Jaguar Vs Lion Size, Weight, Ecological Comparison
A lion will win a Jaguar in a fight because it is larger, heavier, stronger, faster, and more agile. However, a jaguar will still be able to do some damage using its strong jaws and bite force. In this article, we will compare factors such as size, weight, strength, speed, and agility to further understand why a lion would have the upper hand in a physical confrontation. Additionally, we will explore other aspects like habitat, behavior, and danger posed to humans to provide a comprehensive comparison between these two majestic big cats.
Reasons Why a Lion Will Win a Jaguar In a Fight/Physical Confrontation
I). Lions are Larger and Heavier Than Jaguars
One of the main reasons why a lion would win in a fight against a jaguar is its larger size and heavier weight. Lions are known for their impressive size, with adult males weighing between 330 to 550 pounds (150 to 250 kilograms) and measuring around 8 to 10 feet (2.4 to 3 meters) in length. On the other hand, jaguars are smaller, with adult males weighing between 120 to 210 pounds (55 to 95 kilograms) and measuring around 5 to 7 feet (1.5 to 2.1 meters) in length.
The lion’s larger size gives it a significant advantage in a physical confrontation. With its sheer mass, the lion can deliver more powerful blows and strikes, overpowering the jaguar. Additionally, the lion’s larger size provides it with a greater reach, allowing it to deliver devastating blows with its paws and claws.
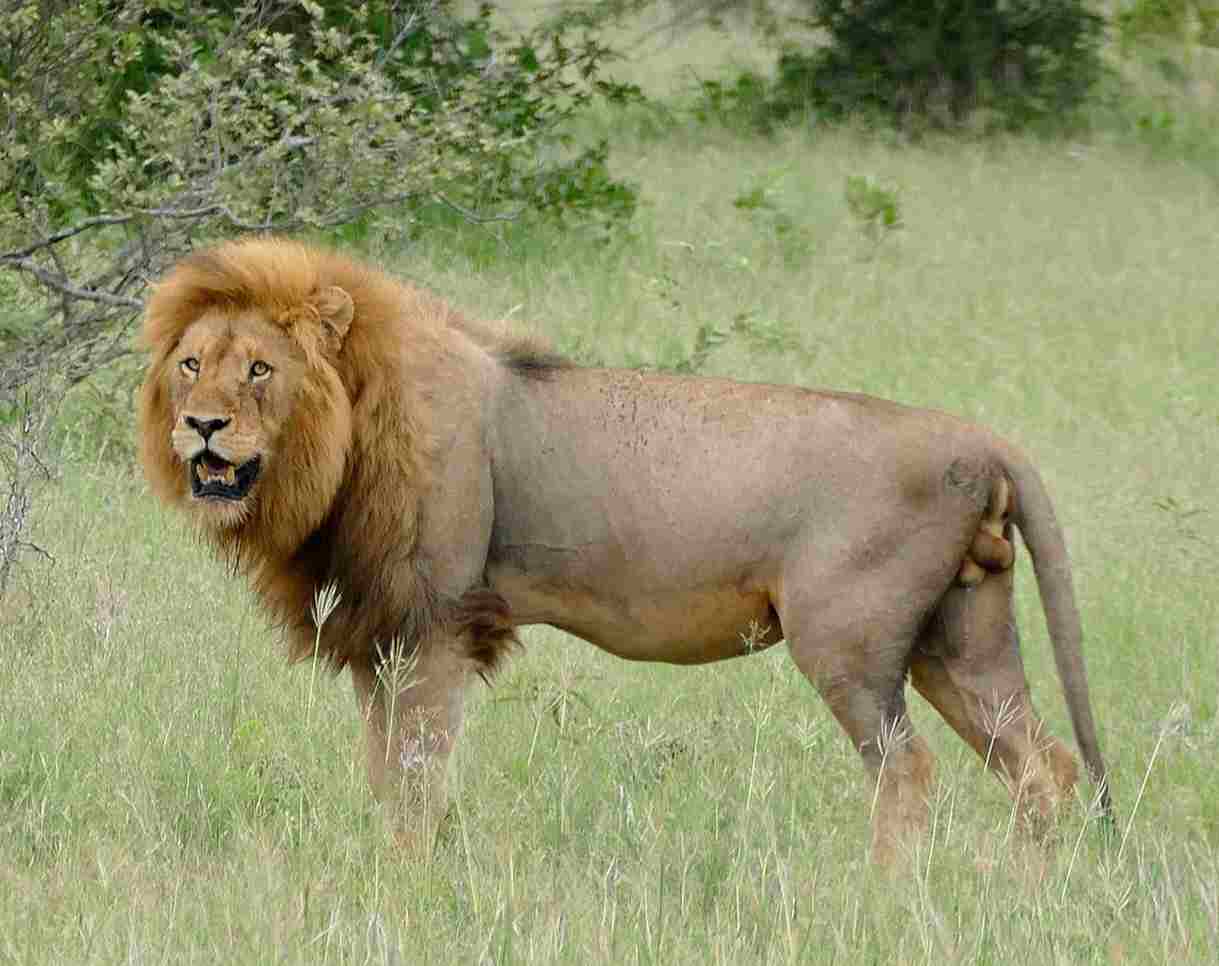

II). Muscular Strength and Endurance
In addition to their larger size, lions also possess superior muscular strength and endurance compared to jaguars. Lions have well-developed muscles, particularly in their forelimbs, which they use to take down large prey and defend themselves.
Their strong muscles enable them to deliver powerful bites and strikes, overpowering their opponents. Furthermore, lions have excellent endurance, allowing them to sustain physical exertion for extended periods of time. This endurance gives them an advantage in prolonged fights, as they can outlast their opponents.
III). Speed and Agility
While jaguars are known for their agility and speed, lions are also surprisingly agile for their size. Lions can reach speeds of up to 50 miles per hour (80 kilometers per hour) in short bursts, allowing them to quickly chase down prey or evade danger.
Their agility enables them to make quick turns and maneuvers, making it difficult for the jaguar to land a successful attack. Combined with their larger size and strength, the lion’s speed and agility make it a formidable opponent in a physical confrontation.
*Details of Comparison
| Feature | Lion | Jaguar |
|
Physical Attributes
|
||
| Size | Larger (males up to 550 lbs, females up to 395 lbs) |
Smaller (males up to 250 lbs, females up to 165 lbs)
|
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Strength | Stronger | Less strong |
| Speed | Faster (up to 50 mph) |
Slower (up to 40 mph)
|
| Agility | More agile | Less agile |
| Bite Force | Stronger (1,100 psi) |
Weaker (1,500 psi)
|
|
Habitat & Behavior
|
||
| Habitat | Grasslands, savannas |
Rainforests, swamps, grasslands
|
| Social Structure | Prides (females, cubs, and 1-2 males) | Solitary |
| Hunting Strategy | Cooperative hunting | Solitary hunting |
|
Conservation Status
|
||
| IUCN Red List | Vulnerable | Near threatened |
1). Taxonomy
The taxonomy of the jaguar (Panthera onca) and the lion (Panthera leo) places them in the same genus, Panthera, but different species. While they share some similarities, there are distinct differences between the two animals.
The jaguar is known for its powerful build and muscular physique. It has a stocky body, short legs, and a large head. Its coat is typically yellow or tan with distinctive rosette patterns, which provide excellent camouflage in its natural habitat. On the other hand, the lion has a more slender and elongated body, with longer legs and a larger mane in males. Its coat is typically a tawny color, which helps it blend into the grasslands where it resides.
In terms of size, the jaguar is smaller than the lion. Adult male jaguars can reach a length of around 6 feet (1.8 meters) and weigh between 120 to 210 pounds (54 to 95 kilograms). In comparison, adult male lions can grow up to 10 feet (3 meters) in length and weigh between 330 to 550 pounds (150 to 250 kilograms).
2). Appearance
The appearance of both the jaguar and the lion is distinct and plays a crucial role in their survival. Starting with their coats, both animals have unique characteristics. The jaguar’s coat is typically yellow or tan, adorned with rosette patterns that provide excellent camouflage in its natural habitat. This allows the jaguar to blend seamlessly into the dense vegetation of the rainforest or the grasslands it inhabits. On the other hand, the lion’s coat is a tawny color, which helps it blend into the grasslands where it resides, making it less visible to its prey.
In terms of stature and build, the jaguar has a stocky body, short legs, and a large head. These physical attributes contribute to its powerful build and muscular physique, enabling it to take down large prey. In contrast, the lion has a more slender and elongated body, with longer legs and a larger mane in males. The mane serves as a visual display of dominance and plays a role in attracting mates.
When comparing the appearance of these two animals, it is evident that their coats, fur, and skin have evolved to suit their respective habitats and hunting strategies. The jaguar’s camouflage allows it to stalk its prey undetected, while the lion’s tawny coat helps it blend into the grasslands during hunting expeditions.
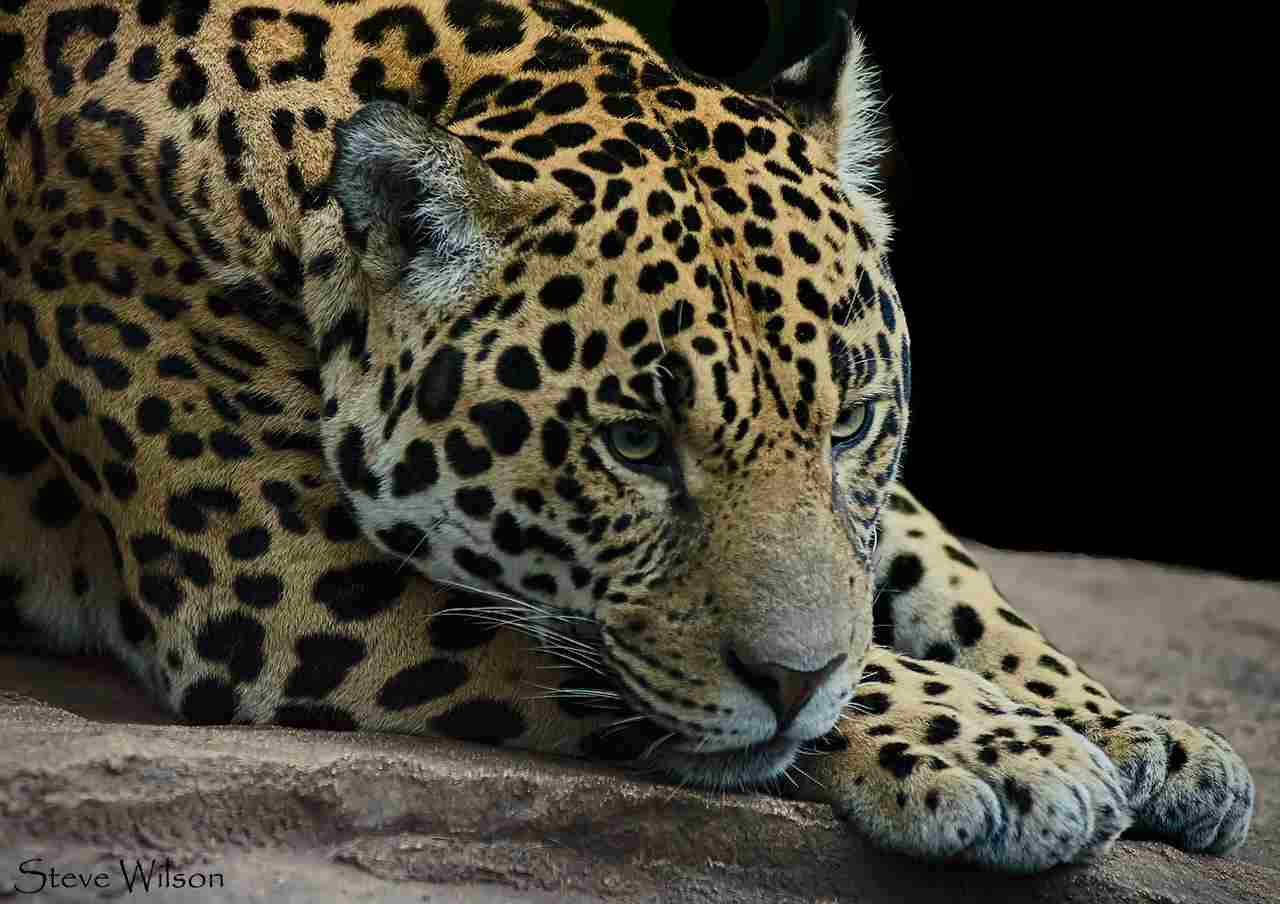

3). Size
When comparing the size of the jaguar and the lion, it is important to consider their total body length and height at the shoulders. The jaguar typically measures around 5 to 6 feet in length, with males being slightly larger than females. In terms of height at the shoulders, jaguars stand at approximately 2 to 2.5 feet tall. On the other hand, lions are known for their impressive size. They can reach lengths of up to 8 to 10 feet, with males being significantly larger than females. Lions also stand taller at the shoulders, measuring around 3 to 4 feet in height.
The difference in size between these two big cats is quite significant. Lions are larger and more imposing, with their size often serving as a visual display of dominance within their social structure. The jaguar, although smaller in comparison, is still a formidable predator due to its muscular build and powerful physique. Both animals have adapted to their respective environments and hunting strategies, utilizing their size to their advantage.
4). Weight
When comparing the weight of a jaguar and a lion, it is evident that lions are significantly heavier than jaguars. Adult male lions can weigh between 330 to 550 pounds, while females typically weigh around 265 to 395 pounds. On the other hand, jaguars have a more compact and muscular build, with males weighing approximately 126 to 250 pounds, and females weighing around 79 to 165 pounds.
The difference in weight between these two big cats is due to various factors, including their size, habitat, and hunting strategies. Lions, being larger in size, require more strength and power to bring down their prey, which often includes large herbivores like zebras and wildebeests. Their weight allows them to overpower and bring down these animals effectively.
Jaguars, on the other hand, have adapted to a different hunting style. They are known for their ability to climb trees and ambush their prey from above. Their muscular build and agility enable them to take down smaller prey, such as capybaras and caimans, which do not require as much strength as the prey of lions.
While lions are heavier and more imposing due to their size, jaguars are still formidable predators despite their smaller weight.
5). Speed and Agility
Jaguars are known for their agility and quick bursts of speed, which allow them to navigate through dense forests and climb trees effortlessly. Their muscular build and flexible bodies enable them to change direction swiftly and pounce on their prey with precision.
On the other hand, lions may not match the agility of jaguars, but they compensate with their remarkable speed. Lions can reach speeds of up to 50 miles per hour in short bursts, making them one of the fastest land animals. This speed is crucial for their hunting strategy, as they rely on stalking and chasing down their prey in open grasslands.
The difference in speed and agility between these two big cats is a result of their distinct habitats and hunting techniques. Jaguars’ agility is essential for navigating their dense rainforest habitats and ambushing prey from trees, while lions’ speed is advantageous for chasing down their prey in open savannahs.
Therefore, while jaguars excel in agility and maneuverability, lions compensate with their impressive speed.
6). Bite Force
Jaguars have one of the strongest bites among big cats, with an estimated bite force of around 1,500 psi. This powerful bite allows them to pierce through the thick hides and shells of their prey, such as caimans and turtles. Their strong jaws and sharp teeth enable them to deliver a lethal bite, quickly incapacitating their prey.
On the other hand, lions also possess a formidable bite force, although slightly lower than that of jaguars. Lions have an estimated bite force of around 1,000 psi. While not as powerful as the jaguar’s bite, it is still more than sufficient for their hunting needs. Lions primarily use their bite force to suffocate their prey by clamping down on the throat or muzzle.
Therefore, both jaguars and lions possess impressive bite forces that are well-suited for their respective hunting strategies. While jaguars have a slightly stronger bite, lions compensate with their cooperative hunting techniques and the ability to bring down larger prey through suffocation.
7). Overall Physical Capacity (Which is Stronger?)
When comparing the overall physical capacity of jaguars and lions, several factors need to be considered to determine which animal is stronger.
In terms of size, lions are generally larger than jaguars, with males weighing up to 420 pounds and measuring around 8 feet in length. On the other hand, jaguars are more compact, weighing up to 250 pounds and measuring around 6 feet in length.
In terms of strength, jaguars have a slightly stronger bite force, with an estimated 1,500 psi compared to the lion’s 1,000 psi. This allows jaguars to pierce through the thick hides and shells of their prey. However, lions compensate for this with their cooperative hunting techniques and the ability to bring down larger prey through suffocation.
When it comes to speed and agility, both animals are impressive. Jaguars are known for their agility and climbing abilities, while lions are known for their speed and endurance.
Therefore, while jaguars may have a slightly stronger bite force, lions possess other physical attributes that make them formidable predators. Their cooperative hunting techniques and ability to bring down larger prey through suffocation give them an advantage in certain situations.
8). Habitat
Jaguars are primarily found in the Americas, inhabiting a variety of ecosystems including rainforests, swamps, and grasslands. They are known for their ability to adapt to different environments, making them highly versatile predators. Jaguars are particularly skilled at swimming and are often found near bodies of water, where they can hunt for aquatic prey.
On the other hand, lions are predominantly found in Africa, with a small population in the Gir Forest of India. They inhabit a range of habitats including grasslands, savannas, and open woodlands. Lions are well-adapted to these open habitats, utilizing their speed and teamwork to hunt down large herbivores.
While both jaguars and lions have adapted to different habitats, their geographic ranges are distinct. Jaguars have a wider distribution, ranging from the southern United States to Argentina, while lions are limited to certain parts of Africa and a small area in India.

9). Lifespan
Jaguars have an average lifespan of around 12 to 15 years in the wild, although some individuals have been known to live up to 20 years. On the other hand, lions generally have a shorter lifespan, with an average of 10 to 14 years in the wild.
Several factors contribute to the difference in lifespan between these two big cats. One factor is the availability of prey. Jaguars have a more varied diet, which includes smaller animals like rodents and fish, in addition to larger prey. This diverse diet provides them with a better chance of survival and can contribute to their longer lifespan.
Another factor is the social structure of the two species. Lions live in prides, which consist of multiple females, their offspring, and a few dominant males. This social structure provides lions with protection and support, increasing their chances of survival. In contrast, jaguars are solitary animals, relying solely on their own abilities to survive.
Additionally, habitat destruction and human activities pose threats to both species. However, jaguars are more vulnerable to habitat loss due to their smaller population size and limited range. This further impacts their lifespan and overall survival.
While jaguars generally have a longer lifespan compared to lions, various factors such as diet, social structure, and habitat play a significant role in determining the longevity of these magnificent big cats.
10). Behavior
When comparing the behavior of jaguars and lions, several key aspects come into play. One significant difference lies in their feeding habits. Jaguars are known for their ability to adapt to various prey, ranging from small rodents to larger animals like deer and caimans. On the other hand, lions primarily rely on hunting large herbivores such as zebras and wildebeests, often employing a cooperative hunting strategy within their pride.
Aggression is another behavioral characteristic that sets these big cats apart. Jaguars are known for their aggressive nature, often displaying territorial behavior and defending their hunting grounds fiercely. Lions, on the other hand, exhibit a more social behavior within their pride, with males cooperating to protect their territory and females working together to raise their young.
Vocalization is also an important aspect of their behavior. Jaguars are known for their distinctive roar, which can be heard over long distances and serves as a means of communication and territorial marking. Lions, on the other hand, have a range of vocalizations, including roars, growls, and grunts, which they use to communicate with other members of their pride.
When it comes to social behavior, lions are highly social animals, living in prides that consist of multiple females, their offspring, and a few dominant males. This social structure allows for cooperative hunting, protection, and parenting. In contrast, jaguars are solitary animals, preferring to live and hunt alone.
Generally, the behavior of jaguars and lions differs significantly. Jaguars exhibit more solitary behavior, while lions are highly social animals.
11). Reproduction
Both jaguars and lions are viviparous, meaning they give birth to live young. However, there are some differences in their reproductive processes.
In terms of gestation period, jaguars have a gestation period of approximately 90 to 110 days, while lions have a slightly longer gestation period of around 100 to 110 days. This slight difference in gestation period may be attributed to variations in their physiological characteristics.
When it comes to the number of offspring produced, jaguars typically give birth to litters of one to four cubs, with two being the most common. On the other hand, lions usually give birth to litters of one to six cubs, with three being the average. This difference in litter size may be influenced by factors such as habitat, prey availability, and social structure.
In terms of parental care, both jaguars and lions exhibit maternal care, with the mother being responsible for nursing and protecting the cubs. However, lions also benefit from the cooperative care provided by other members of their pride, including the dominant male.
Therefore, while both jaguars and lions are viviparous and exhibit maternal care, there are slight differences in their gestation period and litter size. These variations may be influenced by factors such as habitat, prey availability, and social structure.
12). Danger Posed to Humans
Both lions and jaguars have the potential to be dangerous, but there are some notable differences in their behavior and interactions with humans.
Lions, known for their boldness and aggression, have been known to come close to human settlements in certain areas. This proximity increases the chances of human-lion encounters, which can be potentially dangerous. Lions have been known to attack humans, especially in situations where they feel threatened or when their natural prey is scarce. The rate of human deaths caused by lion attacks is relatively higher compared to jaguars.
On the other hand, jaguars are generally more elusive and tend to avoid human settlements. While they have been known to occasionally come into contact with humans, they are less likely to pose a direct threat. The rate of human deaths caused by jaguar attacks is significantly lower compared to lions.
If you happen to encounter a lion or a jaguar in the wild, it is important to take precautions to ensure your safety. Avoid approaching the animal and give it space to retreat. Make yourself appear larger by raising your arms and making loud noises to deter the animal. It is crucial to remember that both lions and jaguars are wild animals and should be treated with caution and respect.
Therefore, while both lions and jaguars have the potential to be dangerous, lions are generally considered to be more aggressive and pose a higher risk to humans.
13). Intelligence
When it comes to intelligence, both lions and jaguars exhibit remarkable cognitive abilities. However, there are some notable differences in their problem-solving skills and adaptability.
Lions are known for their social intelligence and complex social structures. They live in prides, which require coordination and cooperation among members. This social intelligence allows them to strategize during hunts and communicate effectively within the group. Lions also display a high level of adaptability, being able to thrive in various habitats and climates.
On the other hand, jaguars are renowned for their stealth and cunning. They are solitary animals, which requires them to rely solely on their individual intelligence for survival. Jaguars are excellent stalkers and possess exceptional patience and precision when hunting. Their ability to adapt to different environments, including dense forests and open grasslands, showcases their intelligence and versatility.
In terms of which animal is more intelligent, it is difficult to determine definitively. Lions’ social intelligence and cooperative behavior give them an advantage in certain aspects, while jaguars’ solitary nature and adaptability make them highly intelligent in their own right.
14). Tracks
When comparing the tracks of lions and jaguars, there are some distinct differences that can help identify which animal left the mark.
Lion tracks are characterized by their large size and rounded shape. The front tracks typically measure around 4 to 5 inches in diameter, while the hind tracks are slightly smaller. The toes are usually visible, and the overall track pattern resembles that of a large domestic cat.
On the other hand, jaguar tracks are more compact and have a distinct shape. The front tracks are generally round with four toes, while the hind tracks are more elongated and have three lobes at the back. The overall track pattern is more symmetrical compared to lion tracks.
In terms of size, lion tracks are generally larger than jaguar tracks due to the difference in their body sizes. This can be a helpful clue when trying to determine which animal left the track.
It’s important to note that track identification can be challenging, especially in areas where both lions and jaguars coexist. Other factors such as substrate type and weather conditions can also affect the clarity of the tracks. Therefore, it is recommended to consult with experts or field guides for accurate track identification.
15). Conservation Status
When it comes to the conservation status of lions and jaguars, both species face significant challenges in the wild.
The lion, also known as Panthera leo, is listed as vulnerable on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. The main threats to the survival of lion populations include habitat loss, human-wildlife conflict, and poaching. As human populations expand and encroach upon lion habitats, their natural prey becomes scarce, leading to increased conflicts with humans and livestock. Additionally, the illegal wildlife trade poses a serious threat to lions, as their bones, skins, and other body parts are highly valued in some cultures.
On the other hand, the jaguar, scientifically known as Panthera onca, is listed as near threatened. Similar to lions, jaguars face habitat loss due to deforestation and fragmentation. The conversion of their natural habitats into agricultural land and human settlements has resulted in a decline in their population. Additionally, jaguars are often targeted by hunters for their beautiful fur, which is highly sought after in the illegal wildlife trade.

Conclusion
I). SIMILARITIES
When comparing lions and jaguars, it is evident that these majestic big cats share some similarities. Both species belong to the Panthera genus and are known for their powerful physical attributes.
They possess sharp retractable claws, strong jaws, and muscular bodies that enable them to be formidable predators in their respective habitats. Additionally, both lions and jaguars are skilled hunters, relying on their stealth and agility to capture their prey.
II). DIFFERENCES
While there are similarities between lions and jaguars, there are also notable differences that set them apart. One significant difference lies in their size. Lions are generally larger than jaguars, with males weighing up to 420 pounds, while jaguars typically weigh around 200 pounds.
Another distinction is their habitat. Lions are found in grasslands and savannas, whereas jaguars inhabit dense forests and swamps. Additionally, their behavior differs, with lions being social animals that live in prides, while jaguars are solitary creatures.
Therefore, while lions and jaguars share certain similarities in their physical attributes and hunting abilities, they also have distinct differences in terms of size, habitat, and behavior.