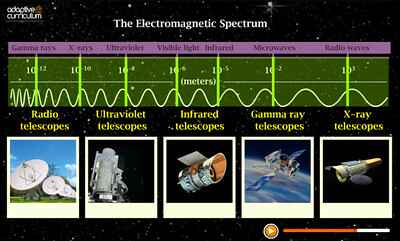
Radio Wave Frequency and Wavelength as Key Characteristics
Radio wave frequency is a measure of the number of crests or troughs of a radio wave that pass through a given point in a second; which can also be derived as the inverse of radio wave period. Radio wave wavelength is the distance between successive crests or troughs of a radio wave.
This article discusses radio wave frequency and wavelength, as follows;
Radio Wave Frequency
Radio wave frequency is the rate of propagation or oscillation of a radio wave through space, which can be measured by the number of crests or troughs of the waveform that pass through a given point in a second.
The frequency of radio waves in hertz (Hz) ranges from 3 kHz to 300 GHz, approximately [2]. This broad frequency range is an advantage that increases the flexibility of radio wave applications.
Radio frequency (RF) is used to modulate radio waves in order to enable them serve as a medium for transmission of information in smart devices.
The purpose of radio frequency modulation in electromagnetic communication systems is to ensure that a receiving terminal like an antenna, can easily achieve clear detection of audio and visual radio-signals, once the terminal is tuned to the same frequency as these signals.
Devices that use radio frequency medium of communication include; portable radios, mobile phones, Wi-Fi transmitters, handheld GPS units, and wireless sensors.

The general importance of radio wave frequency in modern technology, is its role in wireless communication, which is behind many aspects of projects that utilize Internet of Things (IoT) networks. One instance of radio wave frequency in wireless IoT communication is Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), whereby machines are able to extract information from their surroundings through wireless sensing [1].
Radio wave frequency is the lowest in the entire electromagnetic spectrum [2].
This is an advantage that enables radio waves to be used for several technological applications, because it reduces the energy intensity (per unit time), or energy exposition, of radio waves, and hence also reduces their potential hazardous effect [4].
Several studies have in fact shown that the impact of radio waves on human health become negligible as frequencies decrease [3].
Radio Wave Wavelength
Wavelength can be defined as the distance between corresponding points on a waveform; such as between successive crests or troughs.
Radio waves have the longest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum, which corresponds to their low frequency.
The wavelength of radio waves in meters is between 0.001 and 10^5 m on average, with some radio waves exceeding 10^9 m wavelength. It must be noted that wavelength varies inversely with frequency; so that longer wavelengths correspond to lower frequencies for radio waves.
Electromagnetic waves like microwaves and radio waves are non-ionizing due to their long wavelengths and low frequencies, meaning that they are less likely to cause chemical alteration of any medium with which they come in contact.

Asides radio wave wavelength and frequency, other parameters used to assess radio waves are, period and amplitude; where the former is an inverse measure of frequency, and the latter refers to the maximum displacement of radio wave particles from their mean position as they vibrate during propagation.
Conclusion
Radio wave frequency is the number of crests or troughs of a radio wave that pass through a given point in one second. It can be determined by taking the inverse value of wave period.
The purpose of radio frequency modulation is to encode information into radio waves being transmitted, so that this information can be decoded by a receiver that is tuned to an equivalent frequency.
Radio wave wavelength is a measure of the distance between successive, corresponding points like troughs and crests, on a radio waveform. It ranges from 0.001 m to 10^5 m on average.
The general parameters that are commonly used to evaluate radio waves are; wavelength, frequency, period and amplitude.
References
1). Jia, X.; Feng, Q.; Fan, T.; Lei, Q. (2012). "RFID technology and its applications in Internet of Things (IoT)." Available at: https://doi.org/10.1109/CECNet.2012.6201508. (Accessed 30 March 2023).
2). Lucas, J. (2019). "What Are Radio Waves?" Available at: https://www.livescience.com/50399-radio-waves.html. (Accessed 28 March 2023).
3). Ozdemir, F.; Kargi, A. (2011). "Electromagnetic Waves and Human Health." InTech. Available at: https://doi.org/10.5772/16343. (Accessed 30 March 2023).
4). Torres-Duran, P. V.; Ferreira-Hermosillo, A.; Juarez-Oropeza, M. A.; Elias-Viñas, D.; Verdugo-Diaz, L. (2007). "Effects of whole body exposure to extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields (ELF-EMF) on serum and liver lipid levels, in the rat." Lipids Health Dis. 2007 Nov 16;6:31. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-511X-6-31. (Accessed 30 March 2023).