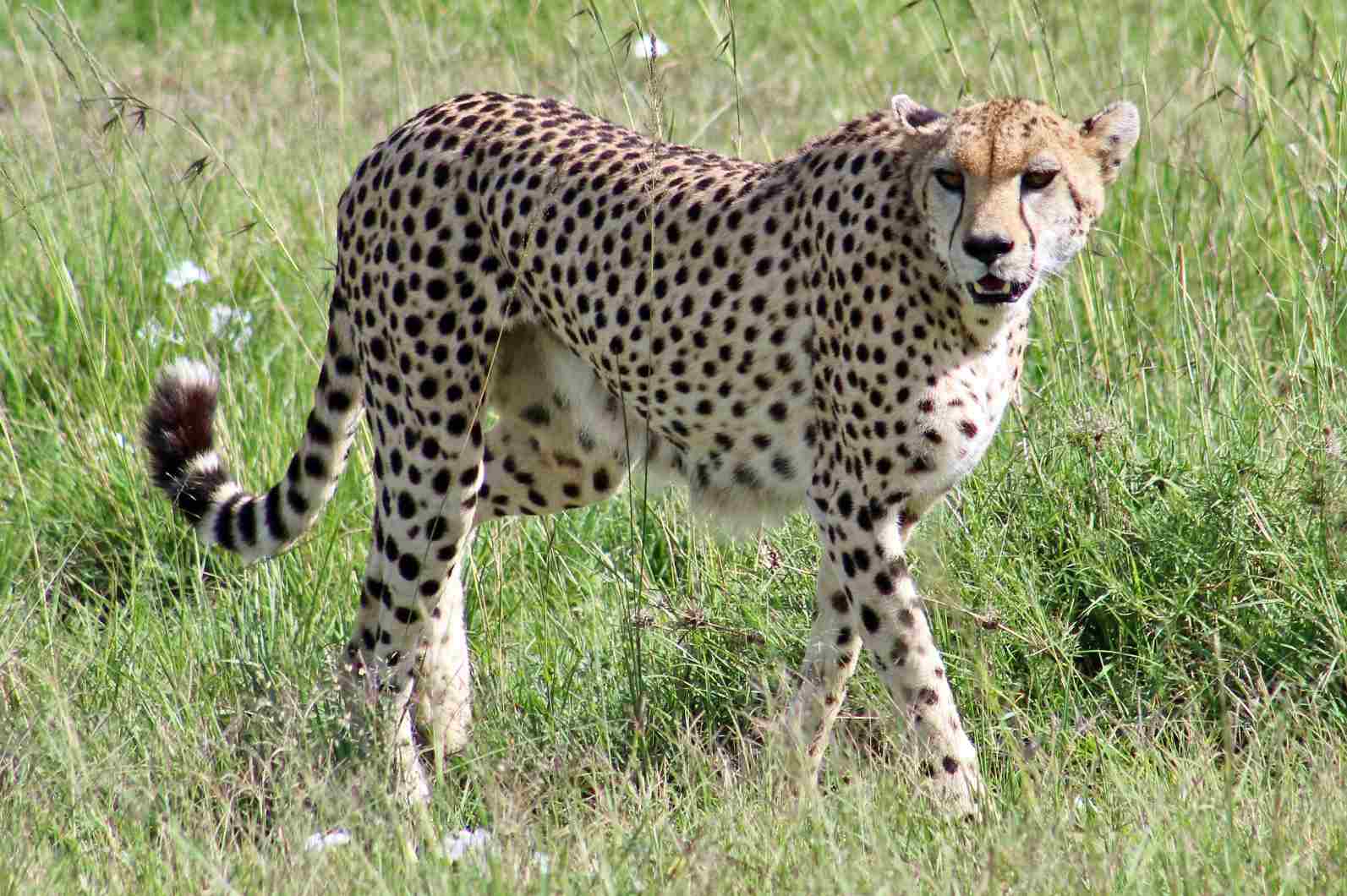
Cheetah Vs Lion Size, Weight, Ecological Comparison
A lion’s size and weight advantage make it a formidable opponent for a cheetah in a fight. With its larger and heavier body, the lion possesses more muscle mass and endurance, giving it a significant physical advantage. Additionally, lions are known to be more aggressive than cheetahs, further increasing their chances of winning in a confrontation.
This article will explore other factors that are used to compare these two big cats.
Reasons Why a Lion Will Win a Cheetah In a Fight/Physical Confrontation
I). Significant Size and Weight Advantages
One of the main reasons why a lion would win in a fight or physical confrontation against a cheetah is its significant size and weight advantages. Lions are much larger and heavier than cheetahs, which gives them a clear advantage in terms of physical strength.
With an average weight of around 420 to 570 pounds, lions are almost four times heavier than cheetahs, which weigh around 75 to 140 pounds. This size difference allows lions to have more muscle mass and overall power, making them more formidable opponents.
II). Increased Muscle Mass and Endurance
The larger body size of lions also means that they have increased muscle mass and endurance compared to cheetahs. Lions have evolved to be powerful predators, capable of taking down large prey such as wildebeests and zebras.
Their muscles are well-developed and designed for strength and stamina, allowing them to engage in prolonged physical confrontations. On the other hand, cheetahs, with their slender bodies built for speed, have less muscle mass and endurance, making them less equipped for prolonged fights.
III). Lions are More Aggressive
In addition to their size and muscle advantages, lions are known to be more aggressive than cheetahs. Lions are social animals that live in prides, and they have developed a hierarchical structure within their groups.
This social structure has made lions more territorial and protective of their pride, leading to increased aggression when faced with threats. Cheetahs, on the other hand, are solitary animals and are generally less aggressive. This difference in aggression levels gives lions an upper hand in physical confrontations, as they are more likely to initiate and engage in fights.
Therefore generally, the significant size and weight advantages, increased muscle mass and endurance, and higher aggression levels make lions more likely to win in a fight or physical confrontation against cheetahs. While cheetahs may have their own strengths, such as speed and agility, these factors give lions a clear advantage in a head-to-head battle.

*Details of Comparison
| Feature | Cheetah | Lion |
| Taxonomy | Acinonyx jubatus | Panthera leo |
| Size | Smaller (3-4 ft height, 4.5-5.5 ft length) |
Larger (3.5-4.5 ft height, 6-8 ft length)
|
| Weight | Lighter (75-140 lbs) |
Heavier (265-420 lbs)
|
| Speed & Agility | Faster (70 mph), more agile |
Slower (50 mph), less agile
|
| Bite Force | Weaker (475 psi) |
Stronger (650 psi)
|
| Habitat | Open grasslands, semi-deserts |
Grasslands, savannas, open woodlands
|
| Lifespan | 10-12 years | 15-20 years |
| Behavior | Solitary hunters, docile, purring sound |
Social hunters (prides), aggressive, roars, growls
|
| Reproduction | Shorter gestation (90-95 days), larger litters (3-5 cubs), solitary breeding |
Longer gestation (100-110 days), smaller litters (2-4 cubs), cooperative breeding
|
| Danger to Humans | Lower | Higher |
| Intelligence | Specialized for speed and agility |
Specialized for social structure and problem-solving
|
| Tracks | Smaller, single pad with 3 lobes, prominent claw marks |
Larger, distinctive 4-lobed pad, less pronounced claw marks
|
| Conservation Status | Vulnerable |
Vulnerable/Endangered
|
1). Taxonomy
The taxonomy of cheetahs and lions reveals interesting differences between these two felines. Cheetahs belong to the genus Acinonyx and species jubatus, while lions are classified under the genus Panthera and species leo.
In terms of their taxonomy, cheetahs and lions are distinct species with unique characteristics. Cheetahs are known for their slender build, distinctive black “tear stripes” running from their eyes to the sides of their mouth, and a lightweight body structure. On the other hand, lions have a more robust stature, a majestic mane (in the case of males), and a larger overall size compared to cheetahs.
While both cheetahs and lions are part of the Felidae family, their taxonomic differences highlight their evolutionary paths and adaptations to their respective environments. Cheetahs have developed a specialized body structure for speed and agility, while lions have evolved to be powerful predators capable of taking down large prey.
2). Appearance
When comparing the appearance of cheetahs and lions, several key differences become apparent. Firstly, their coats, fur, and skin vary significantly. Cheetahs have a unique coat pattern consisting of black spots on a golden background, which provides excellent camouflage in their natural habitat. In contrast, lions have a tawny-colored coat with a lighter belly and a mane that is more prominent in males. This difference in coat pattern and coloration reflects their distinct evolutionary adaptations.
Secondly, their stature and build also differ. Cheetahs have a slender and lightweight body structure, designed for speed and agility. Their long legs and flexible spine enable them to reach incredible speeds in pursuit of prey. On the other hand, lions have a more robust stature, with a muscular build that allows them to overpower larger prey. Their strong jaws and sharp teeth are adapted for hunting and taking down large animals.
In terms of appearance, cheetahs and lions have evolved distinct physical characteristics that suit their respective hunting strategies and environments. Cheetahs’ camouflage and streamlined bodies make them efficient hunters in open grasslands, while lions’ powerful physique and majestic mane reflect their role as apex predators in the savannah.

3). Size
Cheetahs are generally smaller in size compared to lions. On average, cheetahs measure around 3 to 4 feet in height at the shoulders and have a total body length of approximately 4.5 to 5.5 feet. In contrast, lions are much larger, with an average height at the shoulders ranging from 3.5 to 4.5 feet and a total body length of 6 to 8 feet.
These size differences are a result of their distinct evolutionary adaptations and ecological roles. Cheetahs’ smaller size allows them to be more agile and swift, enabling them to chase down their prey with incredible speed. Their slender build and lightweight body make them highly efficient hunters in open grasslands.
On the other hand, lions’ larger size gives them the advantage of overpowering and taking down larger prey. Their muscular build and robust stature provide them with the strength and power needed to bring down animals such as wildebeests and zebras. The size difference between cheetahs and lions reflects their different hunting strategies and ecological niches.
4). Weight
When comparing the weight of cheetahs and lions, it is evident that lions are significantly heavier than cheetahs. Adult cheetahs typically weigh between 75 to 140 pounds, while adult lions can weigh anywhere from 265 to 420 pounds.
The difference in weight between these two big cats is due to their distinct body structures and hunting strategies. Cheetahs have a slender and lightweight build, which allows them to achieve incredible speeds while chasing down their prey. Their lighter weight enables them to swiftly change direction and accelerate rapidly, making them the fastest land animals.
In contrast, lions have a more robust and muscular physique, which contributes to their impressive strength and power. Their heavier weight gives them an advantage when it comes to taking down larger prey, such as wildebeests and zebras. The additional mass provides lions with the necessary force to overpower their prey and bring them down.
5). Speed and Agility
Cheetahs are much faster than lions with a speed margin of 20 miles per hour and above.
When comparing the speed and agility of cheetahs and lions, it is clear that cheetahs are the undisputed champions. Cheetahs are renowned for their incredible speed, capable of reaching speeds up to 70 miles per hour in short bursts. This exceptional speed allows them to swiftly chase down their prey, making them highly efficient hunters.
On the other hand, lions are not known for their speed. While they are certainly capable of running, their top speed is nowhere near that of a cheetah. Lions can reach speeds of around 50 miles per hour, but they cannot sustain this pace for long distances. Instead, lions rely on their strength and teamwork to bring down their prey.
In terms of agility, cheetahs also have the upper hand. Their lightweight build and flexible spine enable them to make quick and sharp turns while in pursuit of their prey. This agility is crucial for their hunting success, as it allows them to outmaneuver their prey and close in for the kill.
Lions, on the other hand, have a more cumbersome and less agile body structure. While they possess strength and power, their size and weight limit their agility. Lions are better suited for ambush-style hunting, where they can rely on their strength to overpower their prey.
6). Bite Force
Cheetahs have a bite force of around 475 psi, which is relatively weaker compared to other big cats. This is because cheetahs have slender jaws and smaller teeth, which are adapted for gripping and suffocating their prey rather than delivering a powerful bite. However, despite their lower bite force, cheetahs are still capable of taking down their prey efficiently by targeting vulnerable areas such as the throat or neck.
On the other hand, lions have a significantly stronger bite force, measuring around 650 psi. Lions have robust jaws and large, sharp teeth designed for tearing through tough hides and bones. Their powerful bite allows them to bring down large prey, such as wildebeests or zebras, by delivering crushing force to their target.
While cheetahs may have a weaker bite force compared to lions, it is important to note that bite force is just one aspect of their hunting strategy. Cheetahs rely on their incredible speed and agility to catch their prey, while lions utilize their strength and teamwork.
7). Overall Physical Capacity (Which is Stronger?)
Lions are significantly stronger than cheetahs, for a variety of reasons.
When comparing the overall physical capacity of a lion and a cheetah, it becomes evident that the lion holds the advantage. The lion is larger and heavier, with more muscle mass and endurance. These factors contribute to its superior strength and power in comparison to the cheetah.
In terms of size, lions can reach lengths of up to 10 feet and weigh between 330 to 550 pounds, while cheetahs are smaller, measuring around 4 to 5 feet in length and weighing between 77 to 143 pounds. The lion’s larger size gives it a significant advantage in terms of physical strength.
Furthermore, lions possess a higher muscle mass, allowing them to exert more force and take down larger prey. Their endurance is also noteworthy, as they can sustain physical exertion for extended periods, making them formidable hunters.
In a violent confrontation between a lion and a cheetah, the lion’s overall physical capacity would likely lead to the defeat of the cheetah. The lion’s size, strength, and endurance would overpower the cheetah, causing it to succumb to the lion’s superior physical abilities.
8). Habitat
Lions are primarily found in grasslands, savannas, and open woodlands across Africa and a small population in the Gir Forest of India. They are highly adaptable and can thrive in various habitats, including semi-arid regions. Lions form social groups called prides and rely on teamwork to hunt and defend their territories.
On the other hand, cheetahs prefer open grasslands and semi-deserts. They are mainly found in sub-Saharan Africa, with a small population in Iran. Cheetahs are solitary animals and rely on their incredible speed and agility to hunt. Their slender body and long legs are well-suited for sprinting in open habitats, allowing them to chase down their prey.
When comparing the habitats of lions and cheetahs, it is clear that lions have a broader geographic range and can adapt to a wider variety of ecosystems. This adaptability gives them an advantage in terms of survival and finding suitable prey.
Therefore, while lions can thrive in various habitats and have a larger geographic range, cheetahs are specialized for open grasslands and semi-deserts. The habitat of each animal has shaped their behavior, hunting strategies, and social structure.

9). Lifespan
Cheetahs have an average lifespan of 10 to 12 years in the wild, while lions can live up to 15 years in the wild and even longer in captivity.
Cheetahs have a relatively short lifespan due to various factors. Their high-speed hunting technique puts a significant strain on their bodies, leading to a higher risk of injuries and exhaustion. Additionally, cheetahs face competition from other predators and often lose their kills to larger carnivores, which can impact their overall health and survival.
On the other hand, lions have a longer lifespan compared to cheetahs. This can be attributed to their social structure and cooperative hunting behavior. Lions live in prides, which provide protection and support for individuals. The collective effort in hunting and defending territories increases their chances of survival and reduces the risk of predation.
While cheetahs have a relatively short lifespan of 10 to 12 years, lions can live up to 15 years or more in the wild. The social structure and cooperative behavior of lions contribute to their longer lifespan compared to the solitary lifestyle of cheetahs.
10). Behavior
When comparing the behavior of cheetahs and lions, several key differences emerge. Firstly, in terms of feeding, cheetahs are solitary hunters, relying on their incredible speed and agility to chase down prey. They often consume their kill quickly to avoid losing it to larger predators. On the other hand, lions are social hunters, working together in prides to bring down larger prey. They have a more opportunistic feeding behavior, often scavenging from kills made by other predators.
In terms of aggression, cheetahs are generally more docile and less confrontational compared to lions. Lions, being apex predators, exhibit more aggressive behavior, especially when it comes to defending their territory or protecting their pride.
Vocalization is another area where the two species differ. Cheetahs are known for their unique purring sound, which they use to communicate with their cubs and other cheetahs. Lions, on the other hand, have a wide range of vocalizations, including roars, growls, and grunts, which they use to communicate with other members of their pride.
Social behavior is also distinct between cheetahs and lions. Cheetahs are mostly solitary animals, except during mating season or when a mother is raising her cubs. Lions, on the other hand, live in prides consisting of multiple females, their offspring, and a few dominant males. This social structure allows for cooperative hunting, protection, and sharing of resources.
In terms of parenting, cheetah mothers are solely responsible for raising their cubs, teaching them hunting skills and providing protection. Lionesses, on the other hand, share the responsibility of raising cubs within the pride, allowing for communal care and learning from multiple adults.
11). Reproduction
Both cheetahs and lions are viviparous, meaning they give birth to live young. However, the gestation period differs significantly between the two species.
Cheetahs have a relatively short gestation period of around 90 to 95 days. This shorter gestation period allows cheetahs to reproduce more frequently, increasing their chances of passing on their genes to the next generation. In contrast, lions have a longer gestation period of approximately 100 to 110 days.
Another notable difference is the size of the litters. Cheetahs typically give birth to a litter of three to five cubs, although larger litters of up to eight cubs have been recorded. Lions, on the other hand, usually have smaller litters, with an average of two to four cubs.
The reproductive strategies of cheetahs and lions also differ. Cheetahs are more solitary in their reproductive behavior, with males and females coming together only for mating. Once the mating is complete, the male has no further involvement in raising the cubs. In contrast, lions have a more cooperative reproductive strategy. Mating within the pride is not limited to a specific breeding season, and multiple males may mate with the same female. This cooperative breeding behavior ensures the survival and protection of the cubs within the pride.
12). Danger Posed to Humans
When it comes to the danger posed to humans, the lion is considered to be more dangerous than the cheetah. This is primarily due to its larger size, greater strength, and bolder nature. Lions have been known to come close to human settlements, especially in areas where their natural habitat has been encroached upon. While cheetahs are generally not aggressive towards humans, lions can exhibit aggressive behavior if they feel threatened or if they perceive humans as a potential source of food.
In terms of the rate of human deaths caused, lions have been responsible for a higher number of fatalities compared to cheetahs. This is partly because lions are apex predators and have the ability to take down larger prey, including humans. Cheetahs, on the other hand, primarily prey on smaller animals and rarely pose a direct threat to humans.
If you happen to encounter a lion or cheetah in the wild, it is important to take precautions to ensure your safety. In the case of a lion, it is advisable to avoid direct eye contact, make yourself appear larger by raising your arms, and slowly back away without turning your back. It is crucial not to run, as this may trigger the lion’s instinct to chase.
13). Intelligence
When comparing the intelligence of cheetahs and lions, it is important to consider their different hunting strategies and social behaviors. Cheetahs are known for their exceptional speed and agility, which they rely on to catch their prey. They are solitary animals and do not form complex social structures like lions. However, cheetahs demonstrate a high level of intelligence when it comes to hunting techniques and adapting to their environment.
On the other hand, lions are highly social animals that live in prides. Their intelligence is evident in their cooperative hunting strategies and complex social interactions. Lions exhibit a higher level of problem-solving skills and communication within their pride. They work together to bring down larger prey and defend their territory.
While both cheetahs and lions possess their own unique forms of intelligence, it is difficult to determine which species is more intelligent overall. Their intelligence is specialized for their respective lifestyles and survival strategies. Cheetahs rely on their speed and agility, while lions rely on their strength and social cohesion.
14). Tracks
When comparing the tracks of cheetahs and lions, there are distinct differences that can be observed. Cheetah tracks are characterized by their unique shape and claw marks. The tracks of cheetahs show a single, rounded pad with three lobes at the back and a prominent claw mark at the front. These tracks are often smaller in size compared to lion tracks.
On the other hand, lion tracks are larger and more robust. They have a distinctive pad shape with four lobes at the back and a prominent claw mark at the front. The size and depth of lion tracks are indicative of their larger body size and weight compared to cheetahs.
In terms of behavior, cheetahs are known for their ability to accelerate quickly and reach high speeds. This is reflected in their tracks, which often show longer strides and deeper claw marks as they dig into the ground for traction. Lion tracks, on the other hand, may show less pronounced claw marks and shorter strides, as they rely more on their strength and power rather than speed.
15). Conservation Status
When it comes to the conservation status of cheetahs and lions, both species face significant challenges in the wild. Cheetahs are classified as “vulnerable” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), while lions are listed as “vulnerable” or “endangered” depending on their specific subpopulations.
The main threats to the survival of wild cheetah populations include habitat loss, fragmentation, and degradation. As human populations expand and encroach upon their natural habitats, cheetahs are losing their traditional hunting grounds and are increasingly coming into conflict with humans. Additionally, illegal wildlife trade and poaching pose a significant threat to cheetah populations, as their skins and body parts are highly valued in some cultures.
On the other hand, lions face similar threats, including habitat loss and degradation due to human activities such as agriculture and urbanization. Additionally, lions are often targeted by trophy hunters, which further exacerbates their declining numbers. Human-wildlife conflict is also a significant issue for lions, as they sometimes prey on livestock, leading to retaliatory killings by farmers.

Conclusion
I). SIMILARITIES
When comparing cheetahs and lions, it is evident that these two big cats share some similarities. Both animals belong to the same family, Felidae, and are known for their incredible speed and agility. Additionally, they are both carnivorous predators, relying on hunting and killing their prey for survival.
II). DIFFERENCES
Despite their similarities, there are also significant differences between cheetahs and lions. One notable difference is their size and weight. Lions are much larger and heavier than cheetahs, with adult males weighing up to 420 pounds, while cheetahs typically weigh around 110 pounds.
Another difference lies in their hunting strategies. Cheetahs are solitary hunters, relying on their incredible speed to chase down and capture their prey, while lions are social animals that hunt cooperatively in prides.
In terms of physical capacity, lions have a more robust build and possess a stronger bite force compared to cheetahs. This is due to their different ecological roles, with lions being apex predators and cheetahs specializing in high-speed pursuits. Additionally, their habitats differ, with cheetahs favoring open grasslands and lions being more adaptable to various habitats, including savannas and woodlands.