Tiny Homes And Energy Conservation: These 13 Minimalist Tips Can Save You Money On Electric Bills In 2024
Tips to save energy and cost in a tiny home include: optimize heating and cooling with a high-efficiency mini-split HVAC system, harvest rainwater, consider energy-efficient appliances and lighting, incorporate natural ventilation, seal air gaps, use a programmable thermostat, install solar panels, utilize LED lights, turn off lights when leaving a room, unplug electronics when not in use, leverage nature with skylights and solar window films, choose energy-saving options like spray foam insulation, and use reclaimed materials to reduce environmental impact.
| Recommendation | Guidelines |
Effects on Energy Consumption
|
| Optimize Heating and Cooling with a High-Efficiency Mini-Split HVAC System | – Choose high EER and SEER mini-split systems – Proper sizing and professional installation – Regular filter maintenance – Implement zoning strategies |
– Significant reduction in energy consumption – Precision heating and cooling with zoning – Year-round efficiency – Lower operating costs – Environmental impact through a smaller carbon footprint
|
| Harvest Rainwater for Practical Purposes | – Install rainwater harvesting system – Use first flush diverter and filtration – Properly sized storage tank – Regular system maintenance |
– Reduced dependency on municipal water – Lower water pump energy consumption – Conservation of water resources
|
| Consider Energy-Efficient Appliances and Lighting Choices | – Choose Energy Star-rated appliances – Opt for LED or CFL lighting – Consider smart appliances |
– Lower electricity bills – Extended appliance lifespan – Environmental benefits through reduced energy consumption
|
| Incorporate Natural Ventilation Strategies | – Design for cross-ventilation – Use adjustable louvers and vents – Install ceiling fans |
– Reduced reliance on air conditioning – Energy savings through natural airflow – Improved indoor comfort
|
| Seal Air Gaps to Prevent Energy Loss | – Identify and seal gaps – Use weatherstripping and caulking – Insulate walls, floors, and ceilings |
– Improved insulation – Energy conservation through minimized air leakage – Reduced heating and cooling workload
|
| Use a Programmable Thermostat for Efficient Temperature Control | – Install programmable thermostat – Set temperature setbacks – Regularly update programming |
– Precision temperature control – Reduced energy waste – Lower heating and cooling costs
|
| Install Solar Panels to Harness Renewable Energy | – Assess energy needs and design system – Optimize panel placement and orientation – Regular maintenance |
– Sustainable energy source – Lower or eliminated electricity bills – Energy independence
|
| Utilize LED Lights for Energy-Efficient Illumination | – Replace with LED bulbs – Choose appropriate color temperature – Turn off lights when not in use |
– Lower energy consumption – Extended bulb lifespan – Environmental benefits through reduced heat production and materials
|
| Turn Off Lights When Leaving a Room to Save Electricity | – Develop the habit of turning off lights – Use motion sensors or smart lighting systems |
– Immediate energy savings – Lower electricity bills – Reduced environmental impact
|
| Unplug Electronics When Not in Use to Minimize Standby Power Consumption | – Unplug devices when not in use – Use smart power strips – Educate occupants on standby power |
– Reduced standby power consumption – Lower electricity bills – Environmental conservation through reduced energy production
|
| Leverage Nature with Features Like Skylights and Solar Window Films for Temperature Regulation | – Install skylights for natural light – Use solar window films for heat control – Choose energy-efficient windows |
– Daylight optimization and reduced reliance on artificial lighting – Temperature regulation for enhanced energy efficiency – Improved indoor comfort
|
| Choose Energy-Saving Options, Such as Spray Foam Insulation, to Improve Efficiency | – Select high R-value insulation materials – Ensure proper coverage in walls, ceilings, and floors – Regular maintenance |
– Thermal efficiency and reduced workload on heating and cooling systems – Energy conservation through effective insulation – Sustainable living practices
|
| Use Reclaimed or Recycled Materials to Reduce Environmental Impact | – Incorporate reclaimed or recycled materials – Prioritize low embodied energy and sustainable sourcing – Consider repurposing existing materials |
– Lower carbon footprint through reduced energy in material production – Resource conservation and support for a circular economy – Environmental stewardship through responsible consumption
|
1. Optimize Heating and Cooling with a High-Efficiency Mini-Split HVAC System:
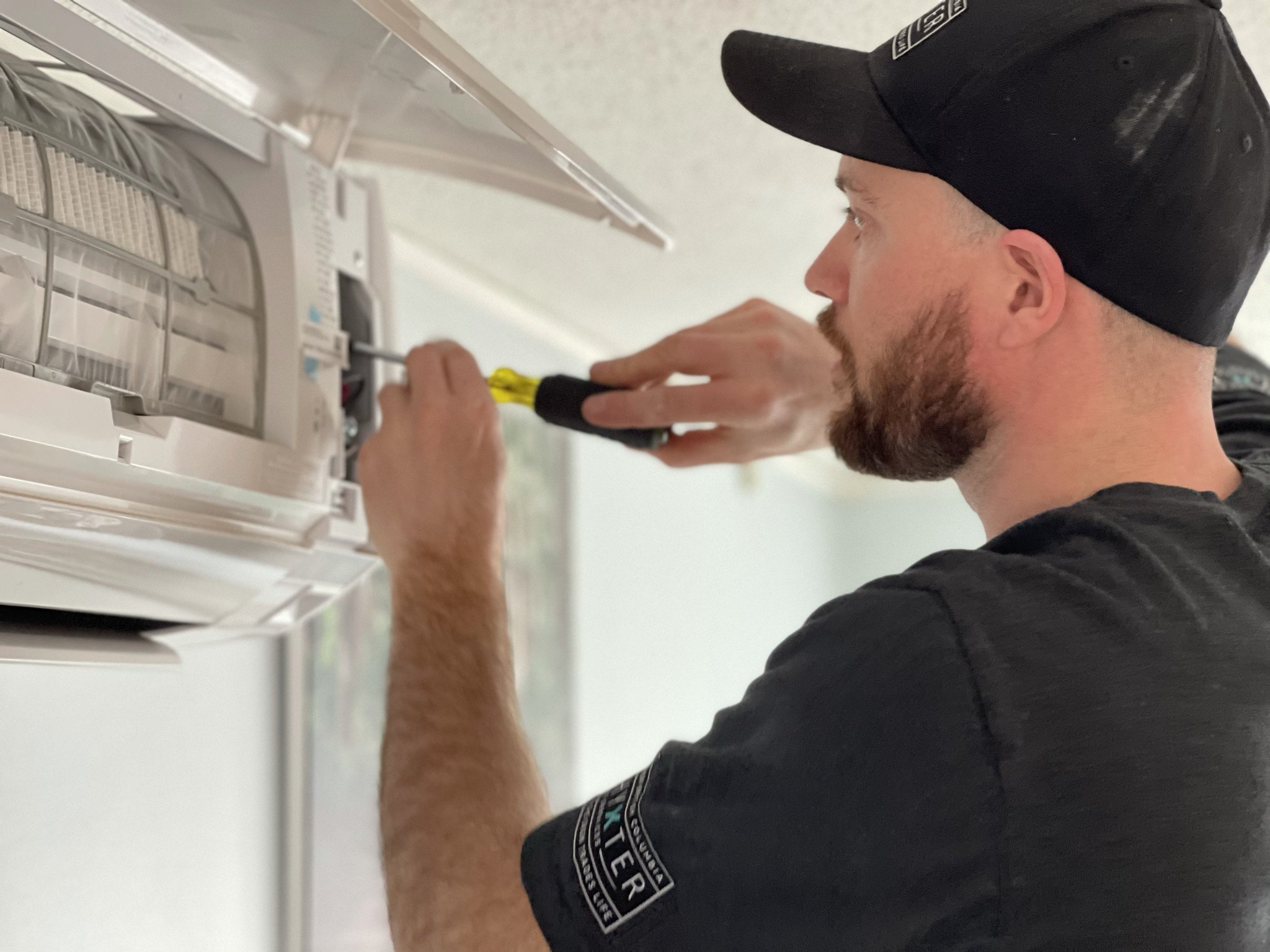

Guidelines:
Choose a mini-split HVAC system with a high energy efficiency ratio (EER) and seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) to ensure optimal performance.
Properly size the system based on the specific heating and cooling needs of the tiny home to avoid overuse and unnecessary energy consumption.
Ensure professional installation to guarantee the system operates at peak efficiency.
Regularly clean and maintain the filters to prevent dust buildup, ensuring unrestricted airflow and efficient operation.
Implement zoning strategies by using multiple indoor units with individual thermostatic controls, allowing for targeted heating or cooling in specific areas.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Significant Reduction: High-efficiency mini-split HVAC systems consume less energy compared to traditional systems, leading to substantial energy savings.
Precision Heating and Cooling: Zoning capabilities enable precise temperature control in different areas, preventing unnecessary energy consumption in unoccupied spaces.
Year-Round Efficiency: Many mini-split systems offer both heating and cooling functions, providing year-round comfort without the need for separate systems.
Lower Operating Costs: The energy-efficient design translates to lower electricity bills, contributing to cost-effective and sustainable energy use in tiny homes.
Environmental Impact: Reduced energy consumption contributes to a smaller carbon footprint, aligning with eco-friendly practices in tiny home living.
2. Harvest Rainwater for Practical Purposes:
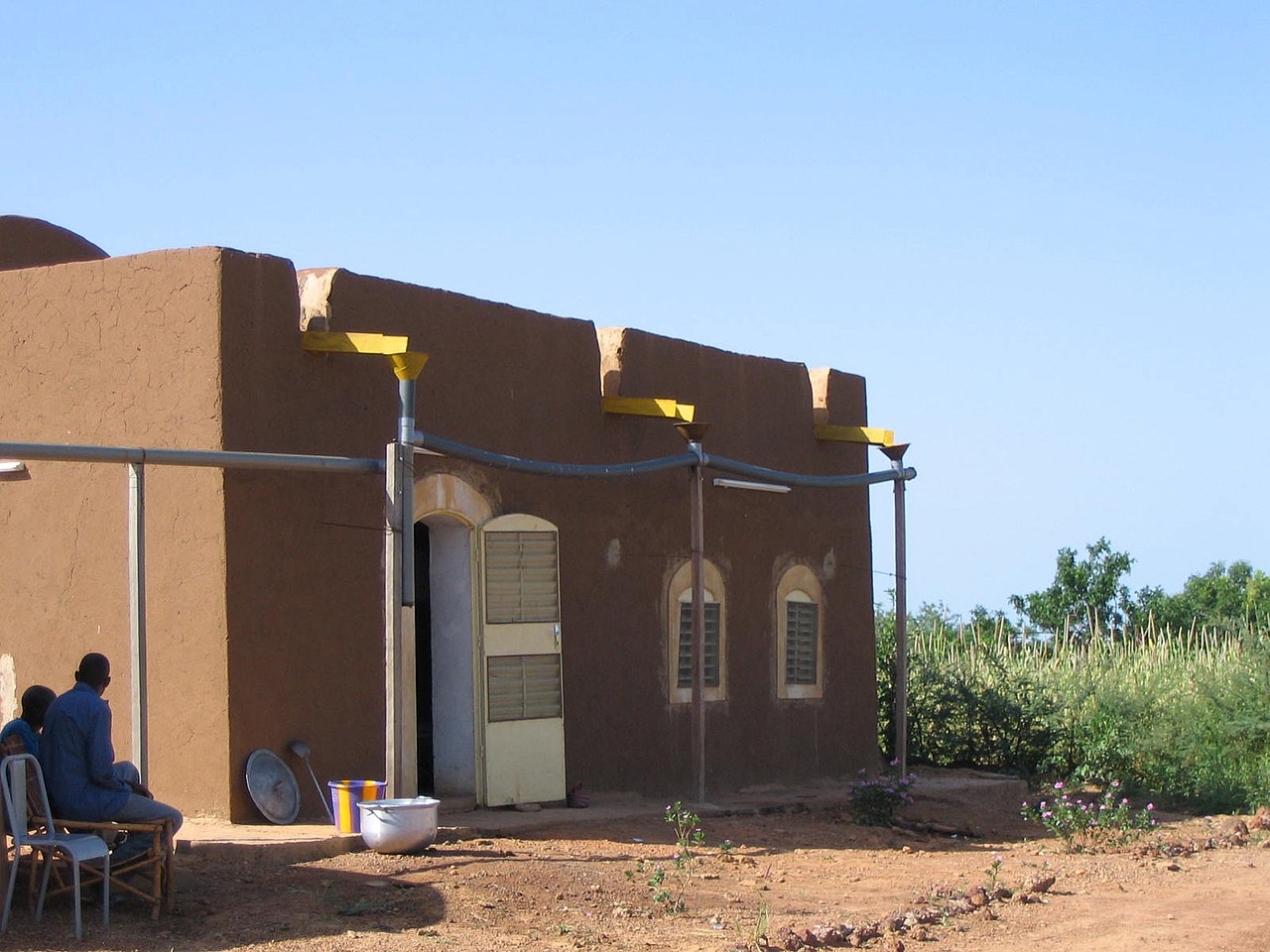

Guidelines:
Install a rainwater harvesting system with gutters and downspouts to collect rainwater efficiently.
Use a first flush diverter to divert initial runoff, which may contain contaminants, away from the storage tank.
Incorporate a filtration system to ensure the collected rainwater is suitable for practical purposes.
Employ a properly sized storage tank to accommodate the tiny home’s water needs and minimize overflow.
Regularly inspect and maintain the system to prevent clogs and ensure optimal functionality.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Reduced Dependency on Municipal Water: Harvesting rainwater reduces reliance on energy-intensive water treatment processes, lowering overall energy demand.
Lower Water Pump Energy: By using stored rainwater for tasks like flushing toilets and irrigation, there is less reliance on electric water pumps, contributing to energy savings.
Conservation of Water Resources: Rainwater harvesting promotes sustainable water use, aligning with eco-friendly practices and reducing the energy-intensive extraction and transportation of municipal water.
3. Consider Energy-Efficient Appliances and Lighting Choices:
Guidelines:
Choose appliances with high Energy Star ratings to ensure energy efficiency.
Opt for LED or CFL bulbs for lighting, as they consume less energy and have a longer lifespan.
Consider appliances with smart features, allowing for energy optimization and scheduling.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Lower Electricity Bills: Energy-efficient appliances and lighting consume less electricity, resulting in cost savings.
Extended Lifespan: Energy-efficient appliances often have longer lifespans, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated energy costs.
Environmental Impact: Reduced energy consumption contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions, promoting environmental sustainability.
4. Incorporate Natural Ventilation Strategies:

Guidelines:
Design the tiny home with strategically placed windows and vents to facilitate cross-ventilation.
Utilize adjustable louvers or vents to control the direction and flow of fresh air.
Install ceiling fans to enhance natural airflow and reduce the need for mechanical cooling.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Reduced Reliance on Air Conditioning: Efficient natural ventilation helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures without relying heavily on air conditioning.
Energy Savings: By maximizing natural airflow, the need for mechanical cooling is minimized, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced electricity bills.
5. Seal Air Gaps to Prevent Energy Loss:
Guidelines:
Identify and seal gaps around windows, doors, and other potential areas of air leakage.
Use weatherstripping and caulking to seal gaps and prevent drafts.
Insulate walls, floors, and ceilings to enhance energy efficiency.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Improved Insulation: Sealing air gaps enhances the insulation of the tiny home, reducing the workload on heating and cooling systems.
Energy Conservation: Minimizing air leakage helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature, leading to energy savings and increased overall efficiency.
6. Use a Programmable Thermostat for Efficient Temperature Control:
Guidelines:
Install a programmable thermostat to automate temperature adjustments based on your daily schedule.
Set temperature setbacks during periods when the home is unoccupied or during sleeping hours to conserve energy.
Regularly update and optimize the thermostat’s programming to align with seasonal changes.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Precision Temperature Control: A programmable thermostat ensures more accurate temperature management, avoiding unnecessary heating or cooling when it’s not needed.
Reduced Energy Waste: Automated temperature adjustments prevent the system from running at full capacity when occupants are away, resulting in energy savings.
Lower Heating and Cooling Costs: By optimizing temperature settings, a programmable thermostat contributes to lower utility bills and increased energy efficiency.
7. Install Solar Panels to Harness Renewable Energy:
Guidelines:
Assess the tiny home’s energy needs and design a solar panel system that meets or exceeds the expected demand.
Ensure proper placement and orientation of solar panels to maximize sunlight exposure.
Regularly clean and maintain solar panels to optimize energy conversion efficiency.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Sustainable Energy Source: Solar panels generate clean, renewable energy, reducing reliance on traditional power sources and minimizing environmental impact.
Lower Electricity Bills: Solar power systems can significantly offset or eliminate electricity costs, leading to long-term financial savings.
Energy Independence: By generating electricity on-site, the tiny home becomes less dependent on the grid, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
8. Utilize LED Lights for Energy-Efficient Illumination:

Guidelines:
Replace incandescent and CFL bulbs with energy-efficient LED lights.
Choose LED bulbs with the appropriate color temperature and brightness for each specific lighting application.
Turn off lights when not in use to maximize energy savings.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Lower Energy Consumption: LED lights are more energy-efficient, consuming less electricity and contributing to reduced energy bills.
Extended Lifespan: LED bulbs have a longer lifespan compared to traditional bulbs, reducing the frequency of replacements and associated energy costs.
Environmental Benefits: LED lighting produces less heat and contains no hazardous materials, making it a more environmentally friendly choice.
9. Turn Off Lights When Leaving a Room to Save Electricity:

Guidelines:
Cultivate the habit of turning off lights when leaving a room, even for short durations.
Install motion sensors or smart lighting systems to automate light control based on occupancy.
Educate occupants on the importance of energy conservation through mindful lighting practices.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Immediate Energy Savings: Turning off lights when not needed directly reduces electricity consumption.
Lower Electricity Bills: Consistent light-switching habits contribute to overall energy savings, reflecting in reduced monthly utility bills.
Environmental Impact: Reduced energy consumption translates to a smaller carbon footprint, aligning with sustainable living practices.
10. Unplug Electronics When Not in Use to Minimize Standby Power Consumption:

Guidelines:
Unplug chargers, electronic devices, and appliances when not in use to prevent standby power consumption.
Utilize smart power strips to automatically cut off power to multiple devices when a master device is turned off.
Educate occupants about the impact of standby power and the importance of unplugging electronic devices.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Standby Power Reduction: Unplugging electronics eliminates standby power consumption, contributing to overall energy savings.
Lower Electricity Bills: Minimizing standby power usage results in reduced electricity bills, reflecting more cost-effective energy management.
Environmental Conservation: Unplugging devices helps reduce unnecessary energy production and lowers the environmental impact associated with electricity generation.
11. Leverage Nature with Features Like Skylights and Solar Window Films for Temperature Regulation:
Guidelines:
Install skylights strategically to harness natural light and enhance daylighting, reducing the need for artificial lighting.
Use solar window films to control the amount of sunlight entering the home and mitigate heat gain.
Choose energy-efficient windows with appropriate glazing to balance natural light and insulation.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Daylight Optimization: Skylights and solar window films contribute to effective daylighting, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and lowering energy consumption.
Temperature Regulation: Solar window films help manage heat gain, improving the overall energy efficiency of the tiny home.
Enhanced Comfort: Natural light and controlled solar heat contribute to a more comfortable indoor environment, reducing the need for heating or cooling.
12. Choose Energy-Saving Options, Such as Spray Foam Insulation, to Improve Efficiency:
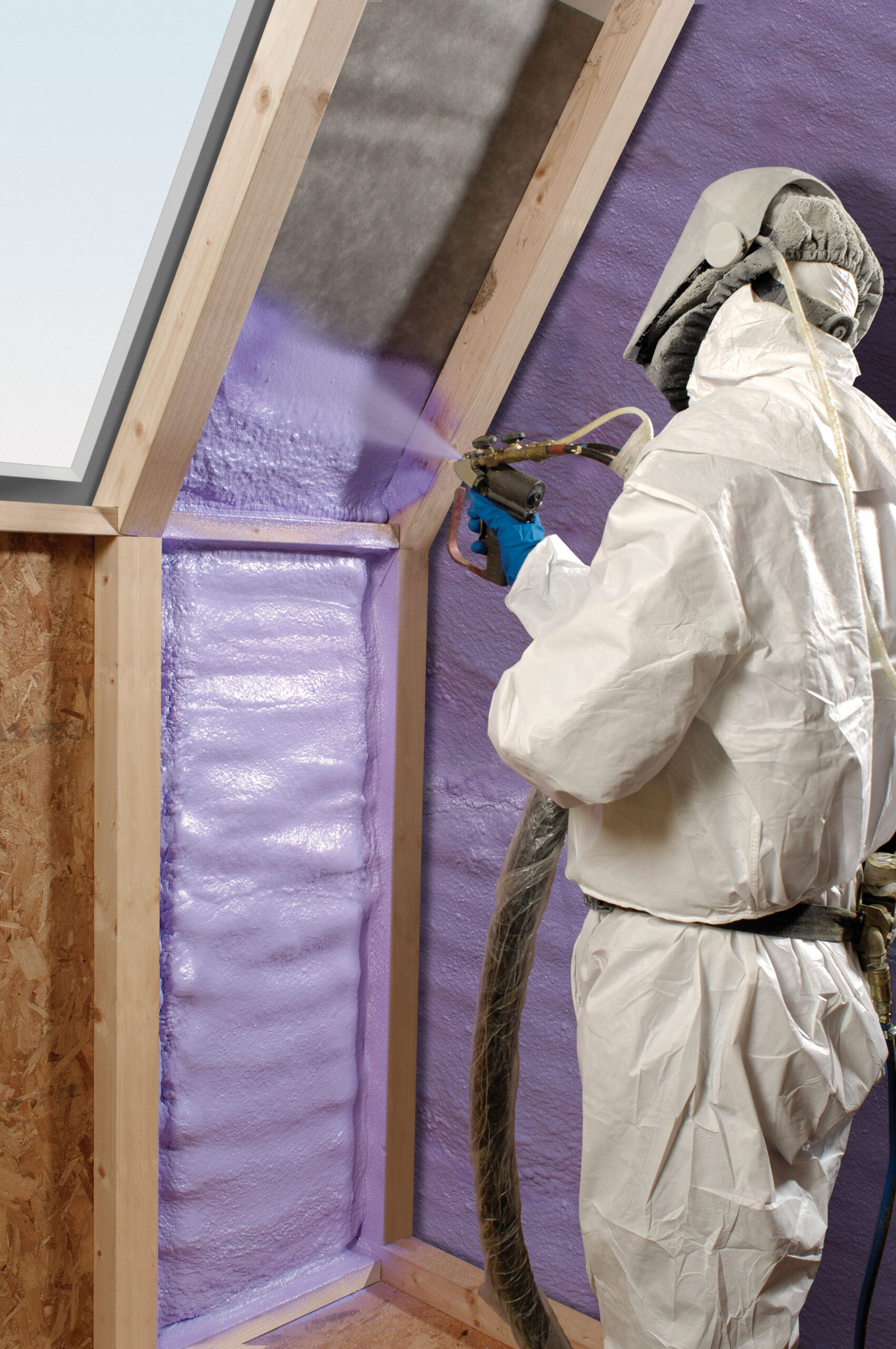

Guidelines:
Select insulation materials with high R-values, such as spray foam insulation, to effectively reduce heat transfer.
Ensure proper insulation coverage in walls, ceilings, and floors to minimize thermal bridging.
Regularly inspect and maintain insulation to preserve its effectiveness over time.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Thermal Efficiency: Spray foam insulation provides superior thermal resistance, reducing the workload on heating and cooling systems.
Energy Conservation: Proper insulation prevents energy loss through walls and ceilings, resulting in lower energy consumption and reduced utility costs.
Sustainable Living: Improved energy efficiency through effective insulation aligns with environmentally conscious practices in tiny home living.
13. Use Reclaimed or Recycled Materials to Reduce Environmental Impact:
Guidelines:
Incorporate reclaimed or recycled building materials in the construction of the tiny home, such as reclaimed wood, recycled metal, or salvaged fixtures.
Prioritize materials with low embodied energy and those sourced sustainably.
Consider repurposing existing materials from deconstructed buildings to minimize environmental impact.
Effects on Energy Consumption:
Lower Carbon Footprint: Reclaimed and recycled materials often require less energy to produce than new materials, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint.
Resource Conservation: Using recycled materials helps conserve natural resources, aligning with sustainable building practices.
Environmental Stewardship: Choosing reclaimed or recycled materials promotes responsible consumption and supports a circular economy, reducing the overall environmental impact of the tiny home.











