Is a Bobcat a Secondary Consumer? Bobcat Food Web Position and Role
A bobcat occupies the role of a secondary consumer in various ecosystems, alongside other mesopredators like coyotes. It feeds on small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles, which places it in the second trophic level of the food chain. As a carnivore, it preys on herbivores, thereby regulating their populations and contributing to ecosystem balance.
Reasons Why a Bobcat is a Secondary Consumer

-
Size and Dietary Habits: Bobcats are smaller carnivores that primarily consume other animals, placing them in the secondary consumer category within food webs.
-
Prey Selection: Their diet mainly consists of herbivores and smaller predators, making them integral components of the ecosystem’s trophic structure.
-
Trophic Level: Bobcats occupy a trophic level above primary consumers (herbivores) but below apex predators, indicating their role as secondary consumers within food chains.
Is A Bobcat A Tertiary Consumer?

No, a bobcat is not typically considered a tertiary consumer in most ecosystems. Tertiary consumers occupy the highest trophic level in food chains and primarily prey on secondary consumers. However, bobcats generally do not feed on other carnivores, which is characteristic of tertiary consumers. Instead, they primarily consume herbivores and smaller prey, placing them in the secondary consumer category.
Reasons Why a Bobcat is Not a Tertiary Consumer
-
Dietary Preference: Bobcats primarily feed on herbivores and smaller predators rather than consuming other carnivores, which is typical behavior for tertiary consumers.
-
Trophic Level: Tertiary consumers occupy the highest trophic level in food chains, primarily preying on secondary consumers. Bobcats, however, typically occupy the trophic level of secondary consumers due to their diet and feeding habits.
-
Ecological Role: While bobcats play a crucial role in regulating prey populations as secondary consumers, they do not exhibit the characteristic behaviors associated with tertiary consumers, such as predation on other carnivores.
What Type of Consumer is a Bobcat?

A bobcat is classified as a carnivore in terms of its dietary habits and ecological role. As a carnivore, it primarily consumes other animals, such as small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles. This places bobcats in the category of secondary consumers within food webs, as they feed on herbivores and smaller predators.
Is a Bobcat an Apex Predator?
No, a bobcat is not considered an apex predator in most ecosystems. Apex predators are at the top of the food chain and have no natural predators of their own. While bobcats are skilled hunters, they are smaller and weaker compared to apex predators such as mountain lions, wolves, and bears. Therefore, they do not hold the position of apex predators and are instead classified as secondary consumers.
Reasons Why a Bobcat is Not an Apex Predator
-
Size and Strength: Bobcats are smaller and less powerful than apex predators such as mountain lions, wolves, and bears, which limits their ability to dominate and control other species in the ecosystem.
-
Prey Selection: Bobcats primarily target smaller prey species and do not typically hunt large herbivores or other carnivores like apex predators do.
-
Predation Pressure: Bobcats themselves may be preyed upon by larger predators, further indicating their position below apex predators in the food chain hierarchy.
Are Bobcats Carnivores?

Yes, bobcats are carnivores. They primarily feed on other animals such as small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles. Their carnivorous diet and hunting behavior classify them as secondary consumers within ecosystems, playing an essential role in controlling prey populations and maintaining ecological balance.
Reasons Why Bobcats are Carnivores
-
Dietary Preferences: Bobcats predominantly consume meat, including small mammals, birds, and reptiles, reflecting their carnivorous nature.
-
Anatomical Adaptations: Their physical features, such as sharp claws and teeth, are suited for hunting and capturing prey, further emphasizing their carnivorous lifestyle.
-
Ecological Role: As carnivores, bobcats help regulate populations of smaller mammals and birds, contributing to the overall balance and health of ecosystems in which they reside.
Is a Bobcat an Omnivore?
No, a bobcat is not an omnivore. Unlike omnivores, which consume both plant and animal matter, bobcats primarily feed on other animals, making them carnivores. Their diet consists mainly of small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles, indicating their classification as carnivores rather than omnivores.
Is a Bobcat a Herbivore, Carnivore, or Omnivore?
A bobcat is classified as a carnivore. Unlike herbivores, which primarily consume plant matter, and omnivores, which consume both plant and animal matter, bobcats predominantly feed on other animals. Their diet consists mainly of small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles, reflecting their carnivorous nature.
Bobcat Food Web/Food Chain Position and Importance
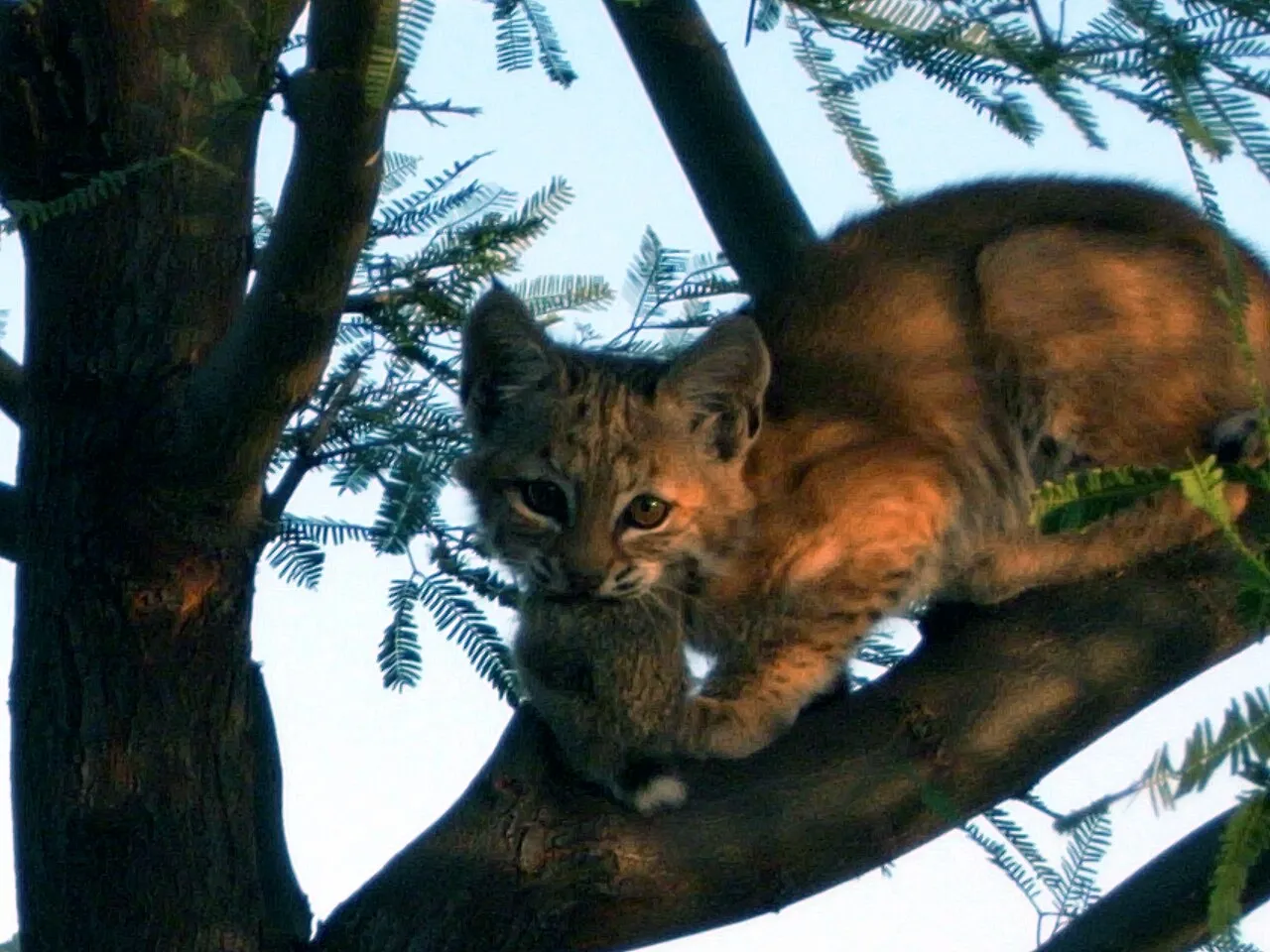

Bobcats occupy a significant role in food webs as secondary consumers. By preying on smaller mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles, they help regulate prey populations, which in turn influences the abundance of vegetation and other organisms lower in the food chain. As integral components of ecosystems, bobcats contribute to the balance and stability of their respective habitats, demonstrating their importance in maintaining ecological health and biodiversity.
*Summary
| Key Points | Details |
| Role in Food Webs |
Bobcats are secondary consumers, feeding on small mammals, birds, and occasionally reptiles.
|
| Prey Regulation |
They play a crucial role in regulating prey populations, contributing to the balance and stability of ecosystems.
|
| Dietary Classification |
Bobcats are carnivores, primarily consuming meat, distinguishing them from herbivores and omnivores.
|
| Ecosystem Importance |
While not apex predators, bobcats are essential components of ecosystems, influencing vegetation abundance and biodiversity.
|
| Anatomical Adaptations |
Physical features such as sharp claws and teeth facilitate hunting and capturing prey, emphasizing their carnivorous nature.
|
| Ecological Balance |
By controlling prey populations, bobcats help maintain ecological health and contribute to the overall balance of their habitats.
|
FAQs about Bobcats
1. What do bobcats eat?
- Bobcats primarily eat small mammals such as rabbits and rodents, but they also consume birds and occasionally reptiles.
2. How big do bobcats get?
- Bobcats vary in size, but on average, they weigh between 15 to 35 pounds and measure around 2 to 3 feet in length.
3. Are bobcats dangerous to humans?
- While bobcats typically avoid humans, they may become aggressive if threatened or cornered. However, attacks on humans are rare.
4. Where do bobcats live?
- Bobcats are found throughout North America, ranging from southern Canada to Mexico. They inhabit a variety of habitats, including forests, swamps, deserts, and suburban areas.
5. What are the main threats to bobcats?
- Habitat loss, fragmentation, and human activities such as hunting and trapping pose significant threats to bobcat populations. Additionally, conflicts with humans and vehicles contribute to mortality rates.
6. How do bobcats communicate?
- Bobcats use vocalizations, body language, and scent marking to communicate with each other. They may yowl, hiss, growl, or purr to convey different messages.
7. Do bobcats have predators?
- Larger predators such as mountain lions, wolves, and bears may prey on bobcats, especially juveniles or weaker individuals. However, bobcats are skilled at avoiding predators through their agility and camouflage.
8. How do bobcats contribute to ecosystems?
- Bobcats play a crucial role in controlling prey populations, which helps maintain the balance of ecosystems. By regulating the numbers of small mammals and birds, they indirectly impact vegetation dynamics and biodiversity.