What is a Canopy in the Rainforest? The Concept and Basic Features of Forest Canopies
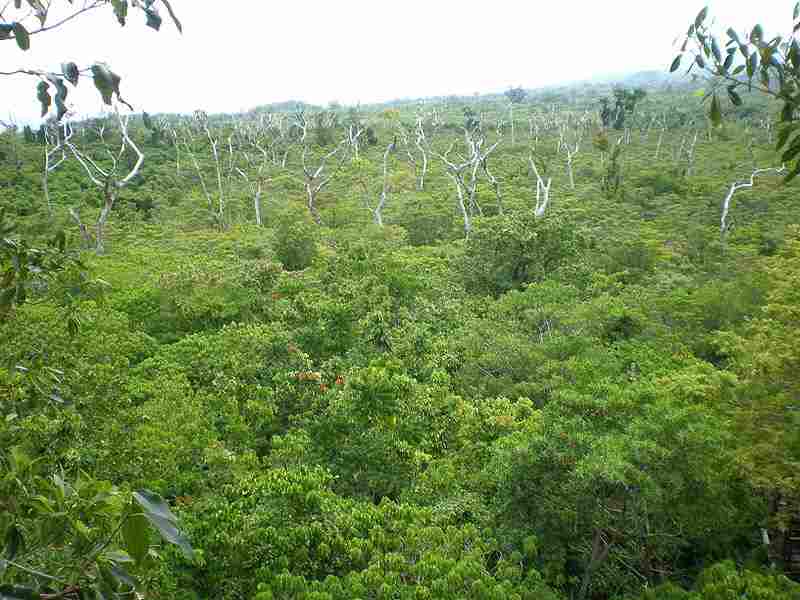
The rainforest canopy is an integral part of the rainforest ecosystem, characterized by its dense layer of vegetation. It acts as a protective roof over the rest of the rainforest, providing shelter and resources for a wide variety of species. Unlike a solid roof, the canopy is partially permeable, allowing sunlight and water to pass through.
The term “canopy” is used to describe this layer because it creates a continuous cover over the rainforest, much like a canopy over a bed. The canopy is formed by the next tallest trees in the rainforest, which typically grow to heights of around 20 feet. These trees have evolved to reach for sunlight, resulting in the formation of a dense and interconnected network of leaves and branches.
The canopy plays a vital role in the rainforest ecosystem. It acts as a barrier, limiting the amount of sunlight and precipitation that reaches the lower layers of the rainforest. This has significant implications for the plants and animals that inhabit the rainforest. The limited sunlight reaching the forest floor means that plants in the understory and ground layers have to adapt to low light conditions. Similarly, the reduced precipitation reaching the lower layers affects the availability of water for plants and animals.
The density of the canopy also provides a unique habitat for a wide range of organisms. Many species of birds, insects, mammals, and reptiles call the canopy home. The abundance of leaves and branches in the canopy offers ample opportunities for these organisms to find food, shelter, and nesting sites. In fact, the canopy is known to support more species than any other zone in the rainforest.
Furthermore, the canopy serves as a bridge between different layers of the rainforest. It connects the understory, ground layer, and forest floor, allowing for the movement of organisms and the exchange of resources. This interconnectedness is essential for the overall health and functioning of the rainforest ecosystem.
The rainforest canopy is not just a layer of leaves and branches. It is a complex and vital component of the rainforest ecosystem. Its dense nature acts as a barrier, limiting sunlight and precipitation, which in turn affects the plants and animals that inhabit the rainforest. The canopy also provides a unique habitat for a wide range of species and serves as a bridge between different layers of the rainforest, facilitating the movement of organisms and the exchange of resources. Understanding the concept and characteristics of the rainforest canopy is crucial for appreciating the intricate web of life that exists within the rainforest.
Concept and Characteristics of The Rainforest Canopy
The concept and characteristics of the rainforest canopy go beyond just being a layer of leaves and branches. This intricate structure serves as a vital component of the rainforest ecosystem, providing shelter and food for numerous organisms. The density of the canopy is a defining feature, as it creates a barrier that limits the amount of sunlight and precipitation that reaches the lower layers of the rainforest.
The dense nature of the canopy has important implications for the plants and animals that inhabit the rainforest. The limited sunlight reaching the forest floor requires plants in the understory and ground layers to adapt to low light conditions. Similarly, the reduced precipitation reaching the lower layers affects the availability of water for plants and animals.
Moreover, the rainforest canopy acts as a unique habitat for a wide range of species. Many birds, insects, mammals, and reptiles call the canopy home, taking advantage of the abundance of leaves and branches to find food, shelter, and nesting sites. In fact, the canopy supports more species than any other zone in the rainforest.
Additionally, the canopy serves as a bridge between different layers of the rainforest, allowing for the movement of organisms and the exchange of resources. This interconnectedness is crucial for the overall health and functioning of the rainforest ecosystem.
In summary, the concept and characteristics of the rainforest canopy extend beyond its physical composition. Its density, role in limiting sunlight and precipitation, and its function as a habitat and bridge make it a crucial element of the rainforest ecosystem.
Why is It Called A Canopy?
The rainforest canopy is referred to as a “canopy” because it functions as a protective covering or tent for the forest. The term “canopy” originates from the ancient Greek word κωνώπειον (konópeion), which means “cover to keep insects off.” This name is derived from the Greek word κώνωψ (kónops), which translates to “cone-face” and is a compound word that signifies “mosquito.”
The choice of the term “canopy” is fitting because it accurately describes the role of this layer in the rainforest ecosystem. Just like a canopy provides shelter and protection, the rainforest canopy acts as a shield for the lower layers of the forest. It creates a barrier that limits the amount of sunlight and precipitation that reaches the understory and ground layers.
By blocking a significant portion of sunlight, the canopy influences the availability of light for plants in the lower layers. This limitation has led to adaptations in the understory and ground-dwelling plants, allowing them to thrive in low light conditions. Similarly, the reduced amount of precipitation that reaches the forest floor affects the water availability for plants and animals in the lower layers.
The dense and intricate structure of the canopy provides a habitat for a diverse range of species. Many birds, insects, mammals, and reptiles make their homes in the canopy, utilizing the abundance of leaves and branches for food, shelter, and nesting sites. In fact, the canopy supports a greater number of species than any other zone in the rainforest.
The canopy serves as a crucial habitat for arboreal animals, such as monkeys and sloths, that spend most of their lives in the trees. These animals rely on the canopy for food, shelter, and protection from predators. The dense foliage and interconnected branches provide a safe haven for these creatures, allowing them to move freely and find resources within the canopy.
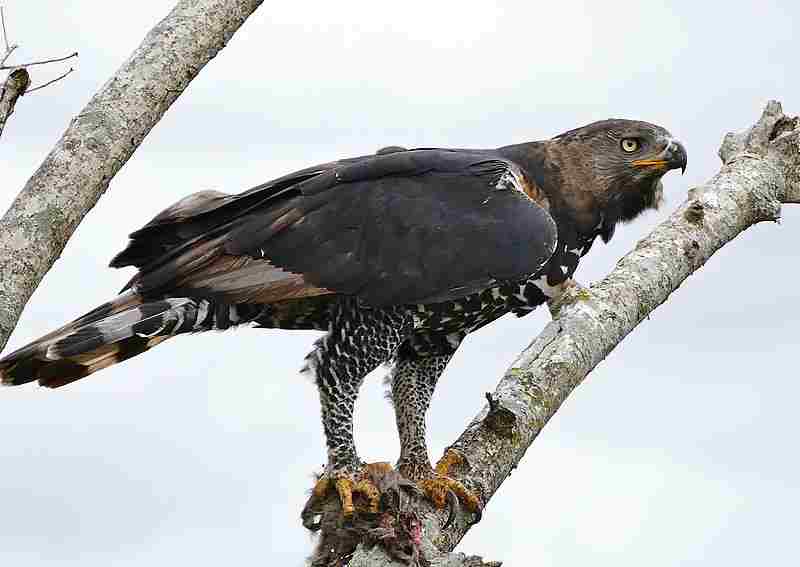
Additionally, the canopy acts as a vantage point for some predators, such as arboreal snakes, leopards, and harpy eagles. These predators take advantage of the height and coverage provided by the canopy to spot their prey and launch surprise attacks. The dense foliage also helps camouflage these predators, making it easier for them to remain hidden from their unsuspecting victims.
The canopy plays a crucial role in regulating and stabilizing the internal temperature and humidity of the rainforest. The dense layer of leaves and branches acts as a natural buffer, reducing the impact of temperature fluctuations and preventing excessive evaporation. This helps to maintain a stable microclimate within the rainforest, which is essential for the survival of many plant and animal species.
Generally, the term “canopy” accurately describes the function and characteristics of this layer in the rainforest. It serves as a protective covering, limiting sunlight and precipitation, and providing a habitat for numerous organisms. The name reflects the importance of this layer in maintaining the balance and biodiversity of the rainforest ecosystem. The canopy is not only a physical structure but also a vital component of the intricate web of life in the rainforest.

What is The Role of The Canopy in the Forest?
The role of the canopy in the forest is multifaceted and essential for the overall functioning and balance of the ecosystem. It serves as a vital component in maintaining the health and biodiversity of the rainforest. Let’s explore some of the key roles that the canopy plays in the forest.
One of the significant roles of the canopy is its function as a carbon sink. The dense vegetation in the canopy absorbs carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through the process of photosynthesis. This absorption helps to reduce the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, mitigating the effects of climate change. By acting as a carbon sink, the canopy plays a crucial role in regulating the global climate and preserving the delicate balance of our planet.
In addition to its role in carbon sequestration, the canopy provides shelter for both arboreal and ground-dwelling animals. The dense foliage and interconnected branches create a safe and secure habitat for a wide range of species. Arboreal animals, such as monkeys, sloths, and tree-dwelling birds, find refuge in the canopy, utilizing the abundance of leaves and branches for food, shelter, and nesting sites. Ground-dwelling animals also benefit from the canopy’s protection, as it provides cover from predators and harsh weather conditions.
The canopy also plays a crucial role in regulating and stabilizing the internal temperature and humidity of the rainforest. The dense layer of leaves and branches acts as a natural buffer, reducing the impact of temperature fluctuations and preventing excessive evaporation. This helps to maintain a stable microclimate within the rainforest, which is essential for the survival of many plant and animal species. The canopy’s ability to regulate temperature and humidity creates a favorable environment for the diverse array of life that thrives within the rainforest.
Furthermore, the canopy serves as a source of food for folivorous and frugivorous animals. Many species of animals in the rainforest rely on the leaves and fruits found in the canopy as their primary source of nutrition. Folivorous animals, such as howler monkeys and sloths, feed on the abundant foliage, which provides them with essential nutrients. Frugivorous animals, such as birds and bats, depend on the fruits found in the canopy for their sustenance. The availability of food in the canopy supports the survival and reproduction of these animals, contributing to the overall biodiversity of the rainforest.
Additionally, the canopy serves as a vantage point for some predators, such as arboreal snakes, leopards, and harpy eagles. These predators take advantage of the height and coverage provided by the canopy to spot their prey and launch surprise attacks. The dense foliage also helps camouflage these predators, making it easier for them to remain hidden from their unsuspecting victims. The canopy’s role as a vantage point for predators contributes to the intricate web of predator-prey relationships within the rainforest.
It can be said that the canopy in the forest plays a vital role in maintaining the wellbeing and equilibrium of the ecosystem. It acts as a carbon sink, reducing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and mitigating the effects of climate change. The canopy provides shelter for both arboreal and ground-dwelling animals, regulates and stabilizes the internal temperature and humidity of the rainforest, and serves as a source of food for folivorous and frugivorous animals. Additionally, it acts as a vantage point for some predators, allowing them to spot their prey and maintain the delicate balance of the rainforest ecosystem. The canopy’s multifunctional role highlights its importance in preserving the biodiversity and sustainability of the rainforest.