5+ Scavengers in The Congo Rainforest Ecosystem Discussed
Examples of scavengers in the Congo rainforest are vultures, ants, millipedes, beetles, hawks, Pied Crows, and African Golden Cats. These creatures play critical roles in maintaining the health and balance of the ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter. Vultures consume carrion, reducing disease risk; ants and millipedes decompose plant material, enriching soil nutrients; beetles process animal waste, contributing to soil fertility; hawks scavenge alongside their predatory habits; Pied Crows are omnivorous scavengers; and African Golden Cats, primarily hunters, will also scavenge when needed. Collectively, these scavengers ensure the rainforest stays clean, vibrant, and ecologically balanced.
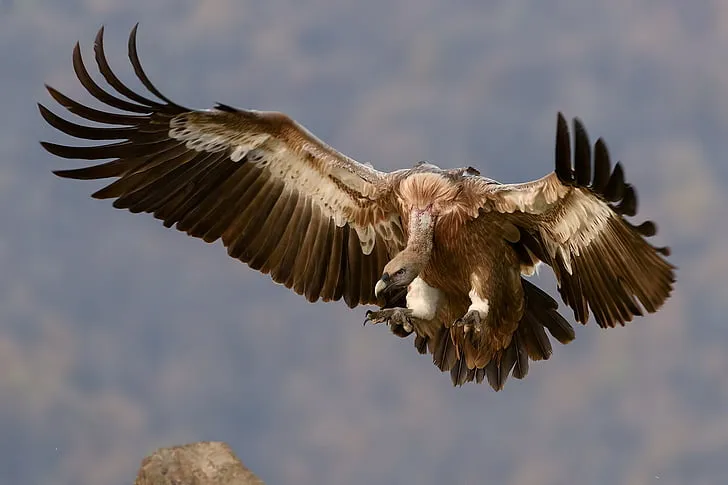
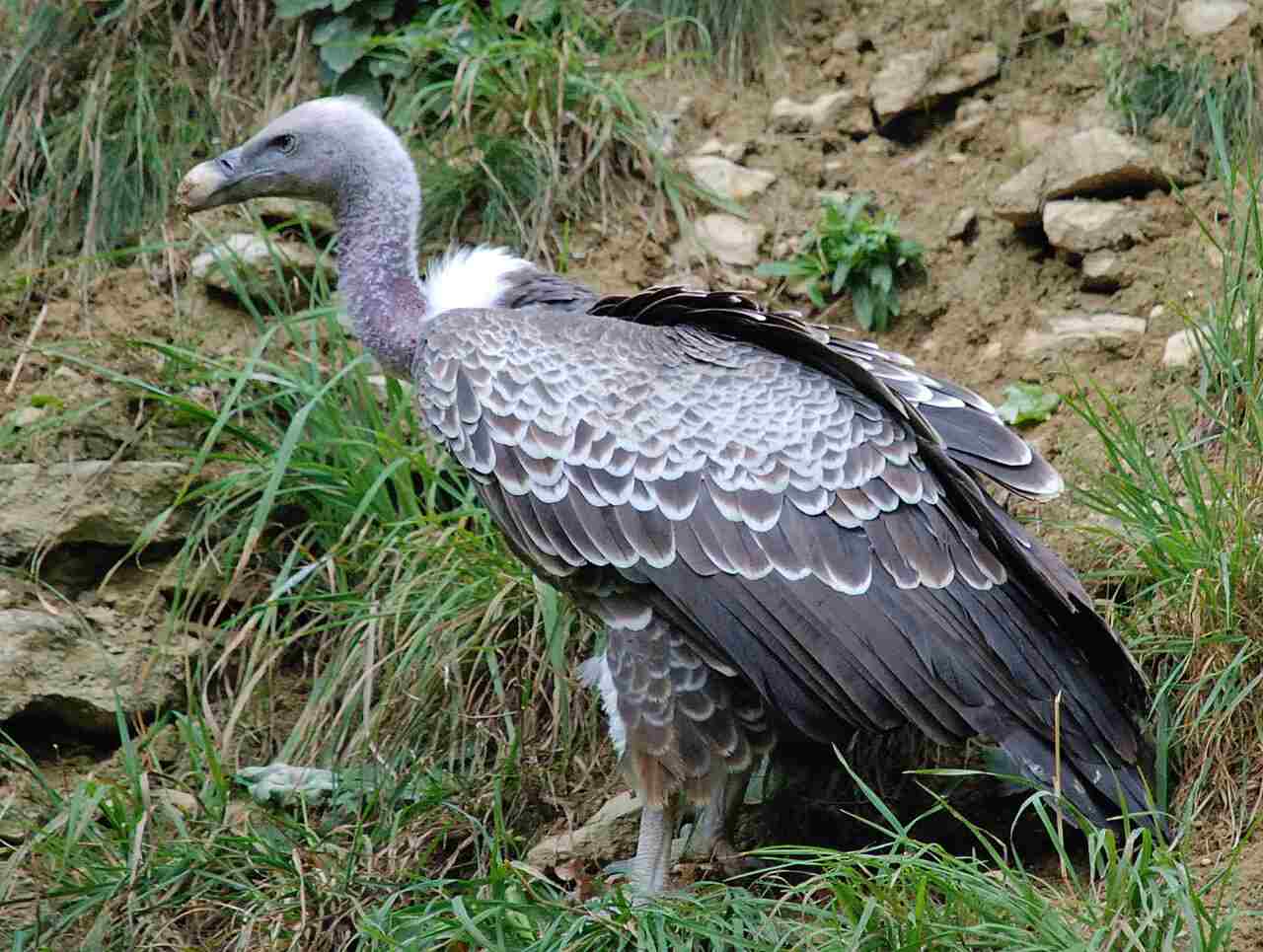
1. Vulture
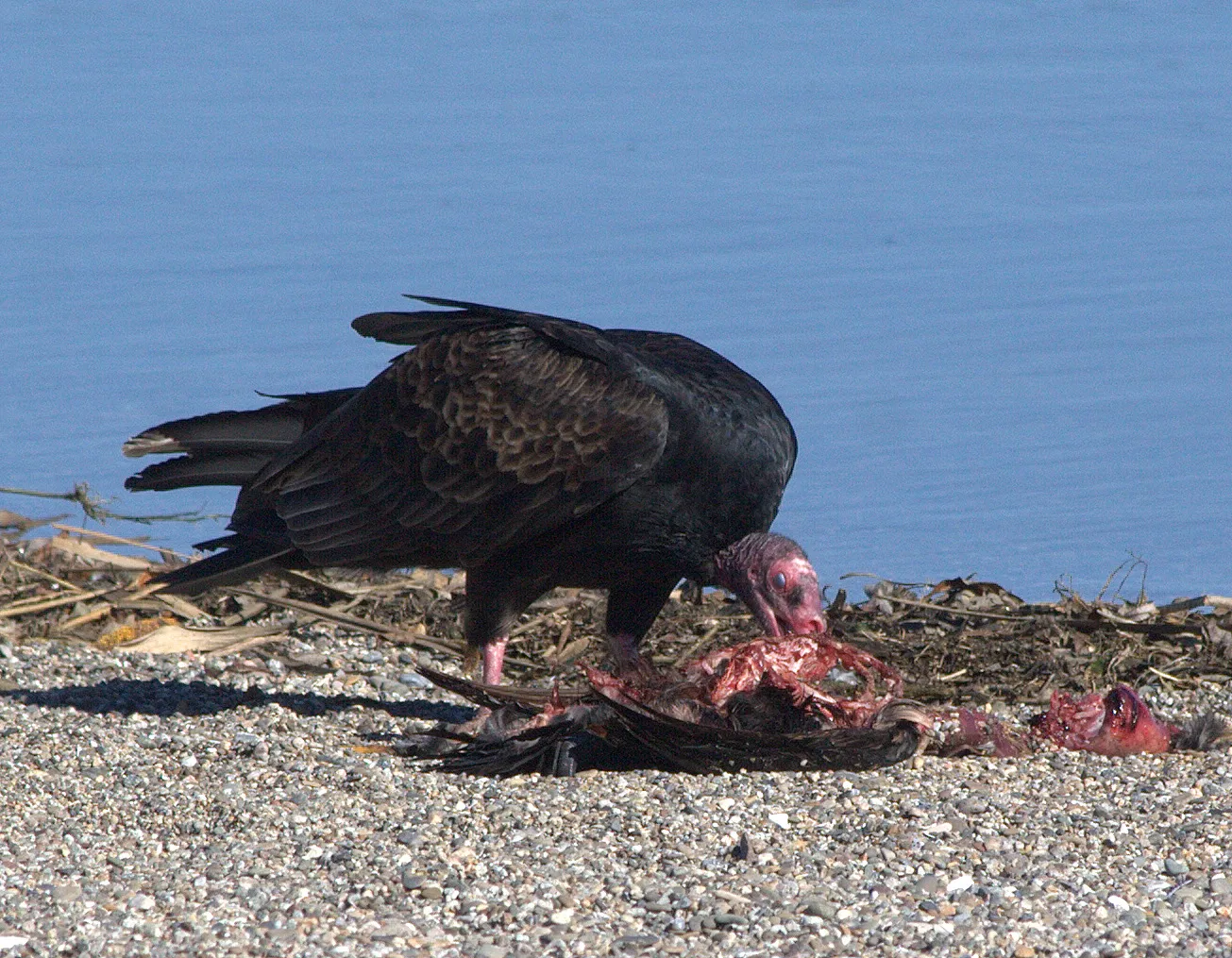
Vultures are crucial scavengers in the Congo rainforest, playing a significant role in the ecosystem by consuming carrion and decomposing matter. Their powerful beaks and keen eyesight allow them to spot dead or decaying animals from great heights. This ability to locate and devour carcasses helps to keep the rainforest clean and prevents the spread of disease. In the Congo rainforest, different species of vultures, like the White-backed Vulture and the Hooded Vulture, can be seen gliding gracefully above the canopy, scanning the forest floor for their next meal.
The presence of vultures also contributes to the ecological balance in the Congo rainforest. By quickly consuming animal remains, they reduce the likelihood of other scavengers, like rodents and insects, proliferating due to an abundance of food sources. This, in turn, helps control pest populations and maintains the health of the forest environment. Vultures are resilient birds, adapted to consume a wide range of organic material, and their role as efficient scavengers is indispensable for the sustainability and cleanliness of the rainforest ecosystem.
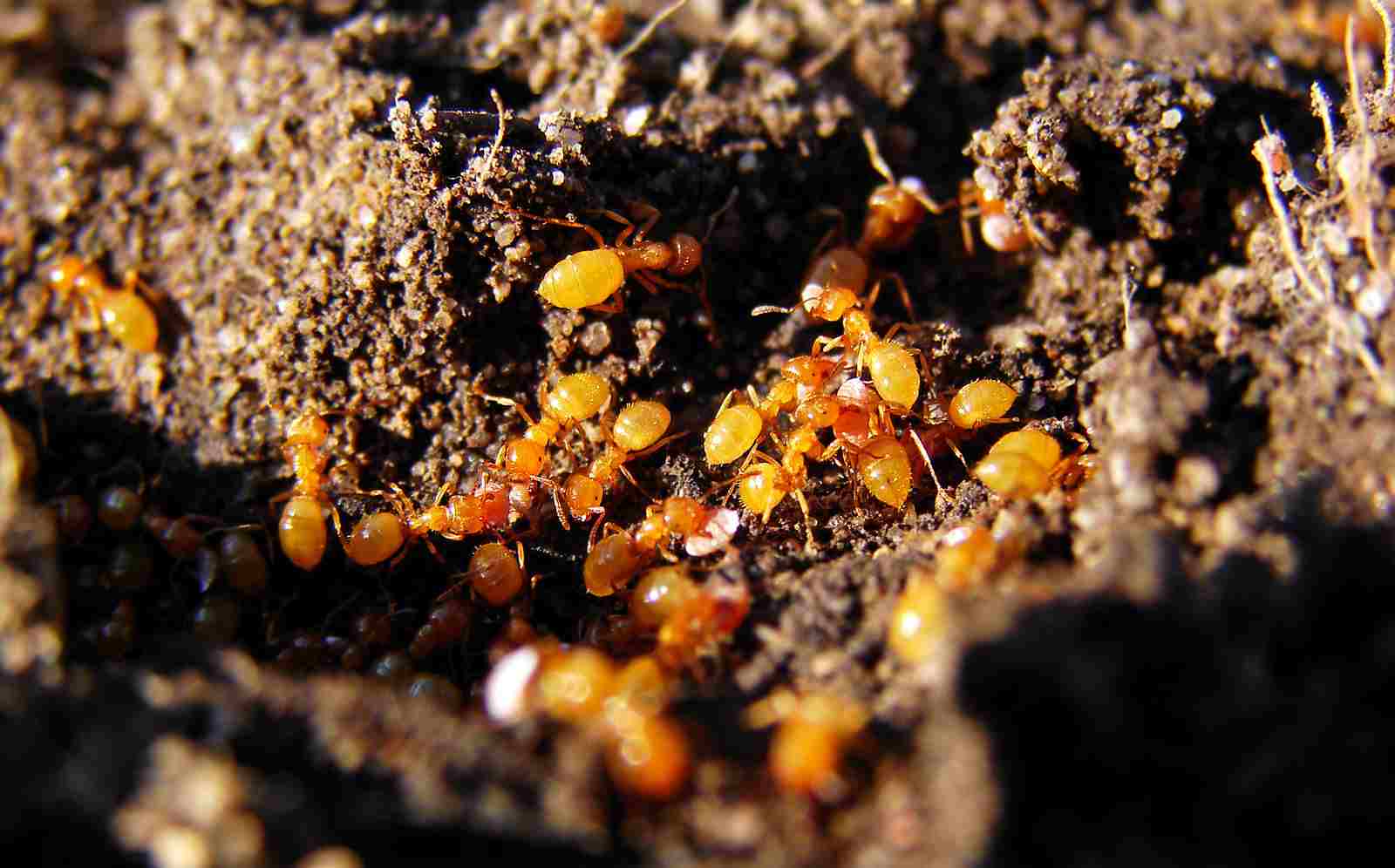
2. Ant
Ants are prolific scavengers in the Congo rainforest, exhibiting remarkable teamwork and organization. As social insects, they operate within colonies, often comprising thousands of individuals, each with specific roles such as workers, soldiers, or queens. Ants play a vital role in decomposing organic material, ranging from fallen leaves to dead insects and other small creatures. This process of breaking down matter enriches the soil with nutrients, promoting plant growth and contributing to the rainforest’s biodiversity.
Ants’ scavenging behavior is not only crucial for nutrient recycling but also for maintaining the forest’s intricate food web. They collect food for their colonies, creating trails that other ants can follow, thereby efficiently transporting resources back to their nests. By clearing dead plant and animal matter, ants prevent the accumulation of decaying materials, reducing the spread of disease and promoting a healthy forest ecosystem. Their adaptability and efficiency make ants indispensable in sustaining the balance within the Congo rainforest.
3. Millipede
Millipedes are vital scavengers in the Congo rainforest, renowned for their role in decomposing organic matter. With their long, segmented bodies and numerous legs, millipedes slowly crawl through the forest floor, feeding on decaying leaves, wood, and other plant debris. As they break down this material, they help recycle nutrients back into the soil, supporting plant growth and contributing to the overall health of the rainforest ecosystem.
Millipedes contribute to the rainforest’s nutrient cycling by ingesting organic matter and excreting nutrient-rich waste, which enriches the soil. Their slow-moving nature allows them to process large amounts of decaying material over time, ensuring that the forest floor remains clean and fertile. Millipedes’ role as decomposers is crucial in maintaining the forest’s structure and supporting the diverse plant life that thrives in the Congo rainforest.
4. Beetle
Beetles are among the most diverse groups of scavengers in the Congo rainforest, with thousands of species contributing to the ecosystem’s health. These insects exhibit a wide range of feeding habits, with many beetles specializing in decomposing dead plant and animal matter. Dung beetles, for example, are essential scavengers that process animal feces, breaking it down and incorporating it into the soil, which helps improve soil structure and fertility.
Scarab beetles and carrion beetles are other examples of scavenging beetles in the Congo rainforest. They play a significant role in recycling organic material by feeding on dead animals, decaying wood, and fallen leaves. This scavenging activity not only keeps the forest floor clean but also prevents the buildup of potentially harmful bacteria and pathogens. Beetles’ adaptability and varied feeding habits make them crucial contributors to the ecological balance and nutrient cycling within the rainforest.
5. Hawk
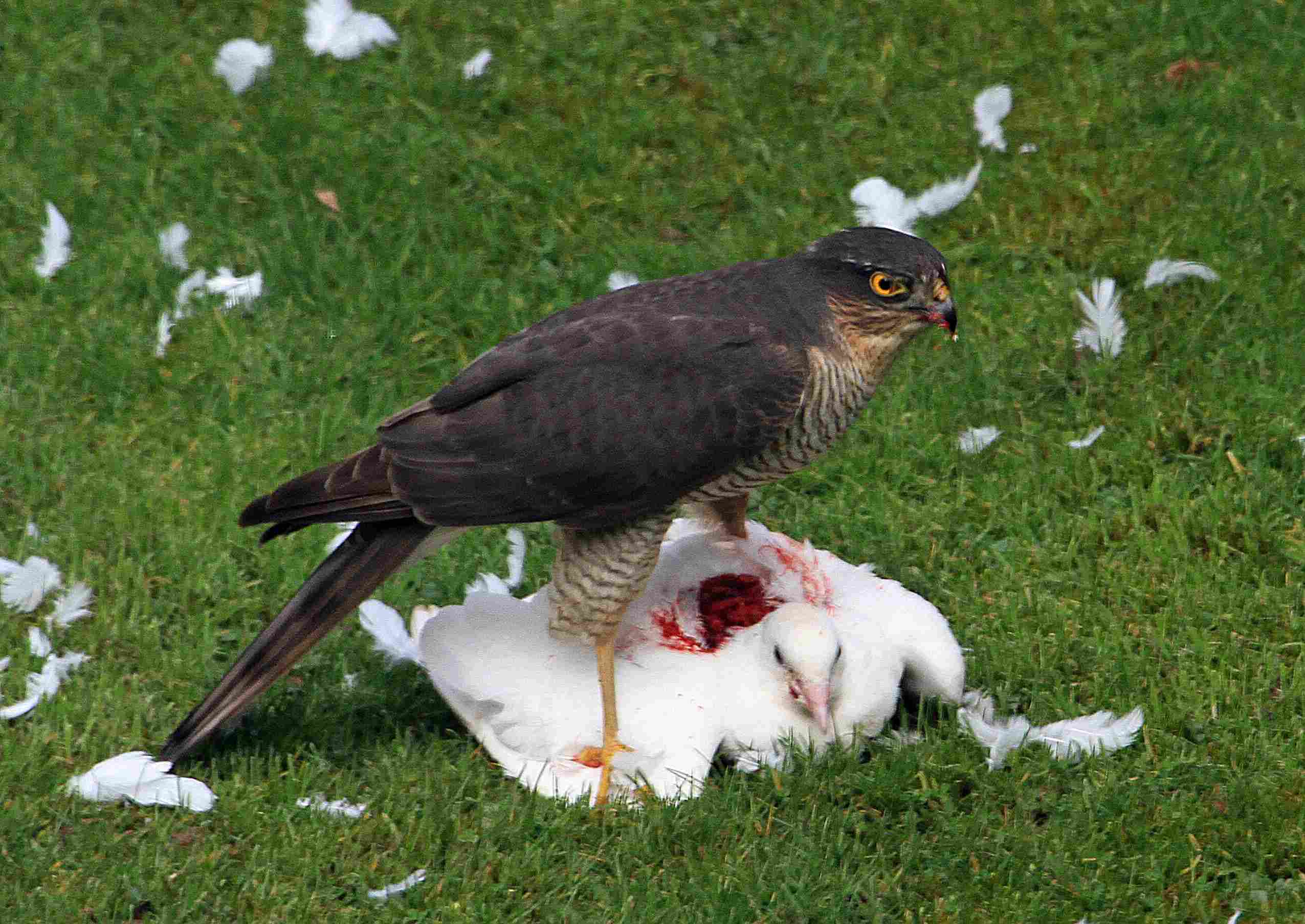
Hawks are predatory birds that also serve as scavengers in the Congo rainforest. While they are primarily known for their hunting prowess, feeding on smaller birds, reptiles, and mammals, they are not above consuming carrion when the opportunity arises. This behavior allows hawks to contribute to the ecosystem’s balance by helping to clean up dead animal remains. Their sharp eyesight and powerful talons enable them to spot carcasses from great heights and swoop down to claim their share.
The scavenging activity of hawks plays an important role in the Congo rainforest, as it helps reduce the spread of disease and maintain a cleaner environment. By consuming dead animals, hawks contribute to the breakdown of organic matter, which in turn supports nutrient recycling. Their versatile diet, which includes carrion, ensures they have a consistent food source even when hunting is less fruitful, illustrating their adaptability in the complex ecosystem of the Congo rainforest.
6. Pied Crow
The Pied Crow is a versatile scavenger in the Congo rainforest, known for its intelligence and adaptability. As omnivorous birds, they feed on a wide range of food sources, including carrion, insects, seeds, and fruits. Pied Crows play a crucial role in scavenging, as they are often seen gathering around dead animals, breaking them down, and consuming the remains. This behavior helps prevent the accumulation of decaying organic matter and reduces the risk of disease spreading through the rainforest.
Pied Crows are social birds, often seen in groups, which adds to their efficiency as scavengers. They are known for their ability to adapt to various environments and their opportunistic feeding habits. By consuming carrion and other organic debris, Pied Crows contribute to the ecological balance and cleanliness of the Congo rainforest. Their scavenging activities complement those of other scavengers, like vultures and beetles, creating a comprehensive system for decomposing and recycling organic matter in the ecosystem.
7. African Golden Cat
The African Golden Cat, a lesser-known resident of the Congo rainforest, is a skilled predator with occasional scavenging tendencies. While primarily a hunter that preys on small mammals, birds, and reptiles, it will opportunistically scavenge if the need arises or if prey is scarce. The African Golden Cat’s scavenging behavior, though less frequent than its hunting activities, contributes to the breakdown of dead animal remains in the rainforest.
As a solitary and elusive animal, the African Golden Cat uses its keen senses and agility to locate food, whether through hunting or scavenging. By consuming carrion, the cat helps maintain a clean environment in the rainforest, reducing the risk of disease spread and promoting nutrient recycling. This dual role as both predator and scavenger underscores the adaptability of the African Golden Cat and its importance in the Congo rainforest’s complex food web.
*Summary
-
Vultures
-
Play a key role in consuming carrion, preventing the spread of disease.
-
Help maintain cleanliness in the Congo rainforest by quickly devouring dead animals.
-
Contribute to ecological balance by reducing food sources for other scavengers, controlling pest populations.
-
-
Ants
-
Operate within large colonies, efficiently scavenging and breaking down organic material.
-
Enrich the soil through their decomposition activities, promoting plant growth.
-
Prevent accumulation of decaying matter, contributing to a healthy forest ecosystem.
-
-
Millipedes
-
Scavenge and decompose plant debris, enriching soil nutrients.
-
Slowly process large amounts of organic material, supporting rainforest biodiversity.
-
Contribute to nutrient cycling and maintain the structure of the forest ecosystem.
-
-
Beetles
-
A diverse group of scavengers with thousands of species, each with unique feeding habits.
-
Dung beetles process animal feces, improving soil structure and fertility.
-
Other beetles, like scarab and carrion beetles, decompose plant and animal matter, aiding nutrient recycling.
-
-
Hawks
-
Primarily predators but can act as scavengers when feeding on carrion.
-
Help maintain a clean environment by consuming dead animals, reducing disease spread.
-
Versatile diet allows them to adapt to various food sources in the rainforest ecosystem.
-
-
Pied Crows
-
Omnivorous scavengers feeding on carrion, insects, seeds, and fruits.
-
Social birds, often seen in groups, contributing to efficient scavenging.
-
Prevent buildup of decaying organic matter, promoting ecological balance.
-
-
African Golden Cat
-
Primarily a hunter but occasionally scavenges, contributing to ecosystem cleanliness.
-
Consuming carrion helps reduce the spread of disease in the rainforest.
-
Combines predatory and scavenging roles, showing adaptability in a complex food web.
-
| Scavenger |
Role in the Congo Rainforest
|
| Vultures |
Consume carrion, prevent disease spread, maintain cleanliness
|
| Ants |
Decompose organic matter, enrich soil, promote plant growth
|
| Millipedes |
Break down plant debris, support nutrient cycling, enrich soil
|
| Beetles |
Decompose animal and plant matter, process animal feces, improve soil structure
|
| Hawks |
Predatory birds, also scavenge, reduce disease risk, adaptable diet
|
| Pied Crows |
Omnivorous scavengers, feed on carrion, maintain ecological balance
|
| African Golden Cat |
Primarily a hunter, occasional scavenger, contributes to forest cleanliness
|
Related FAQs
1. What role do vultures play in the Congo rainforest ecosystem?
-
Vultures are scavengers that consume carrion, helping to prevent the spread of disease and maintain cleanliness in the rainforest. They also contribute to ecological balance by reducing food sources for other scavengers, thus controlling pest populations.
2. How do ants contribute to the health of the Congo rainforest?
-
Ants decompose organic matter such as leaves and dead insects, enriching the soil and promoting plant growth. Their organized scavenging behavior helps prevent the accumulation of decaying matter, contributing to a healthy forest ecosystem.
3. Why are millipedes important to the rainforest’s nutrient cycle?
-
Millipedes break down plant debris, slowly processing large amounts of organic material. This decomposition activity enriches the soil with nutrients, supporting biodiversity and maintaining the structure of the rainforest ecosystem.
4. What types of beetles are common scavengers in the Congo rainforest?
-
Various types of beetles, including dung beetles, scarab beetles, and carrion beetles, are common scavengers in the Congo rainforest. They contribute to nutrient recycling by decomposing animal feces, plant matter, and carrion, improving soil structure and fertility.
5. Do hawks only hunt, or do they also scavenge in the Congo rainforest?
-
While hawks are primarily predators, they also scavenge when the opportunity arises, consuming carrion. This scavenging behavior helps maintain a clean environment and reduces the risk of disease spread in the rainforest.
6. What makes Pied Crows effective scavengers in the Congo rainforest?
-
Pied Crows are omnivorous and versatile scavengers that feed on carrion, insects, seeds, and fruits. They are social birds often seen in groups, which contributes to their efficiency in scavenging and maintaining ecological balance.
7. What role does the African Golden Cat play in the Congo rainforest?
-
The African Golden Cat is primarily a predator that preys on small mammals, birds, and reptiles. However, it can also scavenge, consuming carrion when hunting is less fruitful. This dual role helps reduce the spread of disease and contributes to forest cleanliness.