Groundhog Vs Hedgehog Size, Weight, Overall Comparison
When comparing groundhogs to hedgehogs, several notable differences emerge, encompassing size, habitat, activity patterns, and physical characteristics. Despite both being small mammals, these species exhibit distinct traits and behaviors that set them apart.
I. Size Variation:
– Hedgehogs are significantly smaller than groundhogs, measuring around 5 to 12 inches in length, while groundhogs are much larger, reaching lengths of 16 to 27 inches. This substantial difference in size is evident in their overall body dimensions.
II. Habitat Preferences:
– Groundhogs are known for building complicated burrows and spend much of their lives underground, showcasing a preference for subterranean habitats. In contrast, hedgehogs construct nests above ground, exhibiting a preference for terrestrial environments.

III. Activity Patterns:
– Groundhogs are diurnal animals, meaning they are active during the day, with peak activity around dusk and dawn. On the contrary, hedgehogs are primarily nocturnal, displaying heightened activity levels during the nighttime hours.
IV. Physical Characteristics:
– Hedgehogs possess long snouts and bodies covered in spikes called quills, providing them with a distinctive appearance and defensive mechanism. In contrast, groundhogs have stocky, furry bodies with curved claws and bushy tails, differing significantly from hedgehogs in physical features.

V. Distribution and Taxonomy:
– Hedgehogs have a global presence, with approximately 17 different species distributed across various regions. In contrast, groundhogs are exclusively found in North America, showcasing a more limited geographic range.
*Details of Comparison
| Criteria | Groundhog | Hedgehog |
| Taxonomy | Sciuridae, Marmota monax |
Erinaceidae, Family Erinaceidae
|
| Appearance | Stout, brown/gray fur, short legs, bushy tail |
Small, spiky coat, brown/gray spines, short legs, snout
|
| Size | 16-26 inches | 5-12 inches |
| Weight | 4-9 pounds | 1-2.5 pounds |
| Bite Force (PSI) | Limited information |
Low due to insectivorous diet
|
| Physical Offensive Advantages | Strong digging |
Defensive rolling
|
| Physical Defensive Advantages | Retreat into burrows |
Defensive rolling
|
| Speed | Faster than hedgehog | About 4 mph |
| Agility | Climbers and swimmers |
Limited agility, terrestrial
|
| Senses | Excellent vision, hearing, smell |
Relies on smell and hearing, limited eyesight
|
| Overall Physical Capacity | Robust for digging |
Compact for rolling
|
| Habitat Preference(s) | Open areas, North America |
Various habitats, Europe, Asia, Africa
|
| Tracks | Claw marks, digging emphasis |
Small, round tracks
|
| Lifespan | 3-6 years | 2-5 years |
| Mode of Feeding | Herbivores | Insectivores |
| Intelligence | Problem-solving |
Limited cognitive abilities
|
| Social Behavior | Mostly solitary |
Generally solitary
|
| Mode of Reproduction | Polygynous, 2-6 pups |
Solitary, 4-7 hoglets
|
| Parental Behavior | Prolonged care | Limited care |
| Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas | Near settlements |
Gardens, urban areas
|
| Behavior Toward Humans | Wary |
Tolerant in urban settings
|
| Danger Posed to Humans | Not dangerous; may cause damage |
Not dangerous; spines as defense
|
| Associated Precautions | Secure gardens, avoid close proximity |
Caution when handling, provide safe spaces
|
| Conservation Status | Generally stable | Varied, some species declining |
Key Points
- Groundhogs and hedgehogs have distinct characteristics, including size, appearance, and behavior.
- Groundhogs are larger, herbivorous, and exhibit more pronounced mating behaviors.
- Hedgehogs are smaller, insectivorous, and rely on spiky defense mechanisms.
- Both species play roles in ecosystems, impacting vegetation, soil structure, and invertebrate populations.
- Differences in habitat preferences and geographical distribution contribute to their ecological niches.
- Human interactions can influence their behavior, diet, and overall survival in urban environments.
- Conservation efforts may be needed for specific hedgehog species facing decline.
1. Taxonomy:
Groundhog (Marmota monax):
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Rodentia
Family: Sciuridae
Genus: Marmota
Species: M. monax
Hedgehog (Family Erinaceidae):
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Eulipotyphla
Family: Erinaceidae
2. Appearance:
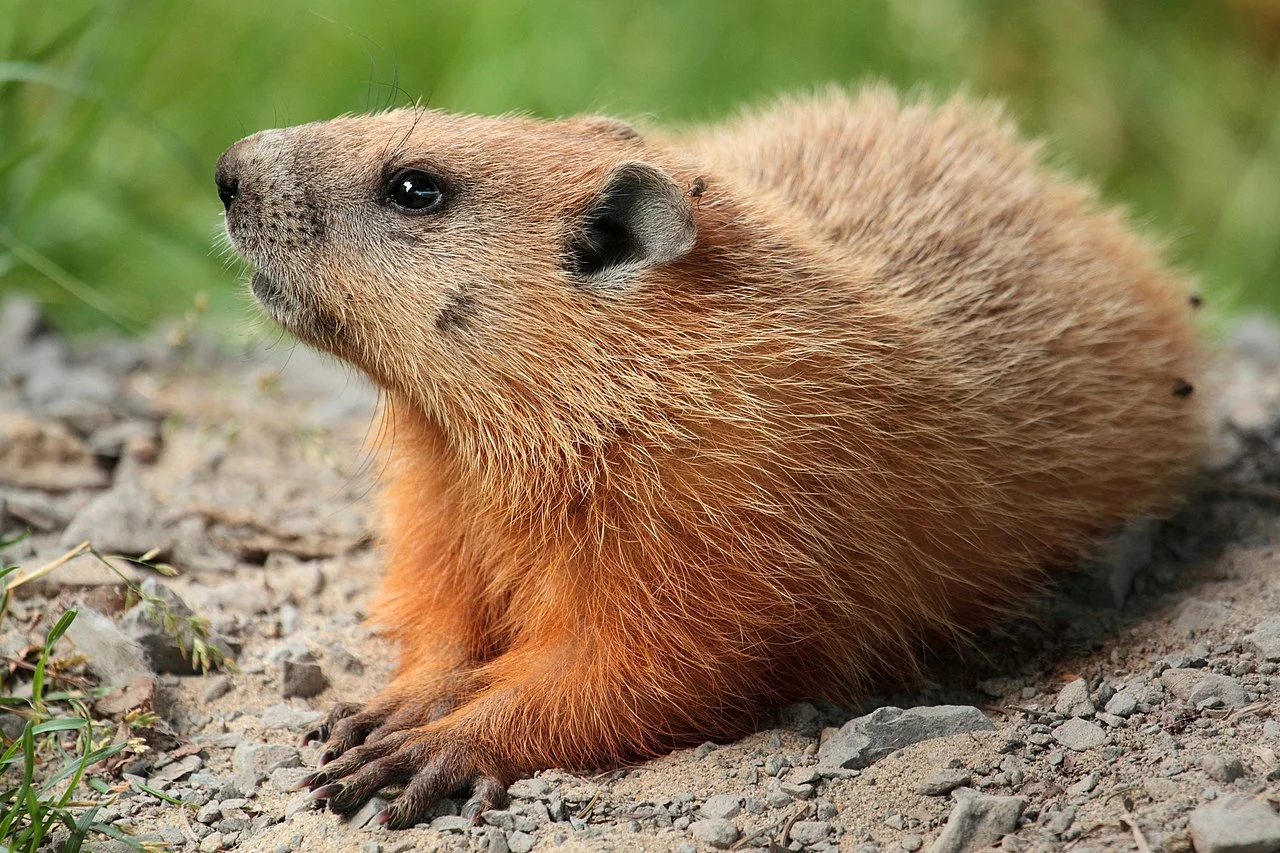


Groundhog:
Stout, with a robust body.
Fur color ranges from brown to gray.
Short legs and a bushy tail.
Sharp, curved claws for digging.
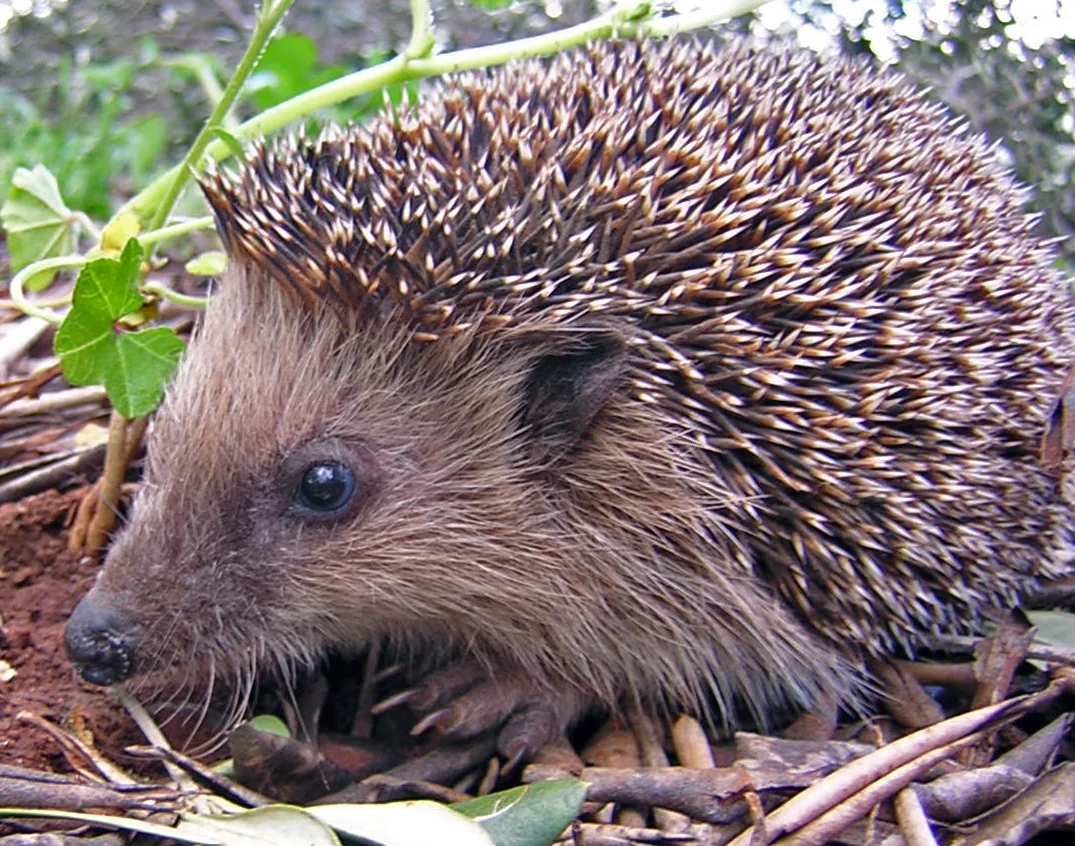
Hedgehog:
Small, with a distinctive spiky coat.
Typically brown or gray spines covering the back.
Short legs and a snout for foraging.
Well-adapted for rolling into a defensive ball.
Comparison: Groundhogs have a more substantial build, while hedgehogs are characterized by their spiky appearance.
Ecological Implications: Groundhogs’ burrowing behavior can influence soil structure, while hedgehogs’ spines serve as protection against predators.
3. Size:
Groundhog:
Length: 16 to 26 inches (40 to 66 cm).
Tail: 4 to 7 inches (10 to 18 cm).
Hedgehog:
Length: 5 to 12 inches (13 to 30 cm).
Tail: Short and often hidden.
Comparison: Groundhogs are significantly larger than hedgehogs, both in body length and tail size.
Ecological Implications: Size differences may affect their roles in ecosystems, with groundhogs having a larger impact on soil structure.
4. Weight:

Groundhog:
Weight: 4 to 9 pounds (1.8 to 4.1 kg).
Hedgehog:
Weight: 1 to 2.5 pounds (0.45 to 1.13 kg).
Comparison: Groundhogs are substantially heavier than hedgehogs.
Ecological Implications: Weight influences the ecological footprint, with groundhogs potentially affecting vegetation more due to their larger size.
5. Bite Force (PSI – Pounds per Square Inch):
Groundhog: Information on groundhog bite force is limited.
Hedgehog: Relatively low bite force due to a diet consisting mainly of insects and soft invertebrates.
Comparison: Groundhogs may have a more powerful bite, but specific data is lacking.
Ecological Implications: Bite force can impact the types of food consumed and influence interactions with other species in the ecosystem.
6. Physical Offensive Advantages:
Groundhog:
Strong digging abilities with sharp claws.
Hedgehog:
Limited offensive capabilities; relies on rolling into a defensive ball.
Comparison: Groundhogs have a more effective offensive strategy through digging.
Ecological Implications: Groundhogs’ digging behavior can impact soil structure and vegetation.
7. Physical Defensive Advantages:

Groundhog:
Quick retreat into burrows for safety.
Hedgehog:
Rolls into a spiky ball as a primary defense mechanism.
Comparison: Hedgehogs employ a more direct and distinctive defensive mechanism compared to groundhogs.
Ecological Implications: Defensive strategies influence interactions with predators and other species in the ecosystem.
8. Speed (Km/hour or Mile/hour):

Groundhog: Limited information on exact speed, but they can move quickly.
Hedgehog: Relatively slow movers, with a top speed of about 4 miles per hour (6.4 km/h).
Comparison: Groundhogs are likely faster than hedgehogs.
Ecological Implications: Speed affects foraging efficiency and evasion from predators.
9. Agility:
Groundhog: Agile climbers and swimmers.
Hedgehog: Limited agility; primarily terrestrial.
Comparison: Groundhogs showcase more diverse agility, being adept at climbing and swimming.
Ecological Implications: Agility influences the range of habitats and niches that each species can exploit.
10. Senses:

Groundhog:
Excellent vision, hearing, and sense of smell.
Hedgehog:
Relies heavily on a well-developed sense of smell and hearing, with limited eyesight.
Comparison: Groundhogs generally have better eyesight than hedgehogs, which rely more on other senses.
Ecological Implications: Differences in sensory abilities can impact foraging strategies and responses to environmental stimuli.
11. Overall Physical Capacity:
Groundhog:
Robust physical build, well-suited for digging and burrowing.
Hedgehog:
Specialized for terrestrial life, with a compact build for rolling into a defensive ball.
Comparison: Groundhogs and hedgehogs are adapted to different physical tasks based on their ecological roles.
Ecological Implications: Physical capacities contribute to their ecological niche and roles within ecosystems.
12. Habitat Preference(s) and Geographic Region:
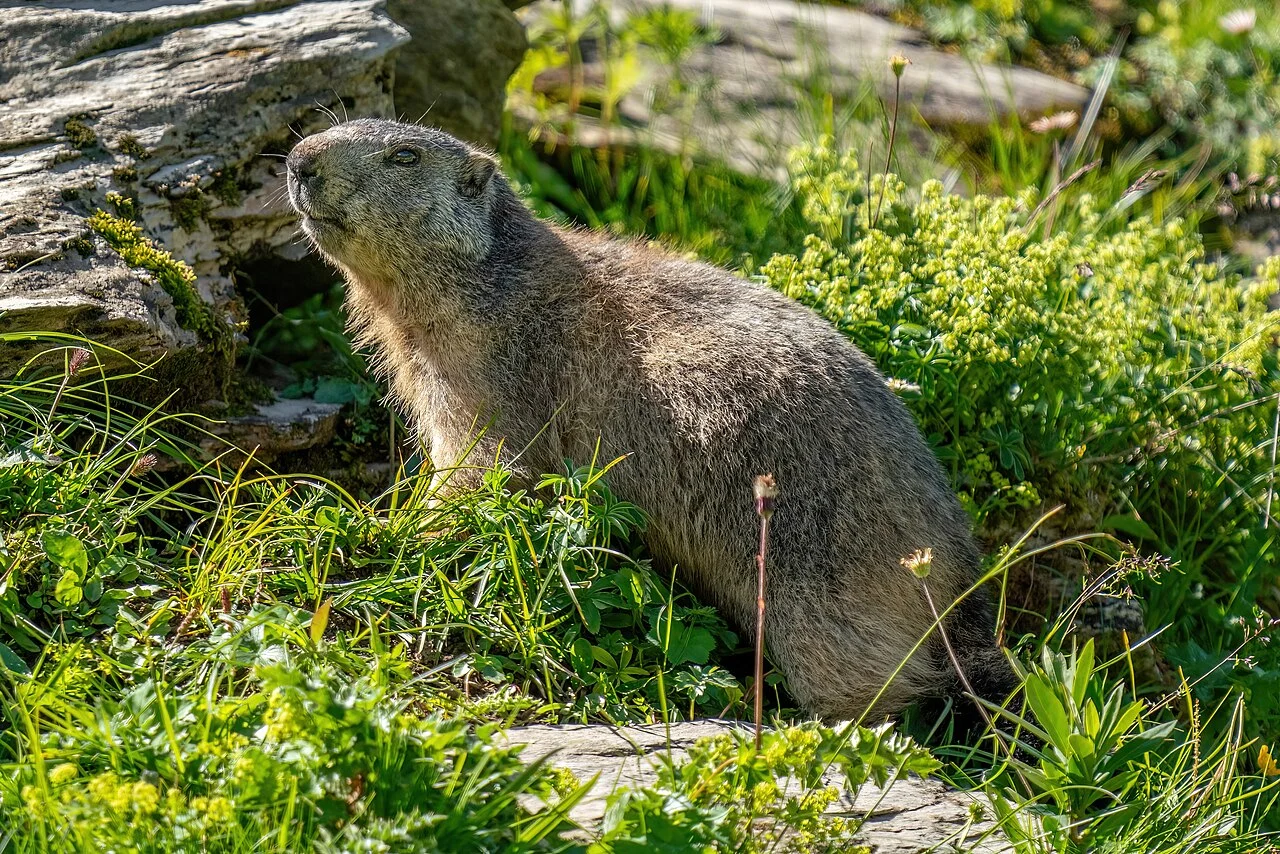

Groundhog:
Prefers open areas like fields and meadows.
Common in North America.
Hedgehog:
Found in a variety of habitats, including gardens, hedgerows, and woodland edges.
Widely distributed in Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Comparison: Groundhogs and hedgehogs exhibit habitat preferences that align with their respective geographical ranges.
Ecological Implications: Habitat preferences influence their interactions with other species and ecosystem dynamics.
13. Tracks:
Groundhog:
Distinctive tracks with claw marks, reflecting their digging behavior.
Hedgehog:
Small, round tracks with the imprint of their feet and claws.
Comparison: Groundhog tracks emphasize digging, while hedgehog tracks showcase a more straightforward pattern.
Ecological Implications: Tracking can provide insights into their movements and habitat use within ecosystems.
14. Lifespan:
Groundhog:
Typically live 3 to 6 years in the wild.
Hedgehog:
Average lifespan ranges from 2 to 5 years in the wild.
Comparison: Groundhogs and hedgehogs have relatively similar lifespans in the wild.
Ecological Implications: Lifespan affects population dynamics and interactions within their respective ecosystems.
15. Mode of Feeding:
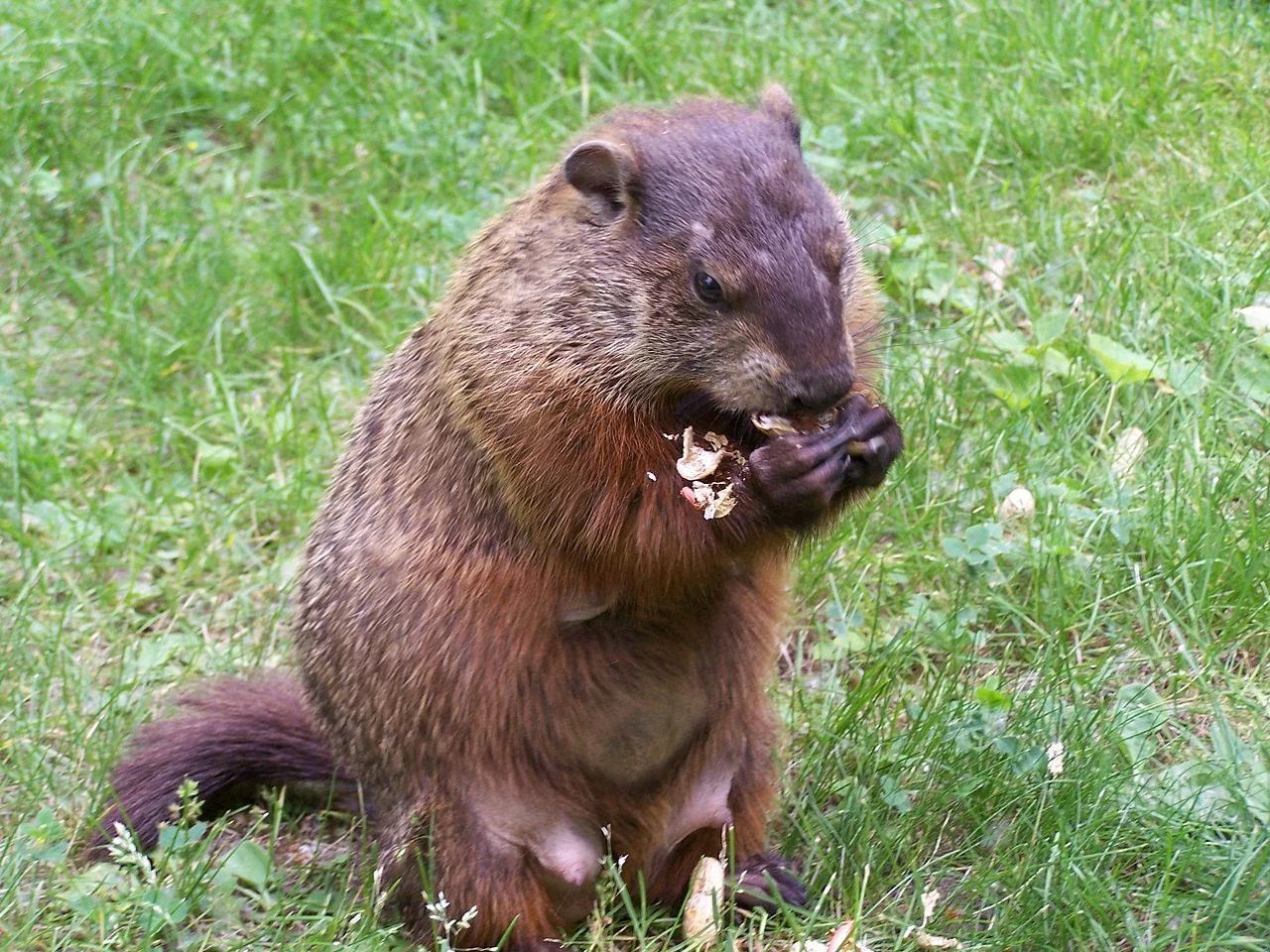
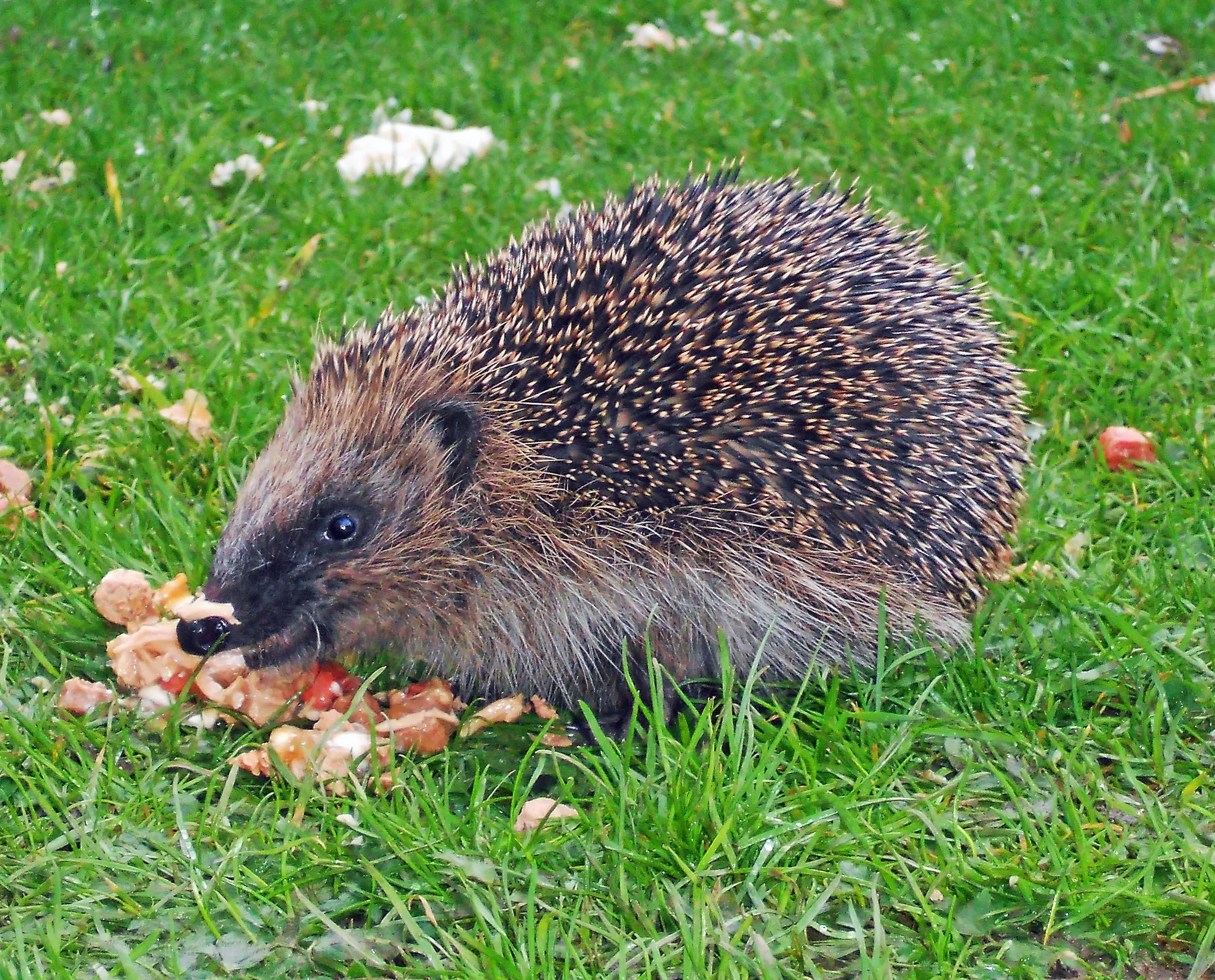


Groundhog:
Herbivores, primarily consuming plants like grasses, fruits, and vegetables.
Hedgehog:
Insectivores, with a diet consisting mainly of insects, worms, and small invertebrates.
Comparison: Groundhogs are herbivores, while hedgehogs are insectivores, reflecting distinct dietary preferences.
Ecological Implications: Differences in feeding habits can influence plant and invertebrate populations in their ecosystems.
16. Intelligence:
Groundhog:
Display problem-solving abilities, especially related to burrow construction.
Hedgehog:
Limited cognitive abilities compared to some other mammals.
Comparison: Groundhogs demonstrate higher problem-solving skills compared to hedgehogs.
Ecological Implications: Intelligence influences how they adapt to their environment and respond to challenges.
17. Social Behavior:
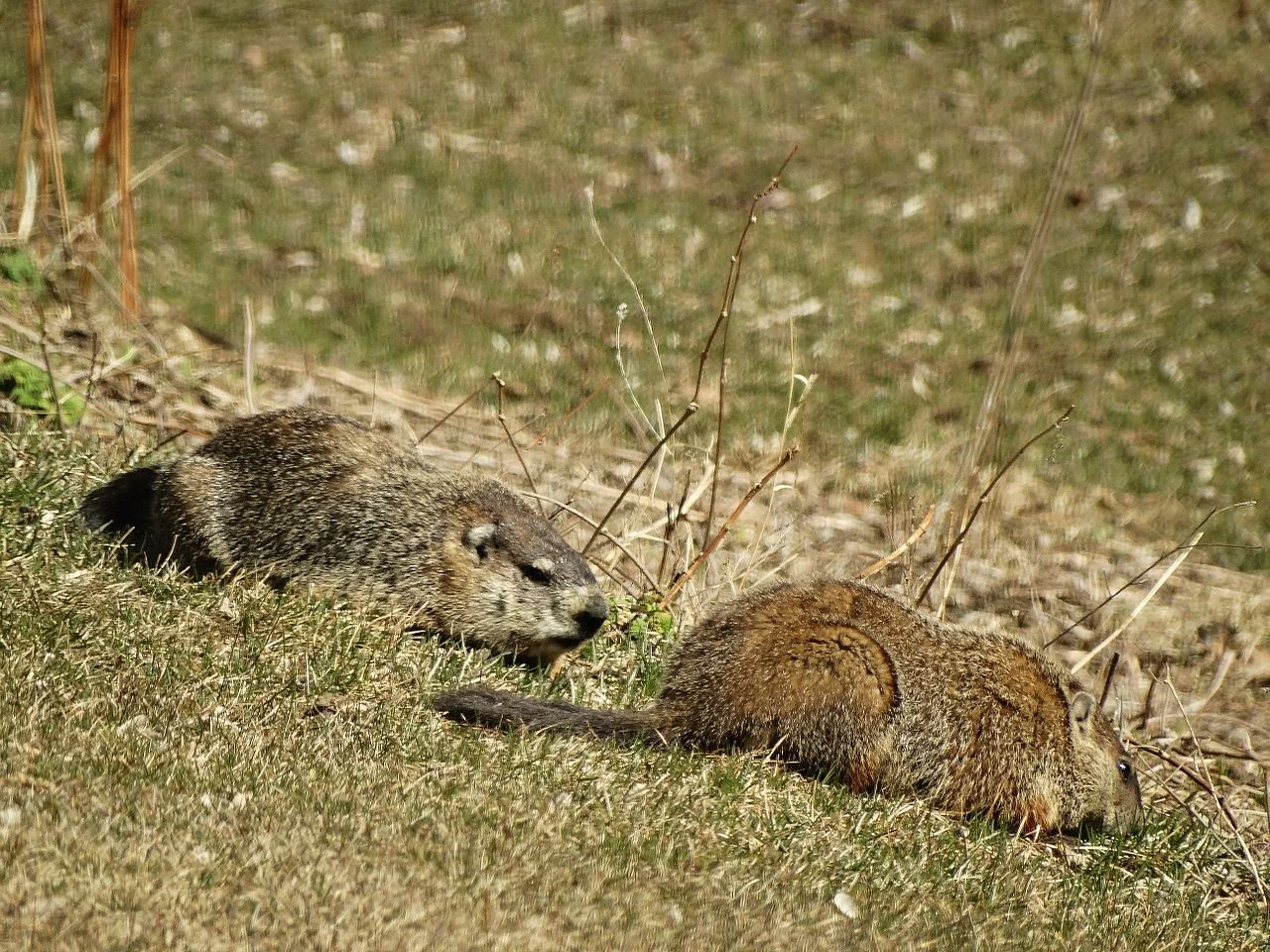
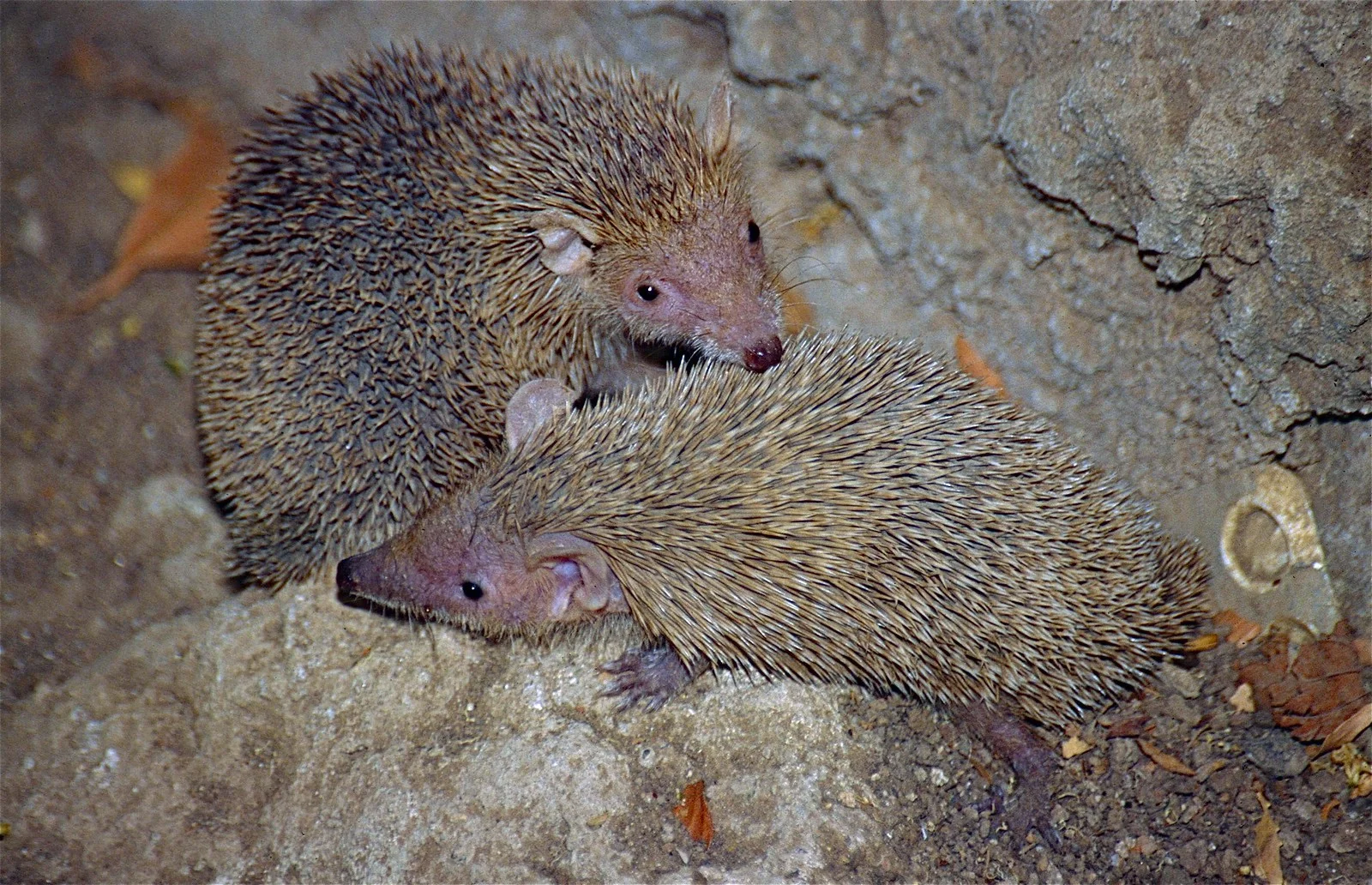


Groundhog:
Mostly solitary, except during the breeding season.
Hedgehog:
Generally solitary, but may tolerate others in overlapping territories.
Comparison: Both groundhogs and hedgehogs exhibit solitary tendencies, with limited social interactions.
Ecological Implications: Social behavior impacts population dynamics and resource utilization within their ecosystems.
18. Mode of Reproduction:
Groundhog:
Polygynous mating system, with males competing for females.
Typically give birth to a litter of 2 to 6 pups in the spring.
Hedgehog:
Generally solitary breeders, with limited social interactions during mating.
Female hedgehogs give birth to 4 to 7 hoglets in a single litter.
Comparison: Both species reproduce through sexual reproduction, but groundhogs exhibit more pronounced mating behaviors.
Ecological Implications: Reproductive strategies influence population dynamics and genetic diversity within ecosystems.
19. Parental Behavior:
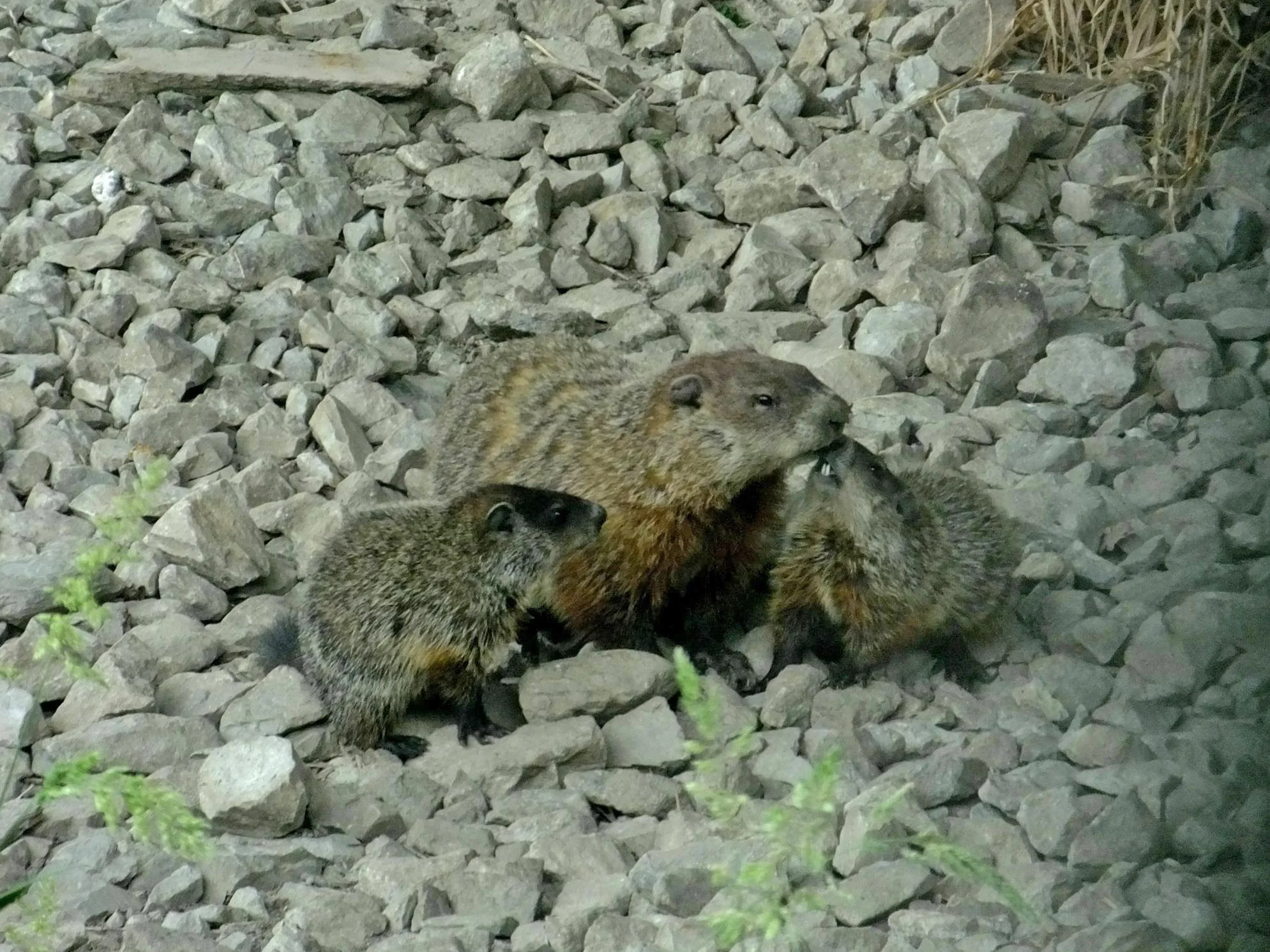

Groundhog:
Females provide care for the offspring, nursing and protecting them in the burrow.
Hedgehog:
Female hedgehogs care for their hoglets but may become solitary soon after giving birth.
Comparison: Groundhogs exhibit more prolonged parental care compared to hedgehogs.
Ecological Implications: Parental behavior affects the survival and development of offspring within their respective ecosystems.
20. Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Groundhog:
Often found near human settlements, causing occasional conflicts due to digging and garden foraging.
Hedgehog:
May inhabit gardens and urban areas, sometimes seeking shelter in human-made structures.
Comparison: Both groundhogs and hedgehogs can coexist in proximity to human-inhabited areas.
Ecological Implications: Human interaction can impact their behavior, diet, and overall survival in urban environments.
21. Behavior Toward Humans:
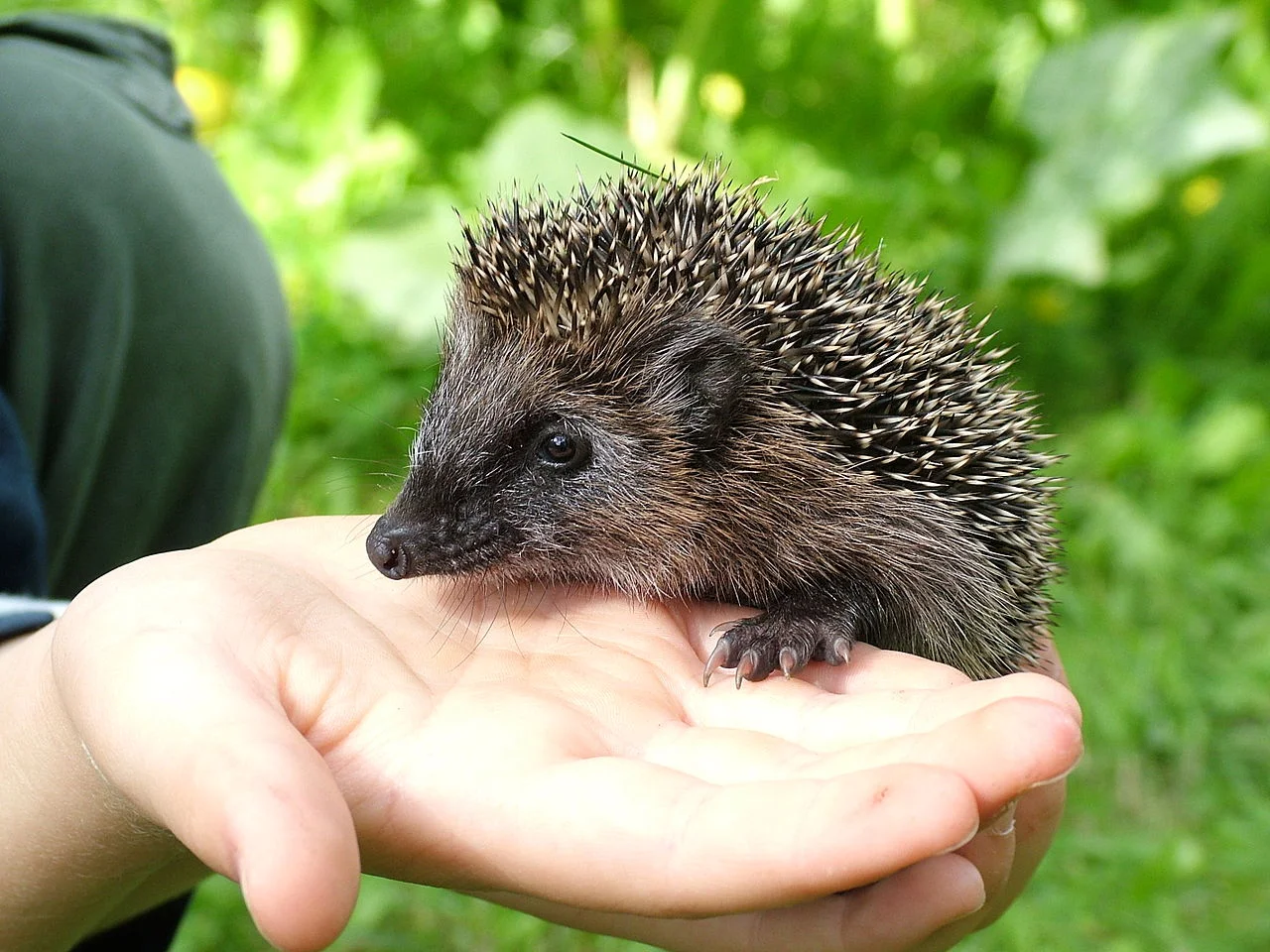

Groundhog:
Generally wary of humans, but may become accustomed to their presence.
Hedgehog:
Can be more tolerant of human proximity, especially in urban settings.
Comparison: Hedgehogs may display more tolerance toward humans compared to groundhogs.
Ecological Implications: Behavioral responses to humans can influence their survival and interaction with human-altered environments.
22. Danger Posed to Humans:
Groundhog:
Typically not considered dangerous to humans.
May cause damage to gardens and crops due to digging behavior.
Hedgehog:
Generally not dangerous; spines serve as a defense mechanism.
May carry diseases like ticks but poses minimal direct threat to humans.
Comparison: Neither groundhogs nor hedgehogs are inherently dangerous to humans.
Ecological Implications: Human perception and interaction with these species can impact local ecosystems and conservation efforts.
23. Associated Precautions:
Groundhog:
Protective measures include securing gardens and using barriers to prevent digging.
Avoiding close proximity to burrows during breeding season can prevent conflicts.
Hedgehog:
Caution is advised when handling hedgehogs to avoid injury from spines.
Providing safe spaces for nesting and avoiding disturbance during hibernation.
Comparison: Both species require some precautions to mitigate potential conflicts or harm.
Ecological Implications: Human awareness and responsible behavior can contribute to coexistence and conservation.
24. Conservation Status:
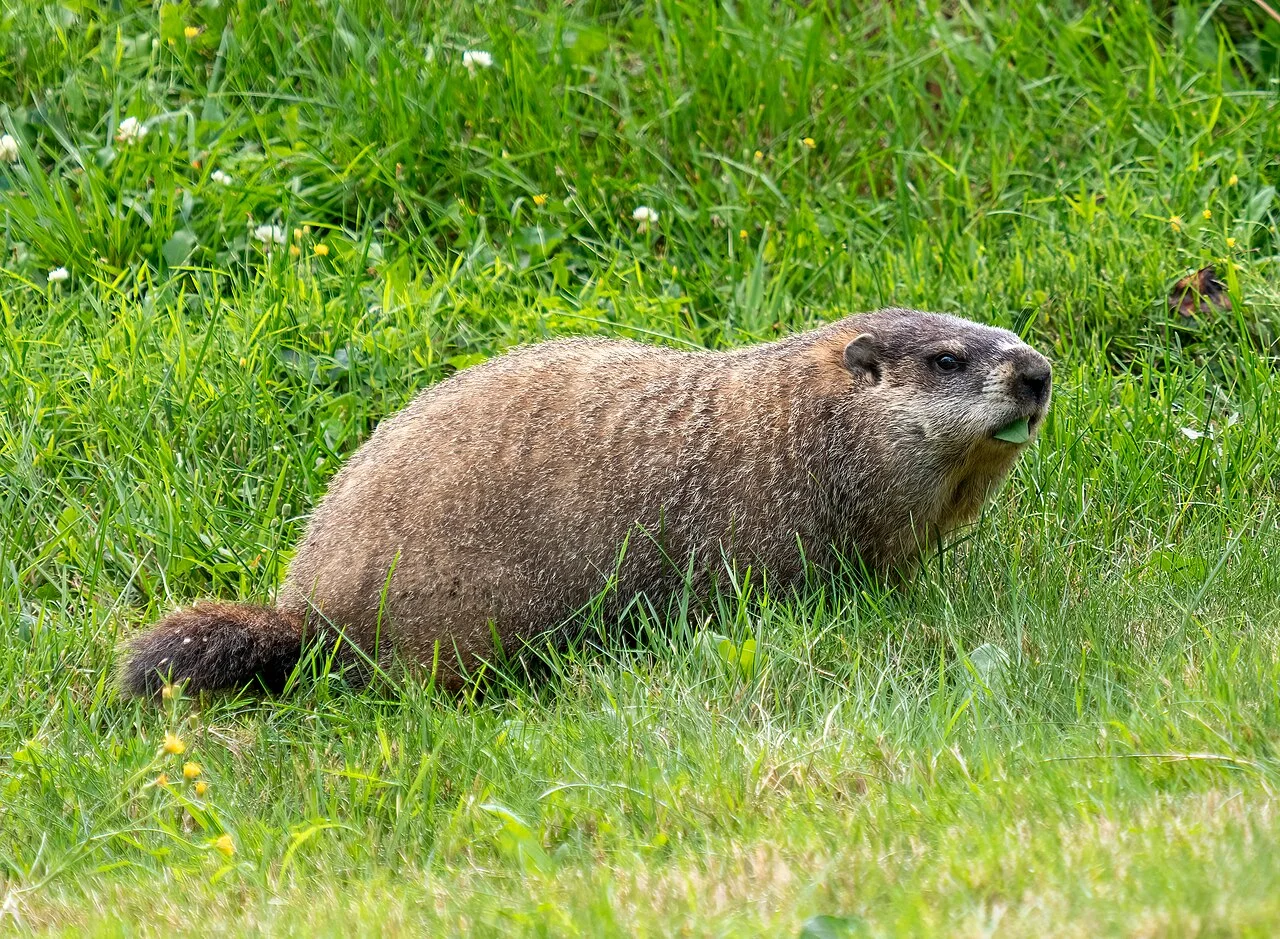

Groundhog:
Not classified as endangered or threatened; population status generally stable.
Hedgehog:
Conservation status varies by species; some are declining due to habitat loss and human activities.
Comparison: Groundhogs are generally more stable in terms of population status compared to some hedgehog species facing decline.
Ecological Implications: Conservation efforts may be needed for specific hedgehog species to maintain biodiversity.
*Summary of Comparison
Taxonomy:
Groundhog: Sciuridae, Marmota monax.
Hedgehog: Erinaceidae, Family Erinaceidae.
Appearance:
Groundhog: Stout, brown/gray fur, short legs, bushy tail.
Hedgehog: Small, spiky coat, brown/gray spines, short legs, snout.
Size:
Groundhog: 16-26 inches.
Hedgehog: 5-12 inches.
Weight:
Groundhog: 4-9 pounds.
Hedgehog: 1-2.5 pounds.
Bite Force (PSI):
Groundhog: Limited information.
Hedgehog: Low due to insectivorous diet.
Physical Offensive Advantages:
Groundhog: Strong digging.
Hedgehog: Defensive rolling.
Physical Defensive Advantages:
Groundhog: Retreat into burrows.
Hedgehog: Defensive rolling.
Speed:
Groundhog: Faster than hedgehog.
Hedgehog: About 4 mph.
Agility:
Groundhog: Climbers and swimmers.
Hedgehog: Limited agility, terrestrial.
Senses:
Groundhog: Excellent vision, hearing, smell.
Hedgehog: Relies on smell and hearing, limited eyesight.
Overall Physical Capacity:
Groundhog: Robust for digging.
Hedgehog: Compact for rolling.
Habitat Preference(s) and Geographic Region:
Groundhog: Open areas, North America.
Hedgehog: Various habitats, Europe, Asia, Africa.
Tracks:
Groundhog: Claw marks, digging emphasis.
Hedgehog: Small, round tracks.
Lifespan:
Groundhog: 3-6 years.
Hedgehog: 2-5 years.
Mode of Feeding:
Groundhog: Herbivores.
Hedgehog: Insectivores.
Intelligence:
Groundhog: Problem-solving.
Hedgehog: Limited cognitive abilities.
Social Behavior:
Groundhog: Mostly solitary.
Hedgehog: Generally solitary.
Mode of Reproduction:
Groundhog: Polygynous, 2-6 pups.
Hedgehog: Solitary, 4-7 hoglets.
Parental Behavior:
Groundhog: Prolonged care.
Hedgehog: Limited care.
Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Groundhog: Near settlements.
Hedgehog: Gardens, urban areas.
Behavior Toward Humans:
Groundhog: Wary.
Hedgehog: Tolerant in urban settings.
Danger Posed to Humans:
Groundhog: Not dangerous; may cause damage.
Hedgehog: Not dangerous; spines as defense.
Associated Precautions:
Groundhog: Secure gardens, avoid close proximity.
Hedgehog: Caution when handling, provide safe spaces.
Conservation Status:
Groundhog: Generally stable.
Hedgehog: Varied, some species declining.
Conclusion
I. Similarities:
Both groundhogs and hedgehogs play roles in ecosystem dynamics, impacting vegetation, soil structure, and invertebrate populations.
II. Differences:
Groundhogs are larger, herbivorous, and exhibit more pronounced mating behaviors, while hedgehogs are smaller, insectivorous, and rely on spiky defense mechanisms.