Continental Giant Rabbit Vs Flemish Giant Differences and Similarities
Exploring the key differences between the Continental Giant Rabbit and the Flemish Giant provides valuable insights into their unique characteristics, size, and origin.
I. Size and Weight:
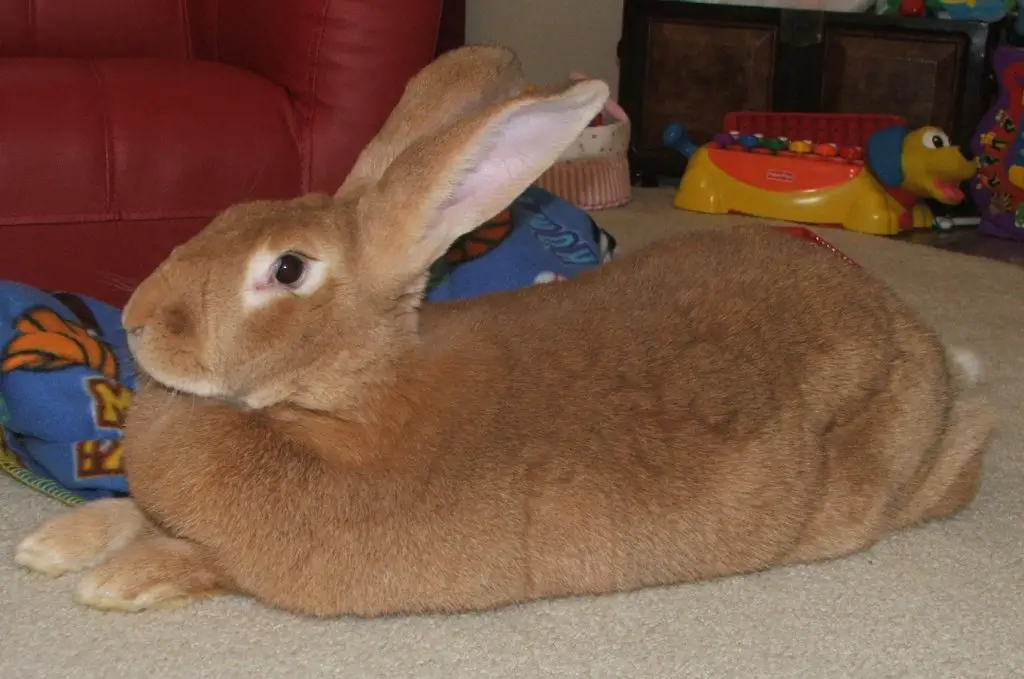
– Flemish Giants, known for their impressive size, can surpass Continentals in sheer magnitude. Unlike Continentals with a maximum length of 3 feet and an average weight of 16-20 pounds, Flemish Giants have no specific size or weight limitations, potentially growing even larger.

II. Appearance and Characteristics:
– While Flemish Giants are recognized for their larger, more robust build and slightly elongated heads, Continentals share similarities but tend to be shorter and slightly less intelligent. The distinction in appearance contributes to the overall recognition of each breed.
III. Breed Origin:
– The Continental Giants trace their lineage to a cross between a Belgian Hare and a Flemish Giant in 1900. This historical breeding endeavor resulted in distinctive maroon-colored rabbits in various shades. Understanding their shared ancestry sheds light on the origin of both breeds.
IV. Behavioral Differences:
– Flemish Giants are acknowledged as docile snuggle bunnies, displaying a gentle temperament. Continentals, while sharing a large size, may exhibit slightly different behavioral traits, showcasing individual nuances that reflect their unique breed characteristics.
V. Physical Traits:
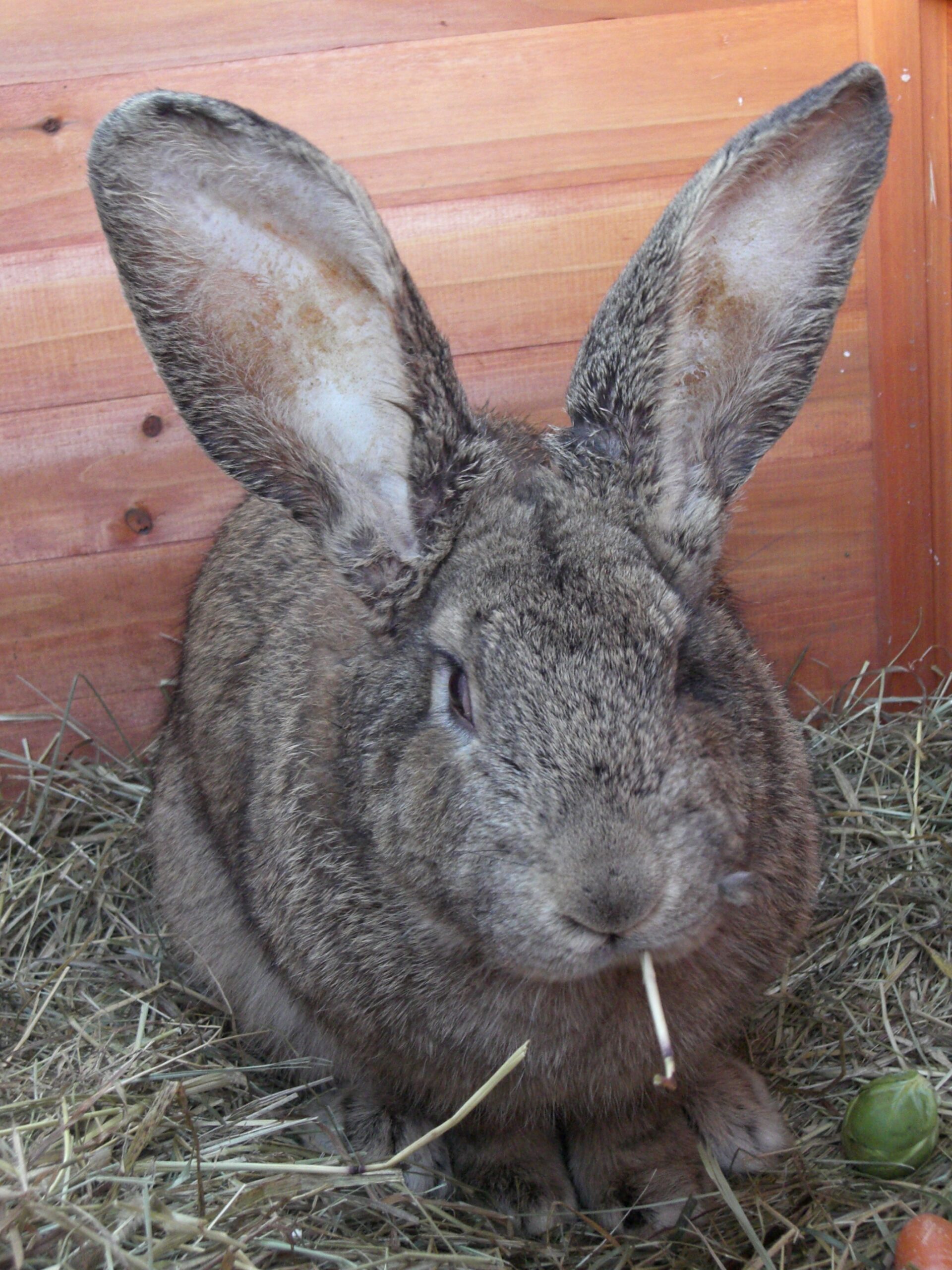
– Notable differences between the ears of Continental Giants and Flemish Giants contribute to their distinct appearance. Continental Giant ears have rounded tips, setting them apart from Flemish Giants. These subtle physical variations become key identifiers for enthusiasts.

VI. Popular Perception:
– Rabbit enthusiasts on platforms like TikTok often share the charm of Flemish and Continental Giants, showcasing adorable aspects of these large rabbit breeds. Understanding the public perception of these rabbits enhances the appreciation for their unique qualities.
VII. Recognition and Naming:
– The Continental Giant is recognized as both the German Giant and the Continental Giant. On the other hand, the Flemish Giant, as the largest breed of domestic rabbit, holds historical significance and contributes to the world of giant rabbit breeds.
*Details of Comparison
| Criteria | Continental Giant Rabbit | Flemish Giant |
| Appearance | Compact, muscular, various coat colors |
Large, robust, glossy coat in fawn, black, blue, and white
|
| Size | Over two feet in length |
One of the largest breeds, often exceeding 14 pounds
|
| Weight | 12-20 pounds |
13-14 pounds on average, some exceeding 20 pounds
|
| Dentition and Bite Force (PSI) | Herbivorous dentition, 200-400 PSI |
Herbivorous dentition, 200-400 PSI
|
| Physical Offensive Advantages | Powerful hind legs for defense |
Utilizes powerful hind legs for defense
|
| Physical Defensive Advantages | Speed and acute hearing |
Robust build and keen senses
|
| Speed | Up to 35 mph | Around 30 mph |
| Agility | Remarkable agility |
Exhibits remarkable agility
|
| Senses | Acute vision, sensitive whiskers |
Motion detection, whiskers for spatial awareness
|
| Overall Physical Capacity | Well-balanced physical attributes |
Well-balanced physical capacity
|
| Habitat Preference and Region | Adaptable to various environments |
Adaptable to various environments
|
| Tracks | Four-toed tracks reflecting lagomorph characteristics |
Four-toed tracks reflecting lagomorph characteristics
|
| Lifespan | 5-10 years | 5-10 years |
| Mode of Feeding | Herbivorous diets, emphasizing plant material |
Herbivorous diets, emphasizing plant material
|
| Intelligence | Moderate intelligence for problem-solving |
Moderate intelligence for problem-solving
|
| Social Behavior | Generally social animals |
Generally social animals
|
| Mode of Reproduction | Prolific breeders with a gestation period of around 31 days |
Prolific breeders with a gestation period of around 31 days
|
| Parental Behavior | Exhibit parental care |
Exhibit parental care
|
| Proximity to Human Areas | Comfortable in proximity to human environments |
Comfortable in proximity to human environments
|
| Behavior Toward Humans | Docile and tolerant, suitable as pets |
Docile and tolerant, suitable as pets
|
| Danger Posed to Humans | Minimal to no danger |
Minimal to no danger
|
| Associated Precautions | Secure enclosures and appropriate care |
Secure enclosures and appropriate care
|
| Conservation Status | Not listed as threatened or endangered |
Not listed as threatened or endangered
|
1. Taxonomy:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Order: Lagomorpha
Family: Leporidae
Genus: Oryctolagus
Species: O. cuniculus domesticus
Flemish Giant:
Order: Lagomorpha
Family: Leporidae
Genus: Oryctolagus
Species: O. cuniculus domesticus
2. Appearance:
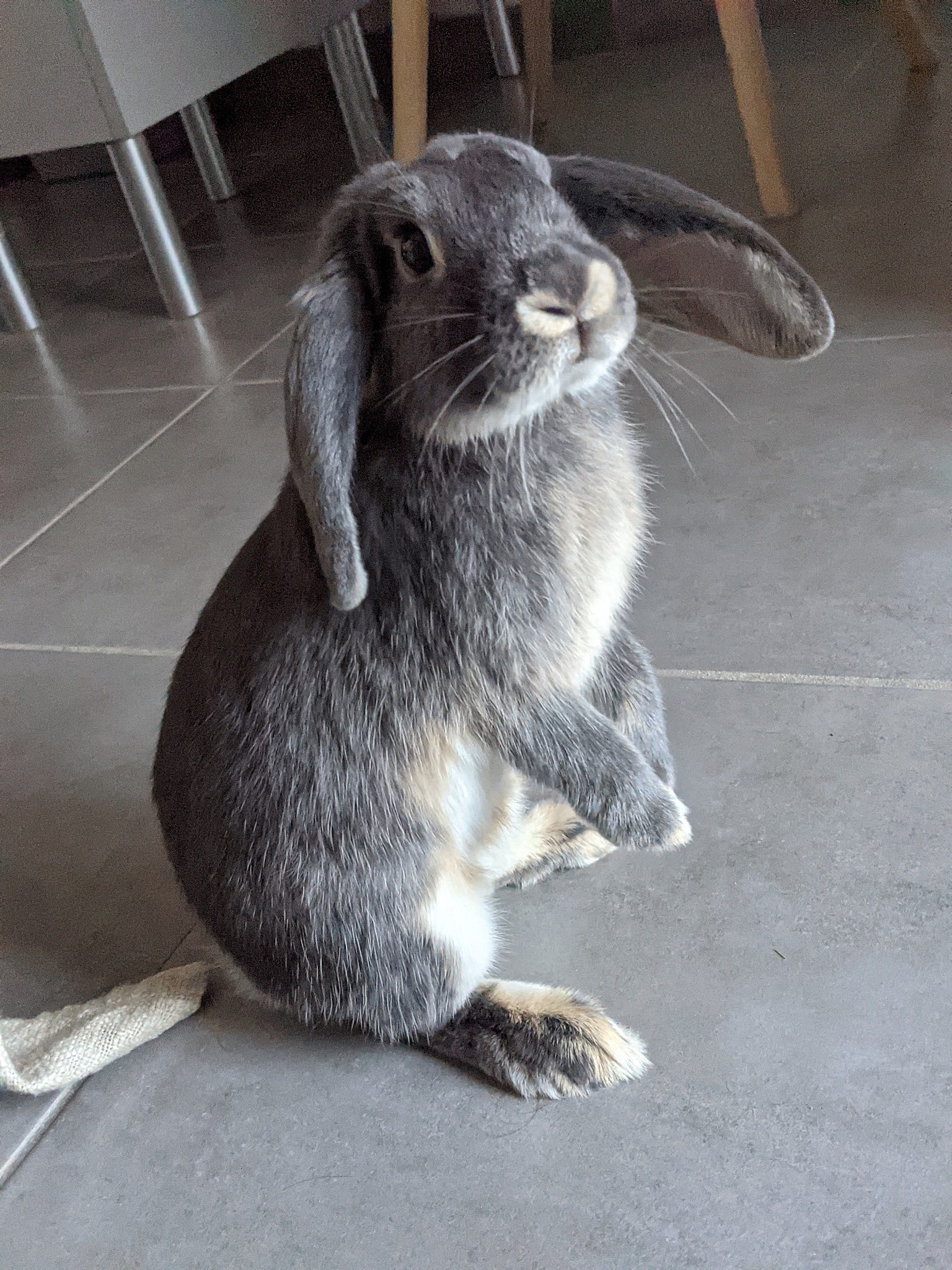


Continental Giant Rabbit:
Features a compact, muscular body with a broad head and erect ears.
Coat color varies, including agouti, white, black, blue, and steel.
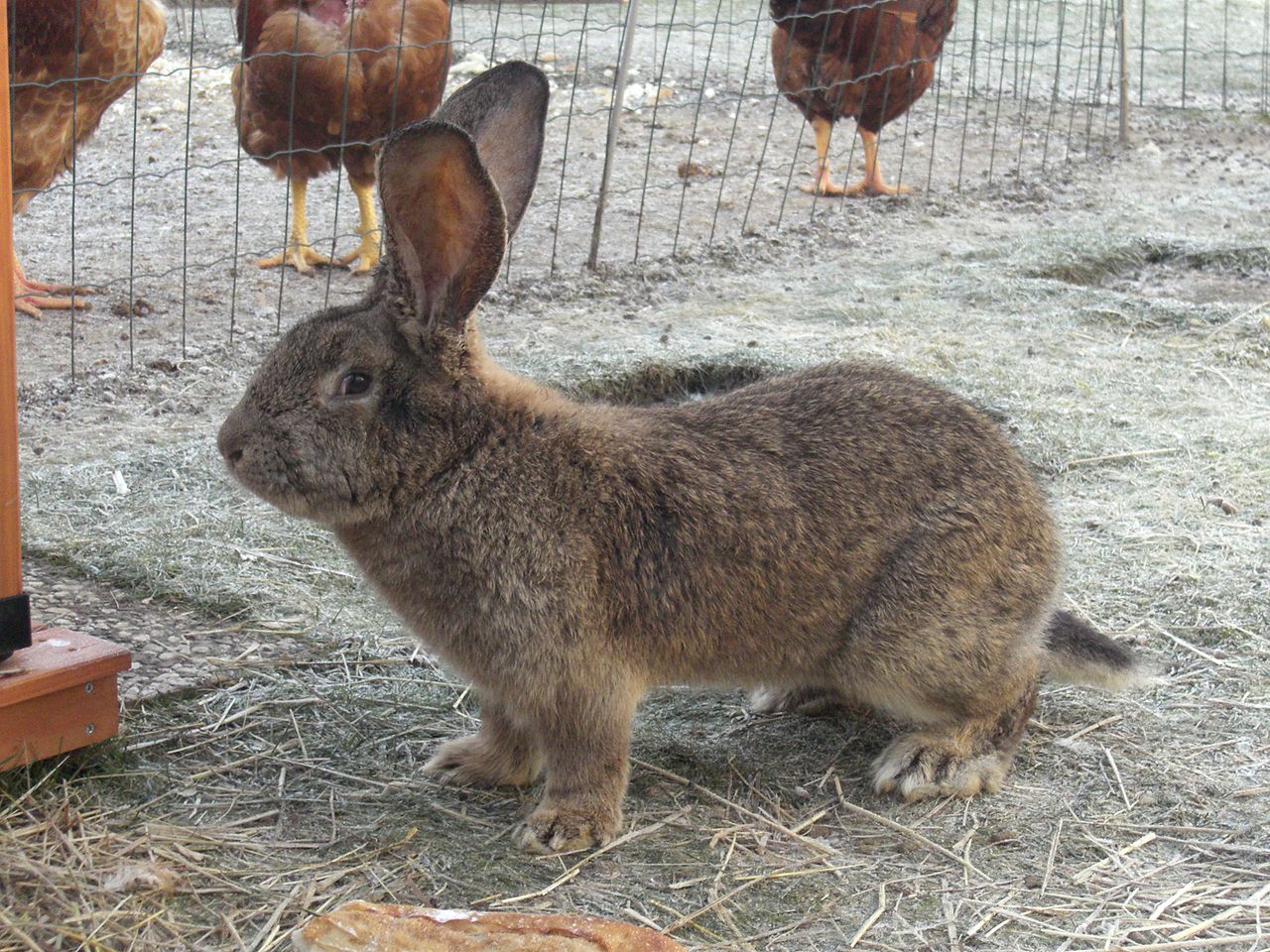
Flemish Giant:
Recognized for its large, robust body structure with semi-arched back and long, upright ears.
Typically exhibits a dense, glossy coat in various colors such as fawn, black, blue, and white.
Comparison:
Both breeds share a distinct, impressive appearance with variations in coat color.
Ecological Implications:
Coat color adaptations may offer camouflage in their respective habitats.
3. Size:

Continental Giant Rabbit:
Typically grows to an impressive size, with some individuals reaching over two feet in length.
Flemish Giant:
Renowned as one of the largest domestic rabbit breeds, with individuals often exceeding 14 pounds.
Comparison:
Both rabbits exhibit substantial size, making them stand out among other breeds.
Ecological Implications:
Larger size may provide advantages in foraging and surviving predation.
4. Weight:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Adult weights commonly range from 12 to 20 pounds.
Flemish Giant:
Adults can weigh between 13 to 14 pounds on average, with some exceeding 20 pounds.
Comparison:
While both are heavyweight breeds, Flemish Giants tend to reach higher average weights.
Ecological Implications:
Weight impacts energy requirements and predator evasion strategies.
5. Dentition and Bite Force (PSI):
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Herbivorous dentition adapted for grinding plant material.
Bite force around 200-400 pounds per square inch (PSI).
Flemish Giant:
Exhibits similar herbivorous dentition for efficient plant consumption.
Bite force also estimated around 200-400 PSI.
Comparison:
Both share a herbivorous diet and comparable bite forces.
Ecological Implications:
Adapted dentition reflects their primary plant-based diet in natural environments.
6. Physical Offensive Advantages:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Powerful hind legs enable swift kicks as a defensive mechanism.
Sharp claws aid in digging for shelter and food.
Flemish Giant:
Robust build provides a solid physical presence.
Strong hind legs contribute to agility and defensive maneuvers.
Comparison:
Both breeds possess physical attributes for defense, leveraging powerful hind legs.
Ecological Implications:
Offensive abilities enhance survival skills in the wild, aiding in territorial disputes or predator evasion.
7. Physical Defensive Advantages:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Agile movements and high-speed sprints aid in escaping predators.
Exceptional hearing allows early detection of potential threats.
Flemish Giant:
Strong hind legs support defensive maneuvers, including rapid escapes.
Keen senses, particularly acute hearing, contribute to predator awareness.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit defensive adaptations for evading predators.
Ecological Implications:
Defensive mechanisms are crucial for survival, influencing habitat selection and interaction with predators.
8. Speed (Km/hour or Mile/hour):

Continental Giant Rabbit:
Capable of reaching speeds up to 35 miles per hour.
Flemish Giant:
Exhibits agility and can achieve speeds around 30 miles per hour.
Comparison:
The Continental Giant Rabbit tends to be slightly faster in terms of top speed.
Ecological Implications:
Speed is essential for evading predators and efficiently foraging in their natural habitats.
9. Agility:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Displays remarkable agility, especially during rapid directional changes.
Flemish Giant:
Despite their large size, exhibits surprising agility in movements.
Comparison:
Both breeds showcase agility, a crucial trait for survival in dynamic environments.
Ecological Implications:
Agility enhances their ability to navigate varied terrains, contributing to overall adaptability in the wild.
10. Senses:

Continental Giant Rabbit:
Possesses acute vision and a wide field of view.
Highly sensitive whiskers aid in navigating surroundings.
Flemish Giant:
Good vision with a focus on motion detection.
Whiskers contribute to spatial awareness.
Comparison:
Both breeds rely on keen senses, with slight variations in emphasis on vision.
Ecological Implications:
Enhanced senses are crucial for detecting predators, finding food, and navigating their habitats.
11. Overall Physical Capacity:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Well-balanced physical attributes, combining speed, agility, and defensive mechanisms.
Flemish Giant:
Impressive overall physical capacity with a focus on robustness and agility.
Comparison:
While both are physically capable, they may excel in different aspects.
Ecological Implications:
Physical capacity influences adaptability to various ecological challenges.
12. Habitat Preference(s) and Geographic Region:

Continental Giant Rabbit:
Originally domesticated, adapts well to a range of environments.
Flemish Giant:
Domesticated breed, adaptable to diverse climates and habitats.
Comparison:
Both exhibit adaptability to various habitats, including human environments.
Ecological Implications:
Versatility in habitat preferences increases the likelihood of survival and successful colonization.
13. Tracks:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Leave distinct tracks featuring four toes with claw imprints.
Flemish Giant:
Similar four-toed tracks, reflective of lagomorph characteristics.
Comparison:
Tracks share common features due to shared taxonomy.
Ecological Implications:
Tracking and identifying species through footprints aid in ecological research and conservation efforts.
14. Lifespan:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Typically lives between 5 to 10 years, influenced by factors such as diet and healthcare.
Flemish Giant:
Has a comparable lifespan of around 5 to 10 years under optimal conditions.
Comparison:
Similar lifespans indicate commonality in domesticated rabbit longevity.
Ecological Implications:
Lifespan impacts reproductive cycles and population dynamics in wild scenarios.
15. Mode of Feeding:


Continental Giant Rabbit:
Herbivorous, primarily consuming grasses, hay, and leafy greens.
Flemish Giant:
Follows a herbivorous diet, with a preference for high-fiber foods.
Comparison:
Both exhibit herbivorous feeding habits, emphasizing the importance of plant material in their diets.
Ecological Implications:
Role as herbivores influences plant growth dynamics and ecosystem balance.
16. Intelligence:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Displays moderate intelligence, with the ability to learn basic commands.
Flemish Giant:
Exhibits similar moderate intelligence, responding to training cues.
Comparison:
Both breeds share a comparable level of intelligence.
Ecological Implications:
Cognitive abilities contribute to problem-solving in natural environments.
17. Social Behavior:

Continental Giant Rabbit:
Generally social animals, showing affinity for interaction with conspecifics.
Flemish Giant:
Socially inclined, thriving in the company of other rabbits.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit social behaviors, reflecting their domesticated and communal nature.
Ecological Implications:
Social structures impact reproductive success and cooperative behaviors within the population.
18. Mode of Reproduction:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Exhibits prolific breeding capabilities with a gestation period of about 31 days.
Flemish Giant:
Similarly prolific breeders with a gestation period of approximately 31 days.
Comparison:
Both breeds share a short gestation period and high reproductive potential.
Ecological Implications:
Rapid reproduction contributes to population dynamics and survival strategies.
19. Parental Behavior:

Continental Giant Rabbit:
Displays maternal instincts, providing care and protection to offspring.
Flemish Giant:
Shows parental care, ensuring the well-being of the young.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit parental behaviors to enhance offspring survival.
Ecological Implications:
Parental care influences juvenile survival rates and population stability.
20. Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:

Continental Giant Rabbit:
Commonly kept as pets, accustomed to human presence.
Flemish Giant:
Frequently raised in captivity, exhibiting tolerance to human interaction.
Comparison:
Both breeds are domesticated, displaying comfort in proximity to human environments.
Ecological Implications:
Adaptation to human-inhabited areas may impact interactions with native wildlife.
21. Behavior Toward Humans:


Continental Giant Rabbit:
Generally docile and tolerant of human handling.
Flemish Giant:
Known for its gentle nature, often used as a pet due to its calm demeanor.
Comparison:
Both breeds exhibit friendly behavior toward humans, facilitating domestication.
Ecological Implications:
Tolerance to human interaction affects the likelihood of successful coexistence in human-altered landscapes.
22. Danger Posed to Humans:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Generally poses no significant danger to humans due to its docile nature.
Flemish Giant:
Poses minimal danger to humans, known for its gentle temperament.
Comparison:
Both breeds are not considered dangerous to humans.
Ecological Implications:
Non-aggressive behavior contributes to their suitability as domesticated pets.
23. Associated Precautions:

Continental Giant Rabbit:
While generally safe, precautions include providing secure enclosures to prevent escapes.
Flemish Giant:
Similar precautions apply, ensuring secure housing and appropriate care.
Comparison:
Both breeds require precautions related to containment and well-being.
Ecological Implications:
Precautions in captivity influence the responsible ownership of these domesticated breeds.
24. Conservation Status:
Continental Giant Rabbit:
Not listed as a threatened or endangered species; considered common in captivity.
Flemish Giant:
Similarly not listed as threatened or endangered, with a stable captive population.
Comparison:
Both breeds are not currently under conservation threat.
Ecological Implications:
Conservation focus may center on their roles in captivity rather than wild populations.
*Summary of Comparison
Appearance:
Continental Giant Rabbit: Compact, muscular, various coat colors.
Flemish Giant: Large, robust, glossy coat in fawn, black, blue, and white.
Size:
Continental Giant Rabbit: Over two feet in length.
Flemish Giant: One of the largest breeds, often exceeding 14 pounds.
Weight:
Continental Giant Rabbit: 12-20 pounds.
Flemish Giant: 13-14 pounds on average, some exceeding 20 pounds.
Dentition and Bite Force (PSI):
Bite force: 200-400 PSI for both, herbivorous dentition.
Physical Offensive Advantages:
Both utilize powerful hind legs for defense.
Physical Defensive Advantages:
Continental: Speed and acute hearing.
Flemish: Robust build and keen senses.
Speed:
Continental: Up to 35 mph.
Flemish: Around 30 mph.
Agility:
Both exhibit remarkable agility.
Senses:
Continental: Acute vision, sensitive whiskers.
Flemish: Motion detection, whiskers for spatial awareness.
Overall Physical Capacity:
Both display a well-balanced set of physical attributes.
Habitat Preference(s) and Geographic Region:
Both adaptable to various environments.
Tracks:
Four-toed tracks for both, reflecting lagomorph characteristics.
Lifespan:
5-10 years for both breeds.
Mode of Feeding:
Herbivorous diets, emphasizing plant material.
Intelligence:
Moderate intelligence for problem-solving.
Social Behavior:
Both are generally social animals.
Mode of Reproduction:
Prolific breeders with a gestation period of around 31 days.
Parental Behavior:
Both exhibit parental care.
Proximity to Human-Inhabited Areas:
Both breeds comfortable in proximity to human environments.
Behavior Toward Humans:
Docile and tolerant, suitable as pets.
Danger Posed to Humans:
Both breeds pose minimal to no danger.
Associated Precautions:
Secure enclosures and appropriate care for both.
Conservation Status:
Not listed as threatened or endangered for both breeds.
Conclusion
I. Similarities:
Both the Continental Giant Rabbit and Flemish Giant share common traits, including herbivorous diets, social behaviors, and adaptability to human environments.
II. Differences:
Differences arise in aspects like size, with Flemish Giants being larger on average, and slight variations in speed and intelligence. These distinctions impact their roles in ecosystems and suitability as domesticated pets.








