11+ Predators in The Rainforest Ecosystem Discussed
Examples of predators in the rainforest are tigers, leopards, and jaguars, each occupying a unique niche. Tigers, known for their strength and striking orange-black stripes, are apex predators that stalk their prey silently through dense vegetation. Leopards are versatile with a spotted coat, often climbing trees to avoid scavengers while feeding. Jaguars, the largest big cats in the Americas, are known for their ability to take down large prey with a single bite.
Other notable rainforest predators include black caimans and anacondas, both powerful reptiles that inhabit rivers and wetlands. Birds like harpy eagles and owls, with their keen senses, are skilled at hunting prey from the canopy. Aquatic predators such as electric eels, piranhas, and arapaimas play crucial roles in maintaining balance in freshwater ecosystems. Social and playful otters and the elusive African golden cat also contribute to the diversity of predators in the rainforest, each facing unique challenges from habitat loss and human activities.
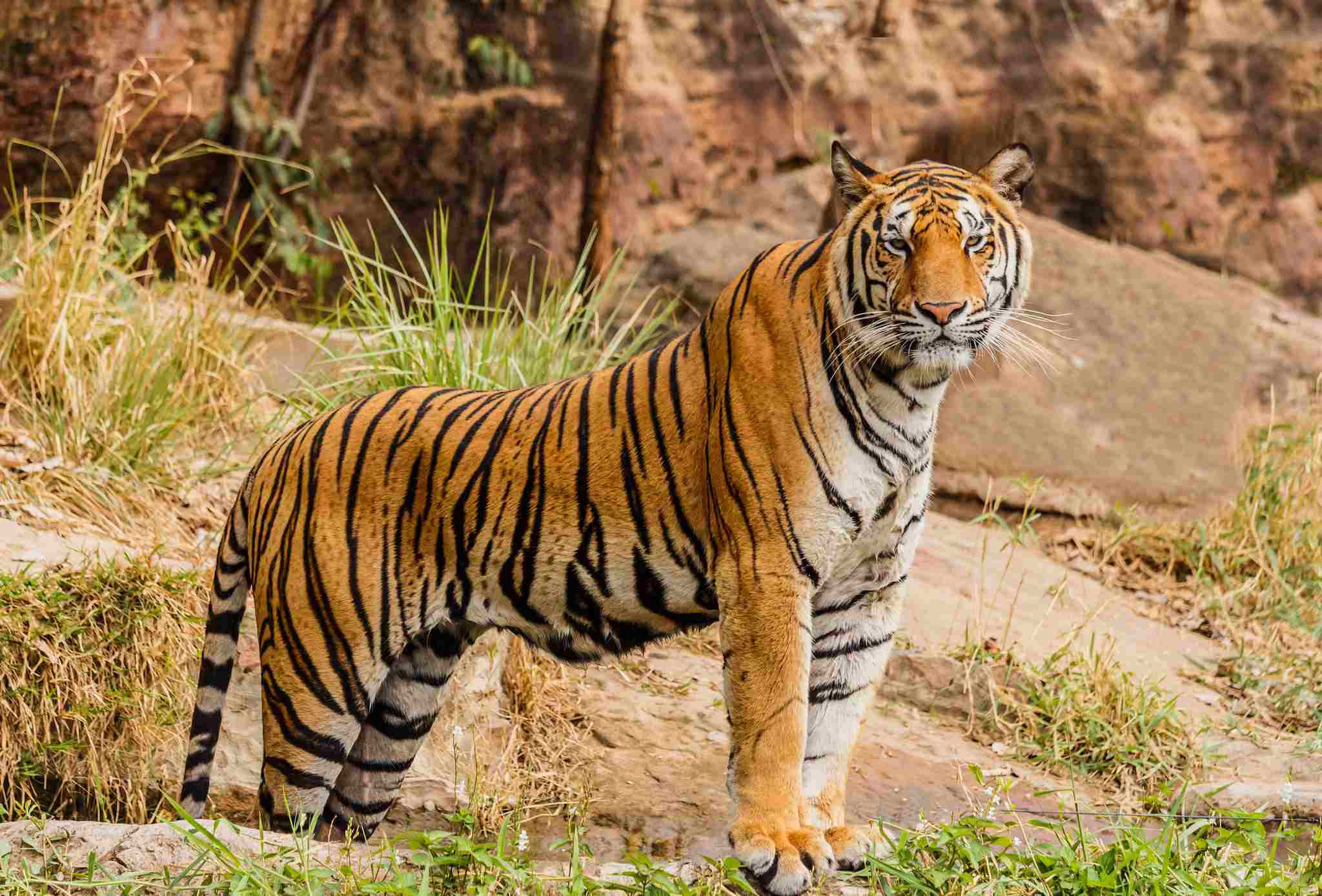
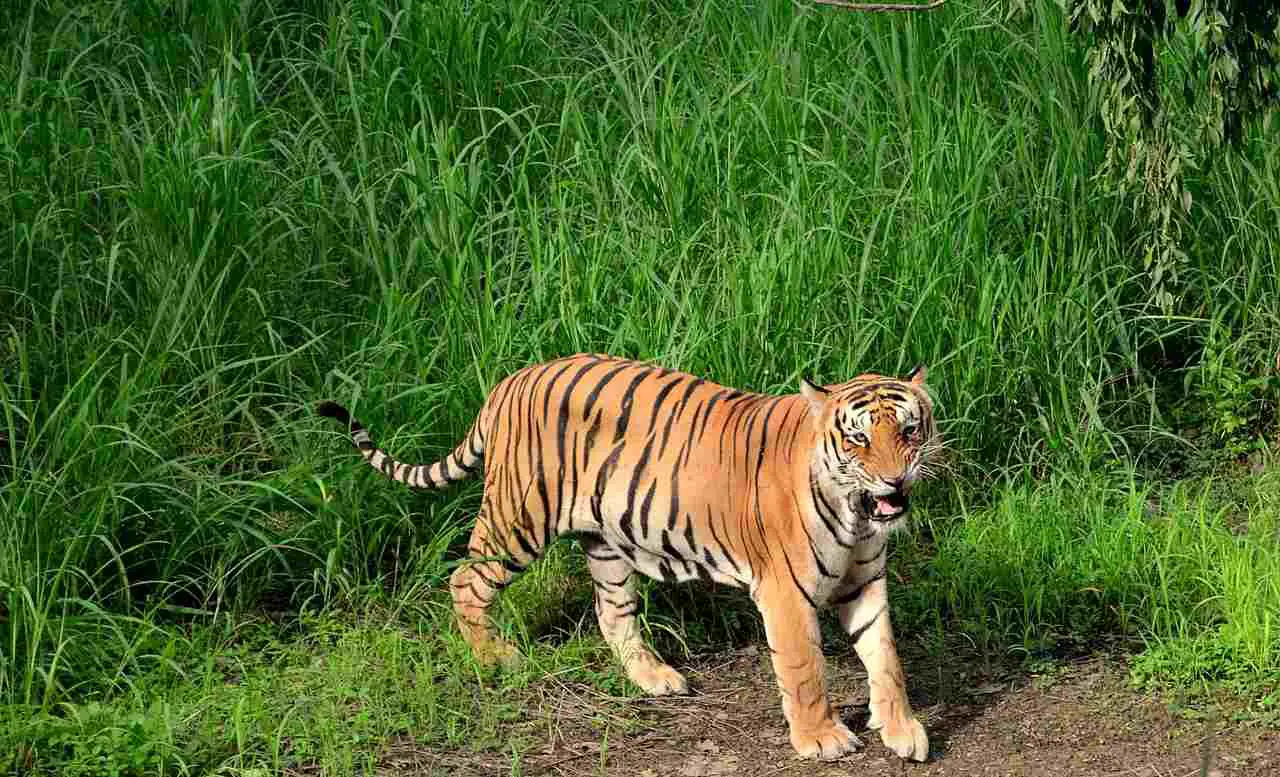
1. Tiger
Tigers are formidable predators in the rainforests, known for their immense strength and distinctive orange coats with black stripes. These large felines are solitary creatures, preferring to roam and hunt alone. They are at the top of the food chain, preying on a variety of animals, including deer, wild boar, and occasionally smaller mammals and birds. The tiger’s hunting strategy involves stealth and surprise; they silently stalk their prey through the dense underbrush, then pounce with explosive force, delivering a powerful bite to the neck or throat to quickly subdue their target.
In the rainforest, tigers play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling prey populations, which in turn helps sustain the health of the forest ecosystem. They are highly adaptable and can be found in different types of forests, but their habitats are increasingly under threat due to deforestation, poaching, and human encroachment. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensure the survival of tigers in the wild, as their presence is an indicator of a healthy rainforest ecosystem.
2. Leopard
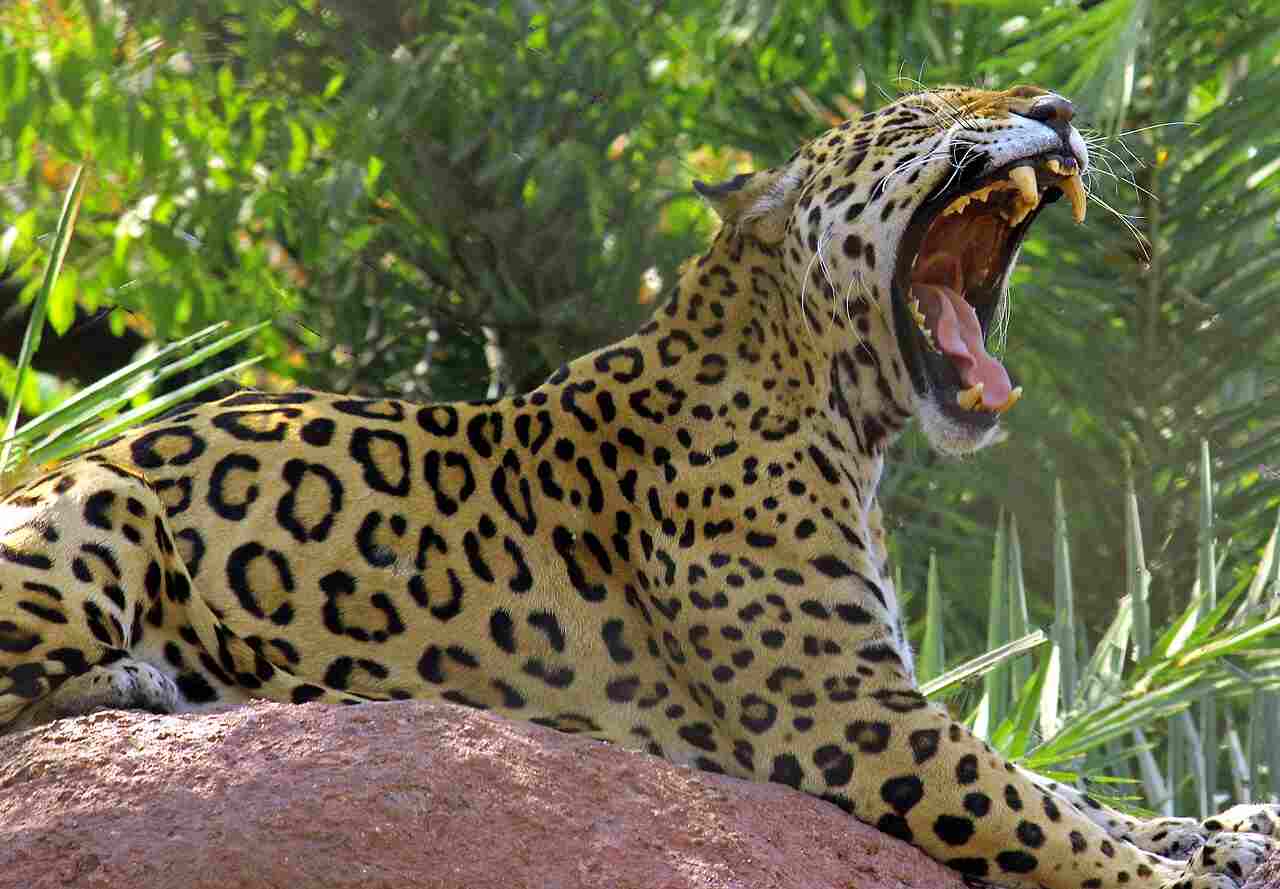
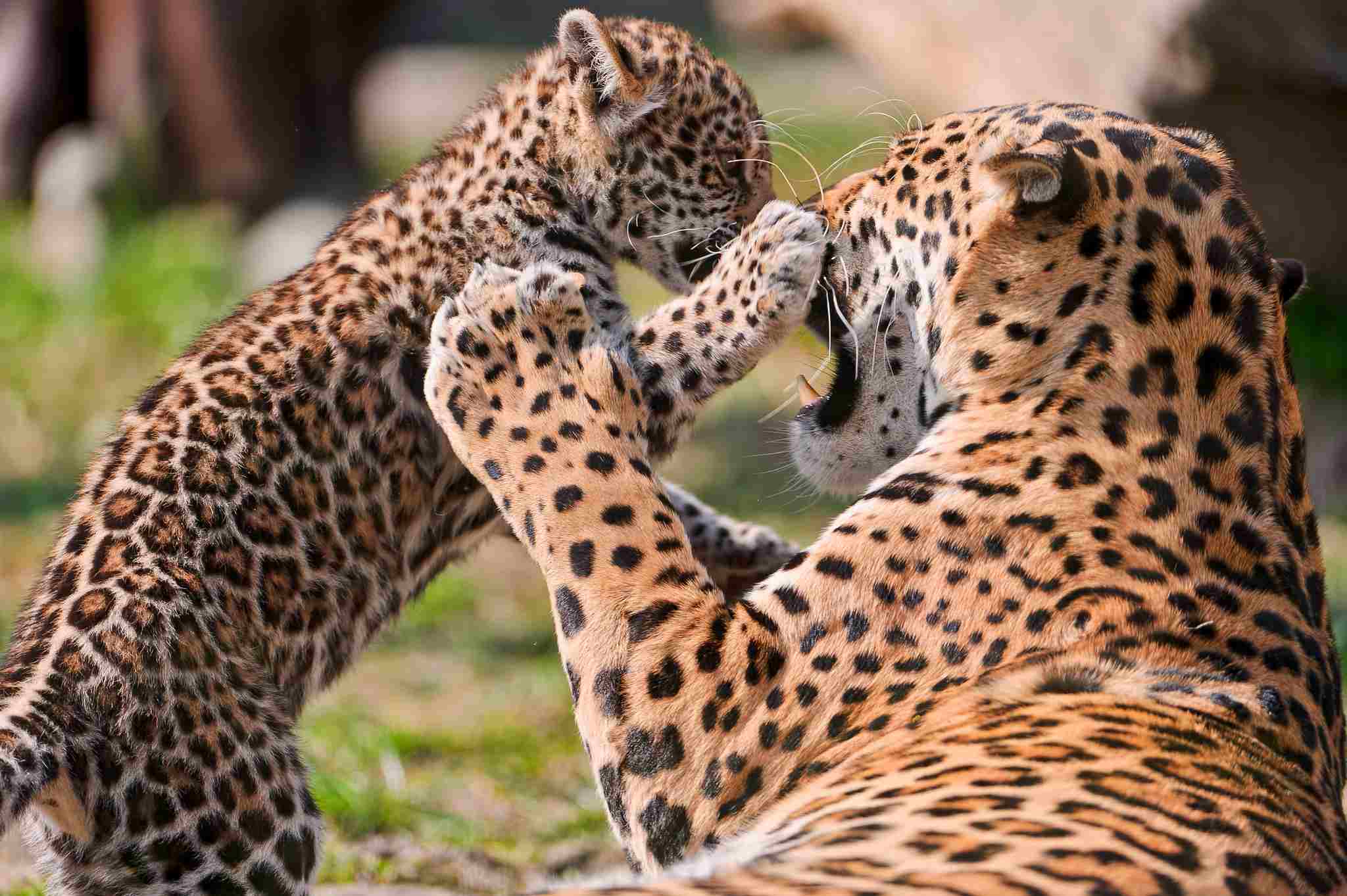
Leopards are versatile predators found in rainforests and other environments. With their spotted coats, leopards blend into the dappled forest light, allowing them to stalk prey undetected. Known for their agility and climbing skills, leopards often take their kills into trees to avoid scavengers. They prey on a range of animals, from small mammals and birds to larger ungulates. This adaptability makes them successful across a wide range of habitats.
Leopards play a significant role in maintaining balance within the rainforest ecosystem by controlling herbivore populations. However, their habitat is increasingly threatened by deforestation and human encroachment. Leopards are also at risk from illegal hunting and retaliatory killings by humans. Conservation efforts focus on protecting habitats and promoting coexistence with human communities to ensure their survival.
3. Jaguar
Jaguars are the largest big cats in the Americas, and they are known for their power and unique hunting techniques. Unlike other big cats, jaguars often kill their prey with a single bite to the skull, showcasing their incredible strength. They are adept swimmers and often hunt near water, preying on animals like capybaras, caimans, and even turtles. Jaguars’ distinctive rosette-patterned fur provides excellent camouflage in the dense rainforest.
The presence of jaguars is a critical indicator of a healthy rainforest ecosystem. However, their populations face significant threats from habitat loss and illegal poaching. Conservation efforts focus on protecting key habitats and creating wildlife corridors to allow jaguars to roam freely. These efforts also aim to mitigate conflicts with humans and promote sustainable practices to ensure the jaguar’s long-term survival.
4. Black Caiman
The black caiman is one of the largest predators in the Amazon rainforest, with a formidable presence and powerful jaws. As a type of crocodilian, black caimans primarily inhabit rivers, lakes, and flooded forests. They are apex predators, preying on fish, birds, and mammals, and they are capable of taking down larger prey like capybaras and even jaguars. The black caiman’s dark coloration helps it blend into murky waters, allowing it to ambush prey.
Despite their status as top predators, black caimans face threats from hunting and habitat destruction. Conservation efforts aim to protect wetland habitats and curb illegal hunting, which has historically reduced black caiman populations. The health of black caimans is a reflection of the broader health of the rainforest’s aquatic ecosystems.
5. Anaconda
Anacondas are among the largest snakes in the world, known for their massive size and constricting abilities. They inhabit the waterways and wetlands of the rainforest, where they prey on a variety of animals, including fish, birds, mammals, and even caimans. Anacondas are adept swimmers and can remain submerged for extended periods, allowing them to ambush prey from the water. Their slow metabolism enables them to survive on infrequent but large meals.
These snakes play an essential role in maintaining ecological balance within their environment. However, anacondas face threats from habitat destruction and illegal hunting. Conservation efforts aim to protect their habitats and raise awareness of their ecological importance. Anacondas’ unique biology and behavior make them a key species in the rainforest ecosystem.
6. Harpy Eagle
The harpy eagle is one of the largest and most powerful eagles in the world, with an imposing presence in the rainforest canopy. Known for its strong talons and keen eyesight, the harpy eagle preys on monkeys, sloths, and other tree-dwelling animals. It is highly adapted to its forest environment, using its broad wings to navigate through dense foliage in search of prey. Harpy eagles are also known for their distinctive feather crests, which add to their majestic appearance.
As apex predators, harpy eagles play a crucial role in regulating prey populations and maintaining the health of the rainforest ecosystem. However, their populations are threatened by deforestation and habitat fragmentation, which disrupt their hunting grounds. Conservation efforts focus on protecting large tracts of forest and raising awareness about the importance of these magnificent birds in maintaining biodiversity.
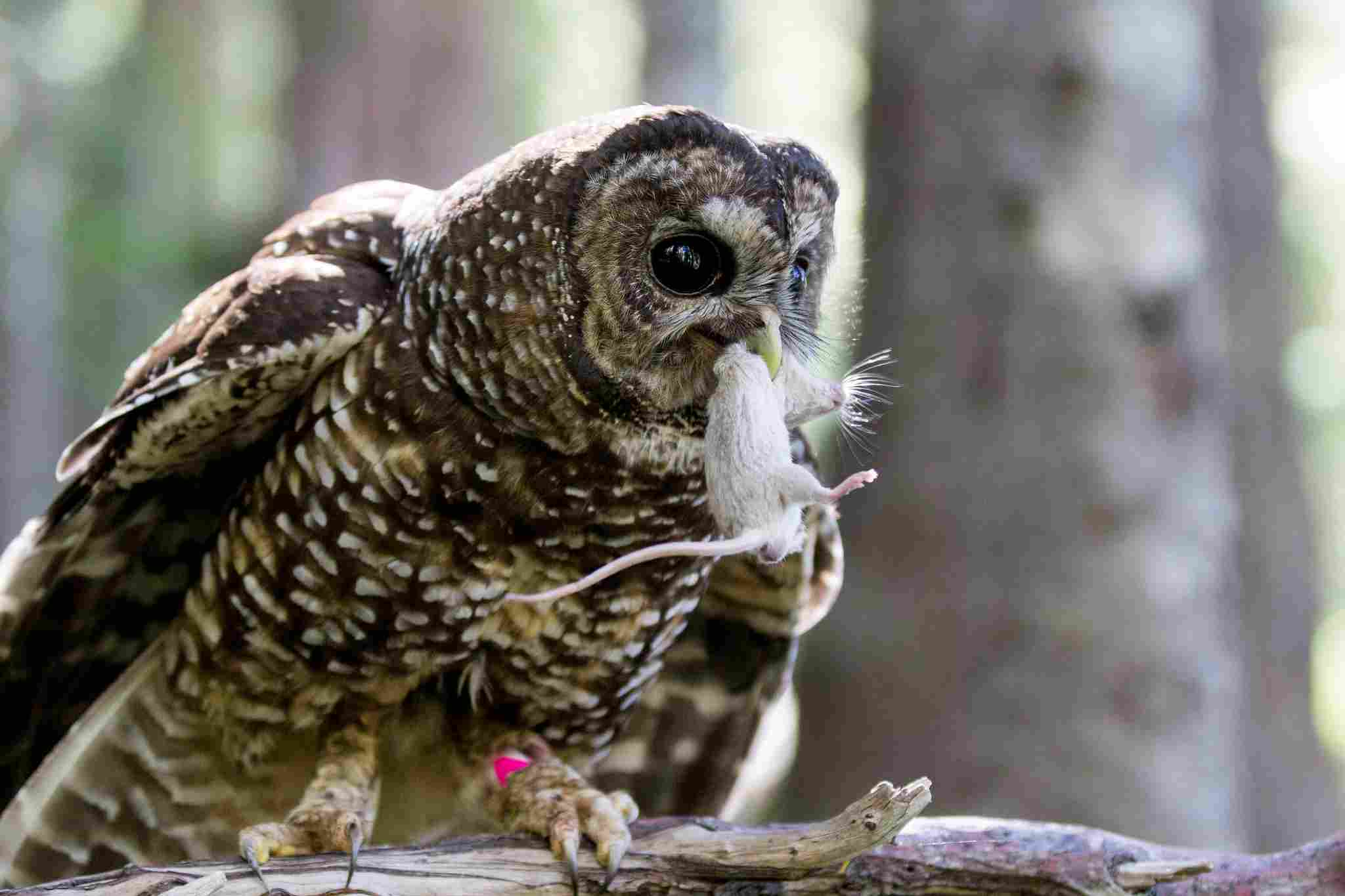
7. Owl
Owls are skilled nocturnal predators that inhabit rainforests, utilizing their acute hearing and silent flight to hunt in the dark. They prey on small mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects, depending on their species and size. Owls are highly adaptable and can be found in various forest types, from dense rainforests to more open woodland areas. Their unique facial discs help them focus sound, allowing them to locate prey even in complete darkness.
Owls play an essential role in controlling populations of small mammals and insects in the rainforest. However, they face threats from habitat loss and environmental changes. Conservation efforts focus on protecting their habitats and ensuring they have suitable hunting grounds. Owls’ presence in the rainforest contributes to the ecosystem’s health by maintaining the balance of prey populations.
8. Hawk
Hawks are swift and agile predators in the rainforest, known for their keen eyesight and powerful flight. They typically hunt during the day, preying on a wide range of animals, including small mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects. Hawks are often seen soaring above the canopy or perched on high branches, scanning the area for potential prey. They rely on their speed and precision to catch their targets, making them highly effective hunters in the forest.
In the rainforest ecosystem, hawks play an important role in controlling prey populations and maintaining balance. However, they face threats from habitat loss and human activities, such as deforestation and illegal hunting. Conservation efforts focus on preserving forest habitats and ensuring hawks have safe areas for nesting and hunting. By protecting these raptors, we help maintain the overall health and biodiversity of the rainforest.
9. Electric Eel
Electric eels are unique predators in the rainforest’s aquatic ecosystems, known for their ability to generate powerful electric shocks. Despite their name, electric eels are more closely related to knifefish than true eels. They inhabit the rivers and flooded areas of the rainforest, where they use their electric capabilities to navigate, communicate, and hunt. Electric eels primarily prey on fish and other small aquatic creatures, stunning them with electric discharges before consuming them.
Electric eels play a significant role in the aquatic food chain, helping to control fish populations. However, their habitats are threatened by pollution, dam construction, and other forms of human activity that affect water quality and flow. Conservation efforts aim to protect freshwater ecosystems and raise awareness about the unique biology and ecological importance of electric eels in the rainforest.
10. Piranha
Piranhas are infamous predators in the rainforest, known for their sharp teeth and aggressive feeding behavior. Found in the rivers and lakes of the Amazon and other tropical regions, piranhas are opportunistic feeders that prey on fish, insects, and occasionally larger animals. Although their reputation for ferocity is somewhat exaggerated, piranhas can be dangerous when hunting in groups or when food is scarce.
In the rainforest ecosystem, piranhas play a crucial role in controlling fish populations and removing weak or injured individuals. However, they are also affected by changes in water quality and habitat loss due to deforestation and dam construction. Conservation efforts focus on maintaining healthy aquatic ecosystems and ensuring piranhas have suitable habitats for breeding and feeding.
11. Otter
Otters are playful and highly adaptable predators in the rainforest, known for their sleek bodies and skillful swimming. They inhabit rivers, lakes, and other freshwater environments, where they hunt for fish, crustaceans, and other aquatic creatures. Otters are social animals, often seen in family groups, and they use their dexterous paws and sharp teeth to catch prey. Their playful behavior and unique vocalizations make them a delight to observe in their natural habitat.
In the rainforest ecosystem, otters play an essential role in maintaining the health of aquatic environments by controlling fish and invertebrate populations. However, they face threats from habitat destruction, water pollution, and hunting. Conservation efforts aim to protect freshwater habitats and ensure otters have safe areas for breeding and hunting. Otters’ presence in the rainforest is a sign of a healthy and vibrant ecosystem.
12. Arapaima
The arapaima, also known as the pirarucu, is one of the largest freshwater fish in the world, found in the rivers and lakes of the Amazon rainforest. With their elongated bodies and large scales, arapaimas are impressive predators that feed on fish, insects, and even small mammals and birds that venture too close to the water’s surface. They are known for their ability to gulp air from the surface, allowing them to survive in oxygen-poor waters.
Arapaimas play a crucial role in the rainforest’s aquatic ecosystem by helping to control fish populations and maintain ecological balance. However, they face threats from overfishing and habitat loss due to deforestation and dam construction. Conservation efforts focus on regulating fishing practices and protecting key habitats to ensure the survival of arapaimas in the wild.
13. African Golden Cat
The African golden cat is a rare and elusive predator found in the rainforests of Central and West Africa. Known for its beautiful golden-brown coat, this medium-sized cat is a skilled hunter that preys on small mammals, birds, and reptiles. African golden cats are primarily nocturnal, using their keen senses and stealth to hunt in the dense forest. They are highly secretive and rarely seen, making them one of the most enigmatic predators in the rainforest.
Despite their elusive nature, African golden cats play an important role in controlling prey populations and maintaining the health of the rainforest ecosystem. However, they are at risk from habitat loss due to deforestation and human encroachment, as well as from hunting and trapping. Conservation efforts focus on protecting rainforest habitats and studying these elusive cats to better understand their behavior and ecology. By preserving the African golden cat, we help ensure the health and biodiversity of the rainforest.
*Summary
-
Tiger: Solitary predator with orange and black stripes; top of the food chain; hunts deer, wild boar, smaller mammals, and birds; faces threats from deforestation and poaching.
-
Leopard: Spotted coat; agile and adaptable; preys on a variety of animals; habitat threatened by deforestation and human encroachment.
-
Jaguar: Largest big cat in the Americas; kills with a single bite to the skull; preys on capybaras, caimans, and turtles; threatened by habitat loss and poaching.
-
Black Caiman: One of the largest predators in the Amazon; inhabits rivers and lakes; preys on fish, birds, and mammals; faces threats from hunting and habitat destruction.
-
Anaconda: Among the largest snakes; lives in waterways and wetlands; preys on fish, birds, mammals, and caimans; faces threats from habitat destruction and illegal hunting.
-
Harpy Eagle: Large and powerful eagle; preys on monkeys and sloths; plays a crucial role in regulating prey populations; threatened by deforestation and habitat fragmentation.
-
Owl: Nocturnal predator with acute hearing and silent flight; preys on small mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects; faces threats from habitat loss and environmental changes.
-
Hawk: Swift and agile predator; hunts during the day; preys on small mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects; threatened by habitat loss and human activities.
-
Electric Eel: Generates powerful electric shocks; inhabits rivers and flooded areas; preys on fish and small aquatic creatures; threatened by pollution and dam construction.
-
Piranha: Known for sharp teeth and aggressive feeding behavior; preys on fish and insects; plays a role in controlling fish populations; threatened by changes in water quality and habitat loss.
-
Otter: Playful predator; hunts fish and crustaceans; social animals in family groups; faces threats from habitat destruction, water pollution, and hunting.
-
Arapaima: One of the largest freshwater fish; preys on fish and insects; gulps air from the surface; threatened by overfishing and habitat loss.
-
African Golden Cat: Elusive medium-sized cat; preys on small mammals, birds, and reptiles; habitat threatened by deforestation and human encroachment.
| Predator |
Characteristics and Threats
|
| Tiger |
Solitary; top predator; orange with black stripes; threatened by deforestation and poaching.
|
| Leopard |
Agile; spotted coat; hunts various prey; threatened by deforestation and human encroachment.
|
| Jaguar |
Largest cat in the Americas; kills with one bite; threatened by habitat loss and poaching.
|
| Black Caiman |
Large predator; preys on fish, birds, mammals; faces hunting and habitat threats.
|
| Anaconda |
Large snake; constrictor; preys on fish, birds, mammals; threatened by habitat destruction.
|
| Harpy Eagle |
Large and powerful; preys on monkeys, sloths; threatened by deforestation.
|
| Owl |
Nocturnal; silent flight; preys on small mammals, birds; threatened by habitat loss.
|
| Hawk |
Swift and agile; preys on various animals; threatened by habitat loss.
|
| Electric Eel |
Generates electric shocks; preys on fish; threatened by pollution and dams.
|
| Piranha |
Sharp teeth; feeds on fish; plays role in controlling fish populations; threatened by water quality changes.
|
| Otter |
Playful; social; preys on fish; threatened by habitat loss and pollution.
|
| Arapaima |
Large freshwater fish; gulps air; threatened by overfishing and habitat loss.
|
| African Golden Cat |
Elusive; hunts small mammals; threatened by deforestation and human encroach
|