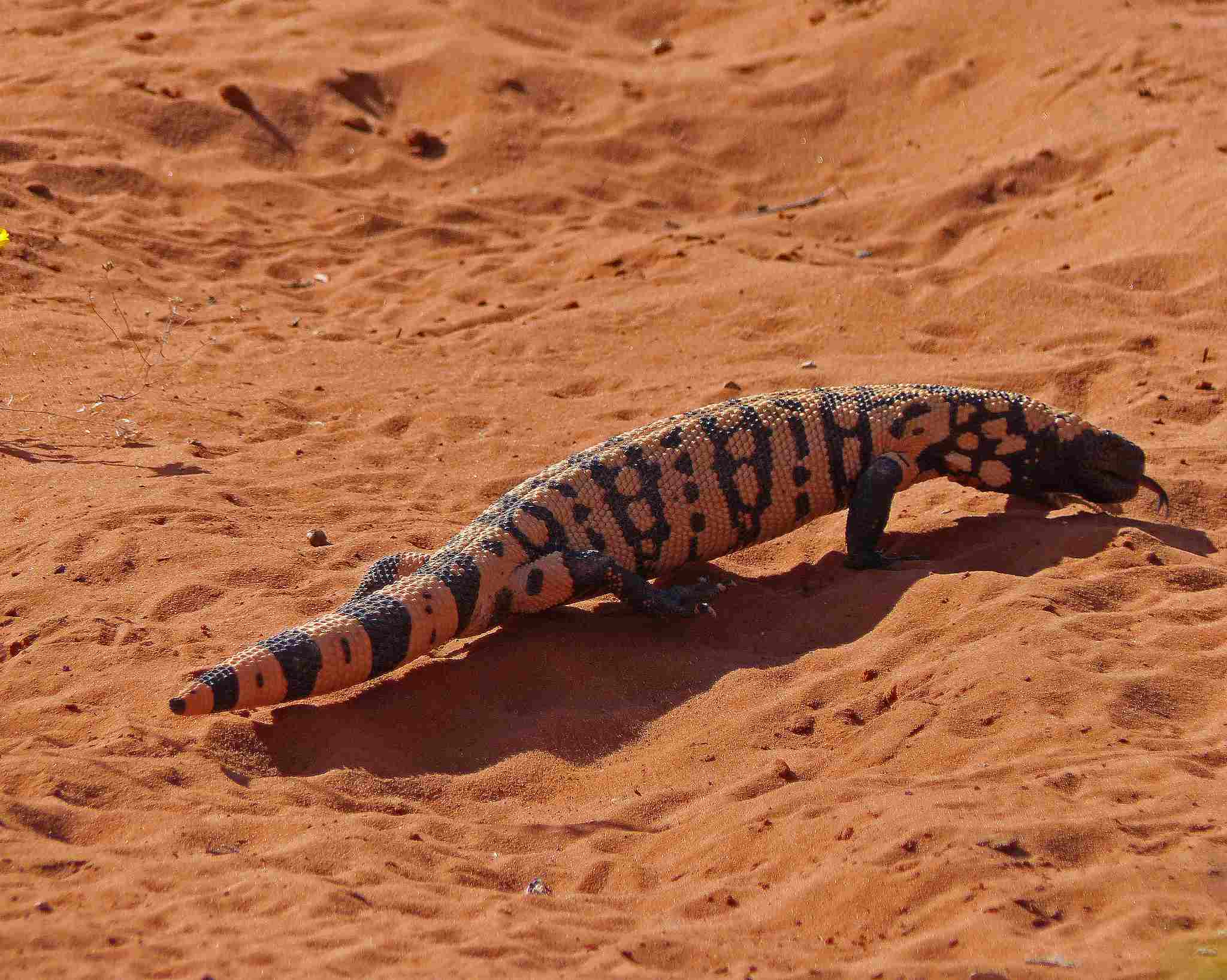


Komodo Dragon:
Prefers tropical savannas and forests, mainly found on Komodo Island in Indonesia.
Gila Monster:
Thrives in desert and arid regions, primarily found in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon favors tropical environments, while the Gila Monster is adapted to arid conditions.
Ecological Implications:
Their habitat preferences influence the biodiversity and dynamics of the ecosystems they inhabit.
13. Tracks:
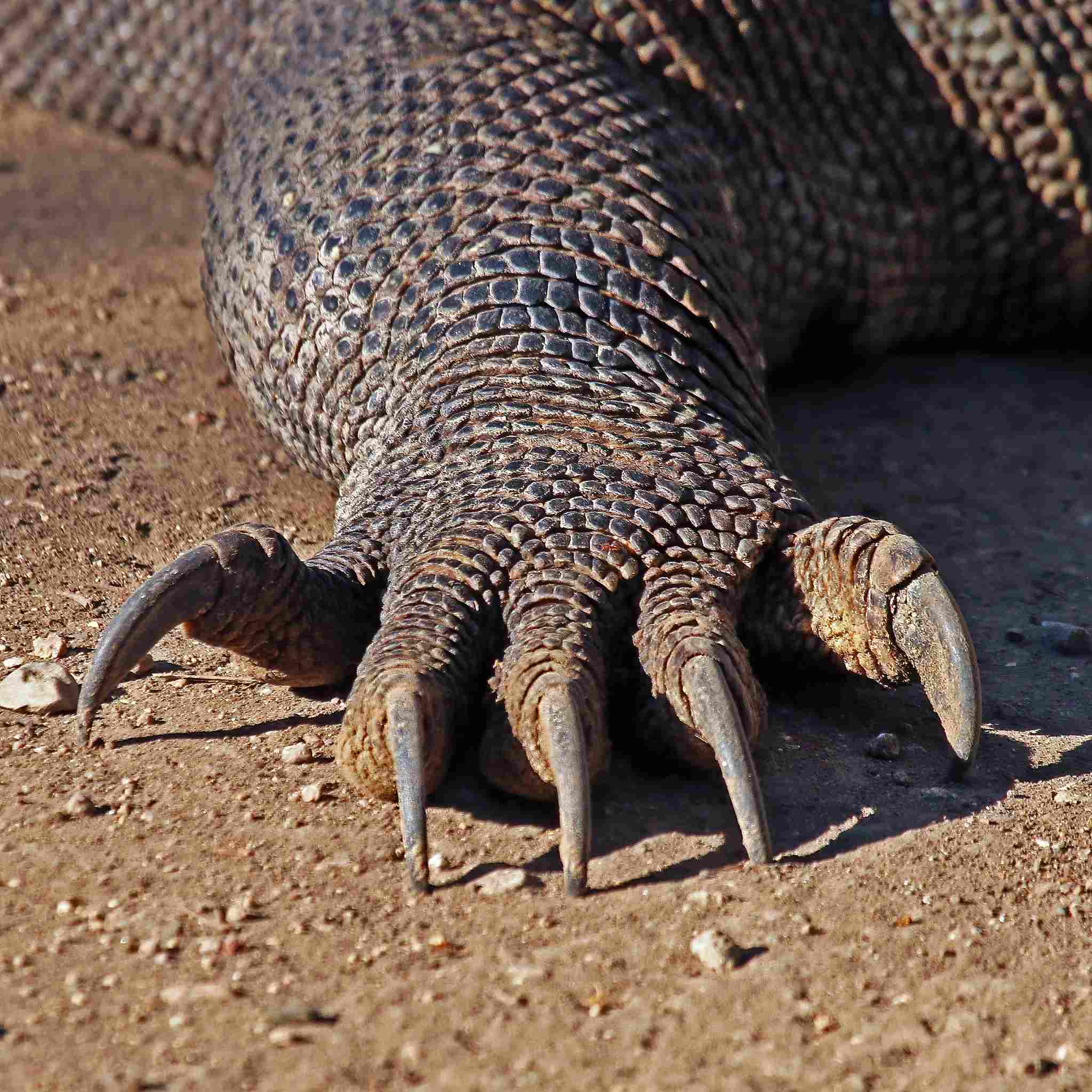

Komodo Dragon:
Distinctive claw marks and relatively large tracks.
Gila Monster:
Short, wide tracks with claw imprints.
Comparison:
Track characteristics differ, with the Komodo Dragon leaving larger and more pronounced marks.
Ecological Implications:
Tracking and identifying these species through footprints can aid in ecological studies and conservation efforts.
14. Lifespan:
Komodo Dragon:
Can live up to 30 years in the wild.
Gila Monster:
Exhibits a lifespan of around 20 years in the wild.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon generally has a longer lifespan compared to the Gila Monster.
Ecological Implications:
Lifespan impacts their contribution to the ecosystem over time, including reproduction and predation.
15. Mode of Feeding:
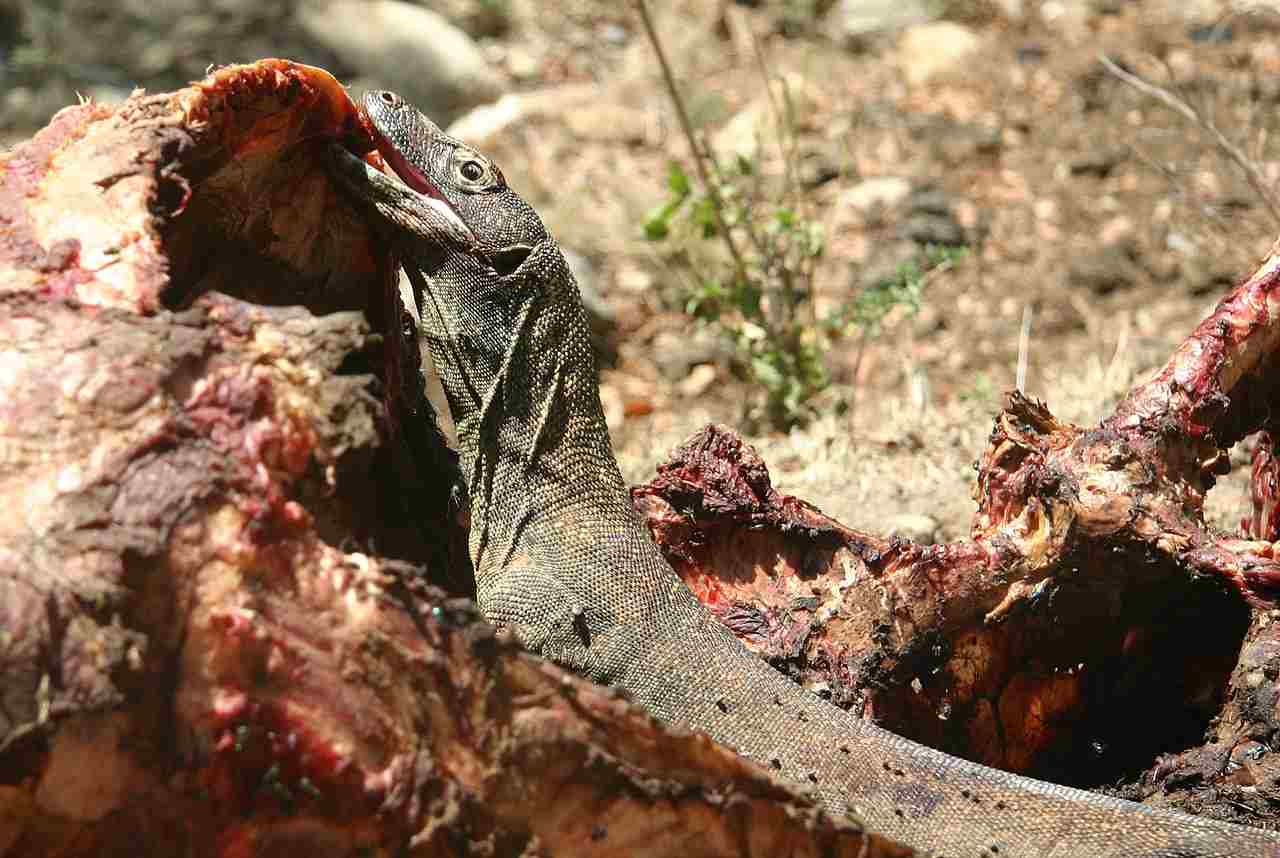

Komodo Dragon:
Carnivorous, with a preference for large prey such as deer and wild boar.
Gila Monster:
Carnivorous, feeding on small mammals, birds, and eggs.
Comparison:
Both species share a carnivorous diet, but the Komodo Dragon targets larger prey.
Ecological Implications:
Feeding habits influence the prey population and contribute to the ecological balance.
16. Intelligence:
Komodo Dragon:
Displays problem-solving abilities and social intelligence.
Gila Monster:
Demonstrates basic cognitive functions but is less known for complex behaviors.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon is generally considered more intelligent than the Gila Monster.
Ecological Implications:
Intelligence affects their ability to adapt to changing environments and interact with other species.
17. Social Behavior:
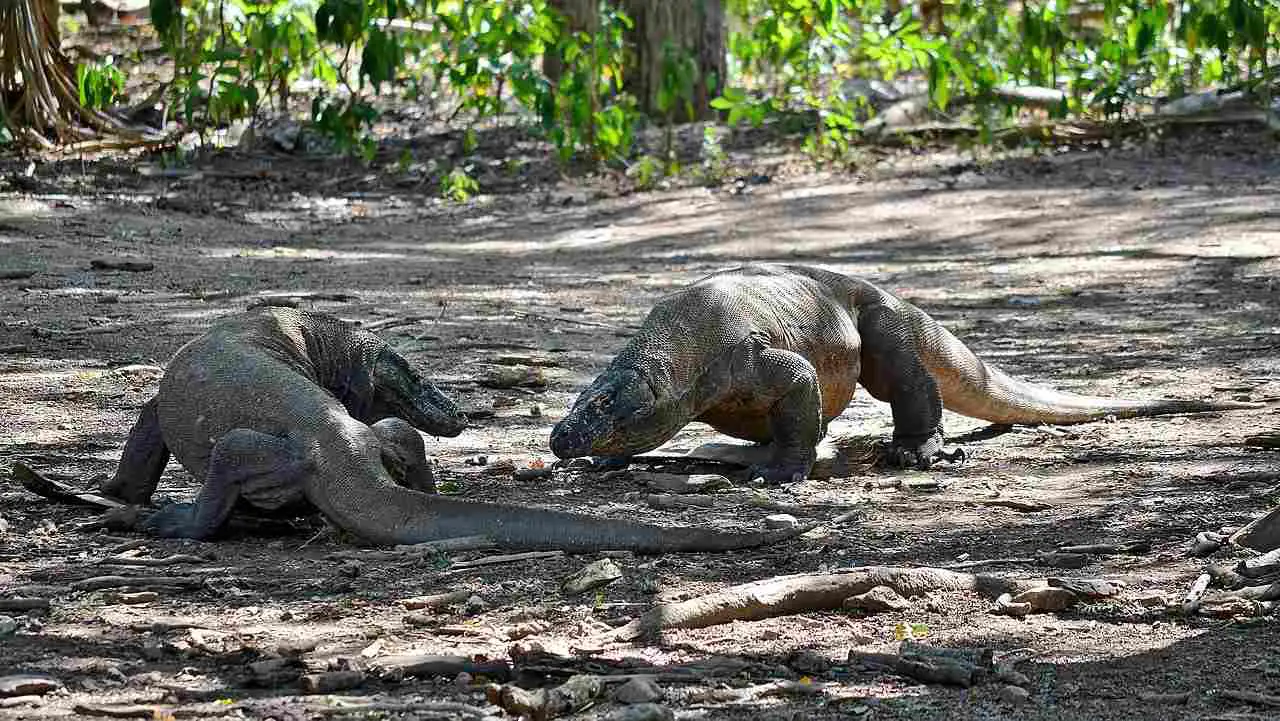
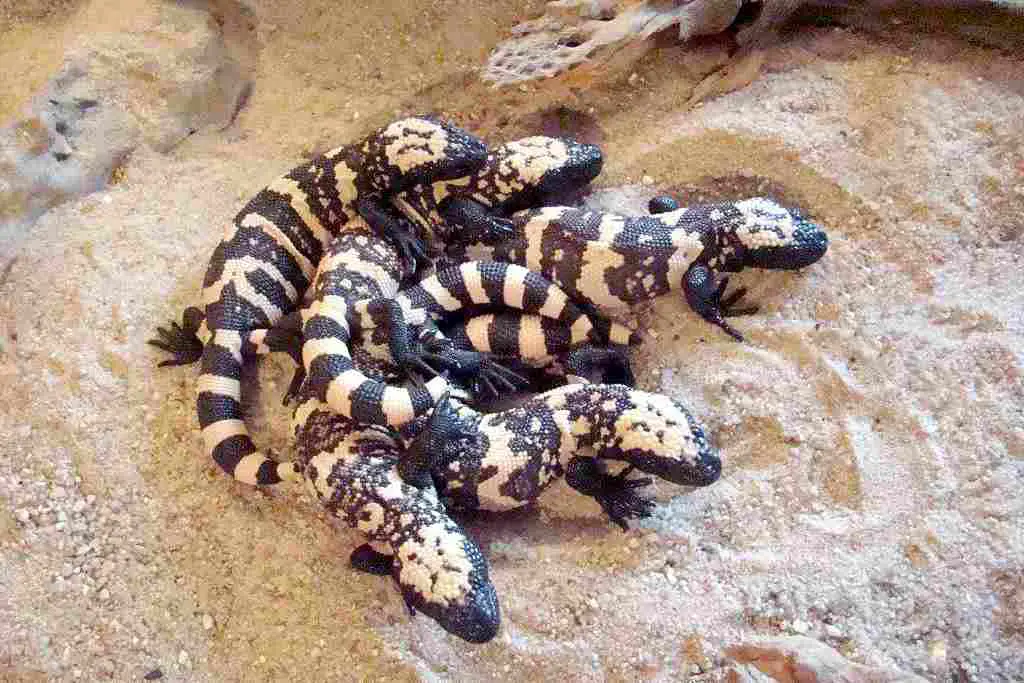


Komodo Dragon:
Can exhibit complex social behaviors, including cooperation in hunting.
Gila Monster:
Primarily solitary, with minimal social interactions.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon is known for more intricate social behaviors compared to the Gila Monster.
Ecological Implications:
Social behaviors impact their roles within ecosystems, influencing aspects like cooperation in hunting or territorial interactions.
18. Mode of Reproduction:
Komodo Dragon:
Oviparous; females lay eggs in nests, and there is no parental care after laying.
Gila Monster:
Oviparous; females lay eggs in burrows, providing some protection until hatching.
Comparison:
Both species follow an oviparous mode of reproduction, but with variations in nesting behavior.
Ecological Implications:
Reproductive strategies impact population dynamics and the distribution of these species within their habitats.
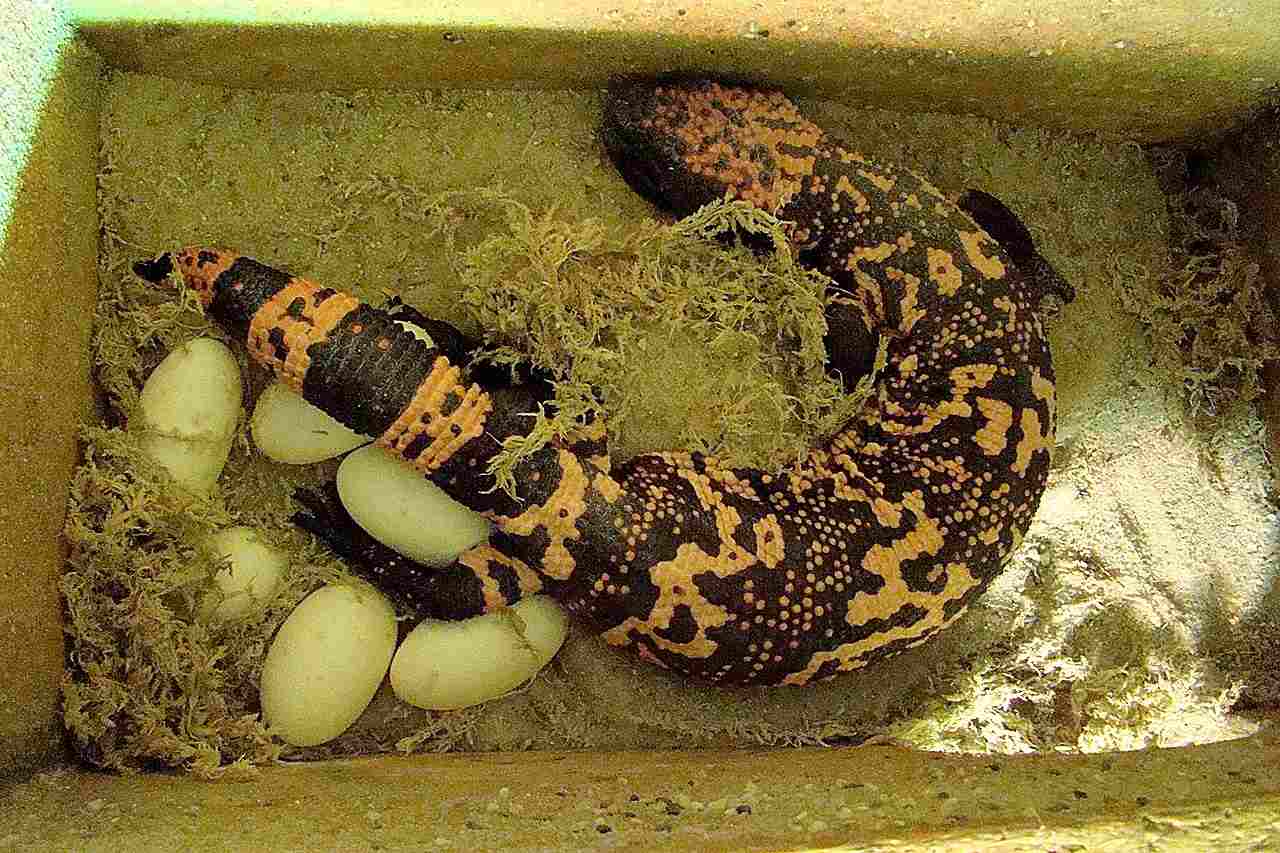

19. Parental Behavior:
Komodo Dragon:
Minimal parental involvement after egg-laying.
Gila Monster:
Females guard the nest until eggs hatch, providing initial protection for offspring.
Comparison:
The Gila Monster exhibits more parental care compared to the Komodo Dragon.
Ecological Implications:
Parental behaviors contribute to the survival rates of offspring and overall population health.
20. Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Komodo Dragon:
Found on remote islands with minimal human presence.
Gila Monster:
Encounters with humans may occur, especially in suburban areas near deserts.
Comparison:
The Gila Monster is more likely to be in proximity to human-inhabited areas than the Komodo Dragon.
Ecological Implications:
Human interaction can pose challenges such as habitat fragmentation and potential conflicts.
21. Behavior Toward Humans:
Komodo Dragon:
Generally avoids human contact, but can be aggressive if threatened.
Gila Monster:
Prefers to avoid humans but may bite if provoked.
Comparison:
Both species tend to avoid humans, but the Komodo Dragon can be more aggressive when provoked.
Ecological Implications:
Human-wildlife interactions can impact the behavior and stress levels of these species, influencing their roles in ecosystems.
22. Danger Posed to Humans:
Komodo Dragon:
Can pose a significant threat if provoked, with the potential for lethal bites.
Gila Monster:
Generally not lethal to humans, but bites can be painful due to venom.
Comparison:
The Komodo Dragon poses a higher potential danger to humans compared to the Gila Monster.
Ecological Implications:
Human safety considerations become crucial in areas where these species coexist with human populations.
23. Associated Precautions:
Komodo Dragon:
Caution and avoidance recommended; respect their natural behavior and habitat.
Gila Monster:
Awareness of their presence and cautious behavior advised; seek professional help if bitten.
Comparison:
Similar precautions for both species involve understanding their behavior and seeking professional help if needed.
Ecological Implications:
Educating the public on precautions helps minimize negative interactions and supports coexistence.
24. Conservation Status:
Komodo Dragon:
Classified as vulnerable due to habitat loss and human-wildlife conflicts.
Gila Monster:
Listed as near-threatened, facing threats from habitat destruction and collection for the pet trade.
Comparison:
Both species face conservation challenges, with the Komodo Dragon being more vulnerable.
Ecological Implications:
Conservation efforts are essential to maintain their ecological roles and biodiversity in their respective habitats.
*Summary of Comparison
Taxonomy:
Komodo Dragon: Varanidae, Squamata, Reptilia, Varanus komodoensis.
Gila Monster: Helodermatidae, Squamata, Reptilia, Heloderma suspectum.
Appearance:
Komodo Dragon: Robust build, variable coloration, up to 10 feet.
Gila Monster: Stocky with black and pink/orange patterns, around 20 inches.
Size:
Komodo Dragon: Up to 10 feet.
Gila Monster: Around 20 inches.
Weight:
Komodo Dragon: Up to 200 pounds.
Gila Monster: 1 to 2 pounds.
Bite Force (PSI):
Komodo Dragon: Around 600 PSI.
Gila Monster: Less powerful compared to the Komodo Dragon.
Physical Offensive Advantages:
Komodo Dragon: Powerful bite with venom.
Gila Monster: Venomous bite.
Physical Defensive Advantages:
Komodo Dragon: Thick skin and scales.
Gila Monster: Stout build and robust scales.
Speed:
Komodo Dragon: Up to 20 km/h.
Gila Monster: Less than 5 km/h.
Agility:
Komodo Dragon: Relatively agile.
Gila Monster: Limited agility.
Senses:
Komodo Dragon: Excellent smell, vision, and hearing.
Gila Monster: Well-developed smell and vision.
Overall Physical Capacity:
Komodo Dragon: Robust with powerful limbs.
Gila Monster: Stocky build adapted to its environment.
Habitat Preference(s) and Geographic Region:
Komodo Dragon: Tropical savannas and forests, Komodo Island.
Gila Monster: Deserts, southwestern U.S., and northwestern Mexico.
Tracks:
Komodo Dragon: Distinctive claw marks, large tracks.
Gila Monster: Short, wide tracks with claw imprints.
Lifespan:
Komodo Dragon: Up to 30 years.
Gila Monster: Around 20 years.
Mode of Feeding:
Komodo Dragon: Carnivorous, large prey.
Gila Monster: Carnivorous, small mammals, birds, and eggs.
Intelligence:
Komodo Dragon: Problem-solving and social intelligence.
Gila Monster: Basic cognitive functions.
Social Behavior:
Komodo Dragon: Complex social behaviors, including cooperation.
Gila Monster: Primarily solitary.
Mode of Reproduction:
Komodo Dragon: Oviparous, no parental care after laying.
Gila Monster: Oviparous, females guard the nest until hatching.
Parental Behavior:
Komodo Dragon: Minimal parental involvement.
Gila Monster: Females guard the nest until eggs hatch.
Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Komodo Dragon: Remote islands, minimal human presence.
Gila Monster: Near deserts, encounters with humans possible.
Behavior Toward Humans:
Komodo Dragon: Generally avoids, aggressive if provoked.
Gila Monster: Prefers to avoid, may bite if provoked.
Danger Posed to Humans:
Komodo Dragon: Potentially lethal bites.
Gila Monster: Bites are not lethal but painful due to venom.
Associated Precautions:
Caution and avoidance recommended for both, seek professional help if bitten.
Conservation Status:
Komodo Dragon: Vulnerable.
Gila Monster: Near-threatened.
Conclusion
I). Similarities:
Both are reptiles with venomous bites, playing crucial roles in their ecosystems.
II). Differences:
Varying in size, habitat preferences, and ecological interactions, the Komodo Dragon and Gila Monster exhibit distinctive characteristics that shape their roles in the natural world.